Construction method of gtpch enzyme deficiency mouse model with motor dysfunction phenotype
A technology of motor dysfunction and construction method, which is applied in the field of construction of a mouse model of motor dysfunction phenotype GTPCH enzyme deficiency, and can solve problems such as inability to use disease mechanism and treatment research.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
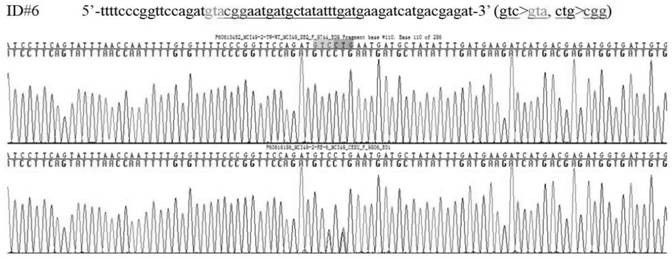
[0053] This example provides a method for constructing a mouse model of motor dysfunction phenotype GTPCH enzyme deficiency disease. For the construction steps, see figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0054] 1. Establishment of Gch1p.Leu108Arg point mutation heterozygous mice based on classical B6 strain (C57BL / 6) mice by CRISPR / Cas9 technology
[0055] 1.1 CRISPR / Cas9 Targeting System
[0056] Human GCH1 p.Leu117 is located at the entrance of the binding pocket of the catalytic substrate GTP of the GTPCH enzyme. Mutation to arginine will cause steric hindrance and affect the binding of the substrate GTP to the enzyme. Mouse p.Leu108 is highly conserved with human p.Leu117. Based on this, a synthetic guide sgRNA (SEQ ID No.1) and an oligonucleotide donor (ssDNA) for homologous recombination repair were designed.
[0057] sgRNA (SEQ ID No.1): CATCAAATATAGCATCATTCAGG
[0058] ssDNA (SEQ ID No. 2):
[0059] AAAATATTTACTATCCTTCAGTATTTAACCAATTTTGTGTTTTCCCGGTTCCAGATGTAC...
Embodiment 2
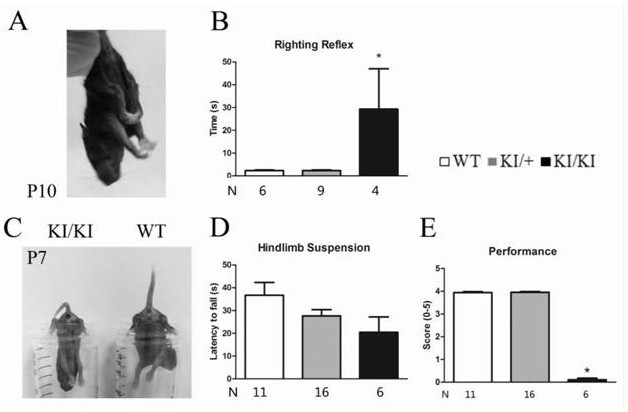
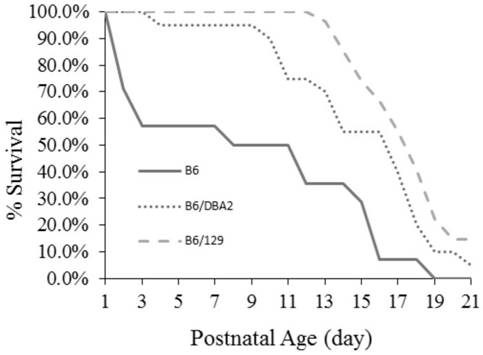
[0108] This example provides a method for constructing a mouse model of motor dysfunction phenotype GTPCH enzyme deficiency disease. The construction steps refer to Example 1, and the changes relative to Example 1 are "2. F1 generation heterozygous mutant mice" In the step, wild-type mice of 129Sv strain were used instead of wild-type mice of DBA / 2 strain. The results are shown in Table 3, Figure 7 , Figure 8 .
[0109] table 3
[0110]
[0111] According to Table 3, it can be seen that, using the construction method of this example, GCH1 homozygous mutant mice almost completely avoid the problem of embryonic lethality. according to Figure 7 It can be seen that, adopting 129Sv strain wild-type mice to cross with Gch1 missense mutant heterozygous mice under the C57BL / 6 strain background and then selfing the F1 generation heterozygotes to obtain homozygous mutant mice can also improve the homozygous mutant mice. (Gch1 KI / KI rats) birth rate and survival time. Althou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com