A kind of nuclide-labeled targeting probe compound and preparation method thereof
A compound and labeling technology, applied in the field of medical imaging, can solve the problems of low sensitivity of early fibrosis, slow imaging time, poor imaging quality, etc., and achieve the effects of short labeling time, high labeling yield and improving specific activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
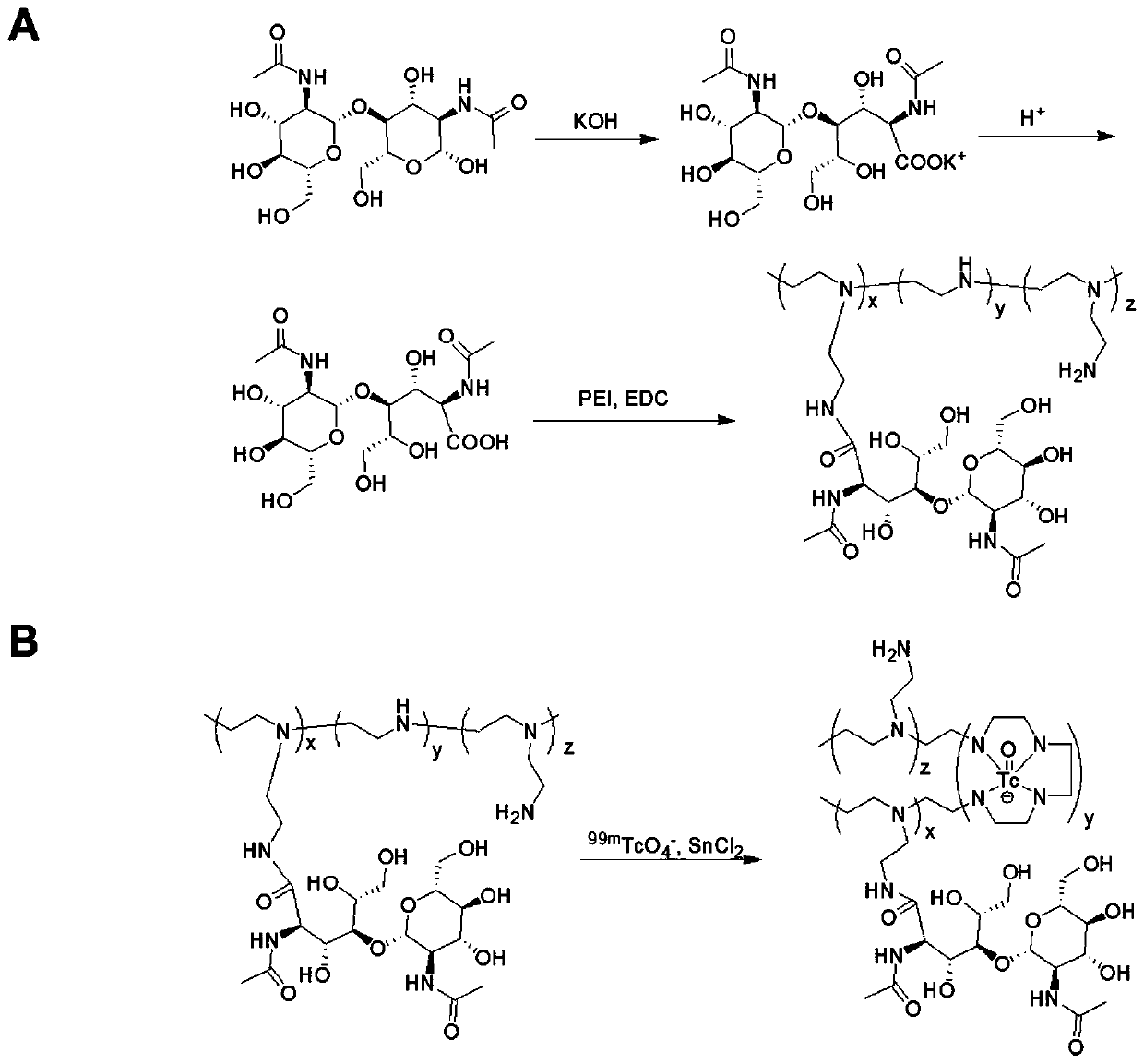
[0038] The preparation of embodiment 1 NAG-PEI and 99m Tc tag
[0039] 1. Synthesis of NAG-PEI
[0040] At room temperature, 0.1 g of chitobiose was dissolved in a mixed solution of water and methanol. Dissolve 0.285g of iodine in 4mL of methanol, dissolve and mix with the above-mentioned chitobiose. A 4% KOH solution was added to the solution until the iodine color disappeared. The solution was recrystallized with ether to obtain potassium chitobioconate. The product is obtained chitobionic acid [(NAG) by IR-120 ion exchange column 2 -COOH]. Chitobionic acid was linked to PEI (molecular weight: 1800) with EDC as a catalyst. Briefly, 25% molar ratio of chitobionic acid [(NAG) 2 -COOH] was dissolved in a solution of TEMED containing EDC to react with PEI, and stirred at room temperature for 72h. The solution was dialyzed in a dialysis bag (MWCO: 2500) for 3 days, and then freeze-dried to obtain NAG-PEI. Such as figure 1 As shown in A.
[0041] 2. Characterization of ...
Embodiment 299
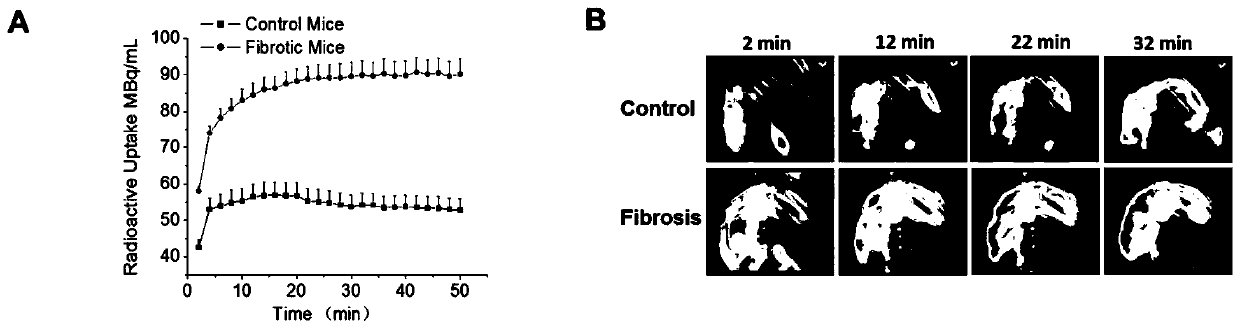
[0045] Example 2 99m Evaluation of liver fibrosis in mice by Tc-NAG-PEI SPECT / CT imaging
[0046] 1. Construction of liver fibrosis mouse model
[0047] The mice used in the experiments were female C57BL / 6 mice purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Xiamen University. CCl 4 Used to induce liver fibrosis in mice. Simply put, CCl 4 Dissolved in olive oil (1:4), C57BL / 6 female mice were intraperitoneally injected with 5 mL / kg of CCl 4 solution, 2 times a week. The control group was given the same dose of olive oil. 5 mice in each group, 4 weeks and 8 weeks respectively.
[0048] 2, 99m Tc-NAG-PEI SPECT / CT Liver Area Dynamic Scanning
[0049] The dynamic SPECT / CT scanning mice were divided into three groups: 3 mice in the control group and 3 mice in the 8-week fibrosis group. The mice were first anesthetized with isoflurane, and then placed in SPECT / CT for scanning. The whole process was anesthetized with isoflurane, the oxygen flow rate was 0.8mL / min, and the ...
Embodiment 3
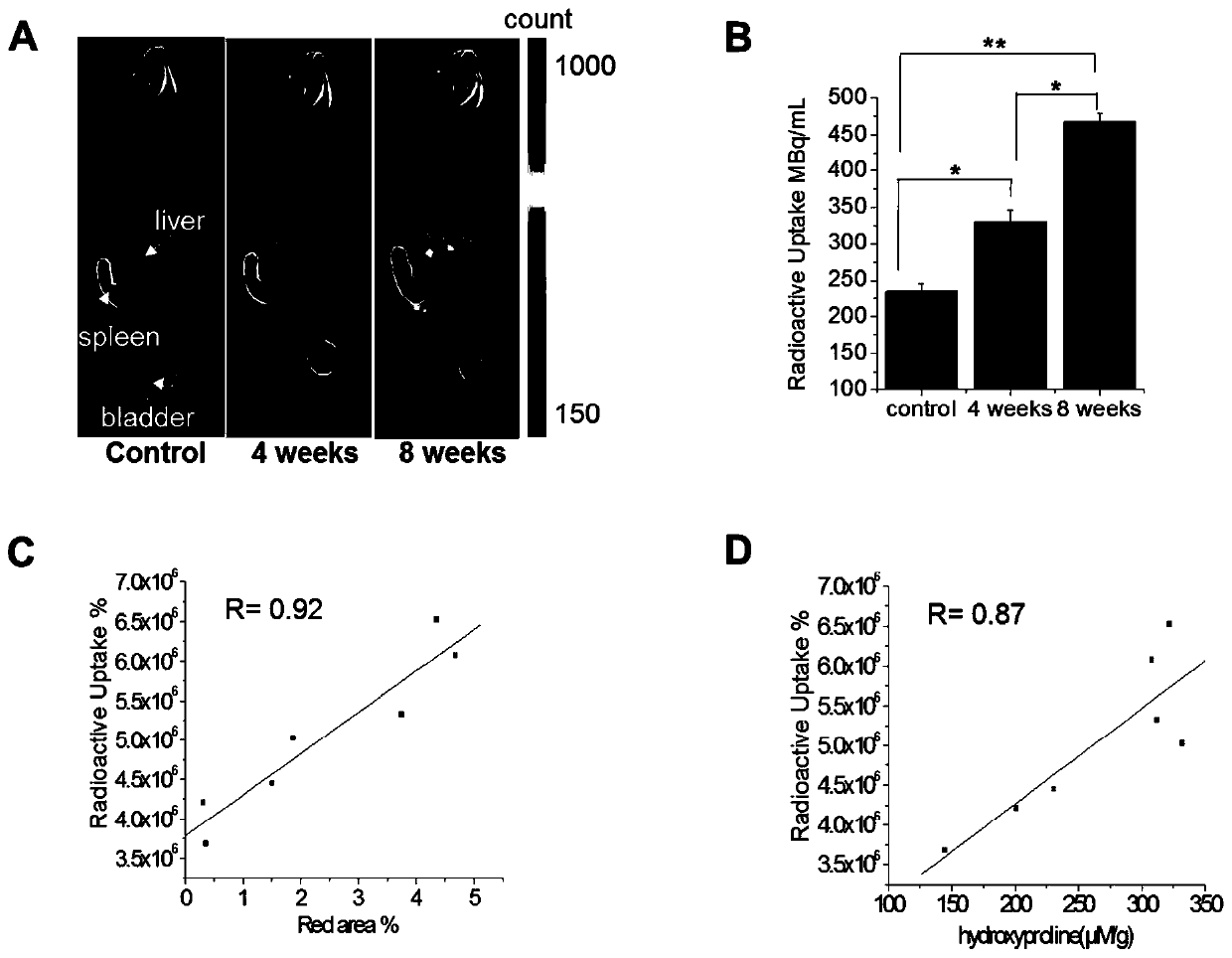
[0054] Example 3 Sirius red staining and autoradiography of fibrotic liver tissue sections
[0055] 1. Tissue section and Sirius red staining
[0056]Tissue embedding: First, the mice in the control group and the fibrosis group that had been imaged were killed by necking, and the liver was taken out. Each liver was cut into two pieces of 1.5×1.5 cm approximately square liver tissue with a razor blade. The edge of the tissue was required to be flat. Wash twice with PBS solution to remove blood cells, and then fix the liver tissue in a centrifuge tube containing 4 ml of 4% paraformaldehyde solution overnight. After washing twice with PBS solution, dehydrate with graded alcohol, with alcohol concentration ranging from 50% to 100% for 30 minutes each time. If something needs to interrupt the experiment, you can put it in 70% alcohol at 4°C overnight. After dehydration, use xylene for transparency, alcohol: xylene 1:1 mixture solution for 30 minutes, then clear twice in xylene, 4...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com