Opposed hydraulic free piston engine with hydraulic synchronizing mechanism and driving method of opposed hydraulic free piston engine.
A piston engine, hydraulic synchronization technology, used in free piston engines, machines/engines, liquid fuel engines, etc., can solve problems such as reducing power density, increasing system volume and complexity, and increasing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
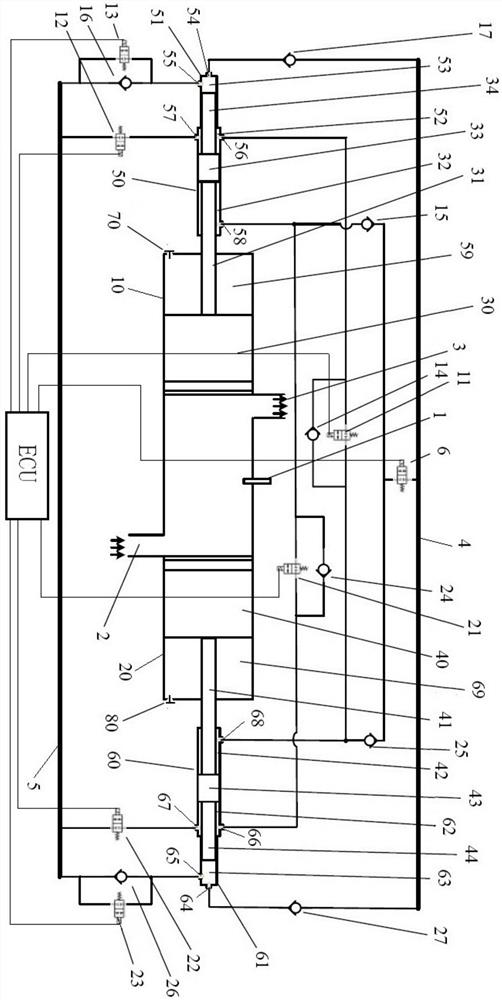
[0070] An opposed free-piston engine with a hydraulic synchronization mechanism, comprising: a high-pressure working fluid circuit 4, a low-pressure working fluid fluid circuit 5, an electronic control unit ECU, an injector 1, an air inlet 2, and an exhaust port 3, a total of The first cylinder liner 10 and the second cylinder liner 20 are axially and symmetrically distributed, the first piston 30 matched with the first cylinder liner, the first piston rod 31 connected with the first piston, and the other end of the first piston rod. The first piston rod sleeve 51, the first high pressure working medium output chamber 53 formed by the first piston rod sleeve and the end face of the first piston rod, the second piston 40 matched with the second cylinder sleeve, the second piston 40 connected with the second piston. Two piston rods 41, a second piston rod sleeve 61 connected to the other end of the second piston rod, a second high pressure working medium output cavity 63 formed b...
Embodiment 2
[0091] The structure of the opposed free-piston engine is exactly the same as that of Embodiment 1, and a method for driving an opposed free-piston engine with a hydraulic synchronizing mechanism implemented on the above-mentioned engine is as follows:
[0092] Close the exhaust port, the intake port is completed and closed, and all solenoid valves are closed by default;
[0093] Step 0: Adjust the piston to the bottom dead center, the specific process is as follows: open the first air valve, the second air valve, the first solenoid valve, the second solenoid valve, the third solenoid valve, the fourth solenoid valve, and the fifth solenoid valve , the sixth solenoid valve and the seventh solenoid valve; part of the liquid working medium in the output chamber of the first high pressure working medium is pumped to the low pressure working medium liquid circuit by the fifth solenoid valve, and part of the liquid working medium in the third synchronizing cavity is pumped by the th...
Embodiment 3
[0101] The structure of the opposed free-piston engine is exactly the same as that of Embodiment 1. Steps 1, 2, 3, and 4 are the same as those of Embodiment 1. The difference lies in Step 3-1, specifically:
[0102] Step 3-1: Taking the position of the first piston as a reference, if the phase of the second piston lags behind, pressurize the second air tank with the intake air through the second valve; if the phase of the second piston is ahead, pass the second The air valve is deflated to depressurize the second air tank, and the amount of deflation or intake is subject to eliminating the phase deviation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com