Method for living-body whole-plant detection of transgenic plant by luciferase and application thereof in transgenic maize
A luciferase and plant technology, applied in the fields of molecular biology and genetic engineering, can solve the problems of complex operation and high cost, and achieve the effects of simple operation, reducing uncertainty and increasing accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
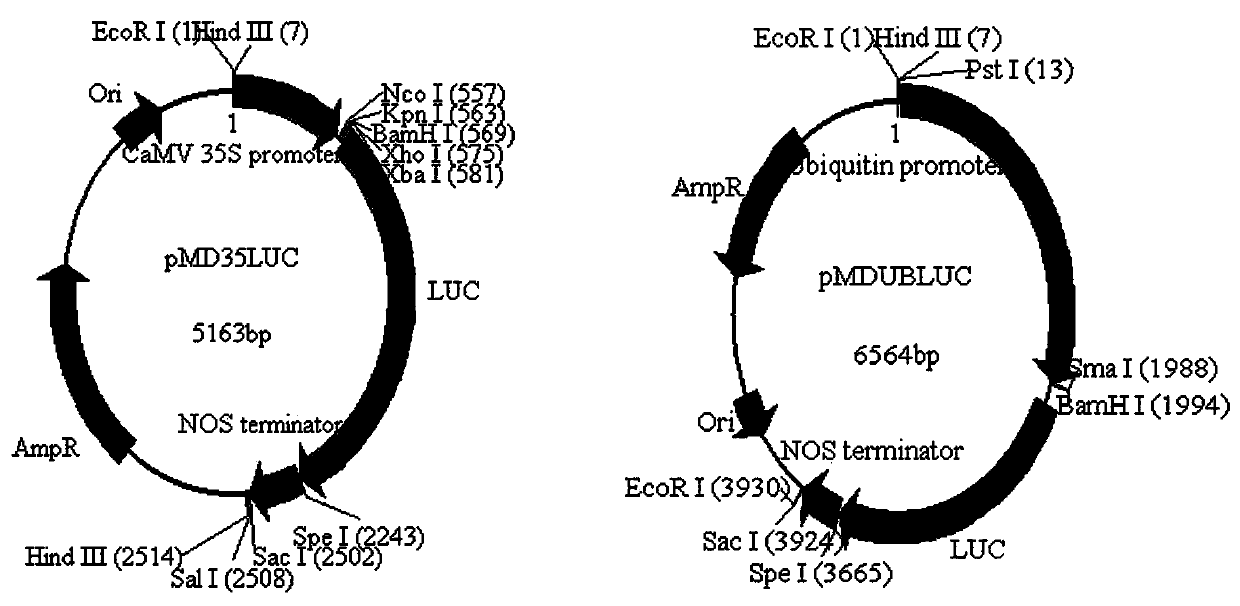
[0027] Embodiment 1: Construction of expression vector
[0028] 1. Construction of pMD18T-Nos: Using the pCAMBIA1305.1 vector (GenBank: AF354045) containing the Nos terminator as a template, use primers NOS-F and NOS-R to amplify by PCR reaction to obtain Nos with restriction sites added at both ends Terminator fragment (the restriction site added at the 5' end is Spe I, and the restriction site added at the 3' end is Sac I ), and connected to the pMD18-T vector, the insertion direction was opposite to the Lacz direction, and the sequence verification was correct, and the intermediate vector pMD18T-Nos was obtained.
[0029] 2. Construction of pMD18T-Luc-Nos: Using the pCAMBIA1305-Luc vector (Genebank: QEG14167.1) containing the Luc luciferase gene as a template, use primers Luc-F (SEQ ID No: 4) and Luc-R (SEQ ID No: 5), the Luc gene fragment with restriction sites added at both ends was amplified by PCR reaction (the restriction site added at the 5' end is Bam H I, xho ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Ultrasonic-assisted pollen-mediated transformation of maize Transformation of maize
[0033] 1. Preparation of transformed plasmids: extract the plasmids by alkaline lysis, dissolve them in TE buffer, and detect the concentration of the plasmids with a micro-ultraviolet spectrophotometer. Adjust the plasmid concentration to 200 µg / ml. A 260 / A 280 The value is around 1.8 for backup.
[0034] 2. Prepare pollen suspension: 9% sucrose + 0.9% NaCl solution (PH7.0), pre-cool at 4°C, and add oxygen to increase its oxygen content.
[0035] 3. Ultrasonic-assisted pollen-mediated maize transformation: collect 3 g of maize pollen at the full flowering stage from 10:00 to 12:00 on the day of transformation, put it in 10 ml of pollen suspension, add 200 g of plasmid DNA, and use an ultrasonic pulverizer (JY92-Ⅱ type) for ultrasonic treatment. Ultrasonic treatment parameters are: power 180 W, working time 6 s, interval 6 s, working times 6 times. Then apply the tre...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3: Optimizing the conditions for live whole plant detection of transgenic maize by live imaging system
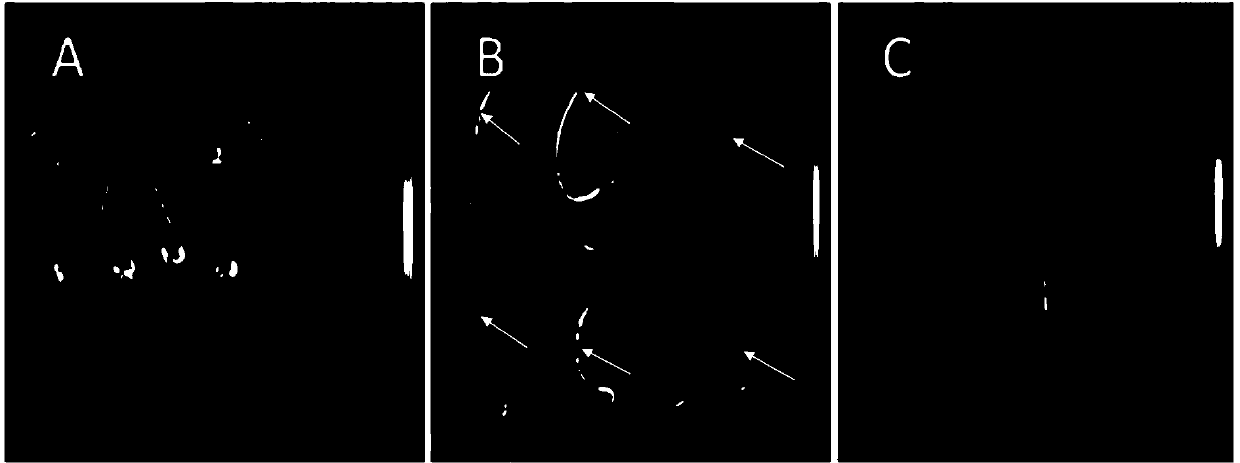
[0037] (1) Determine the parameters of the in vivo imaging system: After spraying the substrate on the young corn sprouts, put them into the dark box of the in vivo imaging system, and after standing for 2 minutes, compare the exposure time of 2 minutes, the pixel binning value binning4×4 and the exposure time of 5 minutes, and the pixel Merge value binning 8×8 imaging effect. It was found that the highest signal value of the former was 124 cps, while the signal value of the latter was 1736 cps, which was more sensitive and suitable for the detection of maize sprouts ( figure 2 ).
[0038] (2) Determine the size of maize plants: Under the above exposure conditions, the fluorescence signals of maize buds and two-leaf stage seedlings were compared. It was found that the fluorescent signal could not be detected when the shoot length was less than 1cm; a clear...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com