System for predicting risk of death of patient
A patient-risk technology, applied in the system field of predicting patient death risk, can solve problems such as high adjusted hazard ratio of in-hospital mortality, reduced predictive value, and changes in physiological parameters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] Embodiment 1 screening patients and collecting experimental data
[0131] From March 2016 to October 2016, patients who visited the emergency department of Beijing Third Hospital and needed treatment in the emergency care unit system (emergency rescue room and emergency care unit) due to their illness. The disease classification of the patients included in the study was grade 1 (endangered patients) or grade 2 (critically ill patients).
[0132] Inclusion criteria:
[0133] 1. Patients who have been treated in the emergency room or emergency care unit;
[0134] 2. Age ≥ 16 years old;
[0135] Exclusion criteria:
[0136] 1. Patients who have no spontaneous breathing or heartbeat when they come to the hospital, and are declared clinically dead;
[0137] 2. Pregnant patients;
[0138] 3. Patients with serious missing data;
[0139] After repeated discussions, the research team specified the data collection plan, made a unified case report form, discussed and unified...
Embodiment 2
[0151] Example 2 Screening the prediction parameters included in the prediction system from the collected patient data
[0152] The new model stage of the prediction system of this application is derived, and logistic regression is used to analyze the association between each variable and the mortality rate. Only variables that were significantly associated with mortality (ie, P<0.1) were used to derive risk-adjusted scores.
[0153] At the initial stage of model establishment, the relationship between each univariate and death was preliminarily studied. Except for age, which has a linear relationship with mortality, other variables have a more complex relationship with death. We therefore adjusted these variables as categorical variables. Different variables were grouped according to their relationship with mortality, and if the variables had standard normal ranges clinically, they were grouped according to their standard ranges.
[0154] The medical history data of the pa...
Embodiment 3
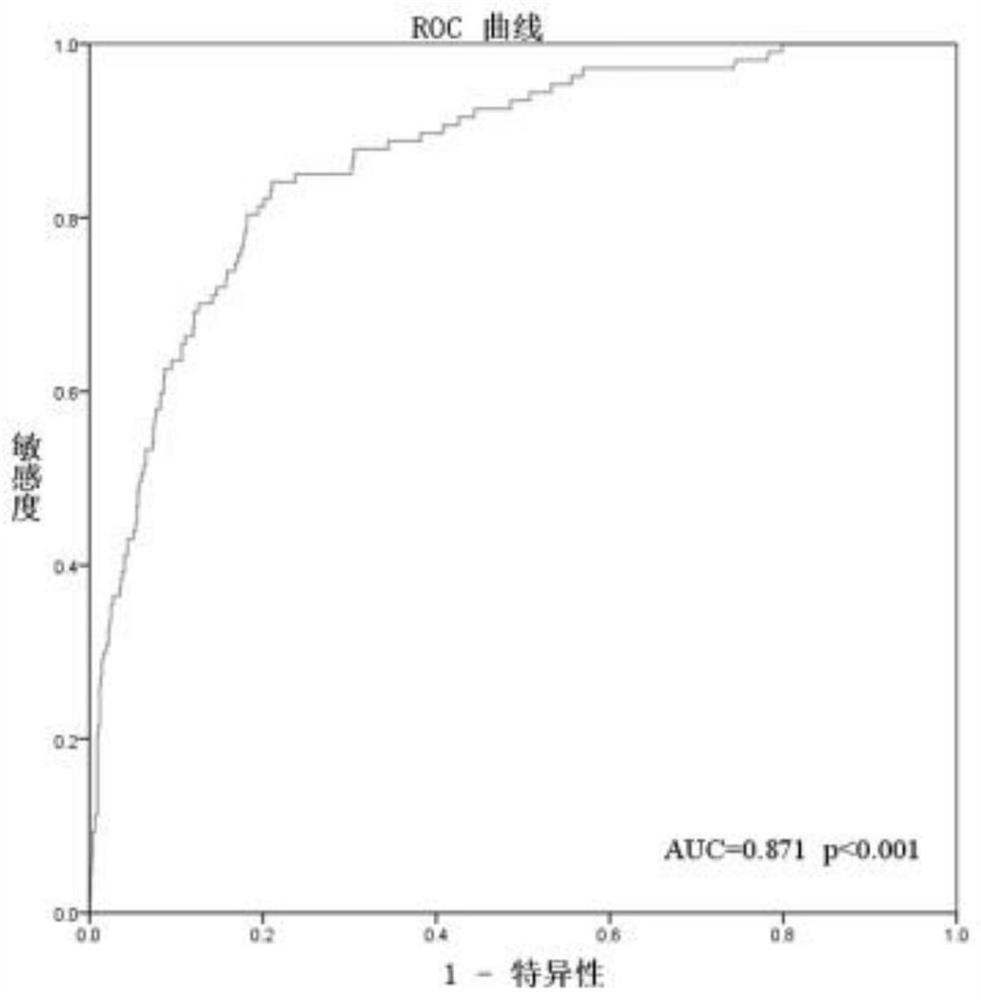
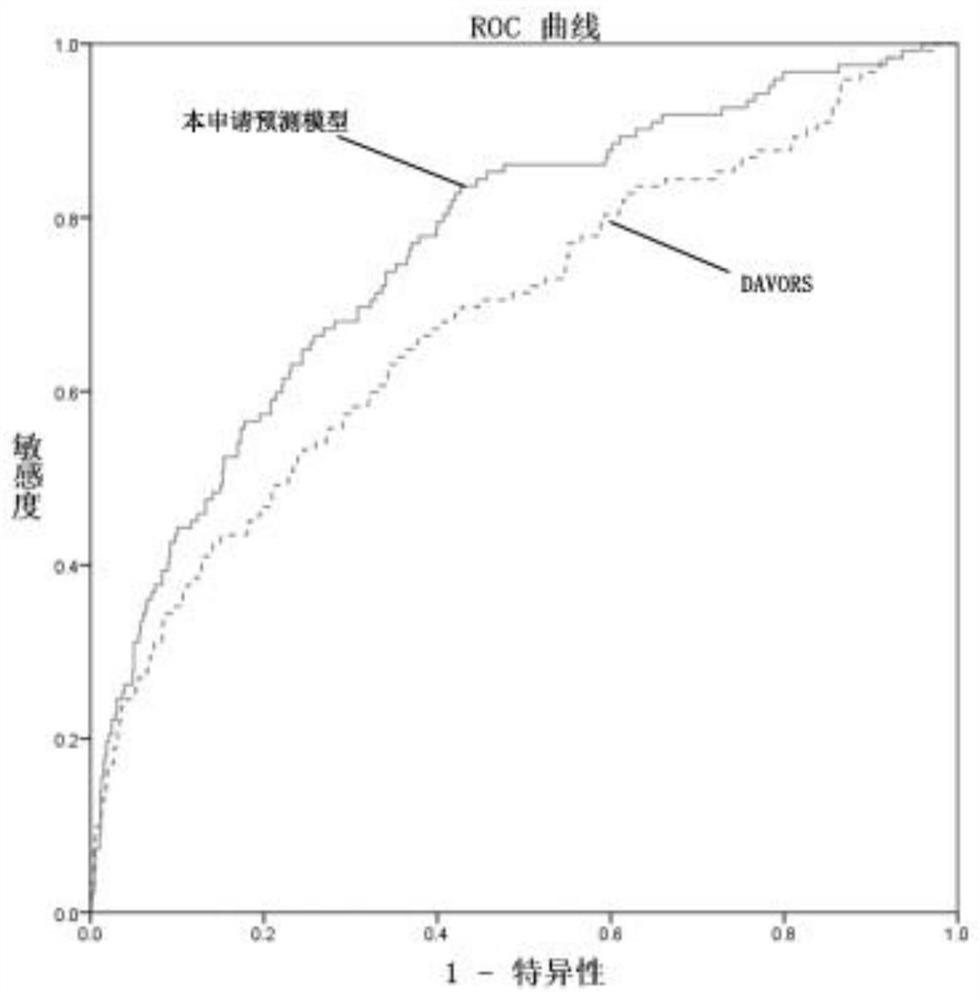
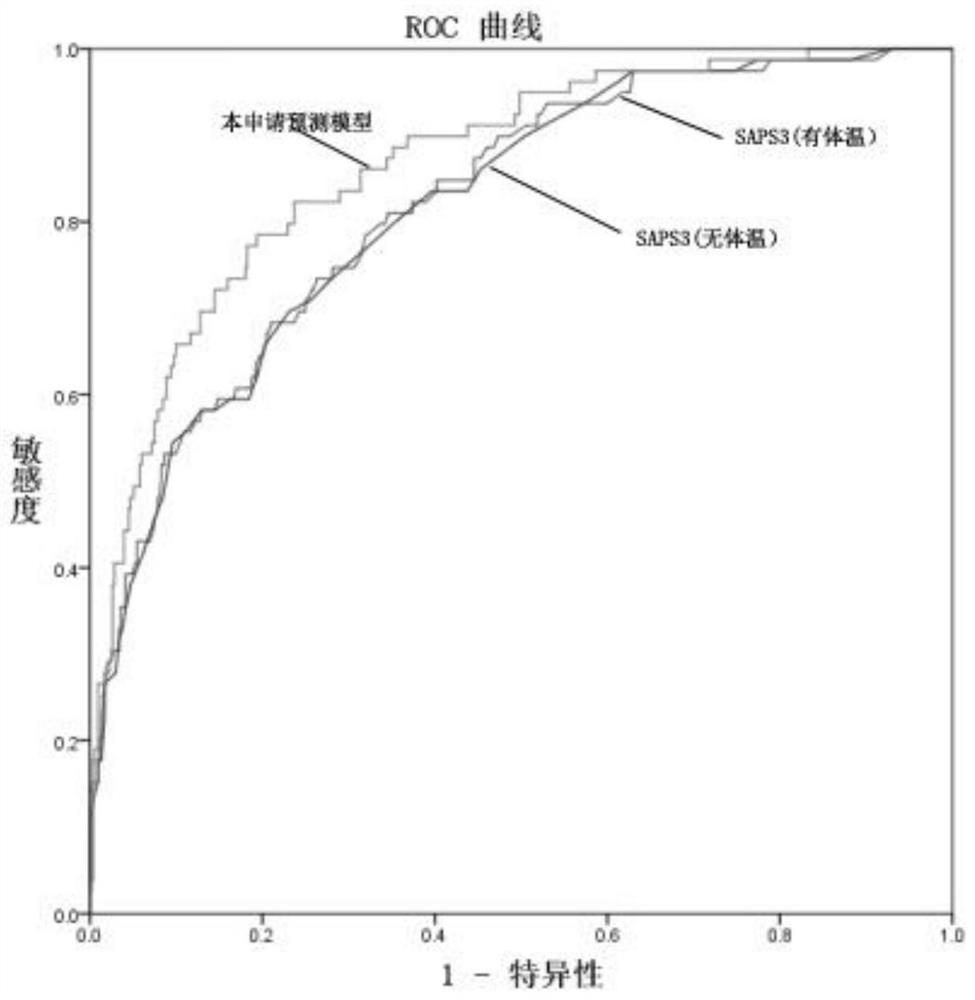
[0159] Example 3 Determination of the 7-day mortality prediction system model for critically ill patients in the emergency department
[0160] A total of 1624 cases were included in the study, with an average age of 64.7±18.1 years, and 969 cases (60%) were male. The basic information of the patients is shown in Table 1.
[0161] Table 1 includes the basic information of the patients
[0162]
[0163] Note: The measurement data of normal distribution is represented by mean ± standard deviation; the measurement data of non-normal distribution is represented by M(P25, P75); *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
[0164] From the considered continuous variables, we classified the variables on the basis of the standard ranges of each variable, combined with clinical experience, expert opinion, the physiological characteristics of patients in my country, and the severity of the disease, and determined the cut-off values for their classification (see Table 2). Based on group discussions and reco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com