Method for 3D printing of a composite structure
A 3D printing and composite structure technology, applied in the field of 3D printing, can solve the problems of restricting the application and promotion of 3D printing, low mechanical strength, and non-wear resistance, and achieve the goals of saving traditional processing cycles, increasing manufacturing costs, and improving structural strength. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
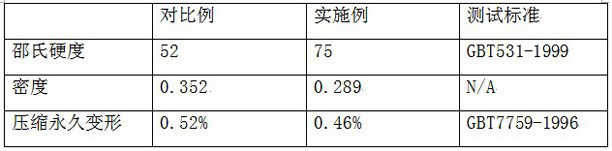
[0029] Print a cube shape with a side length of 10 cm, use Somos 11122 material as the printing material, and print a solid part as a comparison example.
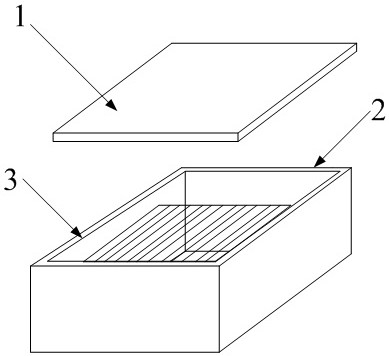
[0030] The cube is decomposed into a prefab with a wall thickness of 1 cm and a semi-open cavity with a side length of 8 cm and a top cover with a thickness of 1 cm.
[0031] After printing out the prefabricated parts, arrange multiple layers of 7628-standard glass fiber cloth in parallel in the cavity, with an interval of 1 cm between the glass fiber cloths. Holes can be opened on the glass fiber cloth to facilitate the flow of semi-solid epoxy resin. After the arrangement is completed, the semi-solid epoxy resin mixed with curing agent is injected to fill the cavity, and a certain cavity space can be reserved according to the expansion characteristics of the epoxy resin after curing. In this embodiment, novolac epoxy resin and aromatic amine curing agent are mixed according to 100:40 parts by weight and then cured and fil...
specific Embodiment 2
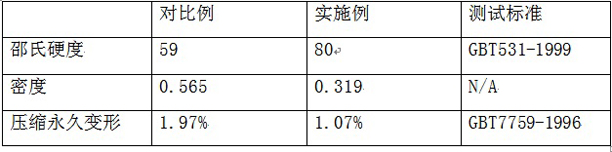
[0035] Print a cube shape with a side length of 10 cm, use PLA (Polylactide, polylactic acid), that is, corn starch resin material as the printing material, and print a solid part as a comparison example.
[0036] The cube is decomposed into a prefab with a wall thickness of 1 cm and a semi-open cavity with a side length of 8 cm and a top cover with a thickness of 1 cm.
[0037] After printing out the prefabricated parts, arrange multiple layers of 7628-standard glass fiber cloth in parallel in the cavity, with an interval of 1 cm between the glass fiber cloths. Holes can be opened on the glass fiber cloth to facilitate the flow of semi-solid epoxy resin. After the arrangement is completed, the semi-solid epoxy resin mixed with curing agent is injected to fill the cavity, and a certain cavity space can be reserved according to the expansion characteristics of the epoxy resin after curing. In this embodiment, novolac epoxy resin and aromatic amine curing agent are mixed accordi...
specific Embodiment 3
[0041] Print a cube shape with a side length of 10 cm, use ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene ternary block copolymer as the printing material, and print a solid part as a comparison example.
[0042] The cube is decomposed into a prefab with a wall thickness of 1 cm and a semi-open cavity with a side length of 8 cm and a top cover with a thickness of 1 cm.
[0043] After printing out the prefabricated parts, arrange multiple layers of 7628-standard glass fiber cloth in parallel in the cavity, with an interval of 1 cm between the glass fiber cloths. Holes can be opened on the glass fiber cloth to facilitate the flow of semi-solid epoxy resin. After the arrangement is completed, the semi-solid epoxy resin mixed with curing agent is injected to fill the cavity, and a certain cavity space can be reserved according to the expansion characteristics of the epoxy resin after curing. In this embodiment, novolac epoxy resin and aromatic amine curing ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com