Method for preparing sub-wavelength metal grating through wide-beam femtosecond laser double pulses
A femtosecond laser and metal grating technology, applied in the directions of diffraction grating, optics, optical components, etc., can solve the problems of uneven distribution of surface structure, small irradiation area of focused spot, low efficiency of large-area preparation, etc., and achieve a relaxed processing environment. , The effect of large irradiation range, efficient and controllable preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, but not to limit the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
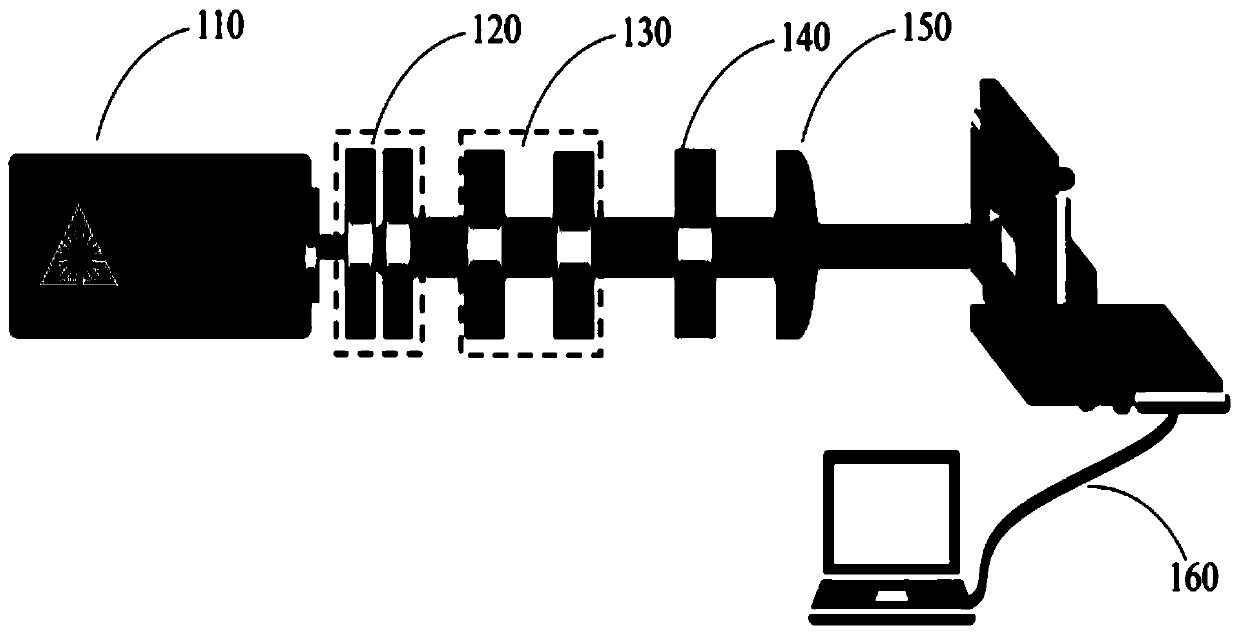
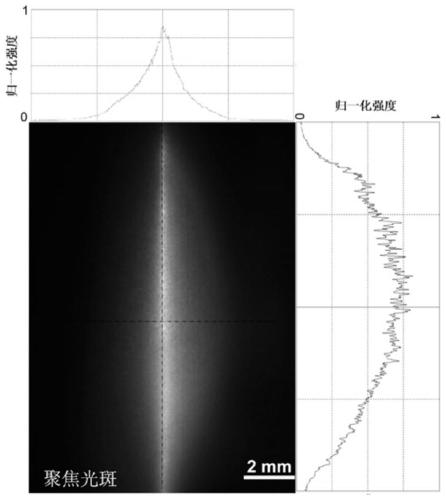
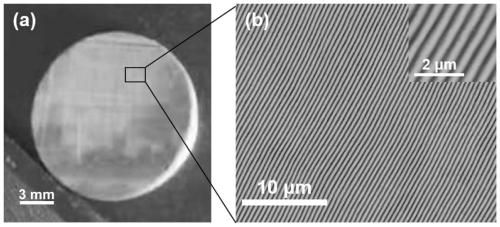
[0030] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the optical path of the method for efficiently preparing a sub-wavelength metal grating with a wide-beam femtosecond laser double pulse in the present invention, wherein a femtosecond laser light source 110, an optical beam expander 120, an energy adjustment device 130, and a double pulse Generating means 140 , beam...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Center wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap