Method for synthesizing xylitol by aspergillus oryzae engineering bacteria with enhanced hemicellulose saccharification capacity
A technology of hemicellulose and Aspergillus oryzae, applied in the field of xylitol synthesis by Aspergillus oryzae engineering bacteria, can solve the problem of low saccharification ability of hemicellulose
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
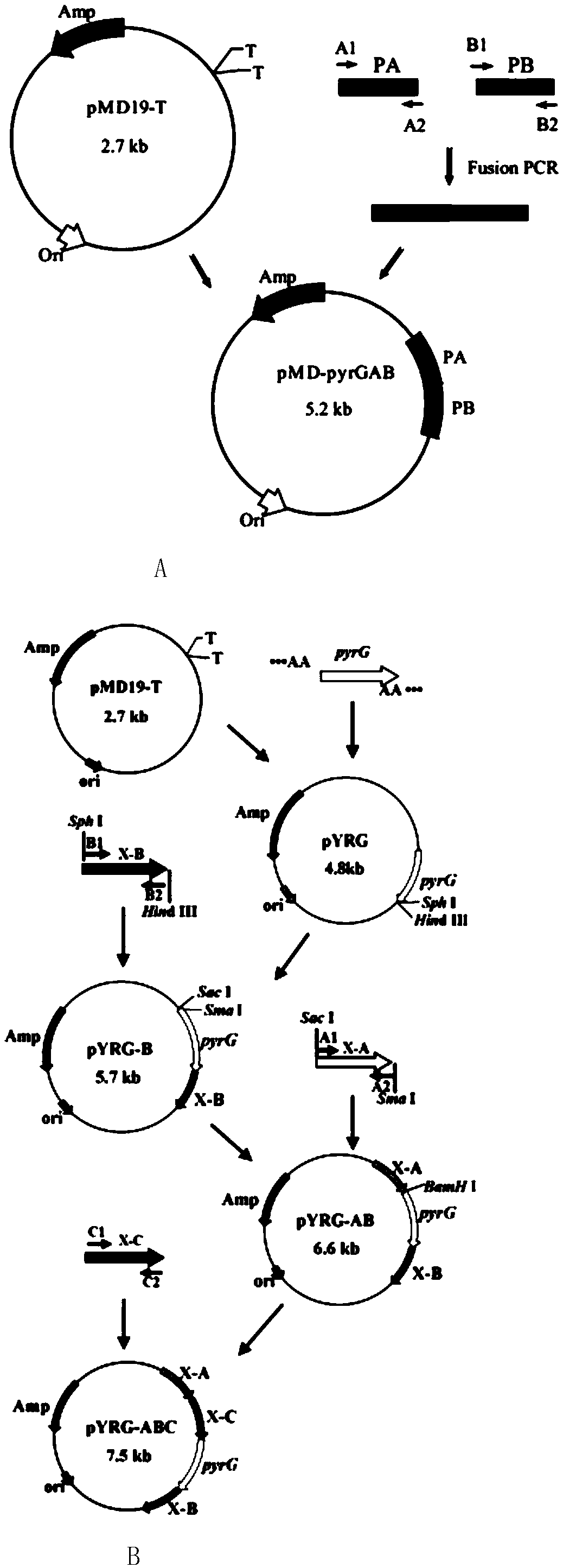
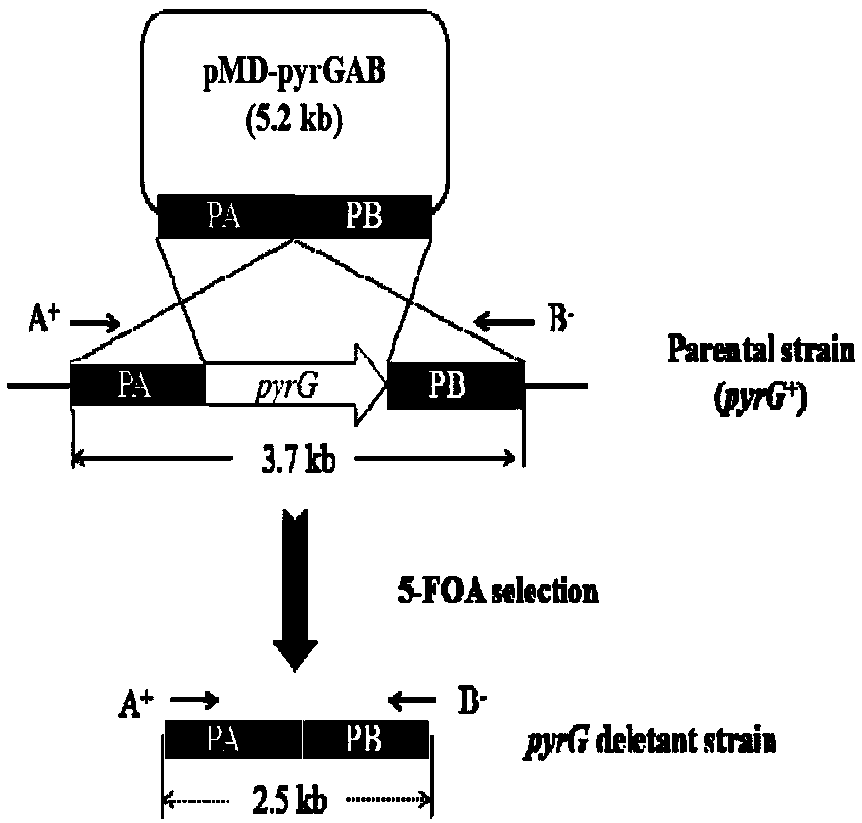
[0042] 1. Construction of pyrG knockout targeting vector pMD19-pyrGAB
[0043] The construction process of pyrG knockout targeting vector pMD19-pyrGAB is as follows: figure 1 (A) shown. Using the genome of A. oryzae CICC2012 as a template, primers PA-F / PA-R and PB-F / PB-R were used to PCR amplify the upstream and downstream homologous recombination fragments 1.0 kb PA and 1.5 kb of pyrG (GenBank accession number: GQ496621) kb PB, using primers PA-F / PB-R to splice the upstream and downstream fragments by overlap extension PCR, the 2.5kb spliced fragment was ligated with the 2.7kb linear vector pMD19-T to obtain the 5.2kb pyrG knockout targeting vector pMD19-pyrGAB, and Enzyme digestion verification.
[0044] 2. In the pyrG knockout box pMD19-pyrGAB, both ends of the fusion fragment PA and PB contain Sac I and BamH I restriction sites, and about 0.6kb of the fusion fragment also contains a BamH I restriction site, so pyrG After the knockout cassette pMD-pyrGAB was digested w...
Embodiment 2
[0052] 1. Construction of xdh traceless knockout targeting vector pMD19-pyrG-xdhABC
[0053] The construction process of the xdh seamless knockout targeting vector pMD19-pyrG-xdhABC is as follows figure 1 (B) shown. The positions of the upstream fragments xdh-A, xdh-B and the downstream fragment xdh-C of Aspergillus oryzae xdh (GenBank accession number: GQ222265) gene are shown in Image 6 . Using primers xdh-A1 / xdh-A2, xdh-B1 / xdh-B2, xdh-C1 / xdh-C2 and pyrG-F / pyrG-R respectively, PCR amplified xdh-A, xdh-B, xdh-C and four fragments of pyrG. The pyrG fragment was connected with pMD19-T to obtain the recombinant plasmid pYRG. Digested with restriction endonuclease SphI / HindIII and ligated with the xdh-B fragment to obtain the recombinant plasmid pYRG-B. Digested with SacI / SmaI and ligated with the xdh-A fragment to obtain the recombinant plasmid pYRG-AB. The plasmid was single-digested with BamH I, then smoothed and dephosphorylated with T4 DNA Polymerase and Alkaline Phos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com