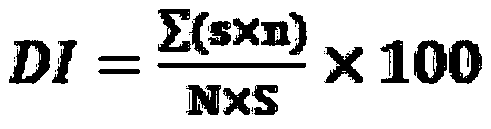Method for identifying southern blight disease resistance of peppers
A technology for disease resistance identification and white silkworm disease, which is applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial determination/inspection, etc. The identification of disease resistance is difficult and random, so as to achieve the effects of accurate and reliable identification results, good stability of results, and high sensitivity of disease discrimination.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The isolation and identification of embodiment 1 pathogenic bacteria
[0037] Pepper white silkworm strain (Sclerotium rolfsii sacc.) was isolated and purified from the diseased plants with typical white silkworm symptoms collected from the pepper planting base in the scientific research demonstration garden of the Hunan Vegetable Research Institute in Changsha City, Hunan Province. The symptoms are : The base of the stem grows white silk-like hyphae, spreading radially. When the humidity is high, the ground and the base of the stem are more obvious. In the late stage, the base of the stem produces a large number of small brown rapeseed-like sclerotias.
[0038] The purification process is as follows: pick out mycelia (Hypha, H) from the collected diseased strains with sterile tweezers and place them in the middle of the PDA medium, and simultaneously pick out the sclerotium (Sclerotium, S) and put them in the middle of the PDA medium. Prepare 5 dishes each of silk and ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2 Identification of Pepper Blight Disease Resistance
[0043] (1) Activating and cultivating the white silkworm of capsicum, preparing pathogenic bacteria inoculated bacterial strips
[0044]1. Preparation of PDA medium: Peel and weigh 200g of fresh potatoes, chop them, add 1L of distilled water, boil them in a pot, filter with 2 layers of gauze, remove the filter residue, add 20g of glucose to the filtrate, and distill to volume to 1L. Prepare five 200mL triangular flasks, add 5g of agar powder to each bottle, and then pour the potato juice containing glucose into the triangular flasks. Put it into a sterilizing pot after being packaged with a parafilm, and sterilize with high-pressure steam for 30 minutes at 121°C. After sterilization, when the temperature of the culture medium is 60-80°C, shake it well, and pour it into a flat plate on a sterile operating table.
[0045] 2. The pathogenic bacteria isolated in Example 1 is preserved for subsequent use. When...
experiment example
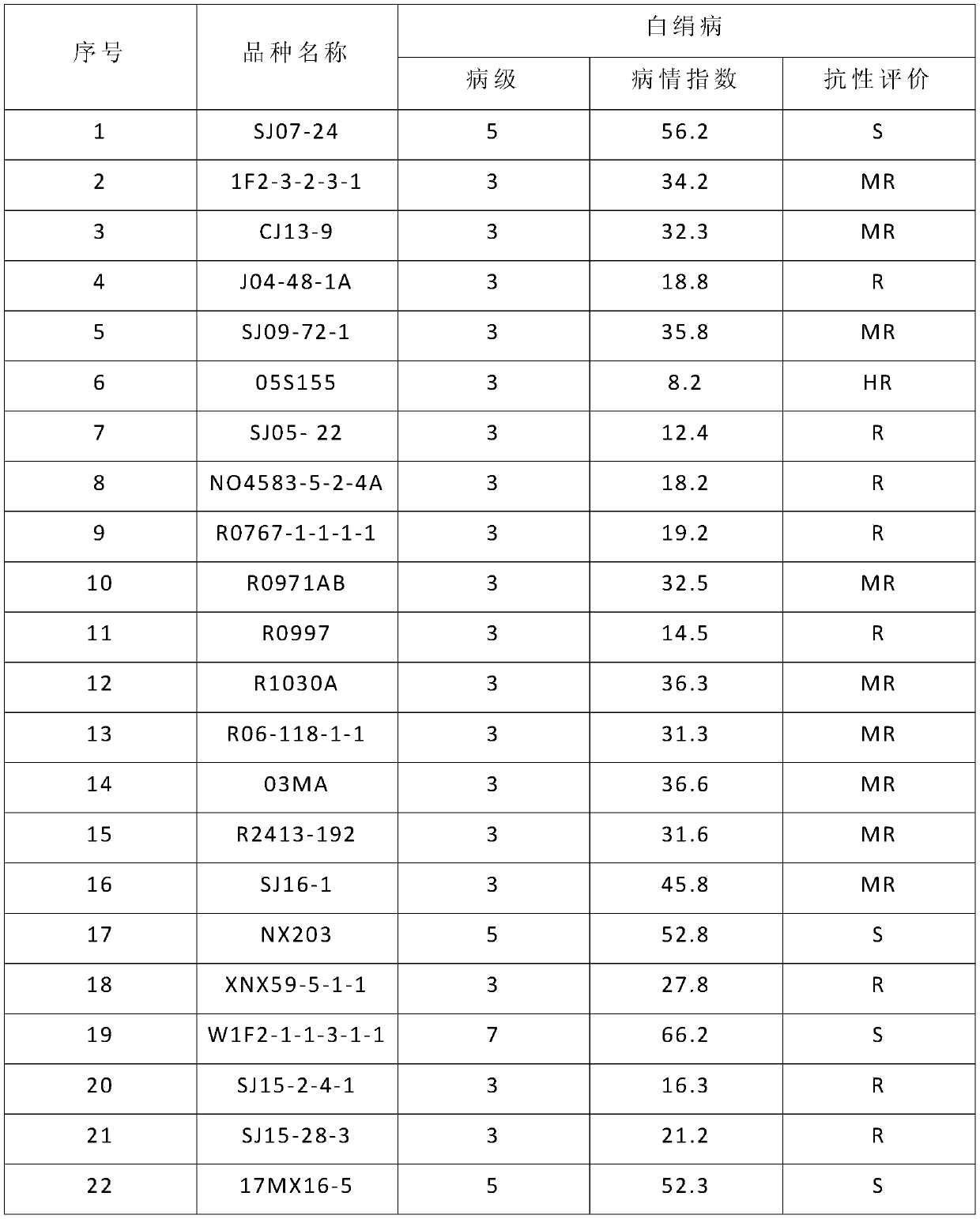
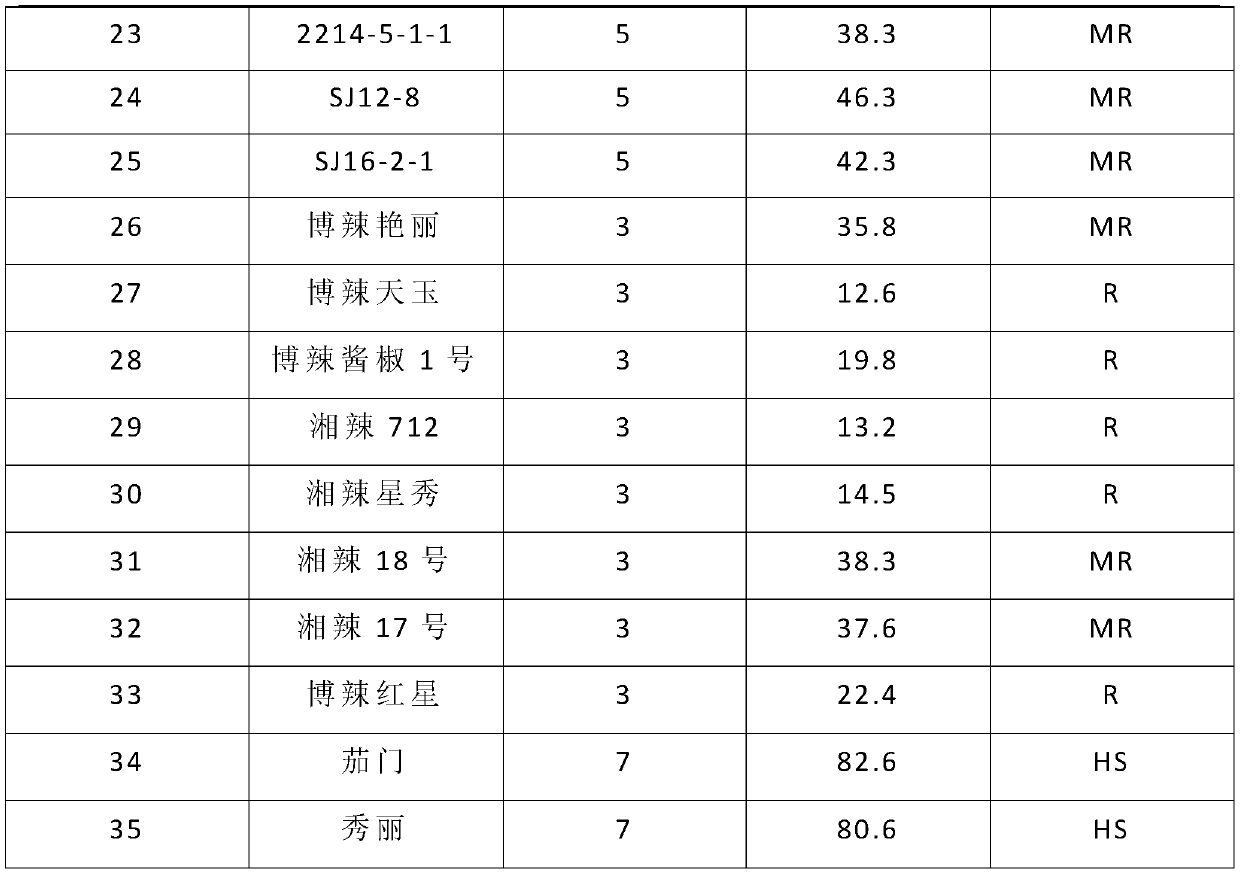
[0074] The indoor inoculation identification of disease resistance was carried out on 25 breeding materials and 10 pepper varieties by the identification method in Example 2. The identification results are shown in the table below. The results show that among the 35 materials (variety) identified, no immune materials have been found, 1 high-resistant material, 13 disease-resistant materials, 15 medium-resistant materials, 4 susceptible materials, 2 A high-sensitivity material. The material (variety) identified in this experimental example is more consistent with the disease incidence rate planted in the disease nursery and in the field, indicating that this identification method is in a controlled environment, has high inoculation efficiency, and the identification results are accurate and reliable. Breeding for disease resistance.
[0075]
[0076]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com