Polyolefin-g-polybenzimidazole grafted copolymer as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of graft copolymers and benzimidazoles, which is applied in the field of polyolefin-g-polybenzimidazole graft copolymers and its preparation, can solve problems such as lowering of proton conductivity, lowering of mechanical properties, loss of phosphoric acid, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0072] The preparation method of the present invention will be further described in detail in conjunction with specific examples below. It should be understood that the following examples are only for illustrating and explaining the present invention, and should not be construed as limiting the protection scope of the present invention. All technologies realized based on the above contents of the present invention are covered within the scope of protection intended by the present invention.
[0073] The experimental methods used in the following examples are conventional methods unless otherwise specified; the reagents and materials used in the following examples can be obtained from commercial sources unless otherwise specified.
Embodiment 1
[0091] Preparation of polyacrylic acid grafted m-polybenzimidazole (PAA-g-mPBI)
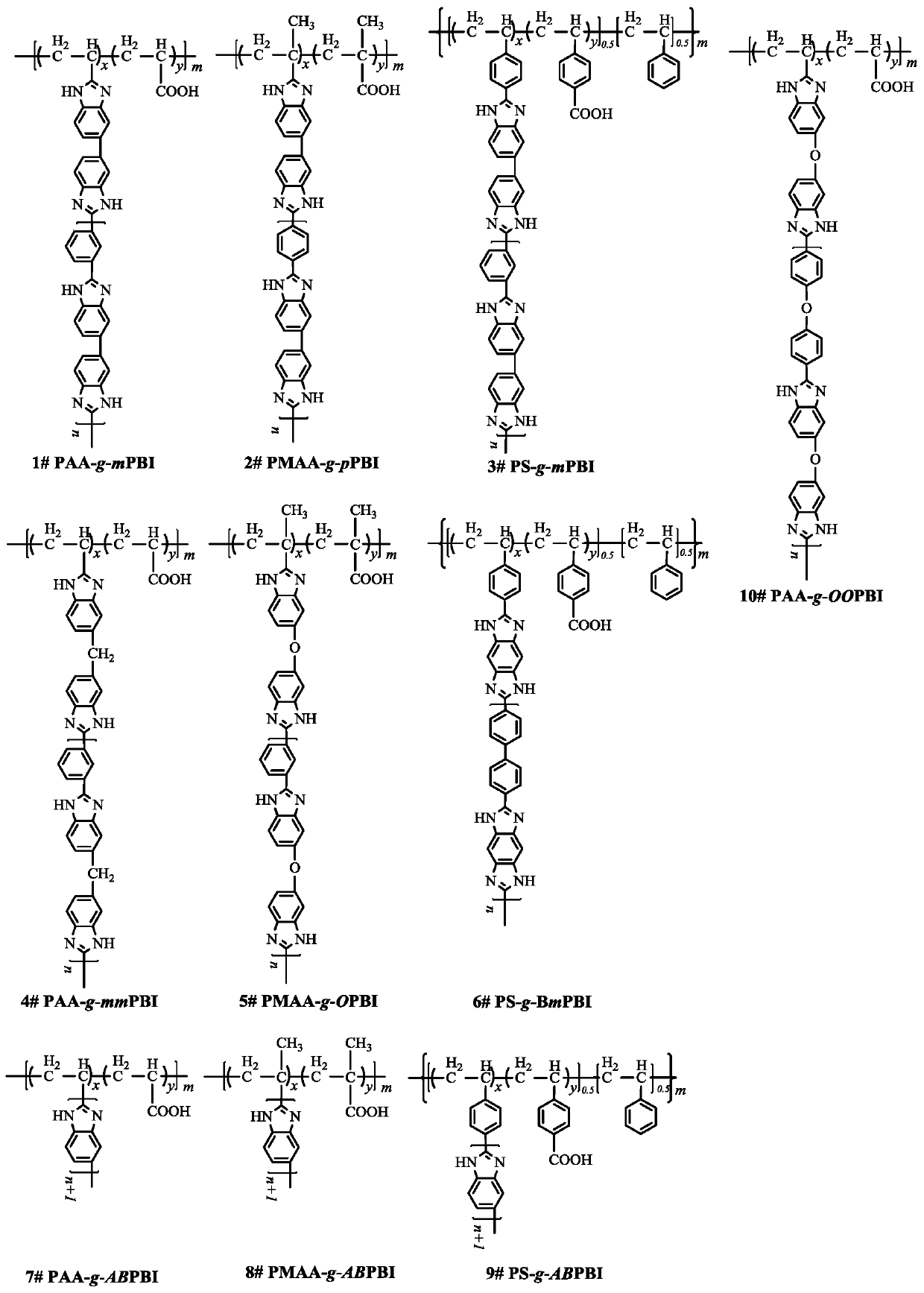
[0092] Select polyacrylic acid (PAA) as the main chain, and mPBI as the branched chain synthesis such as figure 2 The PAA-g-mPBI graft copolymer shown in 1# structural formula.
[0093] Add dry mPBI (6.20 g, 0.2 mmol) and PAA (1.44 g, carboxyl 20 mmol) in DMF according to the molar ratio of mPBI and carboxyl group of 1:100 to form a solution with a solid content of 5%, and then pass it into an inert Gas Argon was refluxed at 150°C and stirred for 24h. After the reaction, the solid content of the solution was increased to 20% by rotary evaporation, and then the solution was poured on the PET film to coat the film with a 300 μm doctor blade, and dried at 80° C. to obtain a film with a thickness of about 50 μm.
Embodiment 2
[0095] Preparation of polymethacrylic acid grafted m-polybenzimidazole (PMAA-g-mPBI)
[0096] Select polymethacrylic acid (PMAA) as the main chain, and mPBI as the branched chain synthesis such as figure 2 The PMAA-g-mPBI graft copolymer shown in 2# structural formula.
[0097] Add dry mPBI (6.20g, 0.2mmol) and PMAA (0.87g, carboxyl 10mmol) and dissolve in DMF according to the molar ratio of mPBI and carboxyl group of 1:50 to form a solution with a solid content of 10%, and then pass it into an inert Gas Argon was refluxed at 180°C and stirred for 20h. After the reaction, the solid content of the solution was increased to 20% by rotary evaporation, and then the solution was poured on the PET film to coat the film with a 300 μm doctor blade, and dried at 80° C. to obtain a film with a thickness of 48 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com