Stable high-internal-phase Pickering emulsion of modified bacterial cellulose nanofibers and preparation method thereof
A technology of bacterial cellulose and nanofibers, applied in the field of high internal phase Pickering emulsion, to achieve good viscoelasticity, simple method and high stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] 1. Preparation of bacterial cellulose nanofibers (BCNs)
[0035] CGMCC 3917 strain (Komagataeibacter hansenii) was used to culture and ferment under static conditions at 30°C, and the medium (pH 5.0) contained glucose 2% (w / v), yeast extract 0.5% (w / v), K 2 HPO 4 0.1% (w / v), MgSO 4 1.5% (w / v) and ethanol 2% (v / v). After 14 days of static culture, the whole piece of cellulose film can be obtained in the culture medium. Rinse the cellulose membrane with tap water overnight, then soak it in 0.1M sodium hydroxide solution at 80°C for 2 hours, and then rinse it repeatedly with deionized water to completely remove the alkali to obtain bacterial cellulose.
[0036] 5.0 g of bacterial cellulose was mixed with 75 mL of HCl (2.5 M), and then magnetically stirred (200 rpm) at 70° C. for 4 h to hydrolyze it. After hydrolysis, cool to room temperature, centrifuge at 10,000×g for 10 minutes, collect the precipitate after hydrolysis, and then perform secondary hydrolysis on the ...
Embodiment 2
[0045] The difference between Example 2 and Example 1 is: in step 2.1), bacterial cellulose nanofibers are prepared with distilled water to form an aqueous solution of bacterial cellulose nanofibers with a mass concentration of about 0.1% (bacterial cellulose nanofibers: the weight ratio of water=0.1 : 100), the mass ratio of BCNs:SPI in step 2.3) is 5:25, and the material obtained by homogenization treatment in step 2.3) is rotary steamed in a water bath (45° C.) to 21.43% of the original mass.
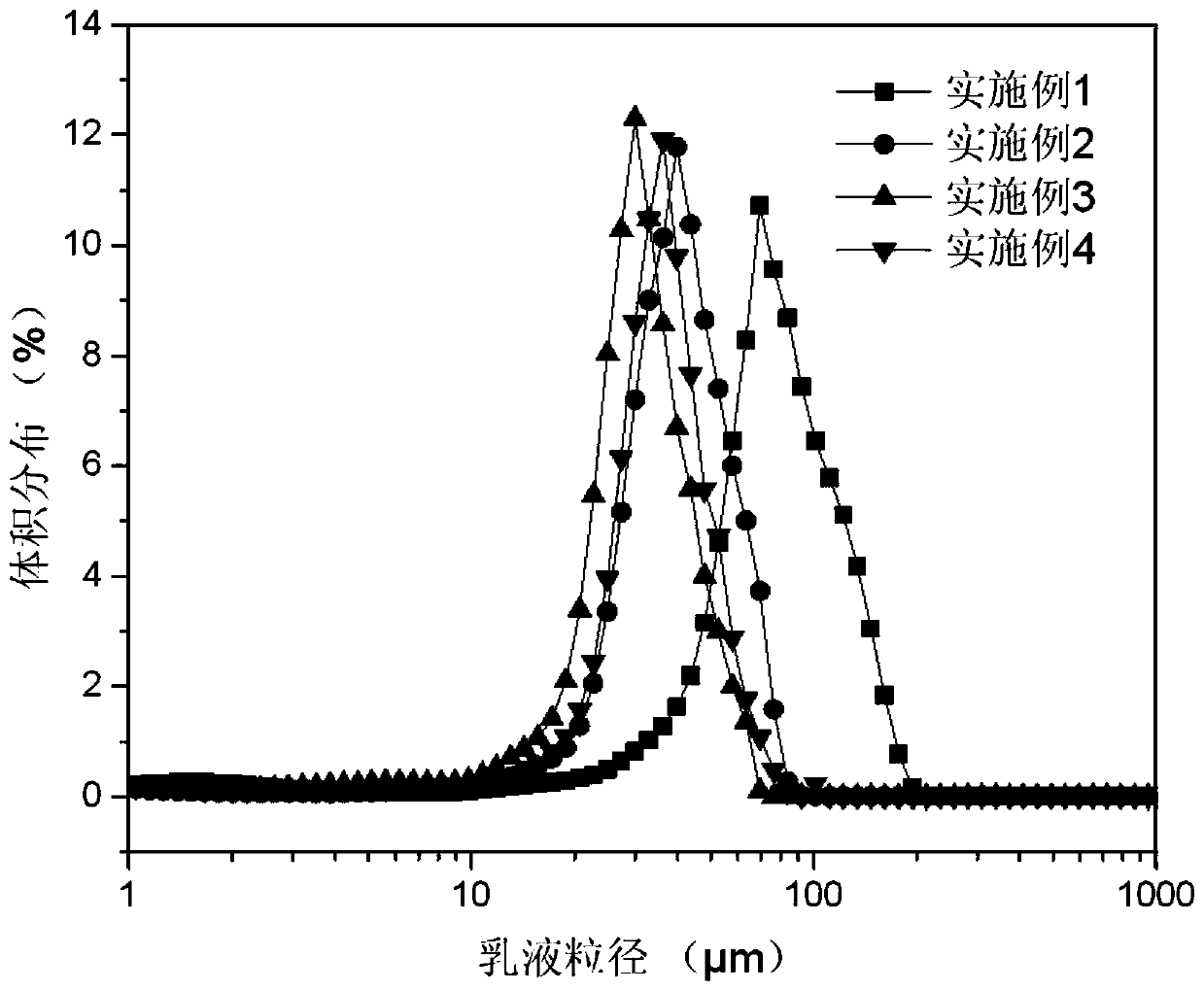
[0046] according to figure 1 and figure 2 The newly prepared high internal phase Pickering emulsion and the appearance of the emulsion after storage for 2 months are shown respectively. The high internal phase Pickering emulsion prepared in Example 2 has strong stability, and it has not been demulsified after being placed at room temperature for 2 months. Use a laser particle size analyzer (LS13320, Beckman, US) to measure the particle size of the new high internal phase Pickering ...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The difference between Example 3 and Example 1 is: in step 2.1), the bacterial cellulose nanofibers are prepared with distilled water to form an aqueous solution of bacterial cellulose nanofibers with a mass concentration of about 0.14% (bacterial cellulose nanofibers: the weight ratio of water=0.14 : 100); step 2.3) in BCNs:SPI mass ratio is 7:25, step 2.3) homogeneous treatment of the material obtained by water-bath rotary steaming (45 ℃) to 22.86% of the original mass.
[0049] according to figure 1 and figure 2 The newly prepared high internal phase Pickering emulsion and the appearance of the emulsion after storage for 2 months are respectively shown. The high internal phase Pickering emulsion prepared in Example 3 has strong stability, and it has not been demulsified after being placed at room temperature for 2 months. Use a laser particle size analyzer (LS13320, Beckman, US) to measure the particle size of the new high internal phase Pickering emulsion, the res...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com