Hierarchical Quantification Method Based on Damage Mapped Finite Element Mesh
A quantitative method and finite element technology, applied in image analysis, design optimization/simulation, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to reflect layered area distribution layered gradients, etc., achieve convenient remaining mechanical properties, high degree of automation, and improve simulation The effect of precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
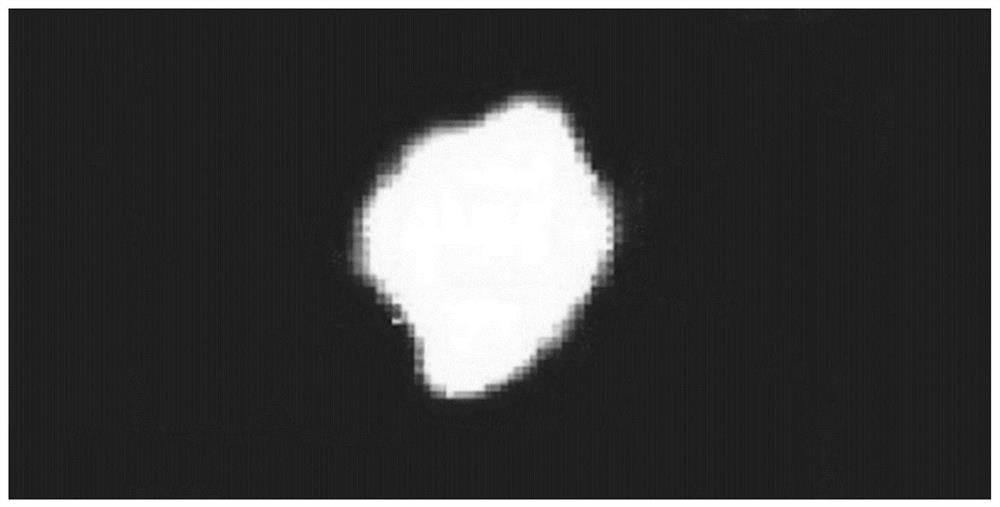
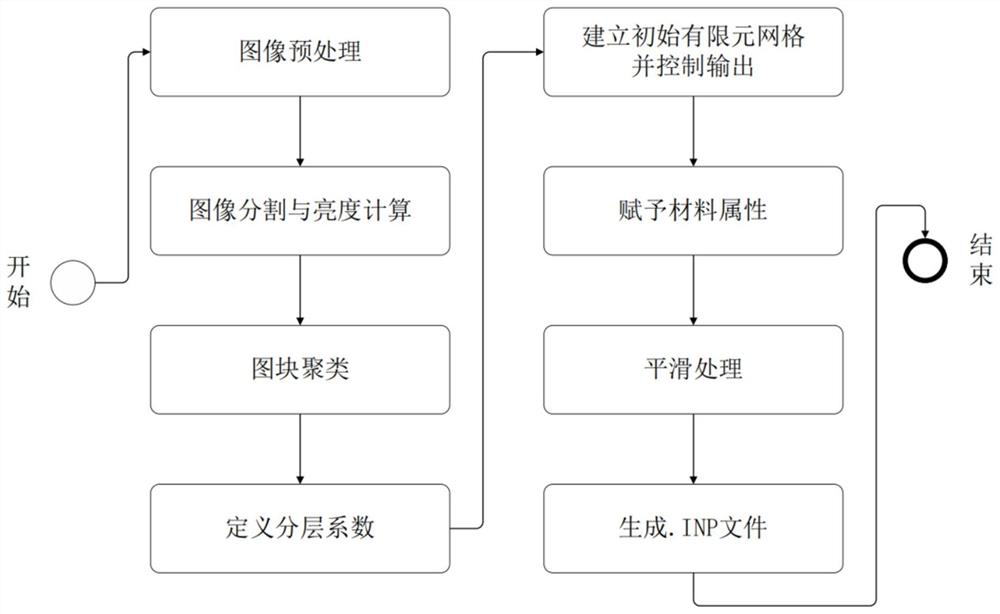
[0024] like figure 1 As shown, this embodiment relates to a method for quantifying drilling layers based on damage mapping finite element grids, including the following steps:
[0025] The first step: put a piece of figure 1 The image of the ultrasonic C-scan of the carbon fiber composite with holes shown and containing p×q pixels is imported into the MATLAB software, and its RGB value is read; then the RGB value is stored in a p×q×3 matrix; then Find the average value of the third dimension and convert it into an integer; finally store the average value in the p×q two-dimensional array D, and each element in D is the brightness of the pixel at the corresponding position.
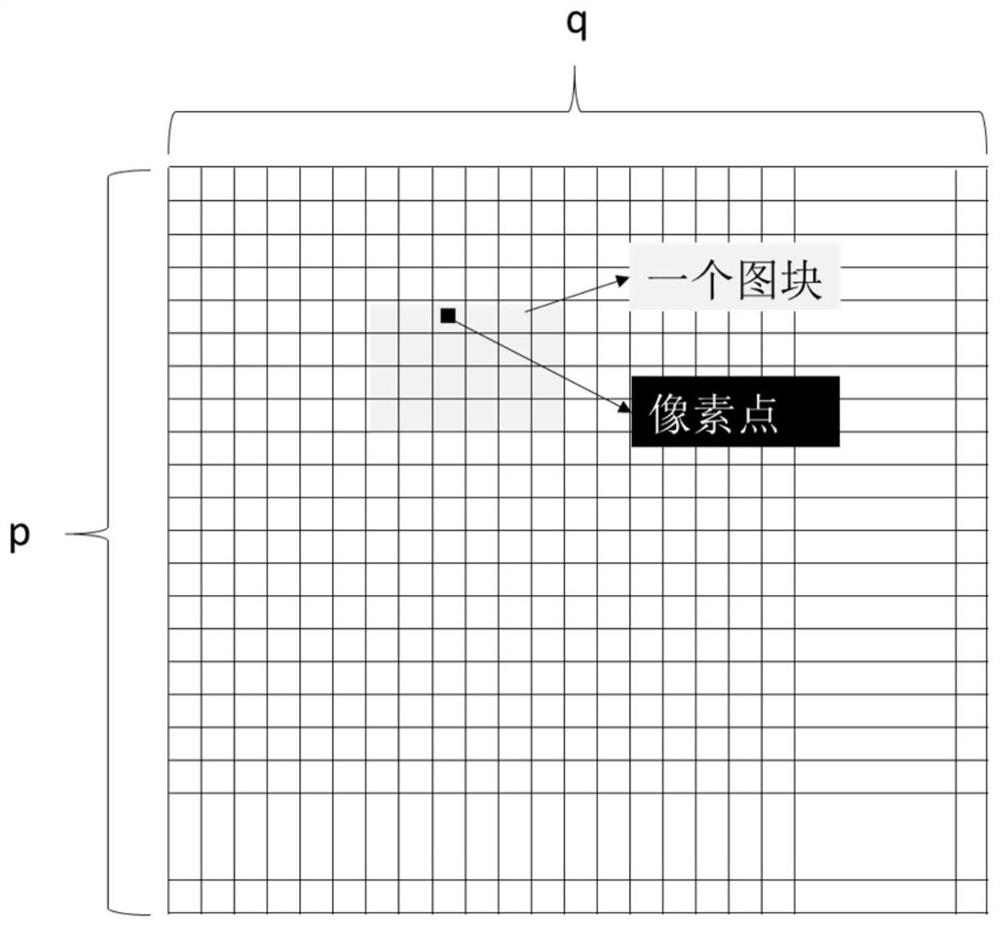
[0026] The second step: discretize the image into m×n blocks according to the precision of the finite element grid, each block defines the number i, i=1,2,...,m×n, such as image 3 shown. Calculate the average brightness of all pixels in each block, convert it into an integer, and store it in the m×n two...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com