PH sensitive probe molecule and application thereof
A CH2, electron-donating group technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of affecting functional properties, changing physical properties, misleading information, etc., and achieves the effects of mild labeling conditions, high sensitivity, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The preparation of embodiment 1 probe compound
[0037] Synthesis of dyes as figure 1 Shown:
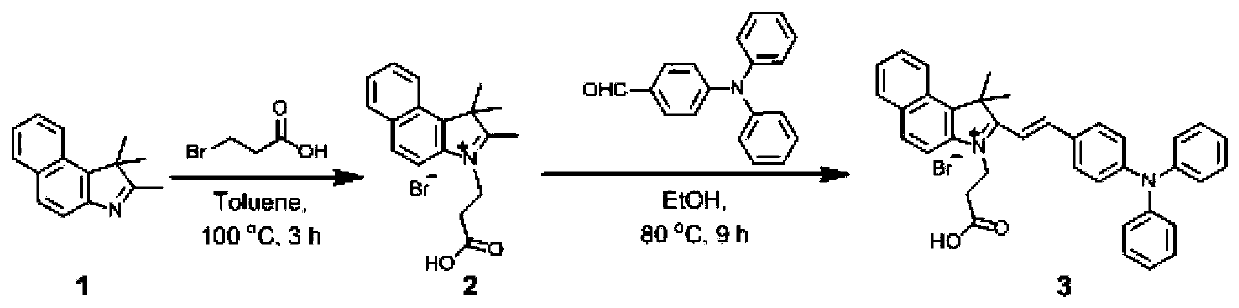
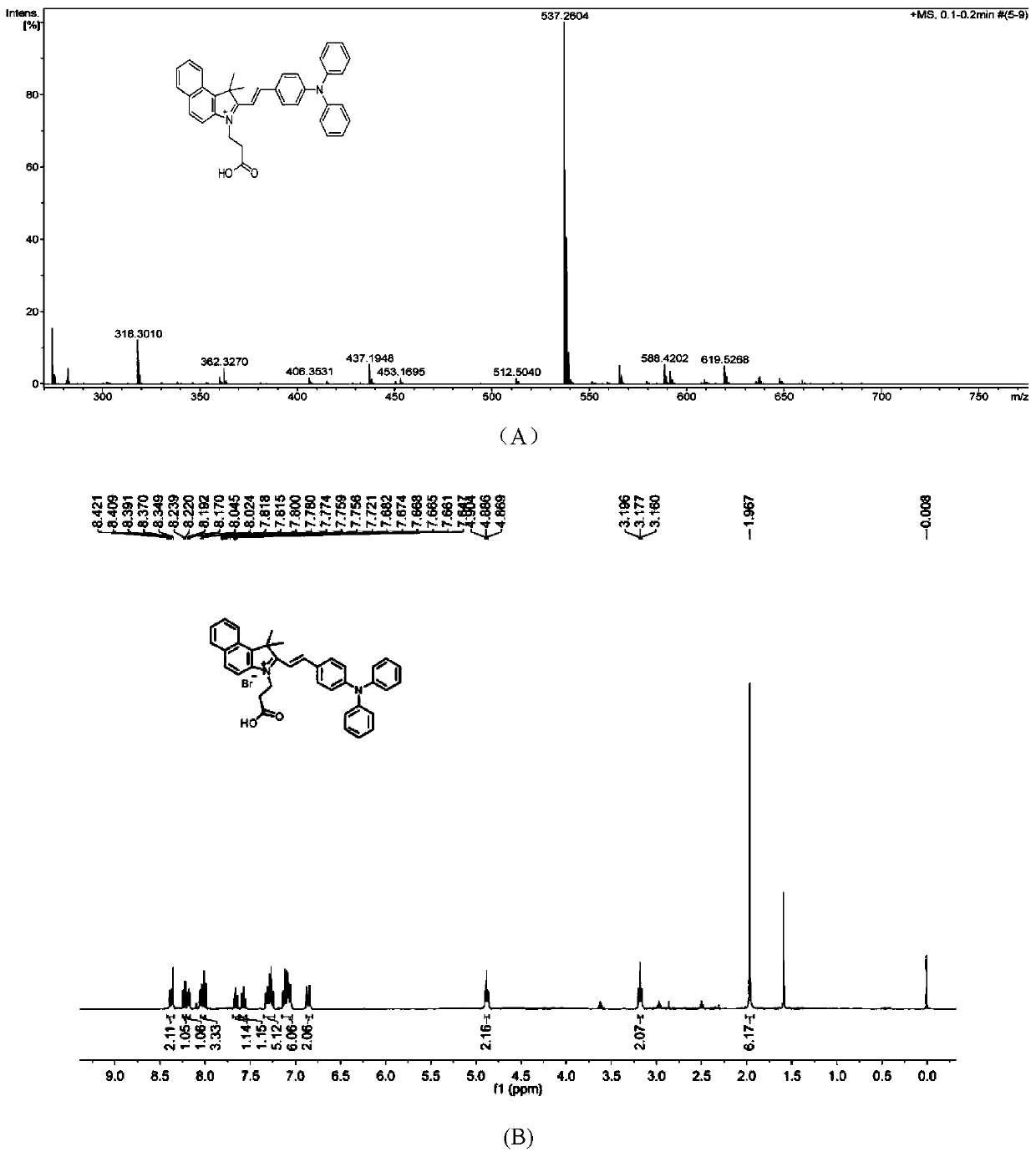
[0038] (1) Synthesis of Compound 2: Compound 1,1,2-trimethyl-1H-benzoindole (3.13g, 15.0mmol) and 3-bromopropionic acid (2.43g, 16.0mmol) were mixed in 5.0mL In toluene, reflux at 100°C for 3 hours under nitrogen protection. After the reaction was monitored by TLC, the reaction solution was gradually cooled to room temperature, and the reaction solution was added dropwise to ether (150mL) solvent. A large number of powder particles were precipitated, and the powder was collected by filtration. Washing with cooled diethyl ether (50 mL) gave a magenta solid powder, compound 2 (4.11 g, yield 76%). HRMS(ESI,m / z) Calcd.for[C 18 h 20 BrNO 2 -Br - ], 282.1489; Found, 282.1613.
[0039] (2) Synthesis of Compound 3: Compound 2 (722.0mg, 2.0mmol) and 4-dianilinobenzaldehyde (546.0mg, 2.0mmol) were mixed in 5.0mL ethanol, refluxed at 80°C for 9h under nitrogen protection, and moni...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The labeling parameter determination of embodiment 2 dyes
[0043]Fluorescence spectroscopic detection of probes in the presence or absence of exosomes. The bladder cancer cell YTS-1 exosomes were used as the experimental object. The probe with a concentration of 50 μM was used for staining at room temperature in the dark for 30 min, and a blank control was set. The result is as Figure 4 Shown: When the probe is not bound to exosomes, the fluorescent signal is very weak, but when combined with exosomes, the fluorescent signal is significantly enhanced.
Embodiment 3
[0044] The screening of the optimum use concentration of embodiment 3 probe
[0045] Optimal concentration of probes for flow cytometry screening. Suspension cell SKM1 was used as the experimental object. Draw about 2.0×10 6 SKM1 cells were placed in a 15mL centrifuge tube, centrifuged at 5000rpm, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde at room temperature for 15min, blocked with 1% BSA / PBS, resuspended in PBS, and evenly divided into 8 flow tubes, respectively using final concentrations of 0μM, 1μM, 2 μM, 5 μM, 10 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM probes were stained at room temperature in the dark for 30 min, neutralized with 100 mM glycine, washed once with PBS, and resuspended in 100 μL PBS for detection.
[0046] The result is as Figure 5 Shown: Compared with the negative control (probe concentration of 0 μM), the peak value of the cells labeled with 50 μM and 100 μM probes shifted greatly, so the probes with a concentration of 10 μM to 100 μM can better label the cells , 10 μM probes can al...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com