Method for rapidly identifying bacteria and fungi by utilizing Raman spectra
A technology of Raman spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy, applied in the field of microbial identification, can solve the problems of high detection cost, high laboratory requirements, and inability to meet detection conditions, and achieve the effects of ensuring accuracy, simple operation, and shortening detection time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
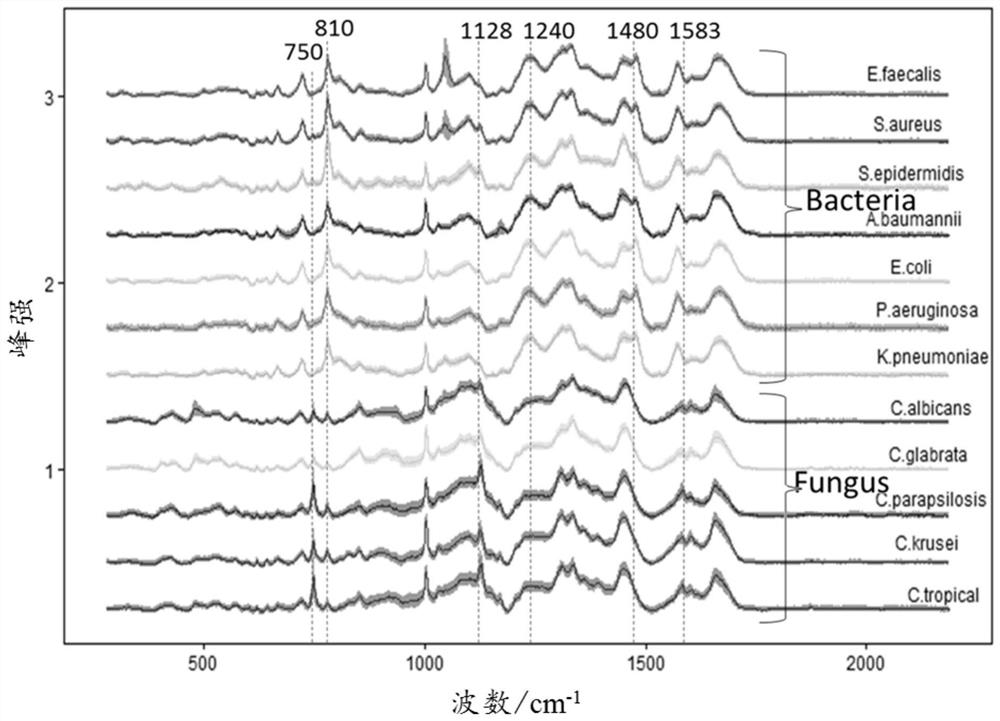
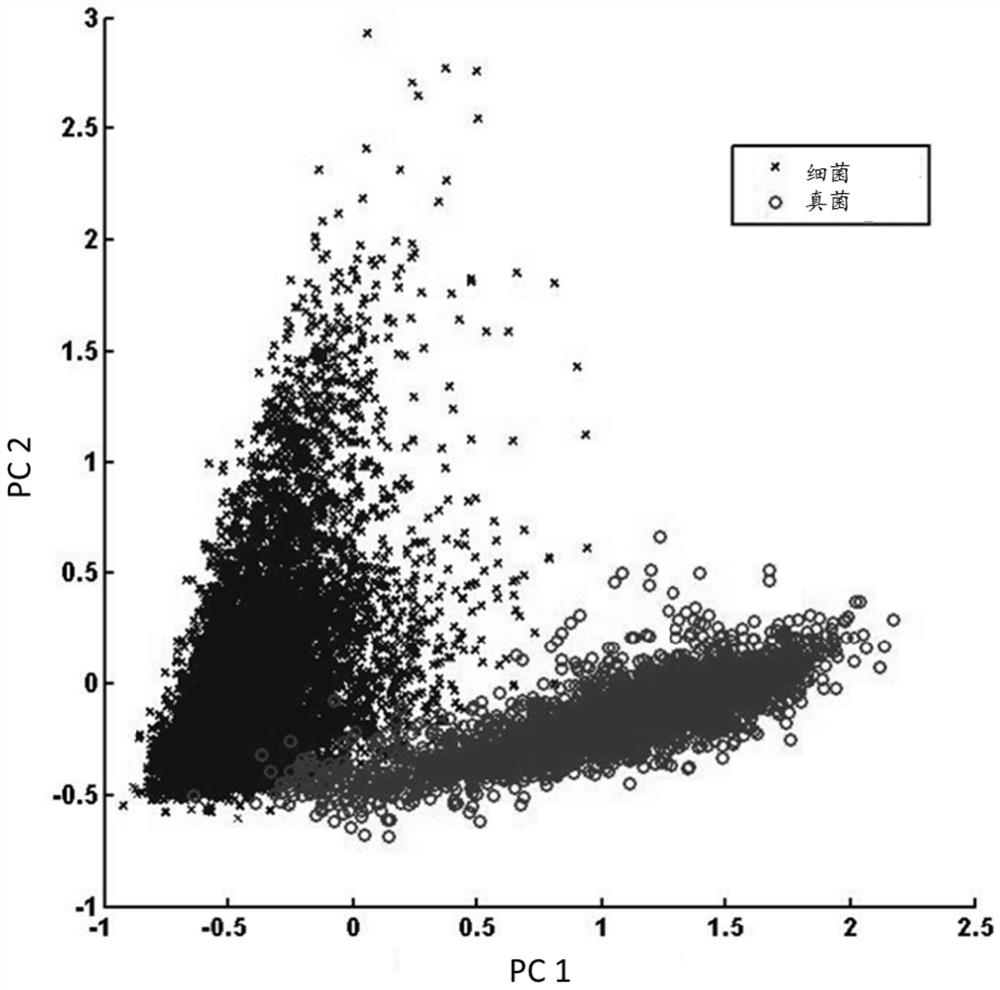
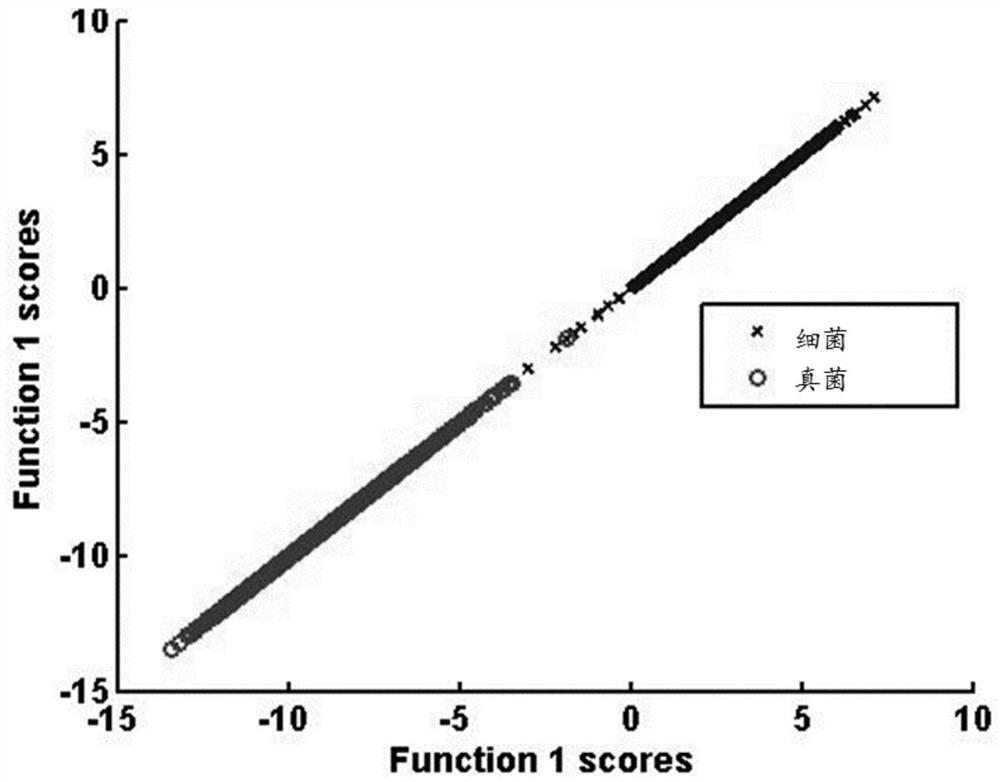
[0060] Five clinical isolates of fungi (3 strains of Candida albicans, 3 strains of Candida krusei, 3 strains of Candida parapsilosis, 3 strains of Candida glabrata, 3 strains of Tropical Candida (Candida tropicalis, a total of 15 strains) and 7 clinically isolated bacteria (2 strains of Escherichia coli, 1 strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae, 1 strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas aeruginosa), 1 strain of Acinetobacter baumannii, 2 strains of Staphylococcus aureus, 1 strain of Enterococcus faecalis, 1 strain of Staphylococcus epidermidis, 9 strains in total ), all strains were from the Institute of Antibiotics, Huashan Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University. Take 1ml of pure culture solution from each strain, centrifuge at 7000rpm for 2min, discard the supernatant, wash the precipitate three times with deionized water, take 2μL of the washed solution and spot it on an aluminum-coated glass slide, and air-dry it at room temperature. Raman detection.
[0061] Use Witec ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com