A method for inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human amniotic membrane epithelial cells
A technology of epithelial cells and human amniotic membrane, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as no effective inhibitors have been found
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] Embodiment 1: Screening of the drug concentration of SB431542
[0103] 1.1 Proliferation curve of human amniotic epithelial cells with different concentrations of SB431542
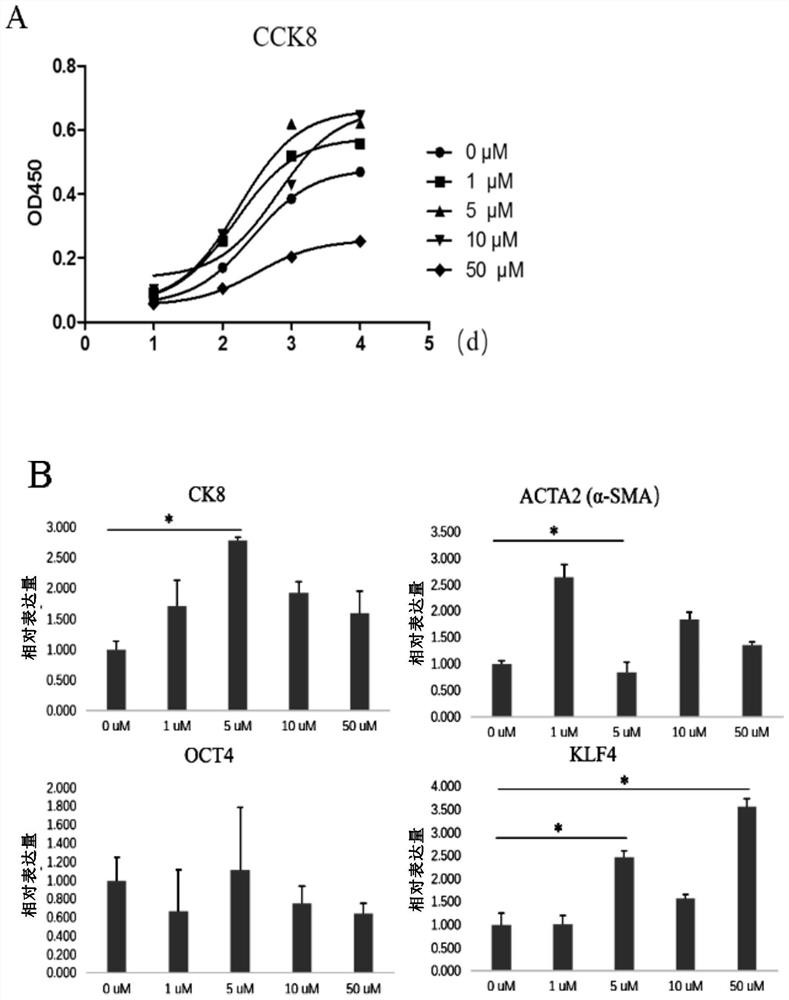
[0104] In this example, using CCK8 as a marker of cell proliferation, the daily metabolic OD values of P2 generation human amniotic epithelial cells under the influence of different concentrations of drugs were detected.
[0105] The result is as figure 1 As shown in A. From the experimental data, 50 μM SB421542 has a significant inhibitory effect on cell proliferation, while low doses of SB431542 (0 μM, 1 μM, 5 μM, 10 μM) have no inhibitory effect on cell proliferation.
[0106] 1.2 Effects of different concentrations of SB431542 on gene expression in human amniotic epithelial cells
[0107] In order to screen out the optimal drug concentration, in this embodiment, qPCR was also used to detect the effect of SB431542 on the expression levels of each gene in the P2 generation human amniotic epit...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Example 2: Effect of 5 μM SB431542 on the proliferation of human amniotic epithelial cells
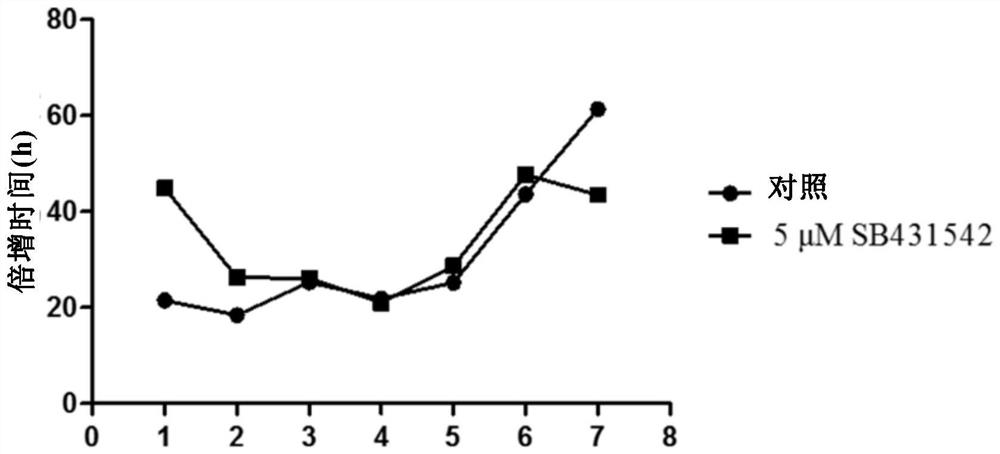
[0111] In this embodiment, the number of cells with 90% confluence and the time (h) of each generation were recorded, and the time required for cell doubling of each generation was calculated. Among them, the control group is the cells without drug addition, and the experimental group is the cells treated with 5 μM SB431542.
[0112] Experimental results such as figure 2 shown. The experimental data showed that the cell doubling time of P1-P6 human amniotic epithelial cells with and without drug was basically the same. In the P7 generation, the doubling time of cells with drugs was 43.5h, and that of cells without drugs was 61.4h.
[0113] Therefore, 5 μM SB431542 can maintain the proliferation of amnion epithelial cells for 7 passages.
Embodiment 3
[0114] Example 3: Effects of 5 μM SB431542 on gene expression levels of human amniotic epithelial cells
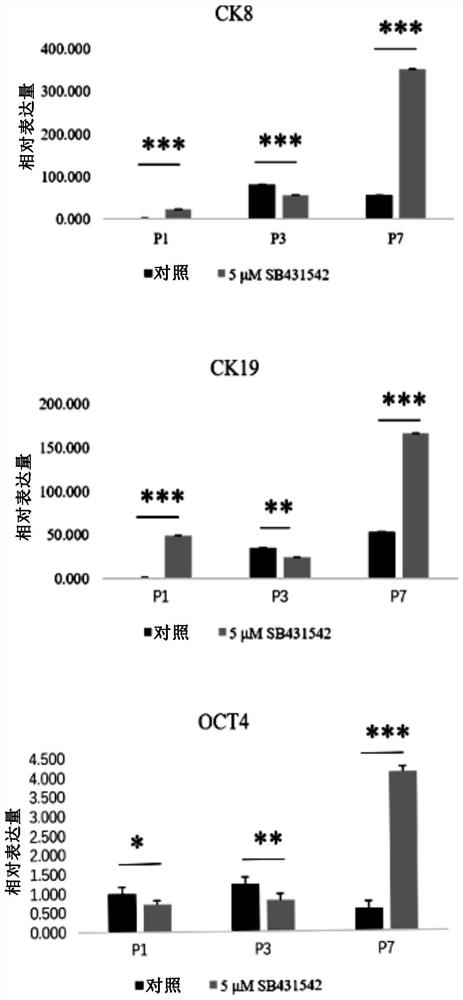
[0115] In this embodiment, the expression levels of each gene in the P1, P3, and P7 generations of human amniotic epithelial cells in the control group and the experimental group were detected by qPCR.
[0116] The control group was cells not affected by drugs, and the experimental group was cells treated with 5 μM SB431542. The markers used were epithelial markers keratin 8 (CK8) and 19 (CK19), stem cell markers OCT4 and KLF4, and mesenchymal stem cell markers Vimentin and ACTA2 (α-SMA).
[0117] Experimental results such as image 3 shown. From the experimental data, there were significant differences in the gene expression levels of CK8, CK19, KLF4, OCT4, Vimentin and ACTA2 (α-SMA) between the control group and the experimental group (P<0.05). In particular, at the P7 generation, the expression levels of CK8, CK19, KLF4, and OCT4 in the experimental group cells were ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com