High polymer material damage in-situ test device and method based on ultrasonic waves
A polymer material, in-situ testing technology, applied in the direction of material analysis, measurement device, analysis material, etc. using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, it can solve the problem of difficulty in ensuring the accuracy of test results, increasing test difficulty and instability, The test results have a great impact on problems such as increasing the difficulty and instability of the test, improving the test efficiency, and saving the test time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
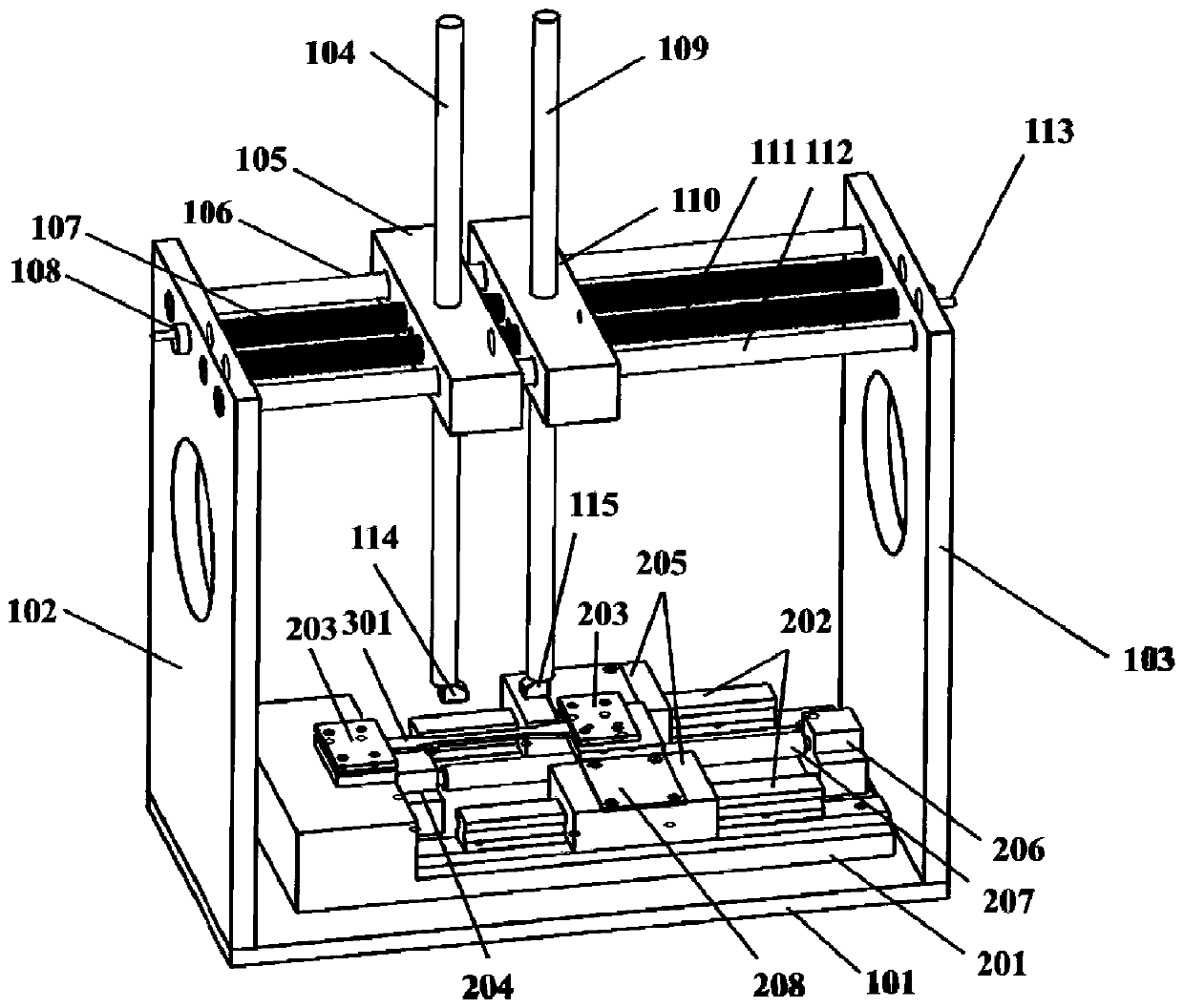
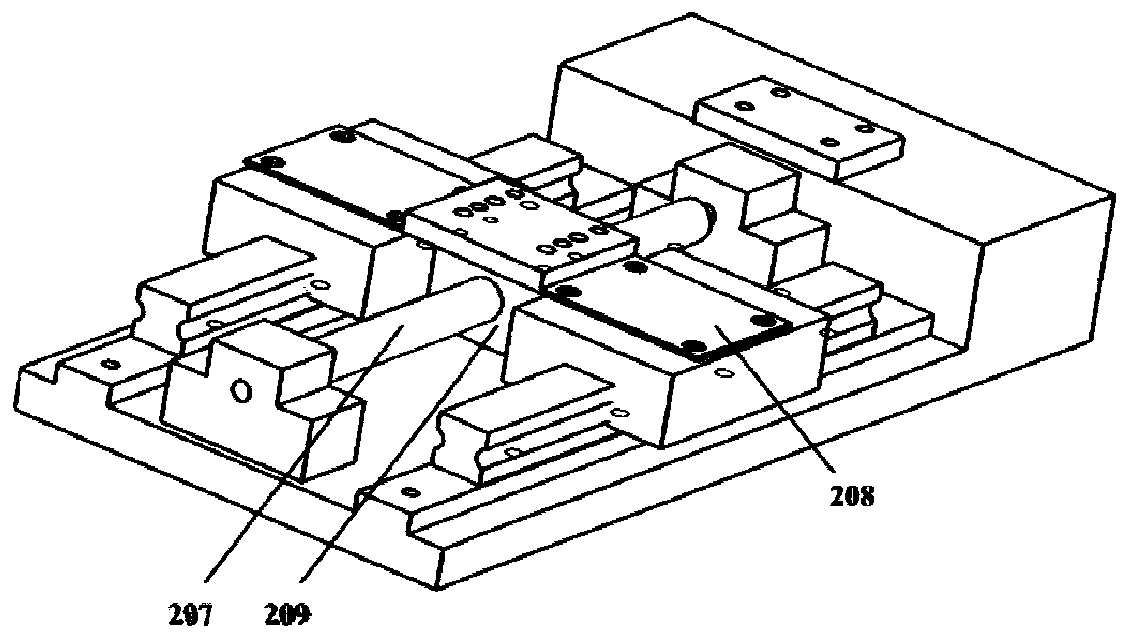
[0045] The testing device comprises an aluminum alloy bottom plate 101, a left side plate 102 and a right side plate 103, a first vertical bar 104, a first slider 105, a first cross bar 106, a first lead screw 107, and a first shaking wheel 108 to form a support. , the second vertical bar 109, the second slider 110, the second lead screw 111, the second cross bar 112, the second rocking wheel 113, the ultrasonic transmitting probe 114, the ultrasonic receiving probe 115, the in-situ stretching base 201, the slide rail 202, clamping plate 203, fixed support 204, slide rail slider 205, movable support 206, ball screw 207, slider connecting piece 208, lead screw nut seat 209 and measured polymer sample 301. In this example, taking the common polymer material-polyethylene as an example, ultrasonic waves are used to quantitatively test the damage variables of polyethylene samples.
[0046] Both sides of the top of the lead screw nut seat 209 are connected with the slide rail slider...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2 test process
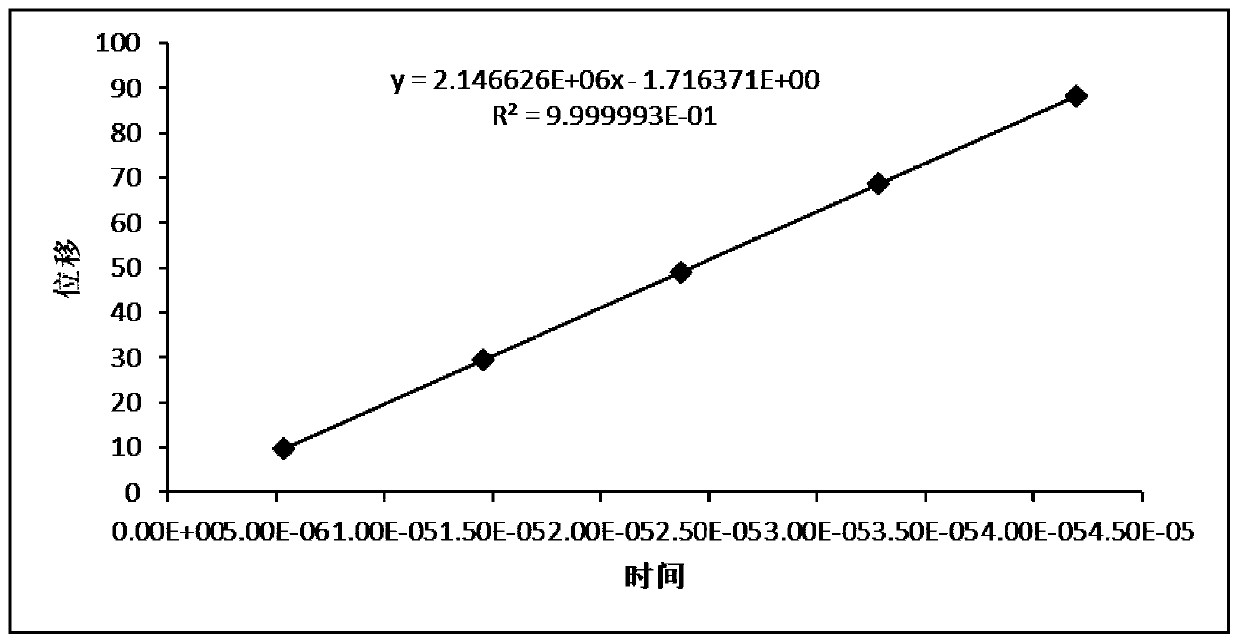
[0052] First, the polyethylene sample 301 is fixed by the sample clamping plate 203, and the ultrasonic transmitting probe 114 is fixed on the sample 301 by moving the first vertical bar 104 downward, and an appropriate amount of coupling agent is applied between the transmitting probe and the sample 301 to Improve sound wave transmission efficiency. Adjust the second rocking wheel 113 so that the second slide block 110 moves to the left to be close to the first slide block 105, and the ultrasonic receiving probe 115 is fixed on the sample 301 by moving the second vertical bar 109 downward, and the receiving probe and the test sample Apply an appropriate amount of couplant between samples 301. The ball screw 207 is controlled by the servo motor to stretch the sample 301 at a constant speed of 1 mm / min until the displacement reaches 1 mm and stops, and the ultrasonic signal is recorded. At this time, the second slider 110 is close to the fir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com