Carbon catabolism regulation protein CcpA mutant I42A
A technology for catabolism and protein regulation, which is applied in the field of recombinant expression vectors and recombinant microbial cells, and can solve the problems of destroying bacterial metabolic pathways and restricting bacterial growth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The selection of the key amino acid of embodiment 1 bacillus licheniformis CcpA protein
[0037] As a global regulatory factor, the CcpA gene of Bacillus licheniformis mainly binds to the nucleic acid site through the protein and then exerts its regulatory function. After the CcpA protein binds to the nucleic acid, the relative position of the substructure of the corresponding binding site will change to a certain extent. The amino acids that act as fulcrums in this transformation process may be located at both ends of the α-helix in the substructure of CcpA protein. At the same time, the binding of CcpA protein to nucleic acid requires the recognition of the protein and the cre site, and the amino acid that plays a major role in the recognition of the protein and the cre site may be located in the middle of the α helix, so when we select the amino acid site, it is mainly distributed in the CcpA protein α Both ends of the spiral and the middle.
Embodiment 2
[0038] The construction of embodiment 2 bacillus licheniformis CcpA protein expression vector
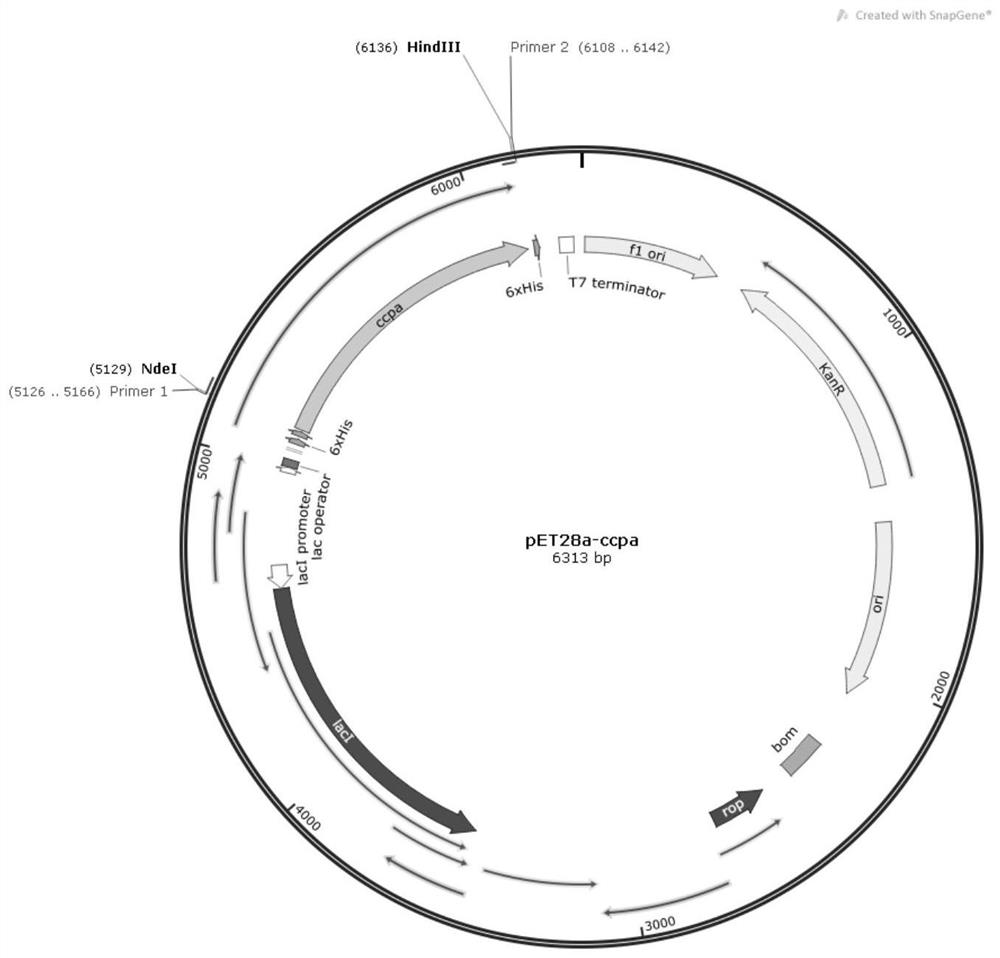
[0039] Using the Bacillus licheniformis CcpA protein genome as a template, the CcpA gene was amplified, and the resulting gene was connected to the pET28a vector to construct the Bacillus licheniformis CcpA protein expression vector ( image 3 ). Transform it into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) to construct a recombinant strain.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3 Site-directed Mutagenesis, Expression and Purification of Bacillus licheniformis CcpA Protein
[0041] The Bacillus licheniformis CcpA protein expression vector constructed in Example 2 was used as a template to perform site-directed mutation on the Bacillus licheniformis CcpA protein. The mutation primers used were:
[0042] I42A-F (SEQ ID NO. 3): 5'aaggtgcttgaagccgccgagcgtcttggctatcgtccaaatgccgtggc3';
[0043] I42A-R (SEQ ID NO. 4): 3'agccaagacgctcggcggcttcaagcaccttctttctcgtcgtcggcttg5'.
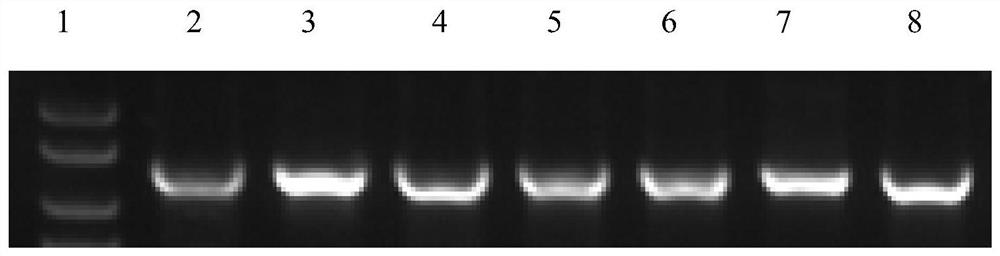
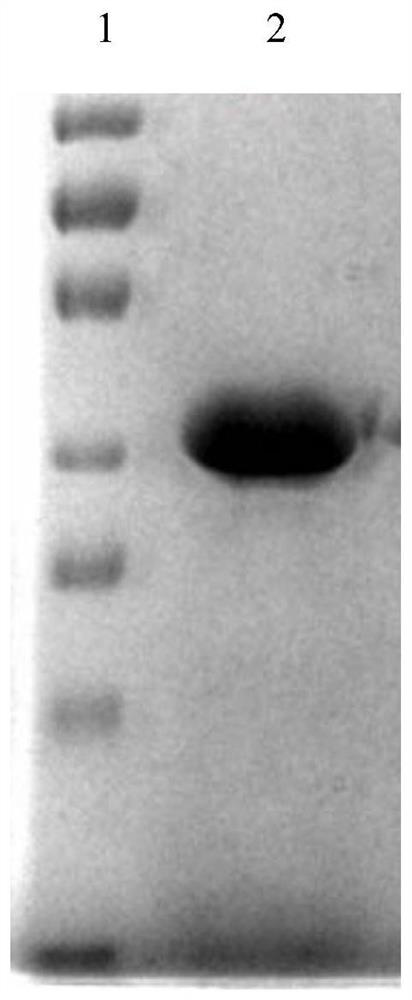
[0044] The CcpA protein after site-directed mutation (the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the gene nucleotide sequence encoding it is shown in SEQ ID NO.1) was heterologously expressed and purified in Escherichia coli, and the colonies were amplified by PCR. The verification diagram is as follows figure 1 As shown, the SDS-PAGE gel verification picture is as follows figure 2 As shown, it indicates that the mutated CcpA protein was successfully transform...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com