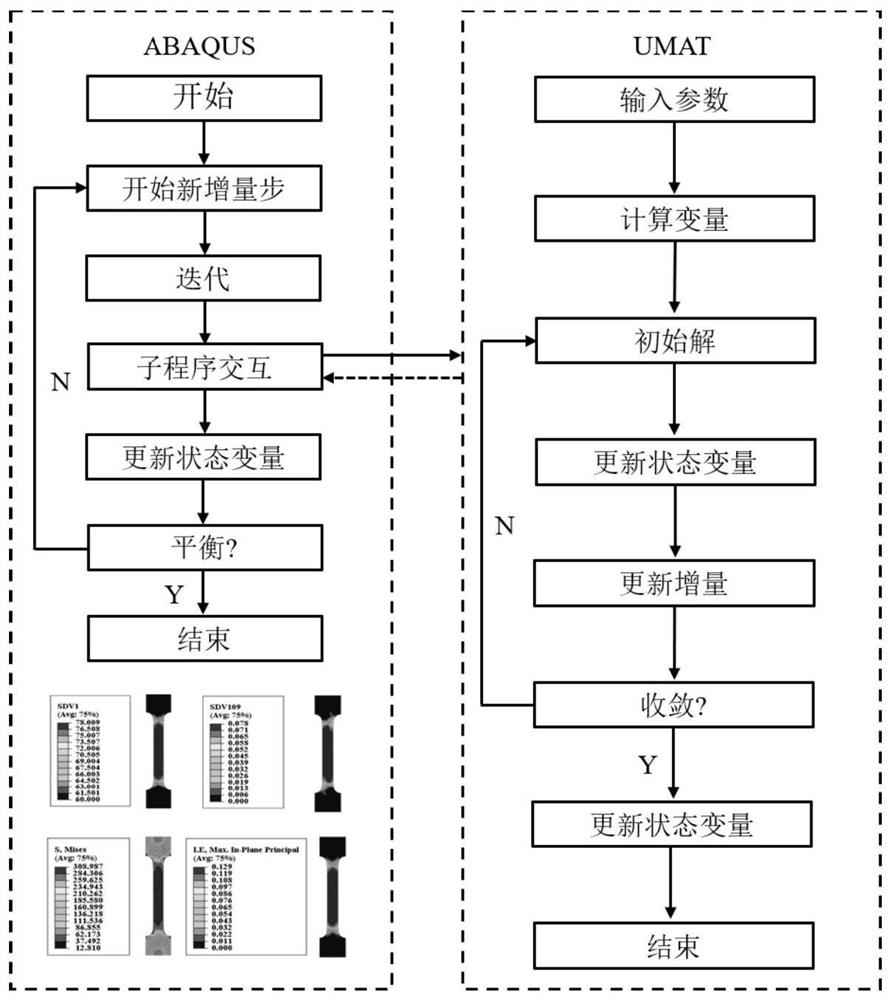
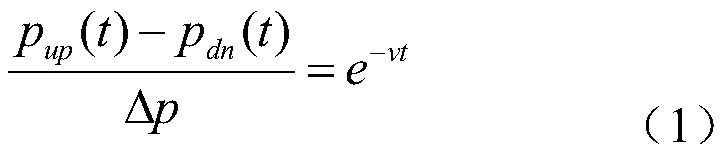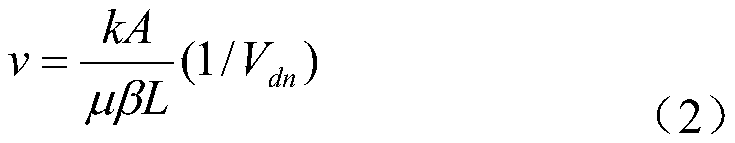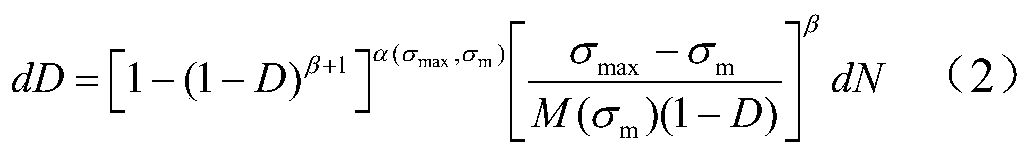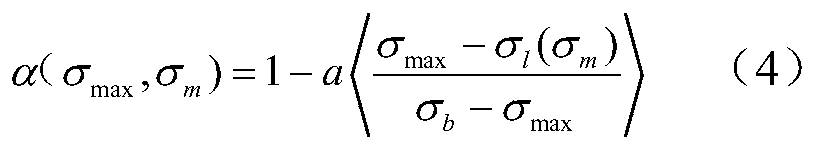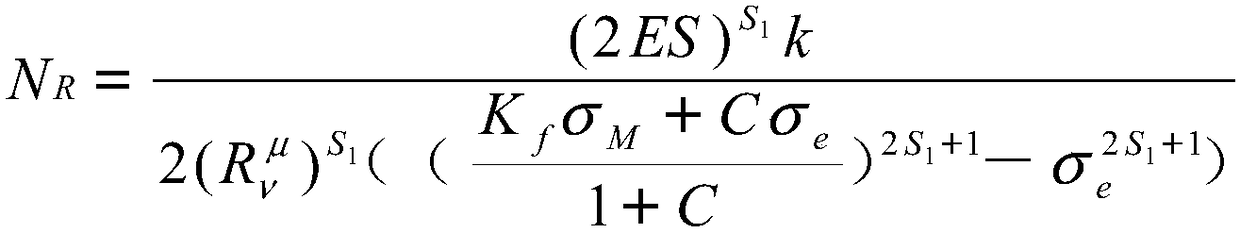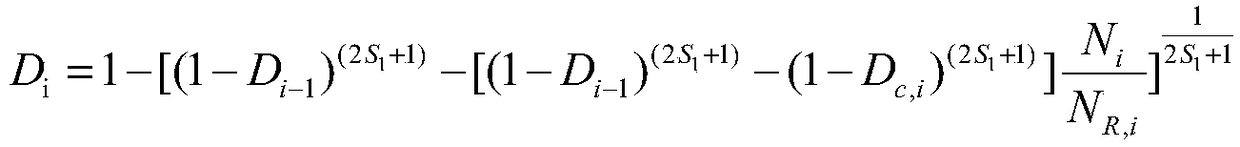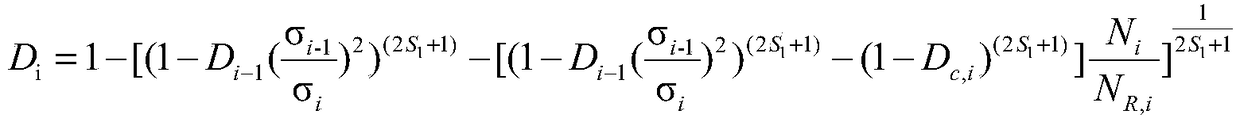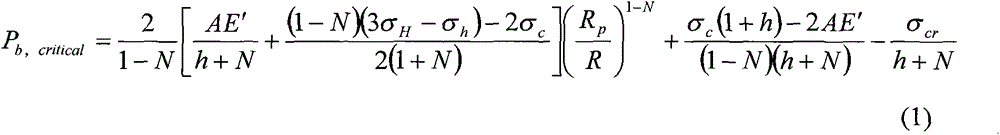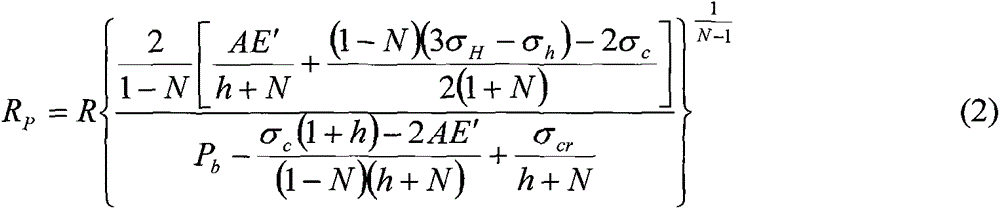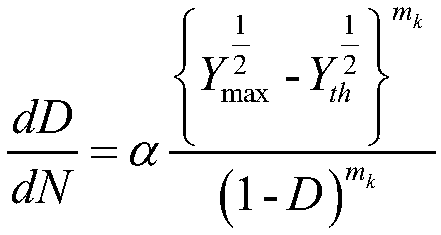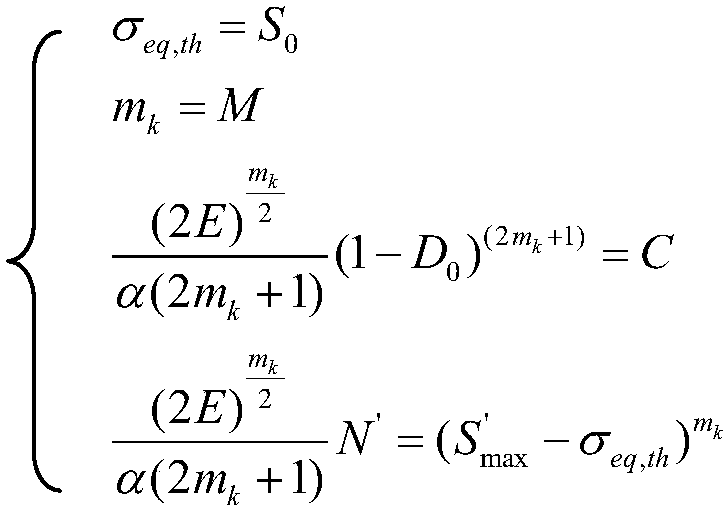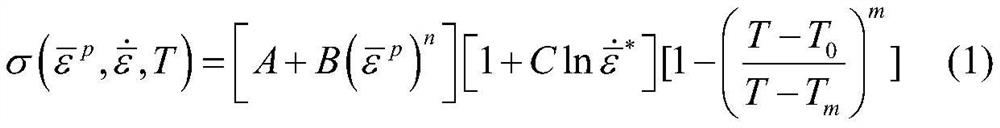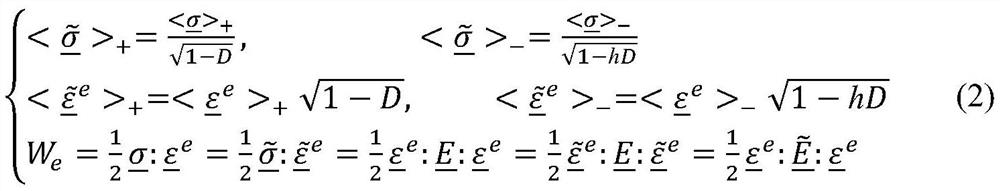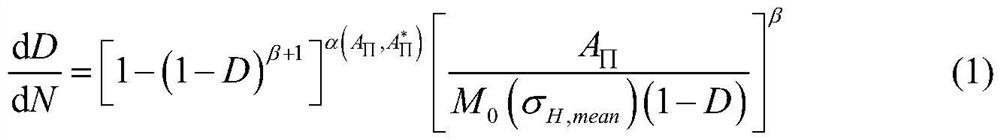Patents
Literature
64 results about "Damage mechanics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
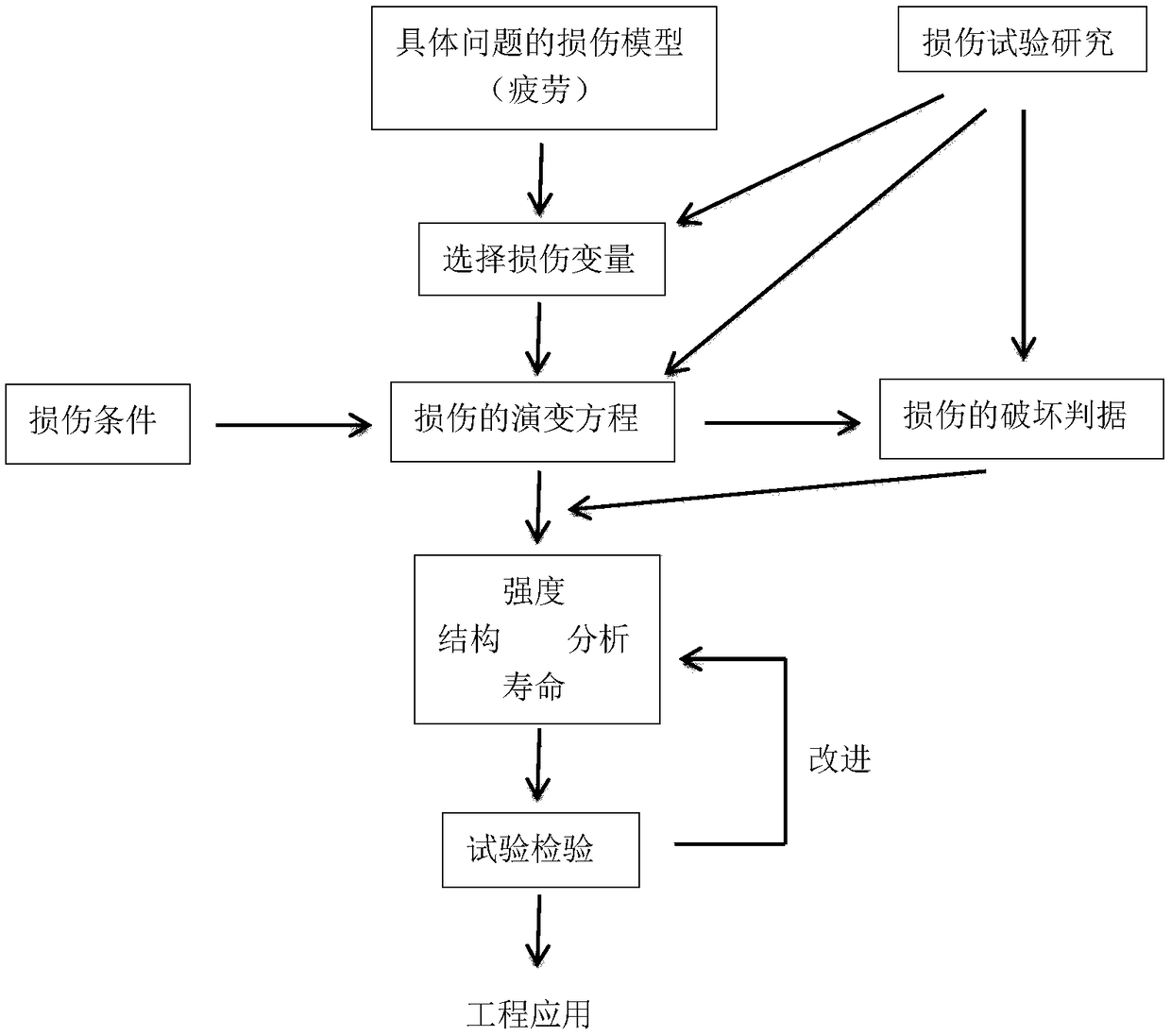
Damage mechanics is concerned with the representation, or modeling, of damage of materials that is suitable for making engineering predictions about the initiation, propagation, and fracture of materials without resorting to a microscopic description that would be too complex for practical engineering analysis. Damage mechanics illustrates the typical engineering approach to model complex phenomena. To quote Dusan Krajcinovic, "It is often argued that the ultimate task of engineering research is to provide not so much a better insight into the examined phenomenon but to supply a rational predictive tool applicable in design". Damage mechanics is a topic of applied mechanics that relies heavily on continuum mechanics. Most of the work on damage mechanics uses state variables to represent the effects of damage on the stiffness and remaining life of the material that is damaging as a result of thermomechanical load and ageing. The state variables may be measurable, e.g., crack density, or inferred from the effect they have on some macroscopic property, such as stiffness, coefficient of thermal expansion, remaining life, etc. The state variables have conjugate thermodynamic forces that motivate further damage. Initially the material is pristine, or intact. A damage activation criterion is needed to predict damage initiation. Damage evolution does not progresses spontaneously after initiation, thus requiring a damage evolution model. In plasticity like formulations, the damage evolution is controlled by a hardening function but this requires additional phenomenological parameters that must be found through experimentation, which is expensive, time consuming, and virtually no one does. On the other hand, micromechanics of damage formulations are able to predict both damage initiation and evolution without additional material properties.
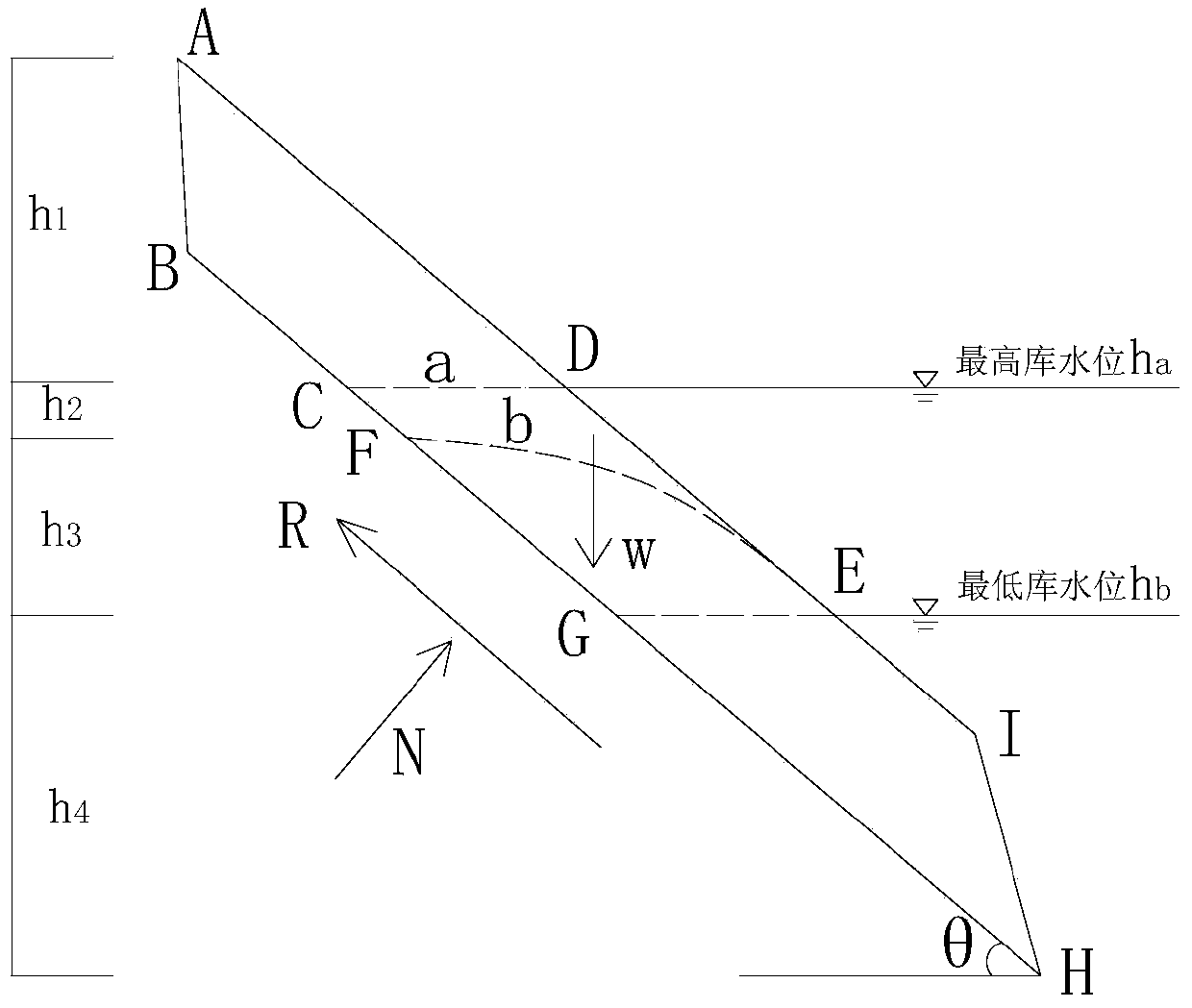
Method for determining stability of reservoir bank slope based on reservoir water level and displacement
ActiveCN103792593AHigh precisionEasy to implementGeological measurementsDisaster monitoringInstability
The invention belongs to the technical field of slope stability diction and slope disaster monitoring and precaution, and particularly relates to a method for detecting a displacement and reservoir water level coupling power prediction parameter and stability of a reservoir type slope geological disaster. According to the basic principle of damage mechanics, a skid resistance force and sliding force loading power parameter on the slope sliding face and a slope displacement response parameter are organically coupled, and the new method for determining the stability of the reservoir type slope is disclosed according to the organic coupling. The method can effectively overcome erroneous judgment or misjudgment caused by errors of slope physical and mechanics parameters, boundary conditions and the like in a traditional ultimate equilibrium mechanical evaluation method and meanwhile solves the problems that a traditional displacement time sequence prediction method cannot describe a slope power action mechanism in a quantitative mode and cannot stably unify instability criterion. The clear criterion is adopted to specifically express the stability state of the slope in different stages of the reservoir, and effective basis is provided for slope prediction forecast and precaution treatment.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
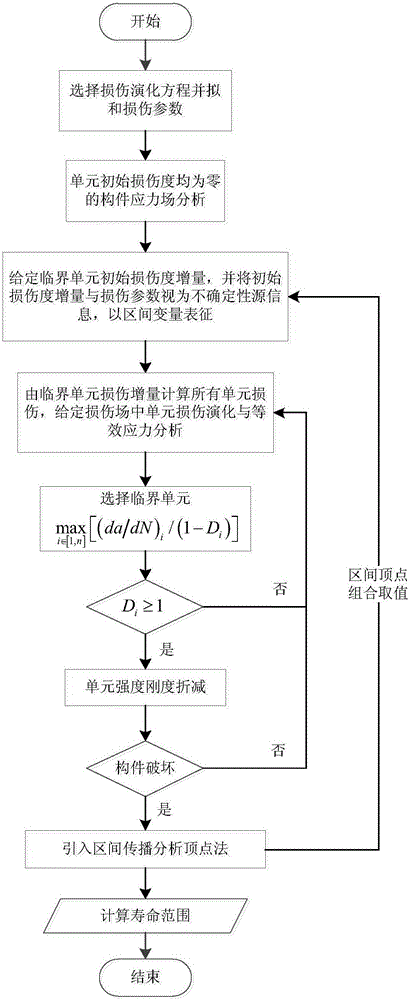
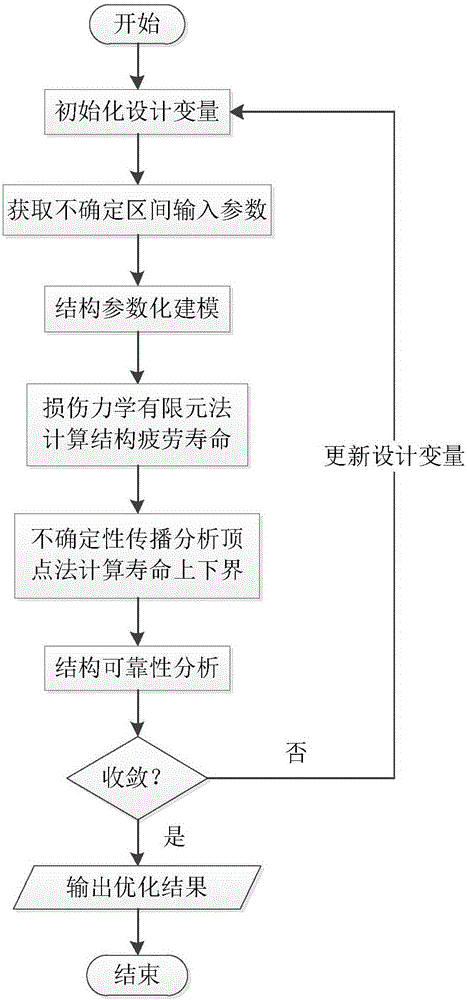
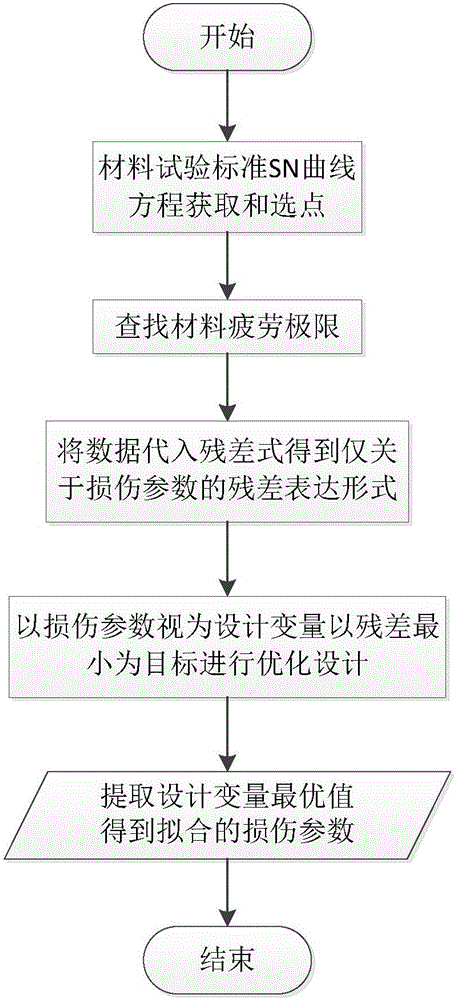
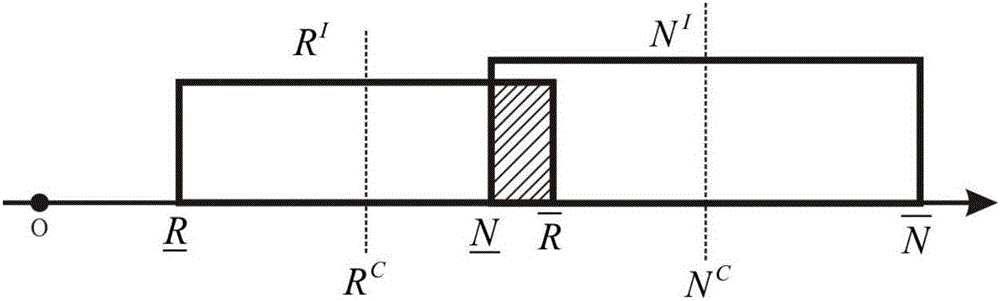
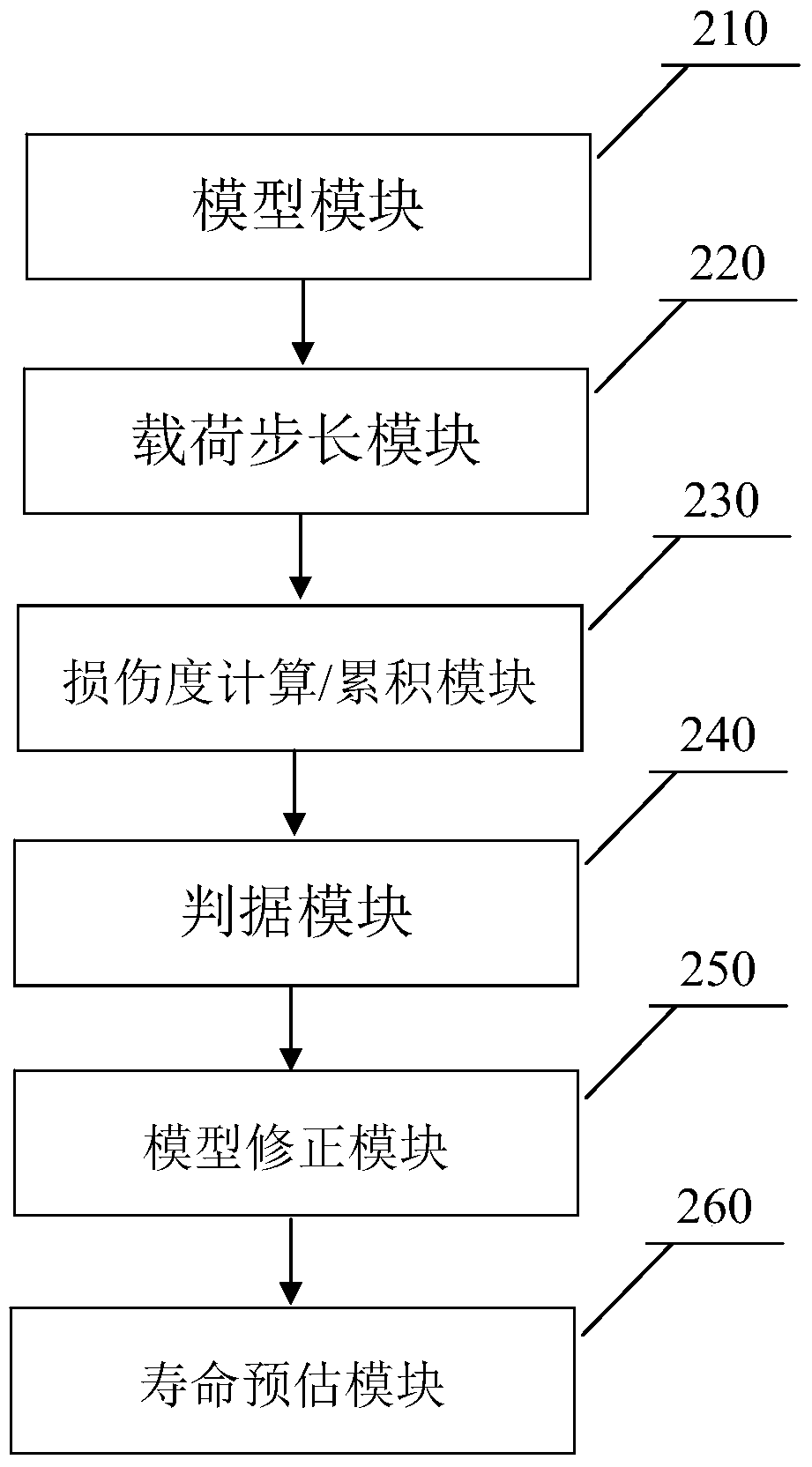
Metal fatigue crack full-life estimation method based on damage mechanics non-probabilistic interval analysis model
InactiveCN106096073AMake up for and perfect limitationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisEstimation methods
The invention discloses a metal fatigue crack full-life estimation method based on a damage mechanics non-probabilistic interval analysis model. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting a damage evolution equation from a damage mechanics model to establish a finite element analysis formation which structurally comprises damage information, and inquiring a fatigue test manual to fit to obtain a parameter in the damage evolution equation; then, combining with a damage mechanics finite element method with an interval finite element method to regard an initial damage degree and a damage parameter as interval uncertainty variables to represent fatigue life dispersivity; further, establishing the finite element analysis model of the structure, giving an initial critical element damage degree increment, constantly carrying out iteration increase on the damage degrees of all elements, judging that the element is damaged through the damage degree of each element, and endowing with intensity and rigidity attributes; and finally, when crack expansion achieves critical crack length, judging that the structure is damaged, and calculating to obtain a fatigue life range via a damage evolution equation variant and an interval vertex propagation analysis method. By use of the metal fatigue crack full-life estimation method, the life of the fatigue crack can be more elaborately estimated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Composite material structure failure analysis method based on continuum damage mechanics degradation model
InactiveCN103592175AComputing performanceAccurate calculationStrength propertiesMatrix damageContinuum damage mechanics
The invention relates to a composite material structure failure analysis method based on a continuum damage mechanics degradation model. According to the method, a three-dimensional continuum damage mechanics degradation model of a unidirectional fiber enhanced composite material is constructed, two types of damage forms such as fiber cracks and matrix cracks and the orientation of damages are considered, and meanwhile, the crack closure effect caused by coupling of the fiber damage and the matrix damage and reverse loading of load in a fiber stretching and compressing damage process is considered; three damage variables are respectively used for representing the fiber crack damage and two mutually-perpendicular matrix crack damages respectively, so that the continuum damage mechanics degradation model for failure analysis of a composite material structure is obtained. Compared with the conventional anti-climax degradation model, the continuum damage mechanics degradation model has the advantages that the behavior characteristics of the damaged composite material under different load states are considered, and the performance of the damaged material can be accurately represented; the composite material structure failure analysis method is suitable for simulation of a composite material structure damage process and forecasting of the intensity under a condition that the load state and a constraint situation are more complicated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
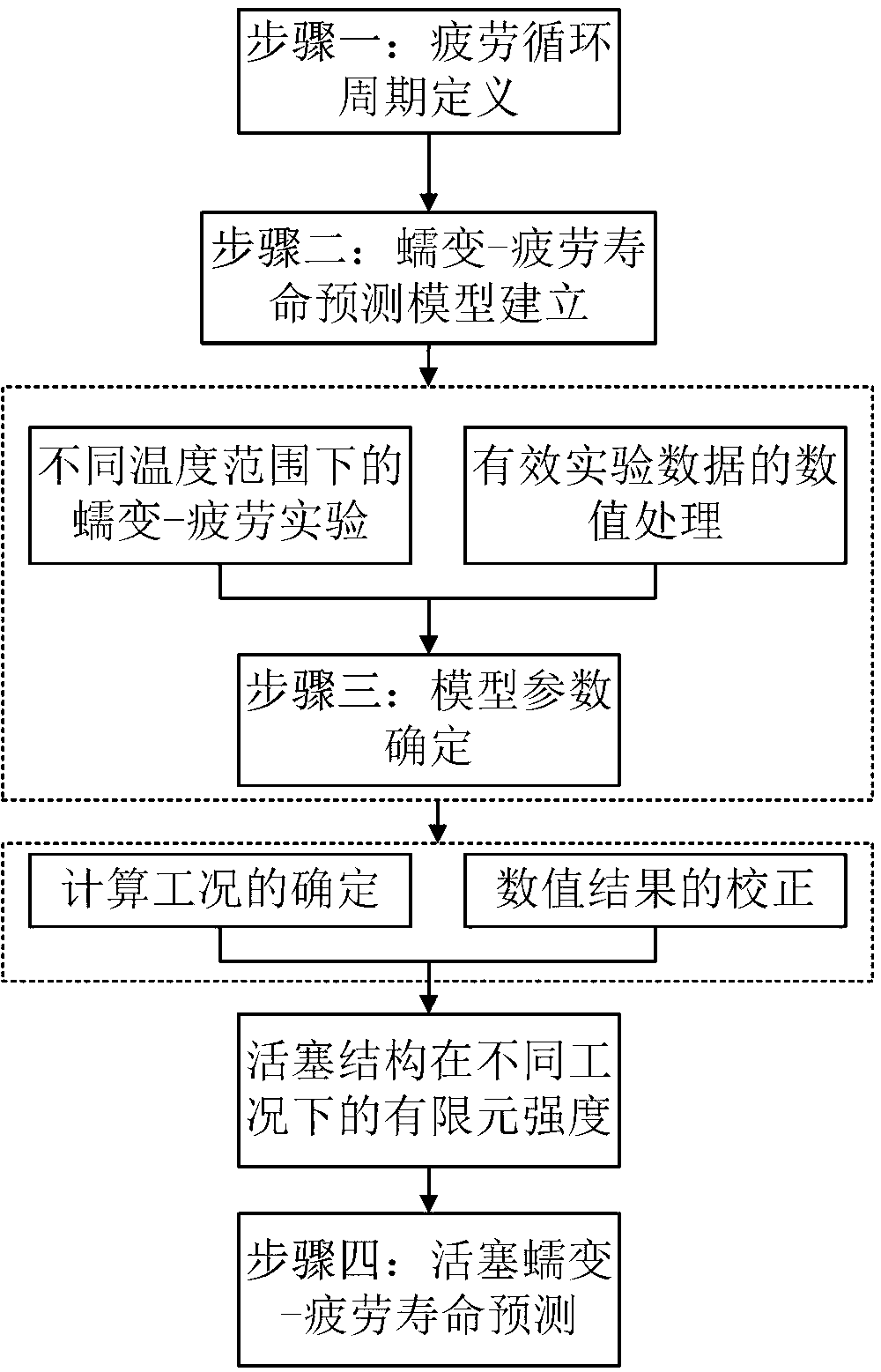
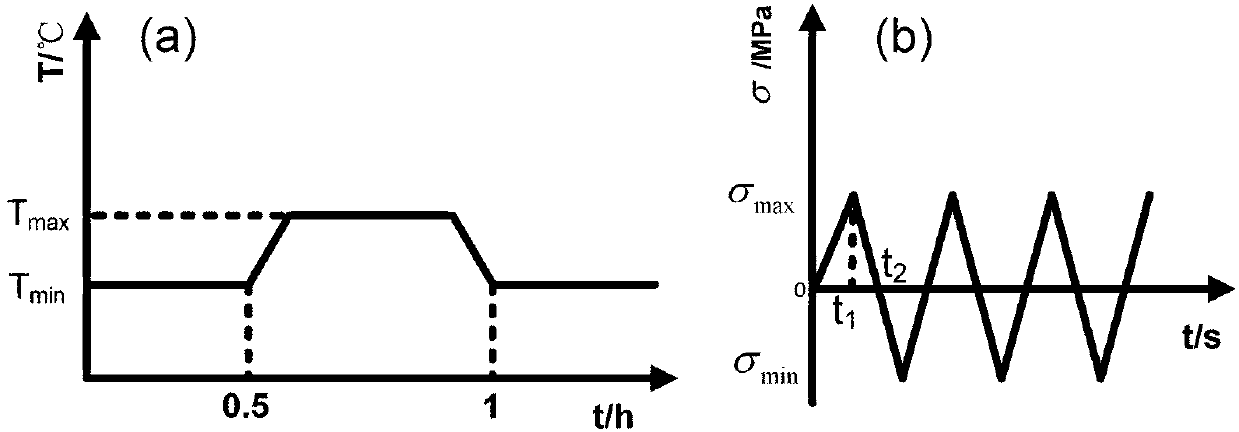
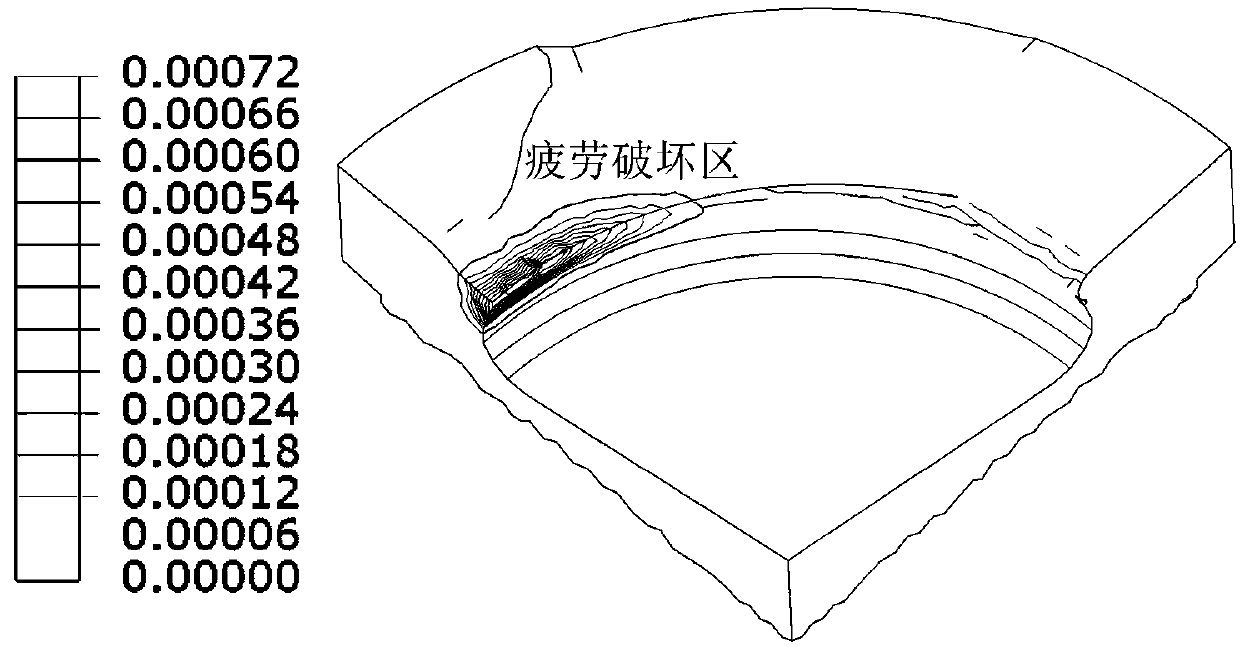
Method for predicting creep-fatigue service life of aluminum alloy piston of high-power diesel engine
InactiveCN103344511ANonlinear Coupling SolutionInvestigating material ductilityMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesFatigue damageNon linear coupling
The invention relates to a method for predicting the creep-fatigue service life of an aluminum alloy piston of a high-power diesel engine, belonging to the field of material science and engineering application technologyies. The influences of large-range and periodic working condition change of the high-power diesel engine on the fatigue service life of the piston structure are taken into account in the method, a new fatigue period is defined to predict the service life of the piston; considering that the engine works under a long-time variable working condition, and the non-linear coupling action between the creep damage and the fatigue damage generated inside a material can be effectively overcome through a creep-fatigue service life prediction model which is built on the basis of damage mechanics.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
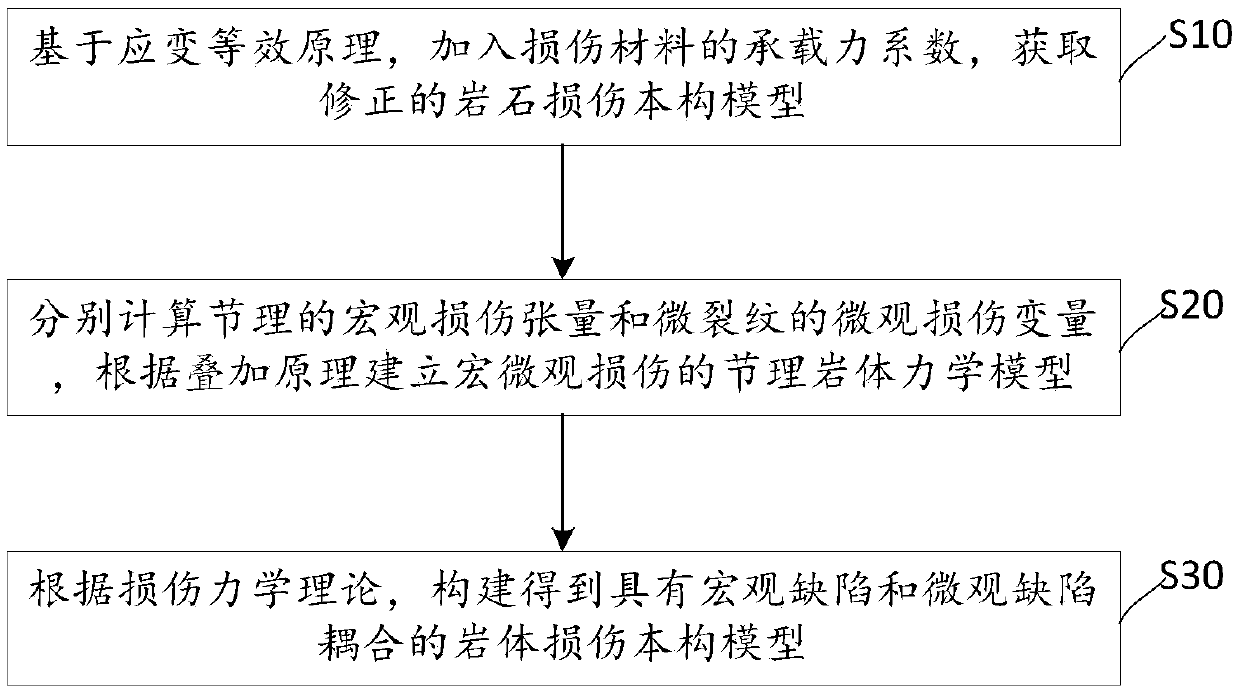
A method and apparatus for construct a new rock mass damage constitutive model
PendingCN109522611AThe principle is simpleReasonable and reliable resultsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMacroscopic scaleMechanical models
The invention relates to a new rock mass damage constitutive model construction method, comprising the following steps: step S10: based on strain equivalence principle, adding a bearing capacity coefficient of a damaged material to obtain a modified rock damage constitutive model; Step S20, respectively calculating a macro damage tensor of the joint and a micro damage variable of the micro crack,and establishing a mechanical model of the macro damage and the micro damage of the joint rock according to the superposition principle; Step S30: According to the damage mechanics theory, constructinga rock mass damage constitutive model with coupling of macroscopic defects and microscopic defects. The novel rock mass damage constitutive model construction method and device provided by the invention provide a simple principle, The damage constitutive model of rock mass, which is easy to operate and low in cost, is reasonable and reliable considering the coupling of macroscopic and microscopicdefects. The mining range can be delineated accurately and reasonably by using the damage constitutive model in the design of excavation slope engineering.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
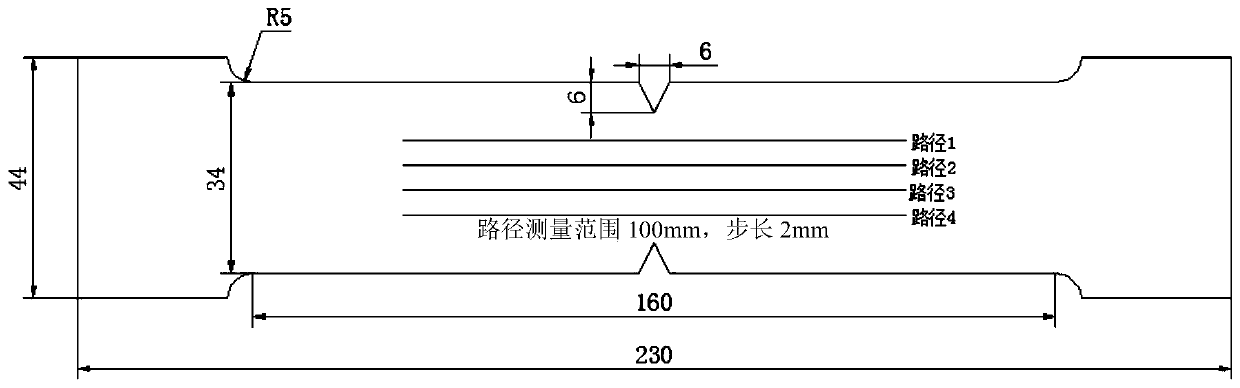
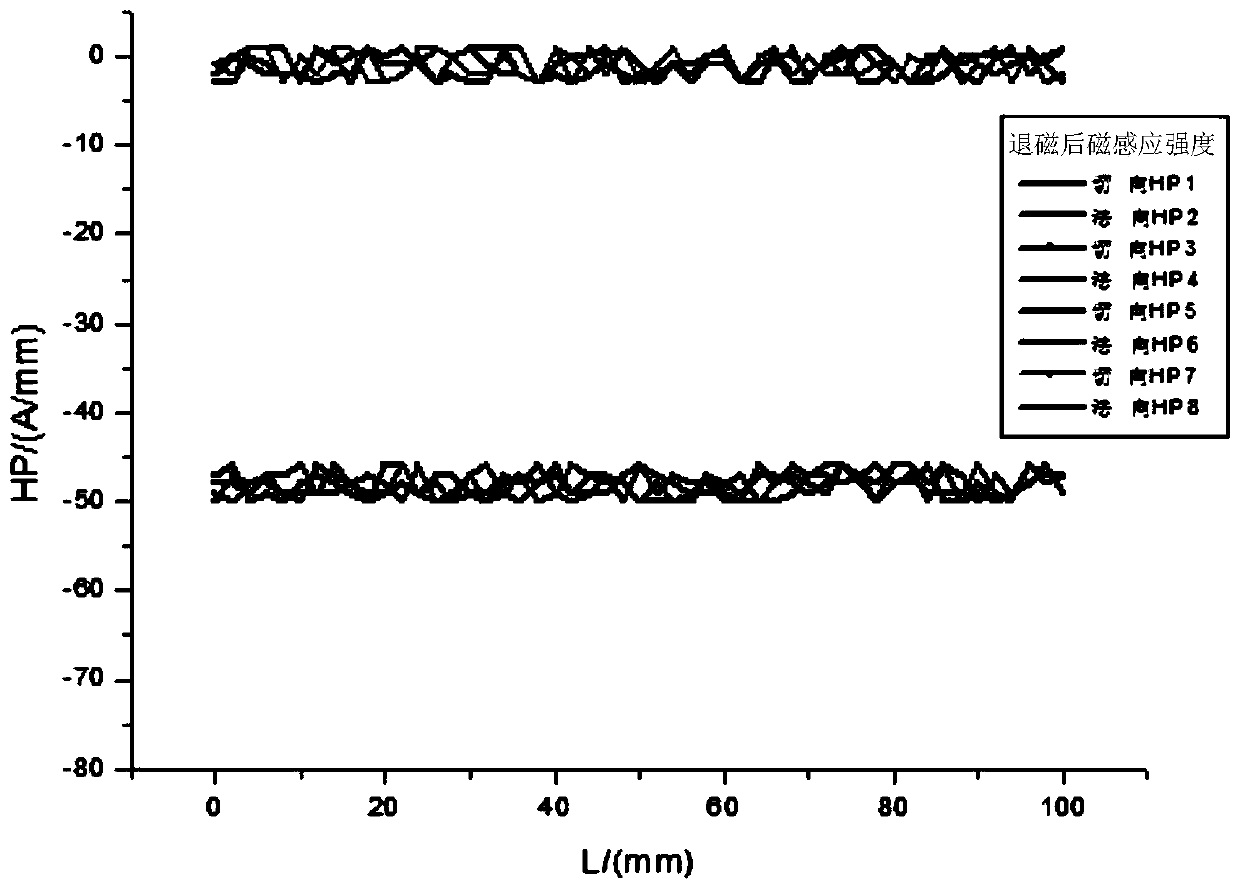
Low-cycle fatigue damage quantitatively characterizing method based on metal magnetic memory detection technology
ActiveCN101393167AReal-timeAchieve securityMaterial magnetic variablesFatigue damageContinuum damage mechanics
The invention utilizes a metal magnetic memory detection technology and relates to a method for the quantitative characterization of low cycle fatigue damage based on the metal magnetic memory detection technology. The method adopts a metal magnetic memory detector to detect gap pieces with different low cycle fatigue damage degrees and obtains magnetic memory signals under different damage degrees; characteristic parameters Hp(y)sub and Kmax of the magnetic memory signal are extracted; the Hp(y)sib and Kmax are used as damage variables in damage mechanics to establish damage degree expression models; and on the basis, a continuous damage mechanical model of low cycle fatigue damage of a quantitative characterization material is established based on the metal magnetic memory detection technology, thereby obtaining the method for the quantitative characterization of low cycle fatigue damage of a ferromagnetic material. The method combines the metal magnetic memory detection technology and the damage mechanics, and carries out the quantitative characterization on the low cycle fatigue damage of the ferromagnetic material. The method adopts a nondestructive detection method to carry out the quantitative mechanical characterization on material damage and can realize on-line real-time monitoring and safety evaluation.
Owner:BEIJING AVIATION MATERIAL INST NO 1 GRP CORP CHINA AVIATION IND
Fatigue damage analysis method considering loading lower than fatigue limit
PendingCN109060497ASpecial data processing applicationsStrength propertiesFatigue damageContinuum damage mechanics
The invention relates to a fatigue damage analysis method considering loading lower than fatigue limit. Since the structure generates initial damage under the action of high amplitude load when the magnitude of the loaded fatigue load is high-low two-stage loading or high-low alternating loading, and the fatigue performance of the material will continue to deteriorate under the effect lower than the fatigue limit load to affect accumulation of the fatigue damage, an improved nonlinear continuous damage accumulation model is proposed based on the fuzzy mathematics theory for considering the damage caused by being lower than the fatigue limit load by using a membership function. Based on the continuous damage mechanics, the model relates load parameters to damage parameters, which reflects the influence of load sequence changes on fatigue damage. At the same time, the damage parameters caused by the small load lower than the fatigue limit is described by using the reinforcement functionsand membership functions. A multi-stage loading fatigue damage accumulation model comprehensively considering the characteristics of load parameters is established by step-by-step derivation, which ensures the reliability of mechanical structure life prediction and damage assessment.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Metal structure fatigue reliability analyzing and optimizing design method based on damage mechanics
InactiveCN106096134AResearch Refinement of Fatigue DispersionReasonable expression of the influence degree of fatigue lifeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelElement analysis
The invention discloses a metal structure fatigue reliability analyzing and optimizing design method based on damage mechanics. The method includes the steps of establishing a parameterized geometric and finite element model according to the key metal structure prone to fatigue through the uncertainty between the interval vector metric structure and material and the damage parameters, and a fatigue life interval range is calculated through the combination of an interval finite element and damage mechanics finite element analysis method; the fatigue reliability analysis of the structure is further achieved through a non-probability interval interference theory; finally, the complete optimization iteration process is achieved with the structure size as the design variable, the reliability degree as the constraint condition and the structure weight as the target function through a global optimization algorithm, and the optimal design variable result found through an output algorithm serves as the final structure optimizing design scheme. By means of the method, the sensitivity of the scheme itself to the design parameters is overcome, the aims of being smallest in weight and making fatigue reliability meet requirements can be achieved under the condition that the structure meets bearing conditions, and thus the design scheme is more economical and reasonable.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for constructing non-penetrated jointed rock mass damage constitutive models under plane compressive shear stress
ActiveCN108509711AAccurate calculationAccurately predict deformationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFracture mechanicsStrain energy
The invention relates to a method for constructing non-penetrated jointed rock mass damage constitutive models under a plane compressive shear stress. The method comprises the following steps of: associating additional strain energy increments caused by crack in fracture mechanics with damage mechanics strain energy burst sizes, and importing the additional strain energy increments and the damagemechanics strain energy burst sizes into a non-penetrated crack extension criterion so as to put forward an external force-considered calculation formula for jointed rock mass damage variables; and finally obtaining a crack parameters (internal causes) and stress conditions (external causes)-considered non-penetrated jointed rock mass damage tensor calculation method, so as to establish a corresponding damage constitutive model. According to the method, the condition of considering external force is suitable for influences caused to rock mass damage variables by common stress states (not comprising positive stress and comprising shearing stress, and suitable for single-axis or double-axis stress states only comprising positive stresses), so that the defect that only rock damage variable calculation under double-axis pressure, namely, influences caused by rock damage variables by confining pressure , is considered in variable calculation of rock mass damages caused to cracks by externalforce in the prior art is overcome.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
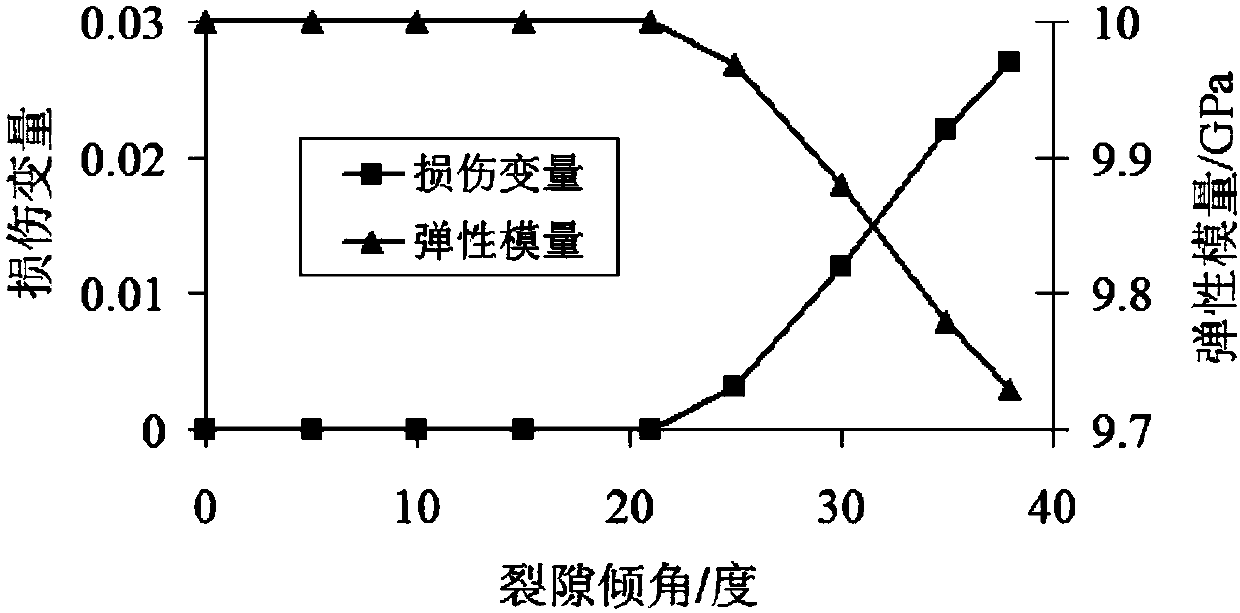
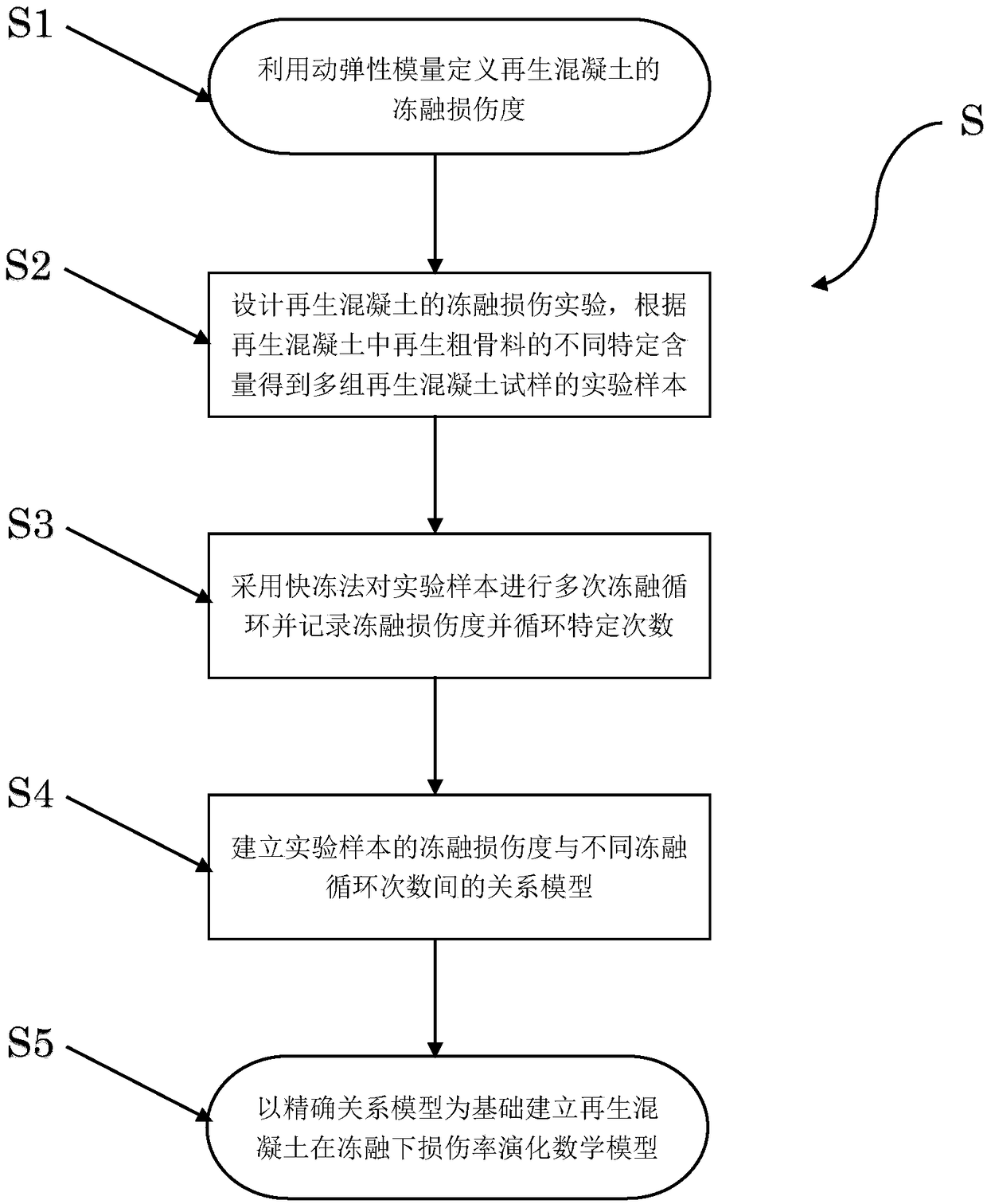
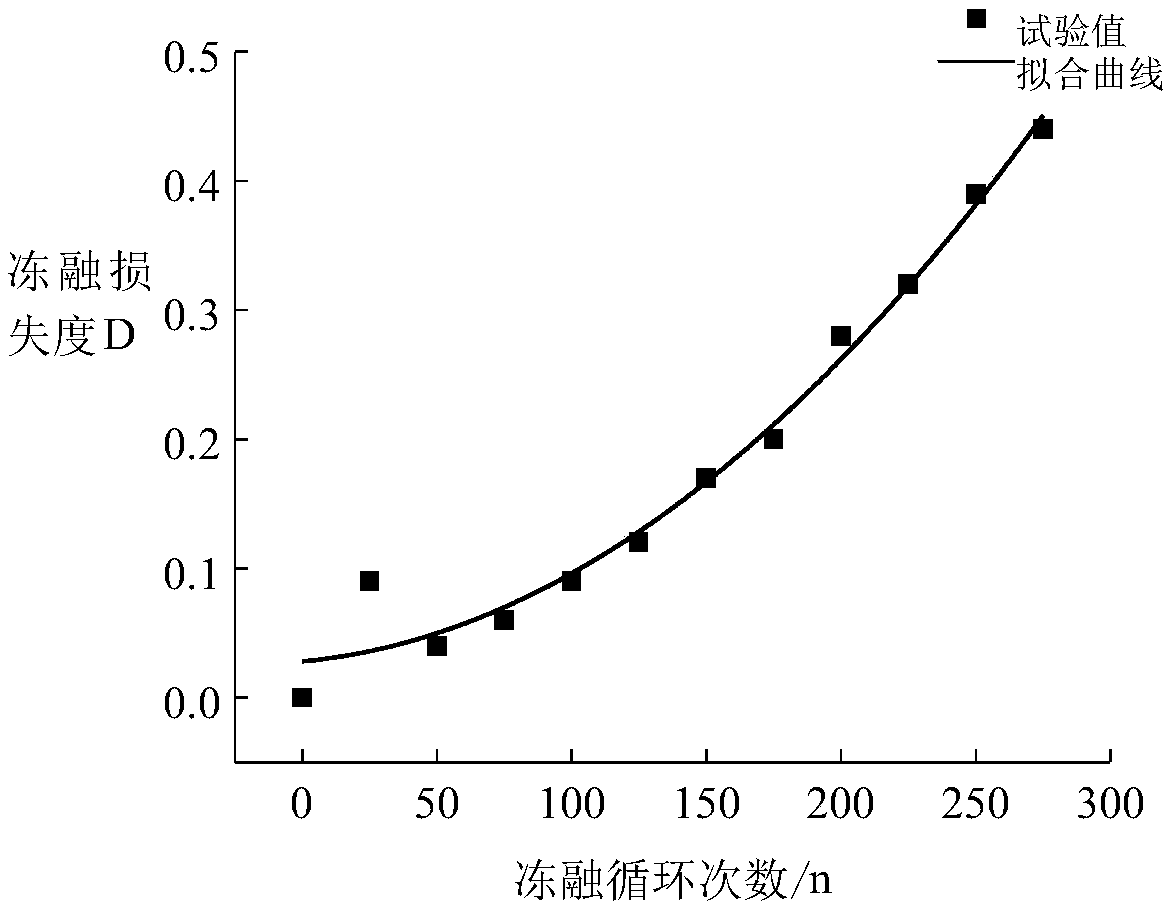
A method for establish a mathematical model of damage rate evolution of recycled concrete under freeze-thaw condition
InactiveCN109472107AEasy to controlShort cycleDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFreeze thawingMathematical model
The invention relates to a method for establishing a mathematical model of damage rate evolution of recycled concrete under freeze-thaw, Because of the application of damage mechanics, The freeze-thawdamage degree of recycled concrete is defined by dynamic elastic modulus, and the freeze-thaw damage experiment of recycled concrete is designed. Then the relationship model between freeze-thaw damage degree of recycled concrete and different freeze-thaw cycles is established by quick freezing method, and the damage rate evolution mathematical model of recycled concrete under freeze-thaw is obtained. Therefore, the method for establishing a mathematical model of damage rate evolution of recycled concrete under freezing and thawing is based on macroscopic damage mechanics theory, and has a solid mechanics theory foundation compared with previous research methods, and the result accords with objective law and mechanics principle, and the conclusion obtained is accurate, clear and convincing. Compared with the previous research methods, the process of the damage rate evolution mathematical model established by the invention is controllable, the period is short, and the time and the costare greatly saved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Quantitative evaluation test method for coal core damage
ActiveCN110631936ASimple test stepsThe calculation method is accurate and intuitiveMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesAxial displacementUltrasound attenuation
The invention discloses a quantitative evaluation test method for coal core damage. According to the method of the invention, a triaxial loading system is used for applying confining pressure and porepressure to the coal rock core; the axial strain of the matrix of the coal core is recorded in real time through a strain gauge; the overall axial displacement of the coal core is recorded through adisplacement sensor; volume strain generated by the microcrack evolution of the coal core can be obtained through calculation; and due to the fact that the volume strain is closely related to a damagedegree, the damage variable of the coal core can be quantitatively calculated according to a continuous medium damage mechanics theory; a permeability change rule in a damage process is measured in real time according to a pulse attenuation method; the permeability change rule is compared with the calculated damage variable, so that a corresponding relation between damage and permeability can bedirectly established. According to the test method of the invention, required equipment structures and test steps are simple; and the calculation method is accurate and visual. The test method has definite physical significance, and can be used for the quantitative evaluation of damage variables and permeability evolution in experimental processes such as cyclic pulse air pressure permeability increase, creep deformation damage, and triaxial compression.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Prediction method for natural-fracture-contained tight oil and gas reservoir volume pressure fracture network
ActiveCN110147561AAccurate predictionPracticalClimate change adaptationDesign optimisation/simulationAnalysis dataRock mechanics
The invention aims to provide a prediction method for a natural-fracture-contained tight oil and gas reservoir volume pressure fracture network. The method includes the steps: collecting geological information, logging data, rock core and rock debris analysis data and fracturing construction data of the target reservoir, and carrying out single well geomechanical analysis and natural fracture distribution analysis to obtain an initial geostress parameter, a rock mechanical parameter and a natural fracture description parameter of the reservoir; establishing a three-dimensional geological modelbased on the data, and performing fine ground stress field simulation by adopting a finite element method to obtain initial ground stress distribution of the reservoir; setting the distribution of aninitial damage variable field in the model according to the natural fracture distribution condition; and calculating the damage evolution of the three-dimensional stratum in the hydraulic fracturingprocess. The prediction method has the beneficial effect that the reservoir volume pressure fracture crack network form containing the natural fractures can be accurately predicted on the basis of thedamage mechanics theory.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Prediction method for crack initiation of secondary surface of heavy-load gear
InactiveCN108256241ASolve long-standing technical problemsPredicted positionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationContact pressurePredictive methods
The invention discloses a prediction method for crack initiation of a secondary surface of a heavy-load gear. The method comprises the following steps that 1, based on a hertz contact theory, the contact of a gear pair is simplified, a meshed position parameter is calculated according to geometric kinematics, and a contact analysis model is established; 2, based on the contact analysis model of the gear pair, by using a value calculation method, the surface contact pressure of the analysis model under the heavy-load condition is obtained; 3, a material constant related to the service life of crack initiation is solved; 4, based on a continuous damage mechanics theory, by using critical damage amount, whether or not a crack occurs on the secondary surface is judged, and a gear contact elastic-plastic constitutive equation of coupling damage is established; 5, the service life of crack initiation is calculated, and the position of crack initiation is obtained. According to the predictionmethod, the technical difficult problem which exists for a long time in the machinery industry is solved, the position and service life of crack initiation of the secondary surface of the heavy-loadgear can be effectively predicted, and the basis is provided for design, manufacturing and use of the gear.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
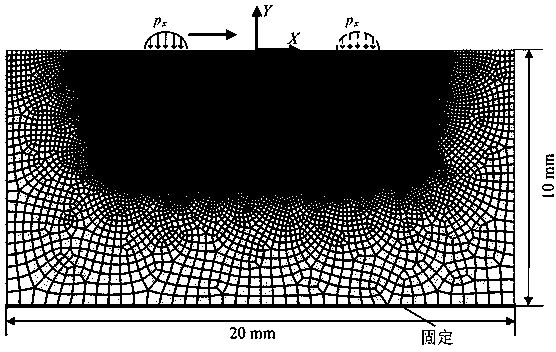
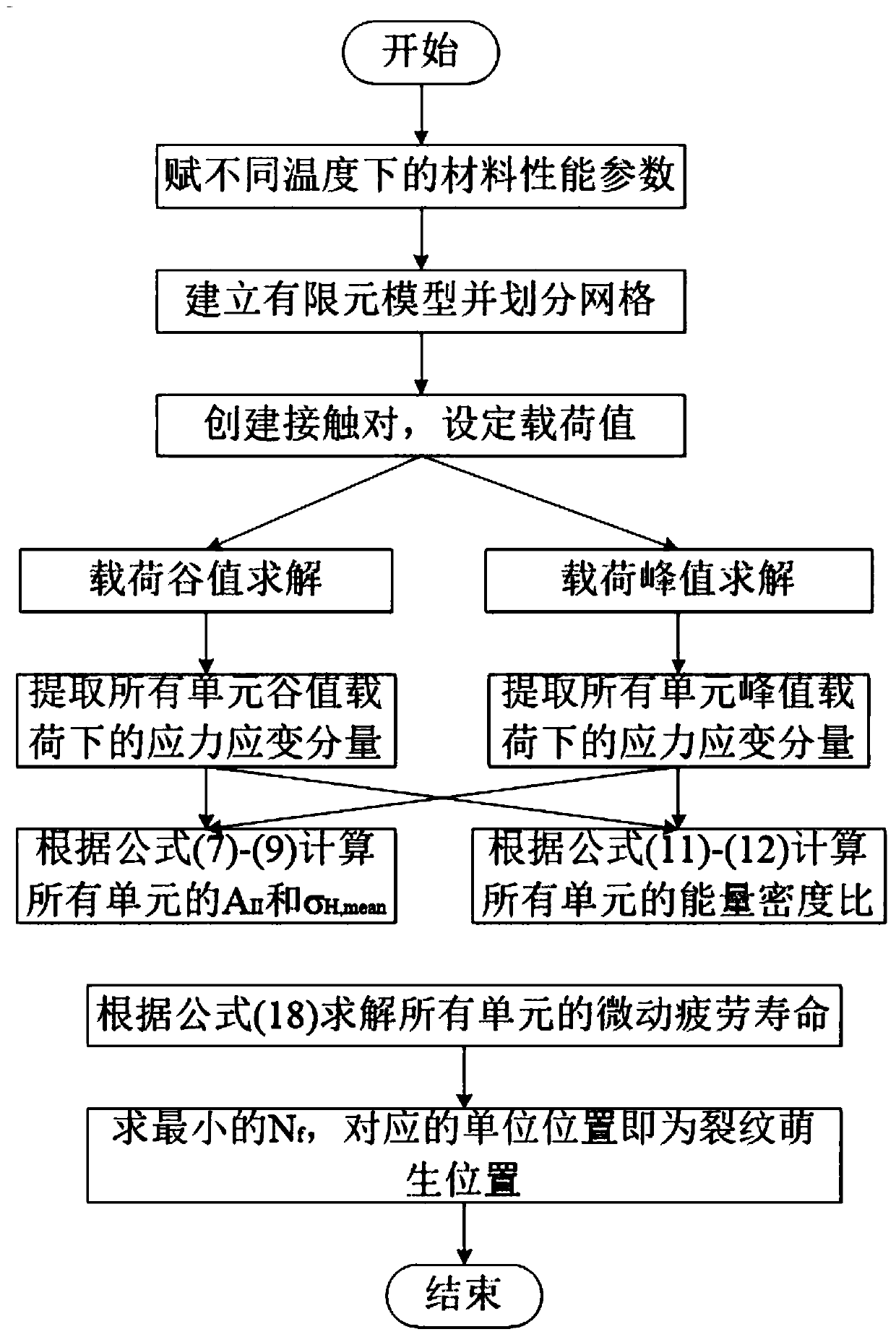
High-temperature fretting fatigue life prediction model based on continuous medium damage mechanics and method thereof
InactiveCN110348056AEffective prediction of fretting fatigue lifeEffective Life PredictionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationFatigue damageElement model
The invention discloses a high-temperature fretting fatigue life prediction model and method based on continuous medium damage mechanics. Based on a nonlinear fatigue damage accumulation model, the invention introduces a critical plane energy density parameter according to the concept of energy density, so as to obtain a life prediction model suitable for fretting fatigue. On the basis, a temperature-related damage rate factor is introduced to consider the influence of temperature on the fretting fatigue behavior of the structure. The application method of the model needs to utilize finite element software ANSYS, and comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a finite element model; (2) carrying out simulation calculation, (3) carrying out post-processing on the calculation result, (4)carrying out parameter fitting, and (5) carrying out calculation to obtain the fretting fatigue prediction life, can effectively predict the fretting fatigue life at high temperature and has important engineering significance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
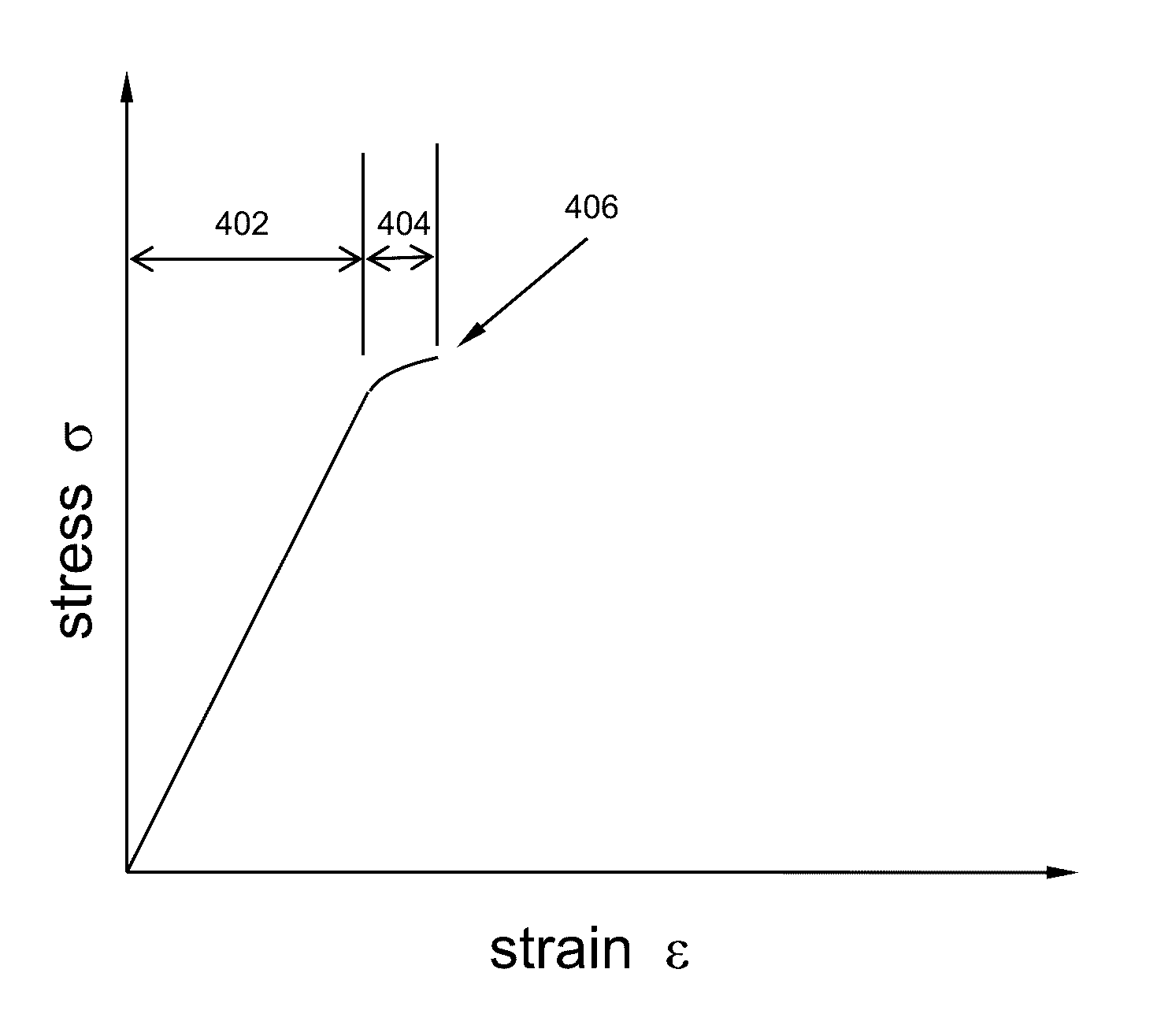
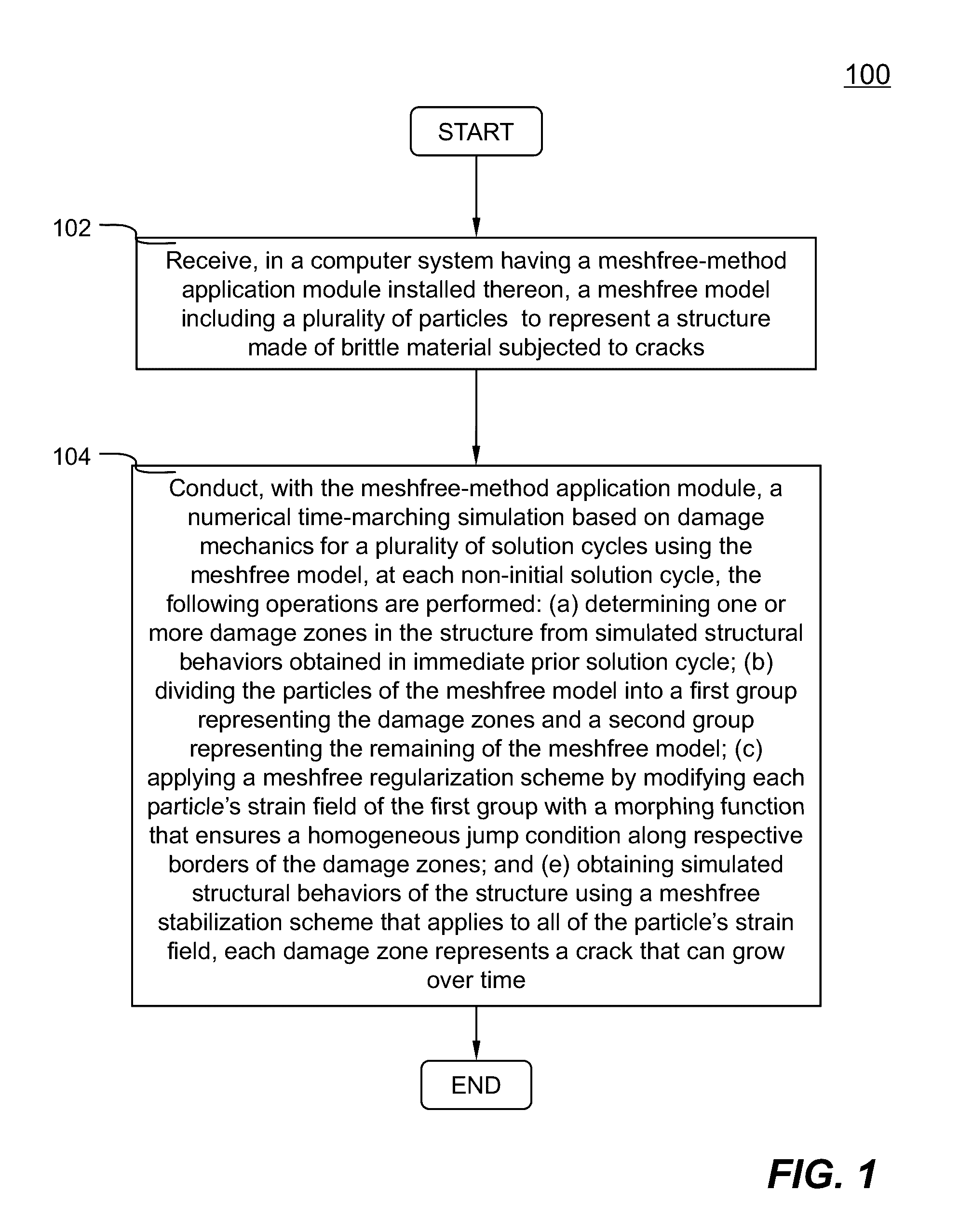
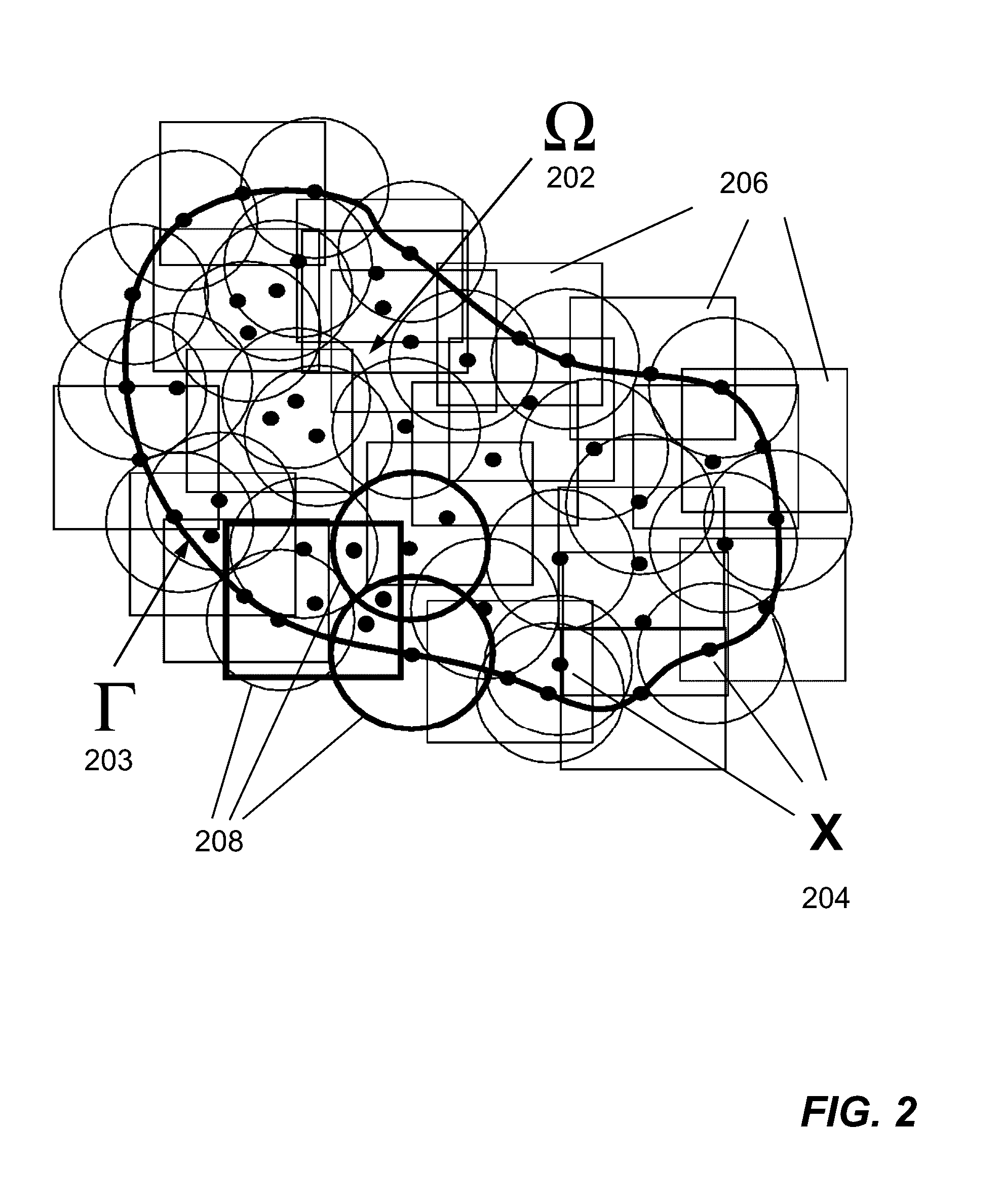
Meshfree Method And System For Numerically Simulating Brittle Material Based On Damage Mechanics
Meshfree model containing a number of particles to represent a structure made of brittle material is defined. At each non-initial solution cycle of a numerical simulation using the meshfree model based on damage mechanics, the following operations are performed: (a) determining one or more damage zones in the structure from simulated structural responses obtained in immediate prior solution cycle; (b) dividing the particles into a first group representing the damage zones and a second group representing the remaining of the meshfree model; (c) applying a meshfree regularization scheme by modifying each particle's strain field of the first group with a morphing function that ensures a homogeneous jump condition along respective borders of the damage zones; and (e) obtaining simulated structural behaviors of the structure using a meshfree stabilization scheme that applies to all of the particle's strain field. Each damage zone represents a crack that can grow over time.
Owner:ANSYS
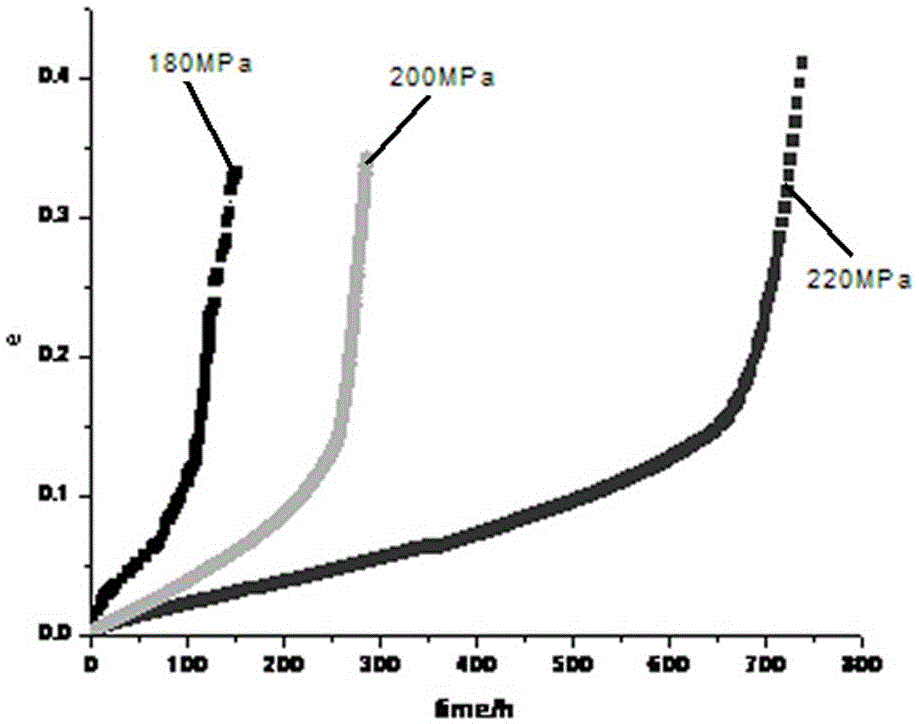
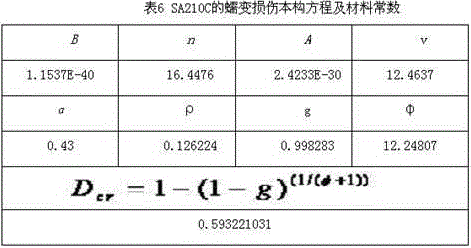
Power station boiler heating surface SA210C steel material state evaluation method
InactiveCN106290775AAvoid repeated high temperature testsImprove timelinessTesting metalsPower stationRoom temperature
The invention relates to a power station boiler heating surface SA210C steel material state evaluation method. Association between normal-temperature physical and chemical data and high-temperature creep data is established by associating room-temperature physical and chemical feature parameters and range, the high-temperature creep performance can be directly queried and called when the normal-temperature physical and chemical properties of a heating surface to be evaluated are matched with the associated feature parameters and range, therefore, repeated high-temperature creep performance testing is avoided, and the evaluation timeliness is improved. Meanwhile, localized creep damage mechanics and a multiaxial stress theory are adopted, an improved creep damage constitutive equation (that is, an improved K-R equation) under multiaxial stress is obtained, a creep critical damage value is obtained through data fitting according to the called high-temperature creep property data, therefore, a data standard is provided for heating surface state evaluation, and the evaluation accuracy is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID HEBEI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Damage mechanics-based high-strength metal material amplitude variation ultra-high cycle fatigue life predication method
ActiveCN108627406AHigh cycle fatigue performanceClear thinkingAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress levelMetallic materials
The invention discloses a damage mechanics-based high-strength metal material amplitude variation ultra-high cycle fatigue life predication method. The method is based on an ultra-high cycle fatigue test result and a damage mechanics model, and the high-strength metal material amplitude variation ultra-high cycle fatigue life predication method is provided. The ultrasonic fatigue test is used to rapidly acquire the ultra-high cycle fatigue performance of a high-strength metal material, the test frequency is 20 kHz, only 13.9 hours are needed to finish 109 cycles; based on the nonlinear damagemechanics theory, a damage factor of the amplitude variation stress level is introduced, a material amplitude variation ultra-high cycle fatigue life predication model is established, and the ultra-high cycle fatigue life is quantitatively predicated on amplitude varied load. The thought of the assessment model is clear, and the computation is simple and fast.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Real-time image observation and acquisition platform and method for microstructure of material with loads
ActiveCN103592182ASimple structureSimple and fast operationStrength propertiesMaterials testingStrength of materials
The invention discloses a real-time image observation and acquisition platform and method for the microstructure of a material with loads. The platform comprises a loading device, an image observation and capture device and an XY double-coordinate micro-control mobile device and a PC, (Personal Computer), wherein the image observation and capture device is fixedly connected onto the XY double-coordinate micro-control mobile device; the XY planes of the XY double-coordinate micro-control mobile device are parallel to the surface to be observed of a material; the image observation and capture device and the loading device are respectively connected with the PC through data lines. The method comprises the following steps: dynamically capturing the images of the microstructure of the material with the loads, and associating a universal material testing machine sensor to synchronously obtain mechanics data; causing the PC to track the mechanics data flow acquired by the sensor, recognize a key point and trigger the image observation and capture device to take pictures; in the late, realizing correlation analysis of the data and the images through a computer and modeling. The acquisition platform and the method perfect the analysis method of mechanics of materials, disclose the damage evolution mechanism of materials, and provide a new method for study of damage mechanics of materials.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Electric pulse coal rock fracturing and permeation enhancing experimental system and experimental method under air environment
PendingCN108593520AGuaranteed reliabilityPrevent backpropagationPermeability/surface area analysisShock waveExperimental methods
The invention discloses an electric pulse coal rock fracturing and permeation enhancing experimental system under an air environment. The system comprises an electric hoist, an electric pulse generation device, a sample fixing bracket, a steel tank, a power control cabinet and two groups of shock wave pressure test devices, wherein the steel tank is of a cylindrical structure provided with an opening in the top; the bottom of the left side of the steel tank is connected with the ground through a ground wire. The experimental device aims to develop visual and dynamic monitoring for a crack extension and evolution process under the action of an electric pulse, and the visual and continuous monitoring process cannot be implemented under the condition of confining pressure, which is also the reason and objective to set the experimental device under the air environment condition. An extension direction and an extension mode of a crack and an evolution law of the length, the width and the density of the crack are analyzed by comparing features of the crack of a coal sample under different impact numbers of times; a fractal theory is used for quantitatively researching a crack extension and evolution process; finally, in combination with related theories of fracture mechanics and damage mechanics, the extension and evolution law of the crack of coal rock under the action of the electric pulse can be disclosed.
Owner:HENAN INST OF ENG
Evaluation method for early damage of additive manufacturing part based on metal magnetic memory detection
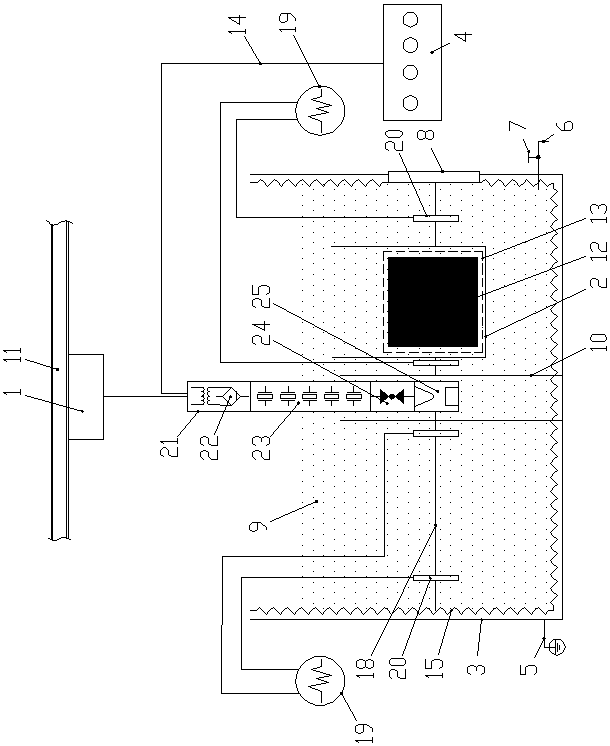
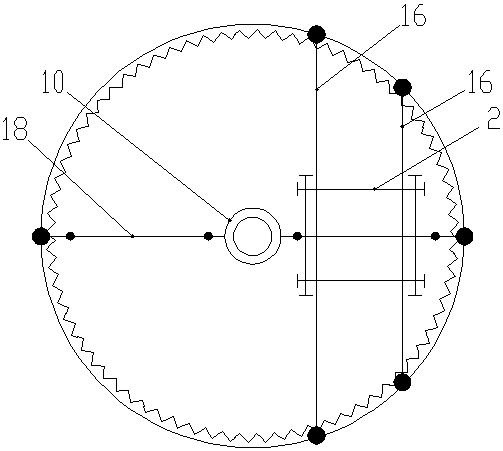
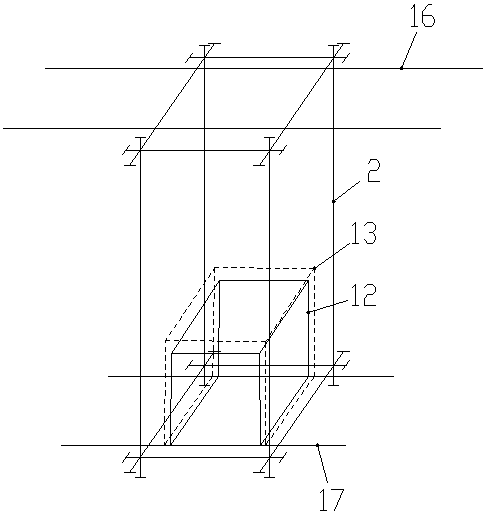
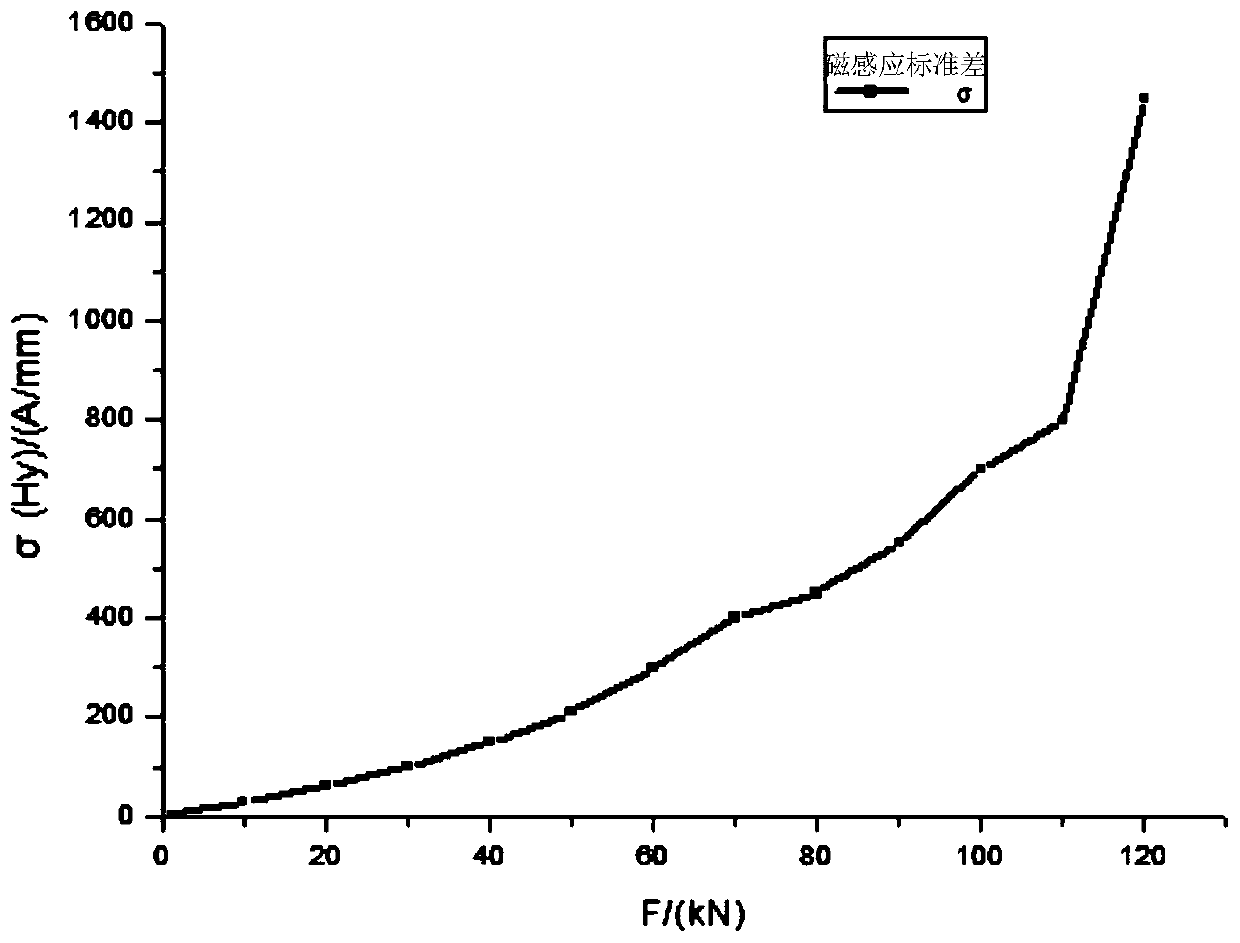
ActiveCN110308043ARealize non-destructive testingHigh discrimination accuracyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial magnetic variablesMagnetic memoryState representation
The invention relates to an evaluation method for early damage of an additive manufacturing part based on metal magnetic memory detection and belongs to the field of metal magnetic memory detection innondestructive detection, wherein a mechanics theory and a force-magnetic coupling theory of ferromagnetic materials are used for guiding, and the variation condition of a residual magnetic inductionintensity standard deviation and a residual magnetic induction intensity gradient maximum value thereof along with the tensile load is used as an early damage state representation method of the additive manufacturing part. The residual magnetic induction intensity of the additive manufacturing part under different stretching states is detected by adopting a metal magnetic memory method, the earlydamage change process of the defect is characterized by the change of magnetic memory signals, and the residual magnetic induction intensity standard deviation and the residual magnetic field intensity gradient maximum value are used for representing the early damage situation of the additive manufacturing part. According to the method in the invention, the metal magnetic memory detection technology is combined with damage mechanics, the magneto-mechanical effect of the ferromagnetic additive manufacturing part is used to achieve nondestructive detection of the early damage of the ferromagnetic additive manufacturing part under the condition of not requiring magnetizing, and the judgment accuracy is high.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
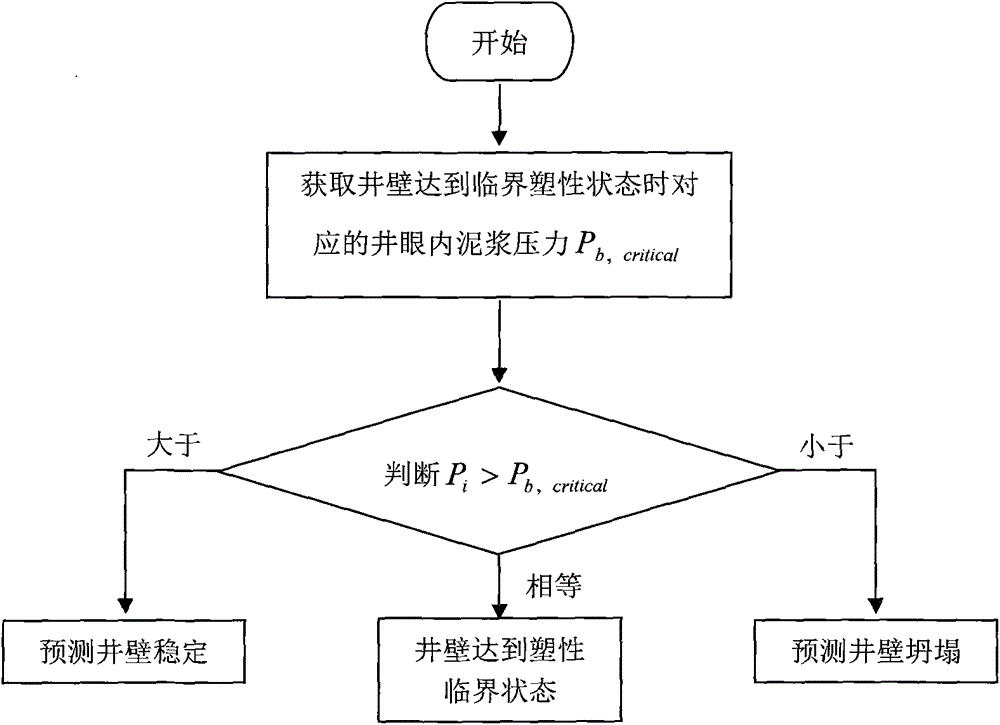
Low-density drilling feasibility fast evaluation method
The invention relates to a low-density drilling feasibility fast evaluation method suitable to be used in a petroleum and natural gas development process. According to the method, whether the well wall in the drilling process is stable or not is judged according to the slurry liquid column pressure P in a corresponding wellbore when a critical plastic state is reached. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining parameters required in a well wall stability prediction model according to complete stress-strain test data of stratum rock and mechanics characteristic parameters of the stratum rock; obtaining the corresponding well wall collapse pressure P<b, critical> when the critical plastic state is reached; and judging whether the slurry liquid column pressure P selected and used in the field is greater than the P<b, critical> or not. If the slurry liquid column pressure P in the well hole is greater than the P< b, critical>, a result shows that the well wall keeps stable; if the P is smaller than the P< b, critical>, a result shows that the well wall loses the stability and can collapse; and if the P is equal to the P< b, critical>, a result shows that the well wall plasticity in the drilling process reaches the critical state. The method is provided on the basis of damage mechanics though being combined with a unified strength failure criterion. Through field practical inspection, the method has good application effects.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
Deformation analysis device, deformation analysis method, and program
ActiveUS20150310143A1Reduce stiffnessComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationAnalysis dataStorage cell
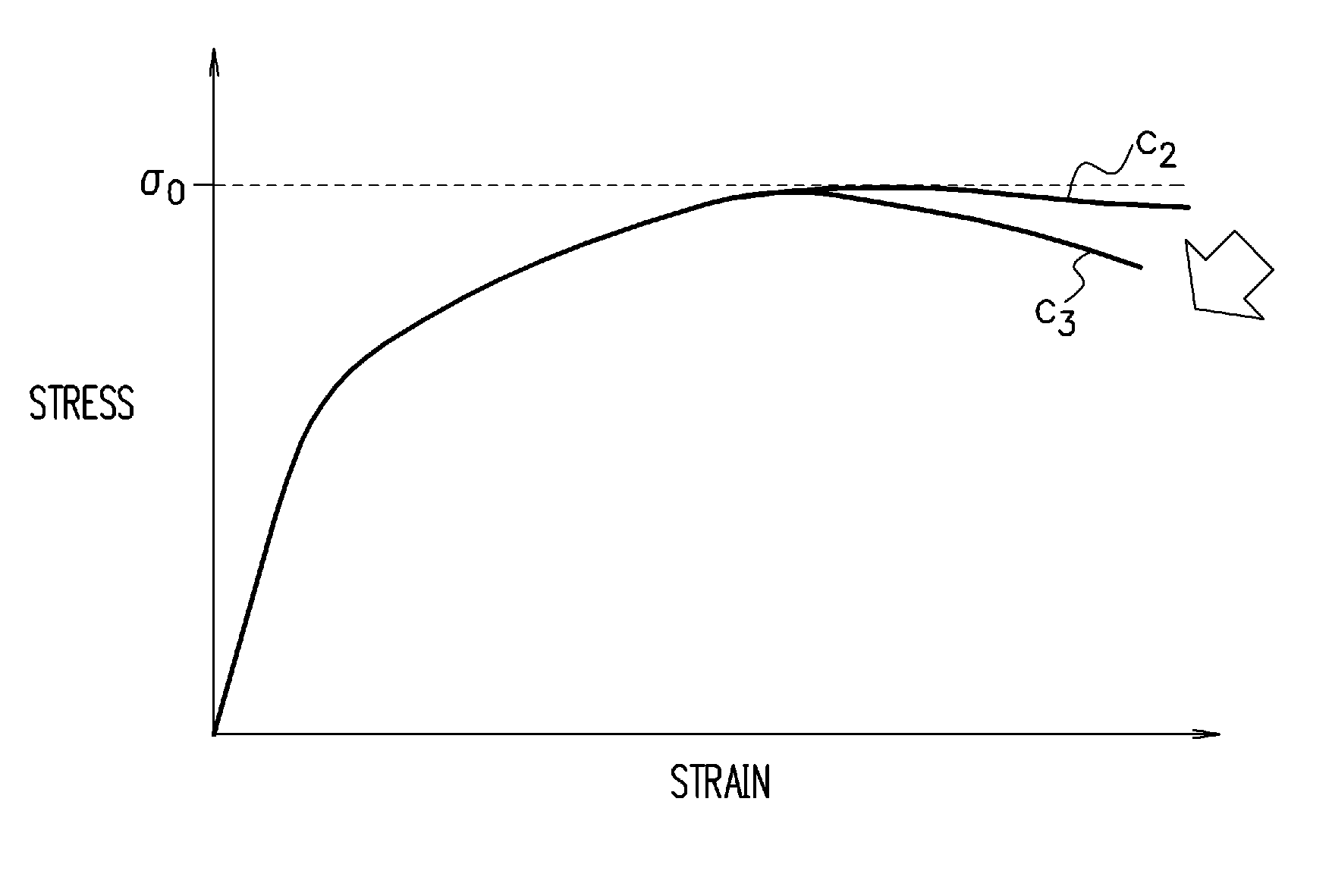
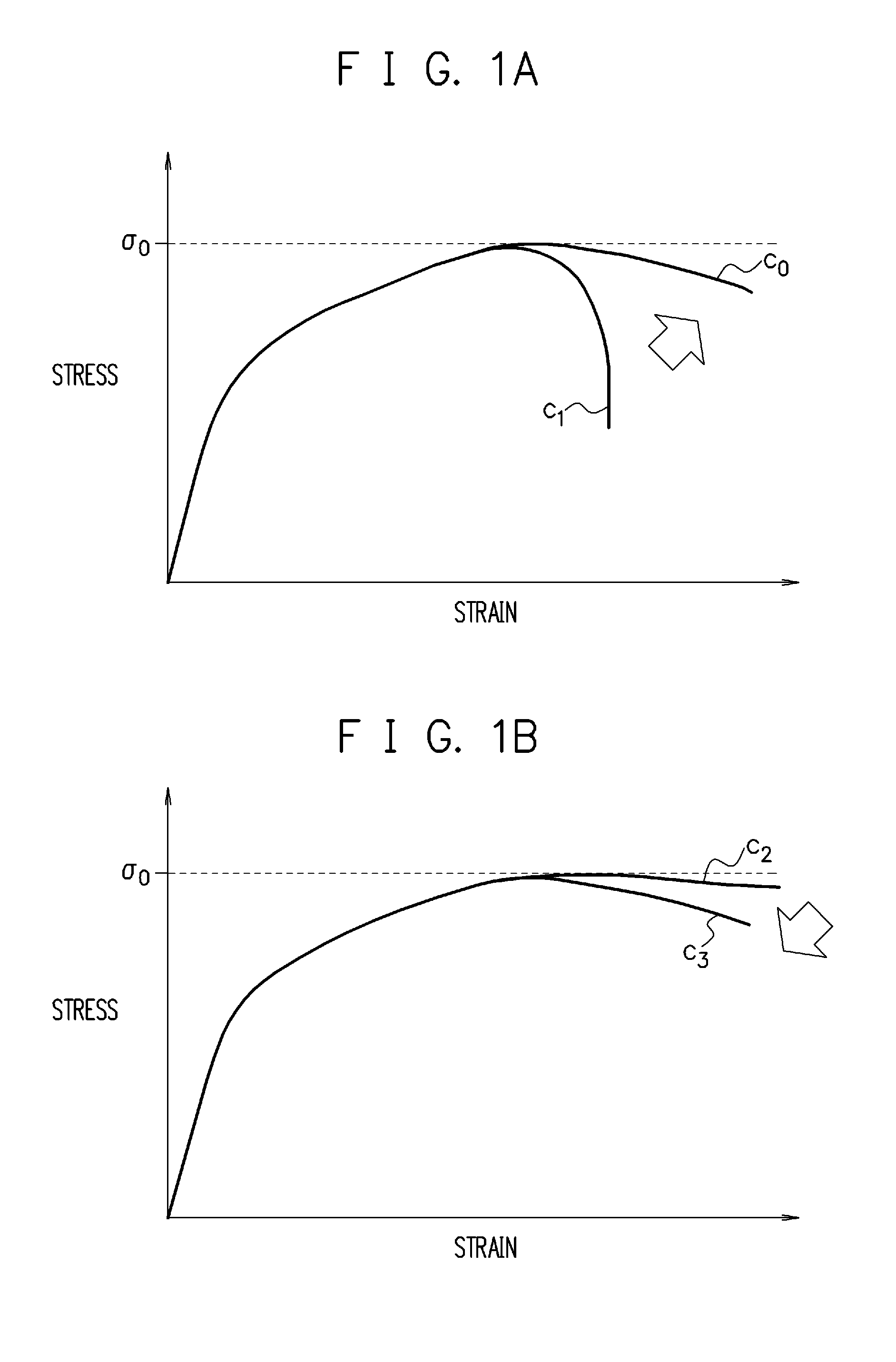
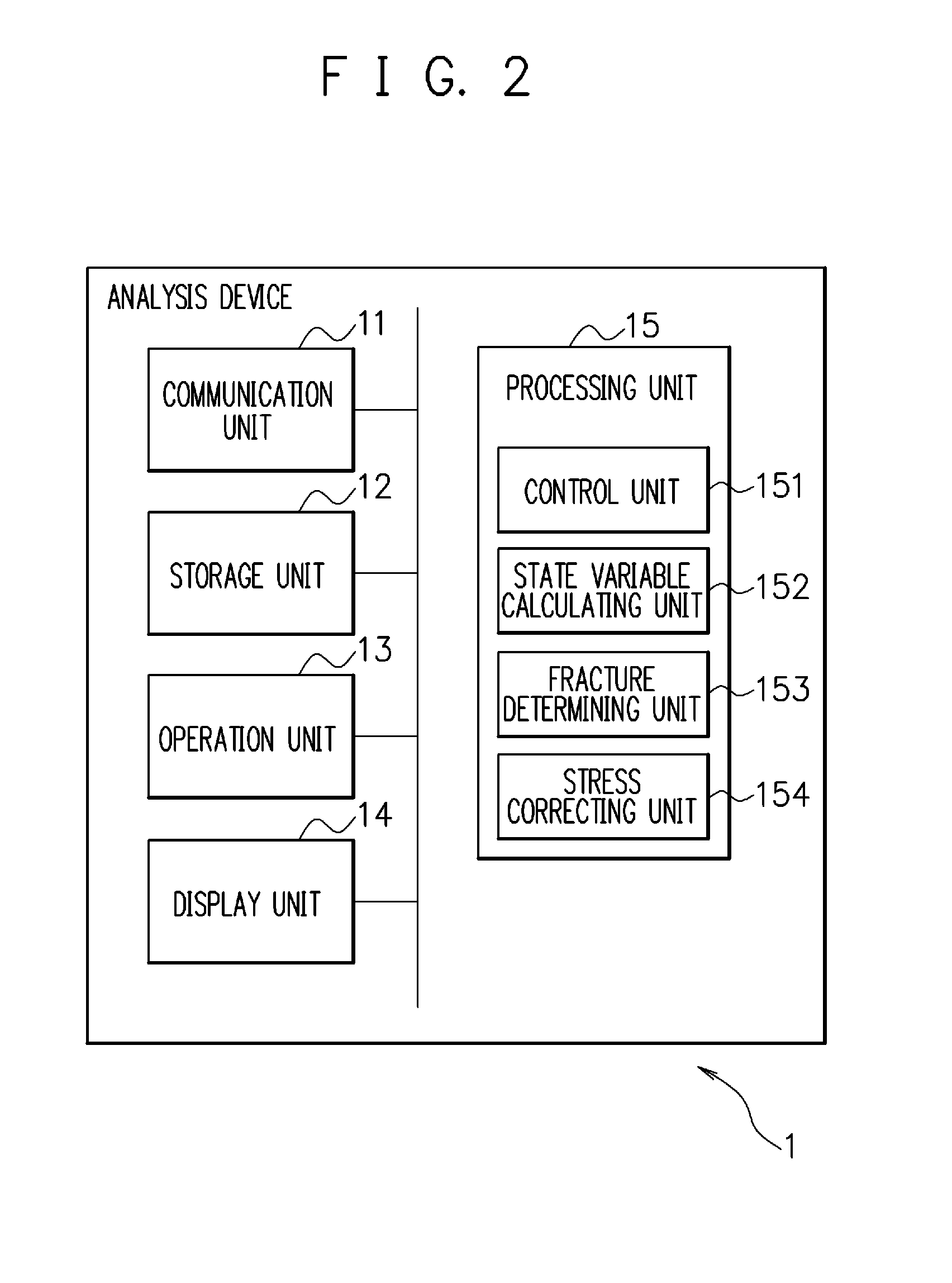
The deformation analysis device includes: a storage unit (12) which stores analysis data of a material; a state variable calculating unit (152) which calculates stresses and other state variables of respective elements of the material at each point in time of deformation of the material, based on the analysis data; a fracture determining unit (153) which, based on the calculated state variables, determines whether or not a fracture has occurred in each of the elements of the material, based on a fracture limit stress curve which is found in advance for the material; and a stress correcting unit (154) which, regarding an element in which it is determined that the fracture has occurred, out of the elements of the material, reduces σ by the following expression σ=(1−D)σ′ where σ is a stress with a rigidity decrease taken into consideration, D is a damage variable (note that 0≦D≦1) in continuum damage mechanics, and σ′ is a stress with the rigidity decrease not taken into consideration, to thereby decrease rigidity of the relevant element, without eliminating the element, and updates the analysis data.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
A device and a method for high throughput representation of microscopic interface performance of a single fiber and resin
InactiveCN108776064AImprove performanceCompare Interface PerformanceMaterial analysis by optical meansMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEpoxyElectric machine
The invention provides a device and method for high throughput representation of microscopic interface performance of a single fiber and resin. The device includes a shell and a fixed bottom plate installed in the shell, a mold group, an interface performance detection device and a microscopic interface observation device are installed on the fixed bottom plate, a mold is equipped with an epoxy resin base, a plurality of the single fiber is inserted into the epoxy resin base, and the upside of the single fiber is bonded with a monofilament negative film. The mold group includes the mold, a mold positioning device, a mold moving device, and a mold fixing device. The interface performance detection device includes an automatic electric machine, a screw bar, a screw bar sliding block, a clamp, and two micro force sensors. The device have important meaning on analyzing the relationship between an interfacial layer and the structure and damage mechanics, the requirements of high throughputexperiments can be satisfied, and the period of research and development is shortened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
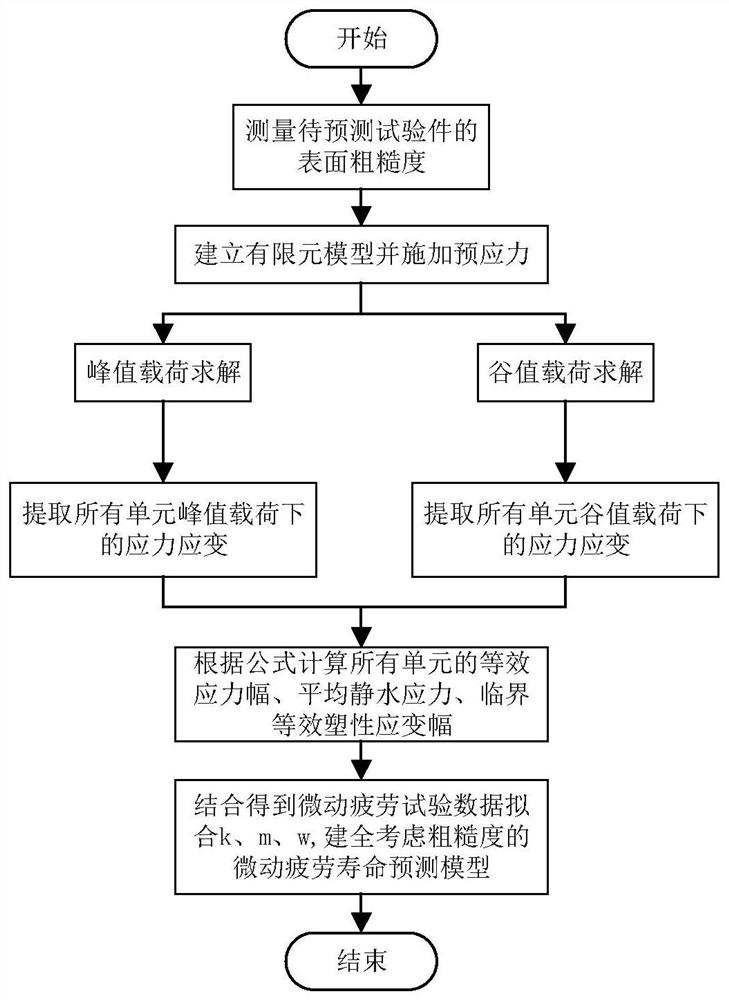
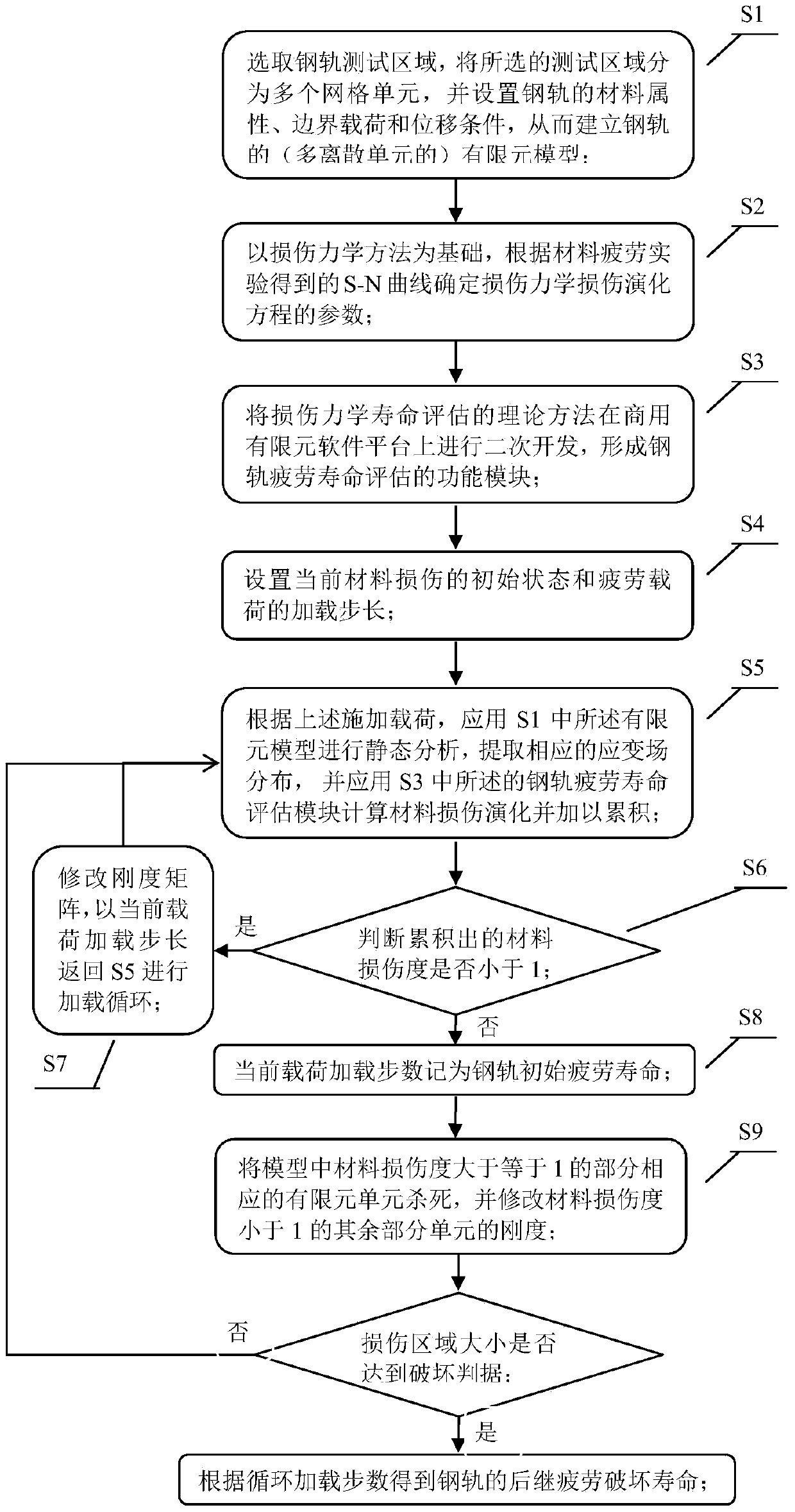
Method and system for predicting fatigue life of steel rail
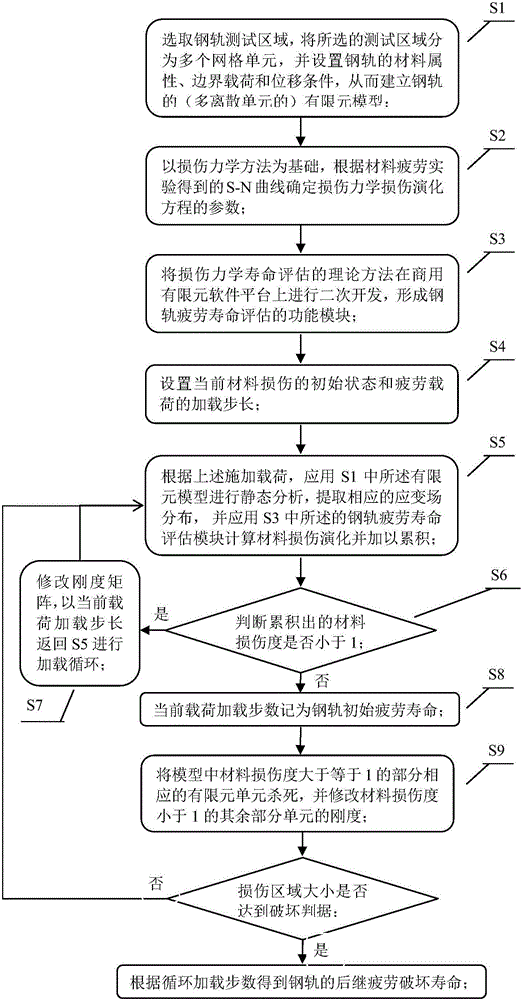
InactiveCN106202863AReduce potential safety hazardsImprove accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelEngineering
The invention provides a method for predicting the fatigue life of a steel rail. According to the method, a steel rail testing area is selected, a damage mechanics method is taken as a basis, damage evolution equation parameters of damage mechanics are determined according to an S-N curve of material fatigue, a theoretical life assessment method of damage mechanics is subjected to secondary development on a commercial finite element software platform, a function module for fatigue life assessment of the steel rail is formed, and theoretical assessment of the fatigue life of the steel rail is obtained through calculation by the aid of a finite element model. With the implementation of the method and the system, the fatigue life of the steel rail can be theoretically predicted, higher accuracy is realized, and the purpose of reducing potential safety hazards during use of the steel rail can be achieved.
Owner:张铮 +1
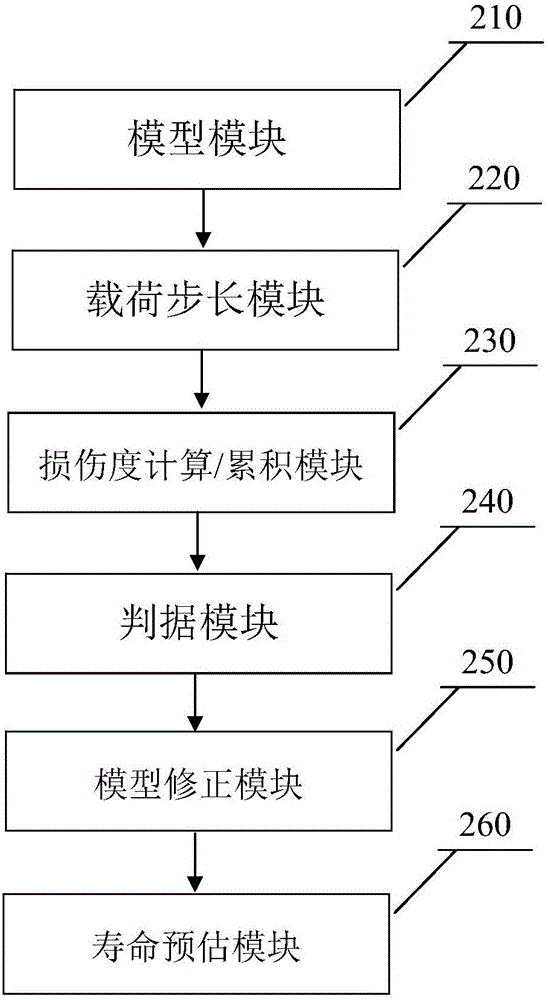
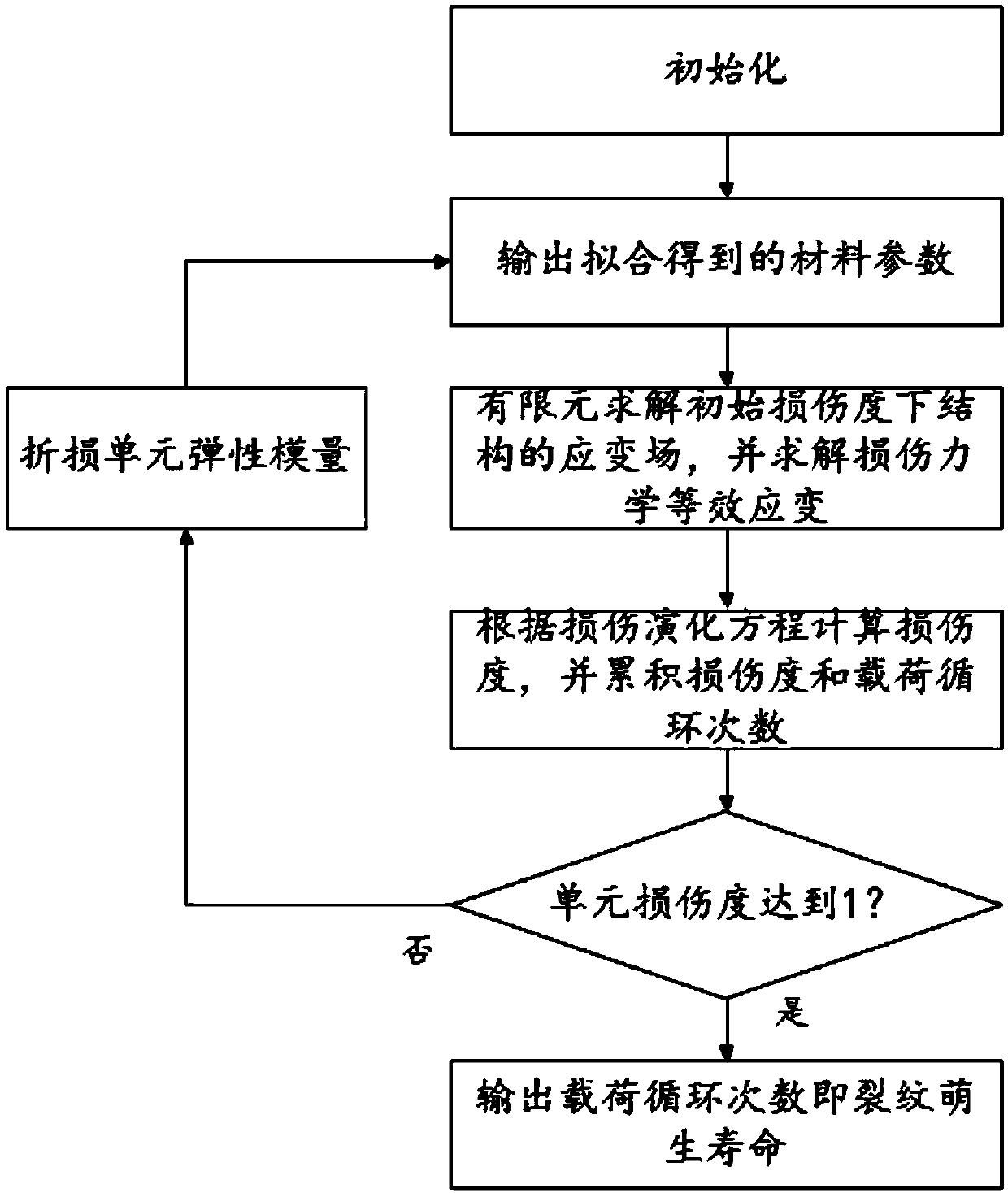
Unmanned vehicle structure damage tracking and fatigue estimating method
InactiveCN109657365AReal-time monitoring of damage evolutionEstimated Fatigue LifeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLoad cycleControl theory
The invention provides an unmanned vehicle structure damage tracking and fatigue estimating method. The unmanned vehicle structure damage tracking and fatigue estimating method comprises the steps that 1, collecting the load-time history at the joint of the structure part of the unmanned vehicle ; 2, according to the the load-time history at the joint of the structure part, carrying out, using damage mechanics-definite element solution to calculate damage degrees of all units of the structural part, and further comprising the following steps: step 21, calculating the damage degree of each unitof the structural member according to the load-time journey; According to the time history, solving a strain field of the structure under the initial damage degree D0 through a finite element method,and solving damage mechanics and other effect variations; Step 22: obtaining a damage degree increment dD under a given step length dN according to a damage evolution equation in a strain form, and accumulating the damage degree D = D0 + dD; wherein The cumulative load cycle number is N = N0 + dN; And 23, breaking the elastic model of the material, ED = E (1-D), repeating the steps 21 and 22 until the damage degree D of a certain unit reaches 1 wherein the number of output load cycles is the crack initiation life. According to the invention, the damage evolution process of each part of the unmanned vehicle structure can be monitored in real time, and the fatigue life of each part is estimated.
Owner:BOCOM SMART INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Finite element simulation method and system considering plasticity and damage constitutive relation
PendingCN111709176AEfficient simulation analysisEmphasis on fully coupled relationshipsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMetal formingClassical mechanics
The invention provides a finite element simulation method and system considering plasticity and damage constitutive relation, and the method comprises the steps: building a constitutive equation through employing continuous damage mechanics and a Johnson-Cook plastic flow criterion, so as to precisely predict the damage behavior in a metal forming and machining process. According to the method, plastic damage and a Johnson-Cook model are coupled through a strain path represented by stress triaxality and a Lode coefficient, and plastic mechanical behaviors and damage evolution in the metal forming and machining process are subjected to simulation analysis under the environments of different temperatures and loading speeds.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHENG ZHIYAO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
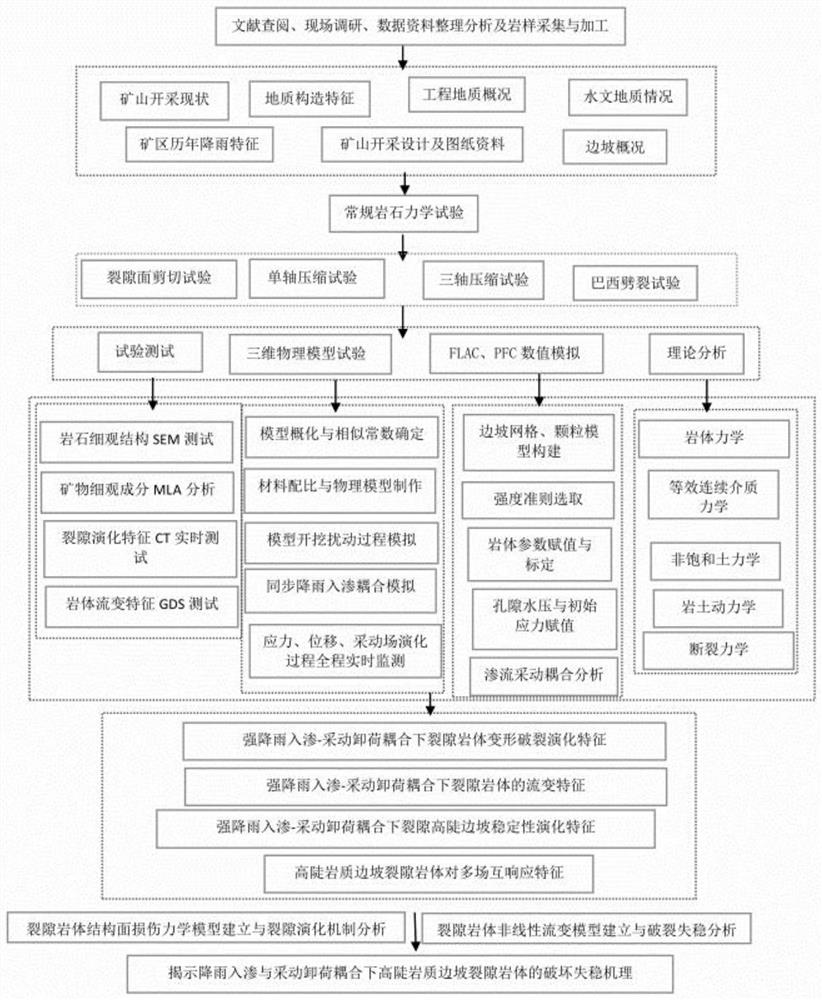
Rock mass structural surface shear failure surface morphology evolution law system
PendingCN113155636AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesMechanical modelsData information
The invention discloses a rock mass structural surface shear failure surface morphology evolution law system. The system comprises the steps of: performing literature lookup, field investigation and survey, data information arrangement and analysis and rock sample collection and processing; performing a conventional rock mechanics experiment; performing experimental test operation, three-dimensional physical model experiment, FLAC and PFC data simulation and theoretical analysis operation; carrying out operation analysis on the deformation characteristics of a rock mass under heavy rainfall infiltration-mining unloading; analyzing a fractured rock mass structural surface damage mechanical model and a fracture evolution mechanism; establishing a fractured rock mass nonlinear rheological model and analyzing fracture instability; and revealing the fracture instability mechanism of the fractured rock mass of a high and steep rock slope under the coupling of rainfall infiltration and mining unloading. The system has the advantage that safety control and stability evaluation of a mine slope are facilitated.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
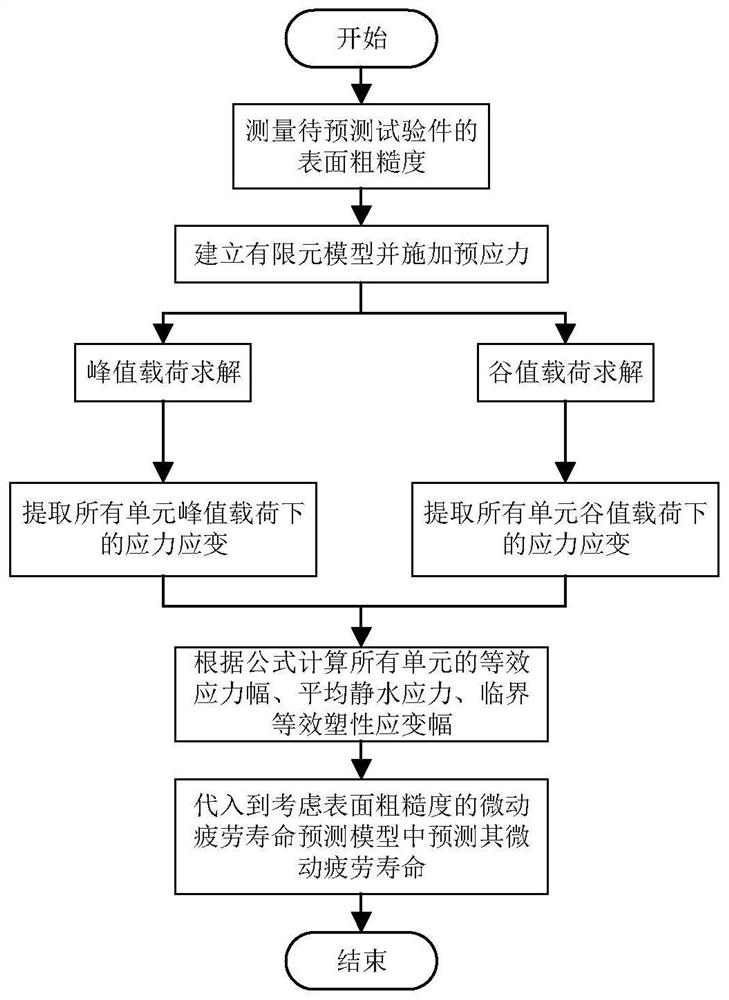
Fretting fatigue life prediction model and method considering surface roughness
PendingCN113158511ADesign optimisation/simulationComputational theoretical chemistryElement modelElement analysis
The invention discloses a fretting fatigue life prediction model and method considering surface roughness, and the method is based on continuous medium damage mechanics, and the surface roughness of a material surface impacted by different laser energy is different. The residual compressive stress is introduced into the finite element model, and the fretting fatigue life can be predicted more accurately by considering the change of the surface roughness. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a finite element model, and adding residual compressive stress introduced by laser shock peening into the model as initial stress; (2) carrying out simulation calculation and extracting related parameters in the model; (3) fitting parameters in the life prediction model, and establishing a full fretting fatigue life prediction formula; and (4) establishing new finite element analysis, and calculating the fretting fatigue life by using a life prediction formula. The model and the method can effectively predict fretting fatigue life of different surface roughness, and have important engineering application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
A method and system for estimating fatigue life of rails
InactiveCN106202863BReduce potential safety hazardsImprove accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelFatigue life assessment
Owner:张铮 +1
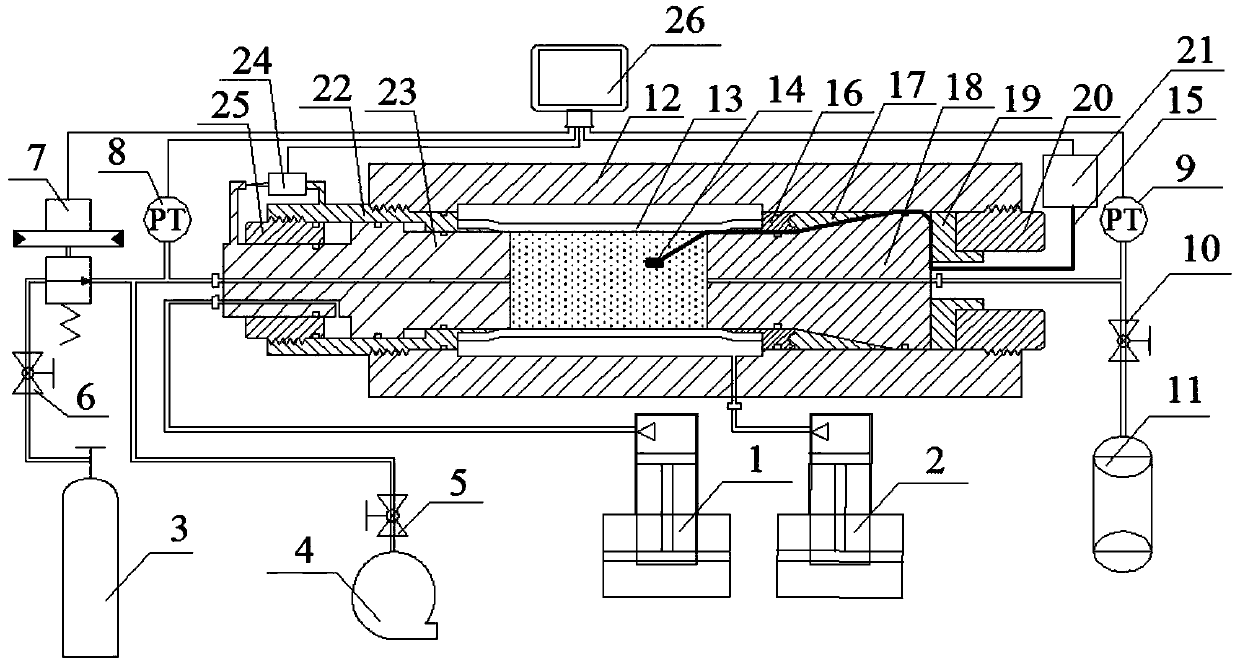
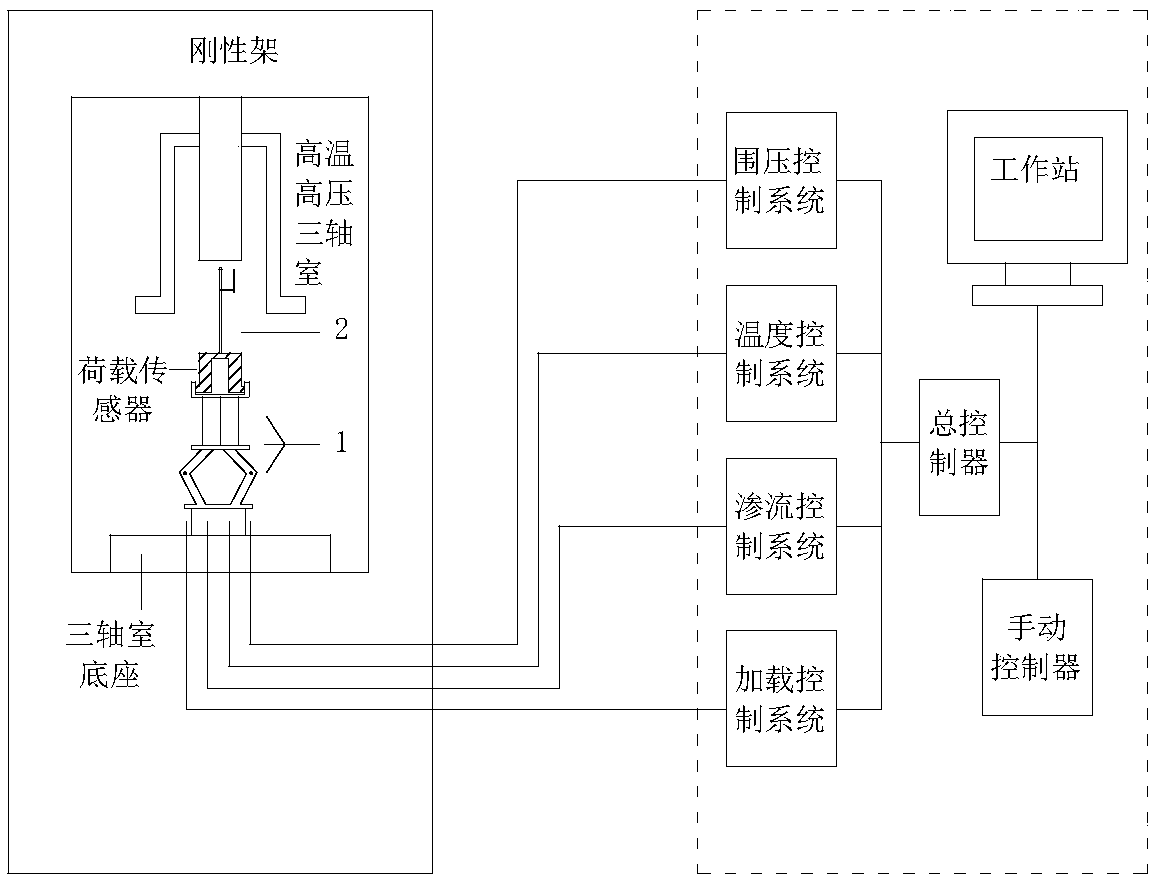
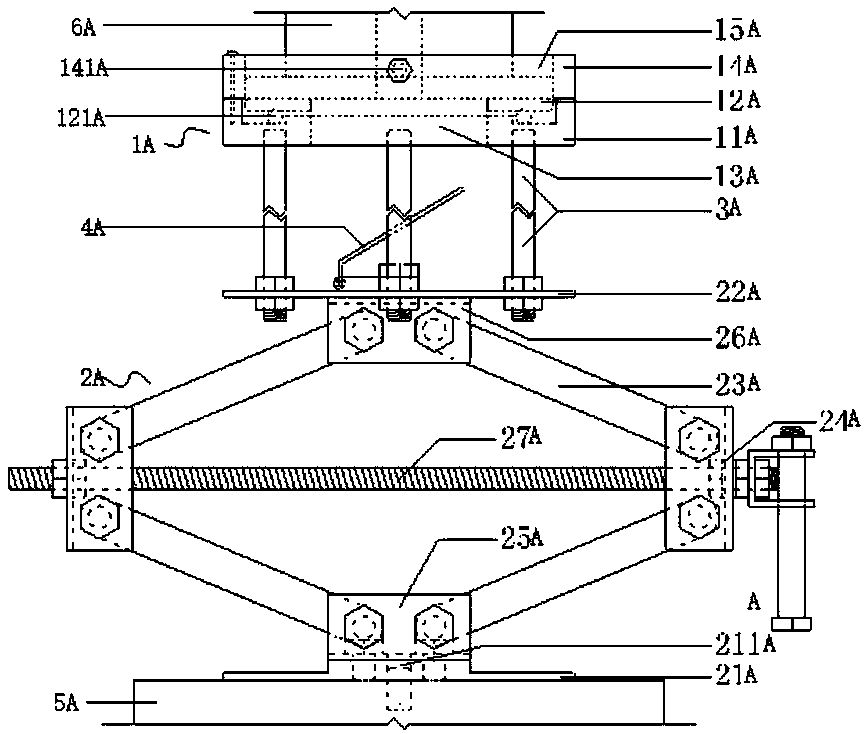
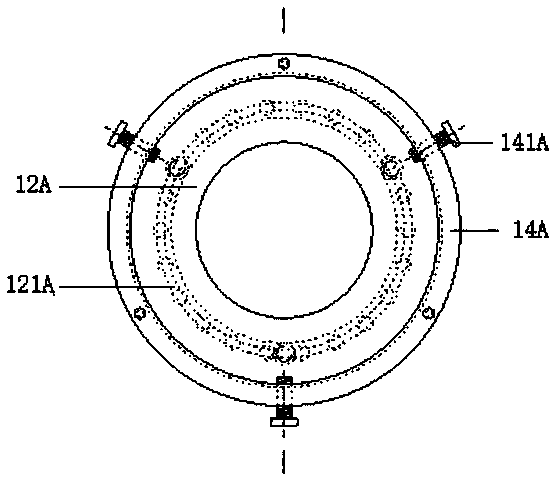
Rock damage mechanics test system under deep high-temperature high-pressure environment
PendingCN108507883AStable and strong supportAvoid damageEarth material testingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention belongs to the field of engineering rock mass experimental equipment, and in particular provides a device matched with protection, repair and maintenance of a mechanics test system (MTS). The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide a rock damage mechanics test system under a deep high-temperature high-pressure environment, improve the mounting and dismounting efficiency of a triaxial force sensor of the MTS, improve the lifting reliability, simultaneously solve the problem of mounting the force sensor in a hole, and improve the mounting efficiency.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com