Solid-state sodium battery high-load electrode and preparation method and application thereof
A sodium battery, solid-state technology, which is applied to high-capacity electrodes of solid-state sodium batteries and their preparation and application fields, can solve the problems of inability to achieve, reduce interface impedance, and complex processes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0043] The preparation method of the high-capacity electrode of the solid-state sodium battery allows the electrode active material to be filled into the electrolyte porous layer as much as possible, thereby increasing the loading capacity of the electrode active material. The loading capacity per unit area of the positive active material is 1-20 mg / cm 2 . The area refers to the area of the ceramic pole piece. Specifically, in an embodiment, the loading amount of the electrode active material may be 1-20 mg, preferably 4-8 mg.
[0044] The present invention also provides a method for loading negative electrode active materials. Metal sodium is melted and infiltrated into the porous electrolyte layer as the negative electrode, which relieves the stress concentration caused by the uneven deposition of sodium during the battery charge-discharge cycle, destroys the dense electrolyte layer, and effectively prevents the formation of sodium dendrites, further improving battery ...
Embodiment 1
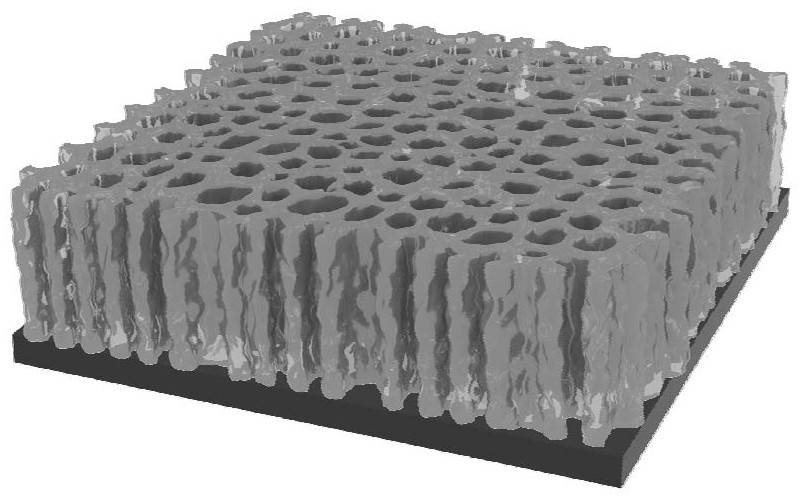
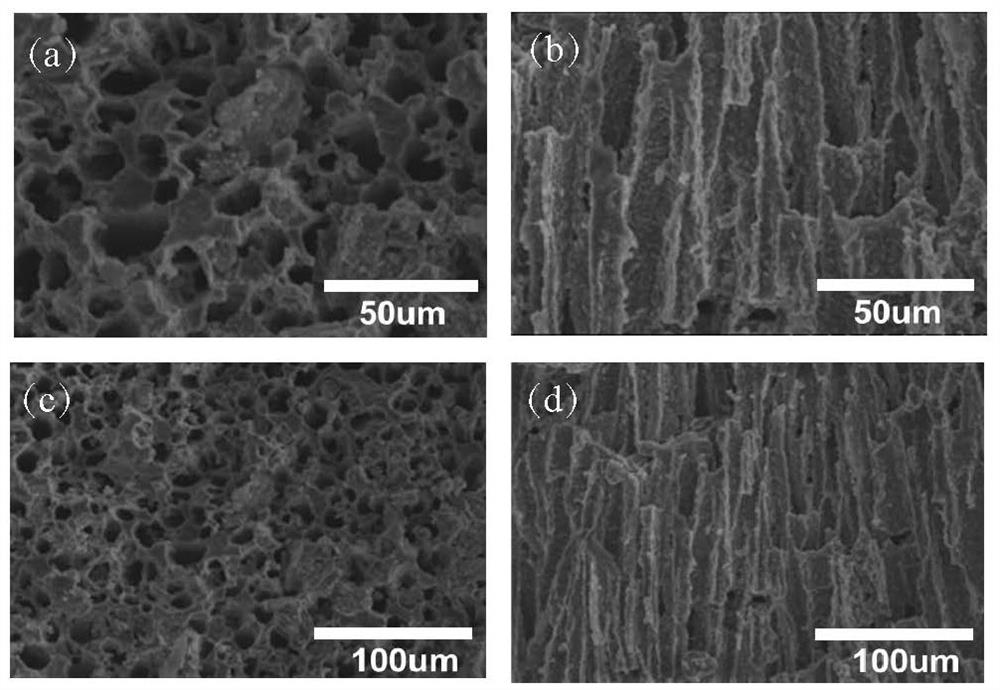
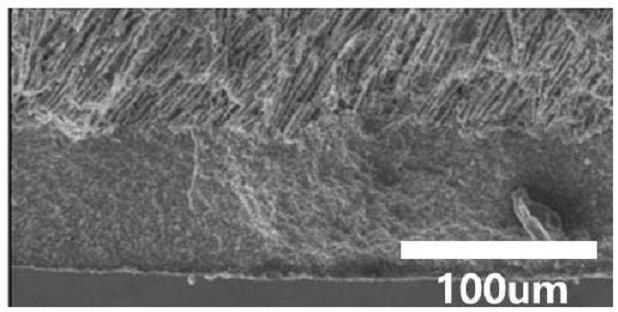
[0051] First put 6g of beta-Al 2 o 3 The powder was dissolved in 10 g of tert-butanol (solid content 35%, mass percentage)), and 1 g of polymerization agent PEG was added thereto, and stirred on a heating platform at 40° C. for 4 h to form a porous layer slurry. Then, a sponge template with a diameter of 16 mm was used to absorb the porous layer slurry, placed on a semiconductor refrigerator at -50°C for vertical freeze-drying, and placed in a freeze dryer for 12 hours. Finally, it is sintered at 1000° C. for 2 h with a heating rate of 2° C. / min to obtain a vertical porous structure. One side of the vertical porous structure is repeatedly impregnated with the dense layer slurry, and sintered at 1550°C for 10 minutes by buried powder sintering method to obtain a porous / dense composite structure beta-Al 2 o 3 Electrolyte (the schematic diagram is as figure 1 shown). The porosity of the porous layer measured by the Archimedes method was 54%. Sodium vanadium phosphate was sy...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Preparation of beta-Al with porous and dense composite structure 2 o 3 Electrolyte, specific implementation steps with reference to embodiment 1, only change the beta-Al in the porous layer slurry 2 o 3 The amount of powder added reaches the purpose of adjusting the solid content, so that the solid content is 40%. The porosity of the porous layer measured by the Archimedes method is 50%. Sodium vanadium phosphate was synthesized by sol-gel method, and sodium vanadium phosphate was dissolved in NMP to form a solution, and then the solution was dropped into the porous layer, and the solvent was evaporated at 100°C, so that the active material sodium vanadium phosphate was successfully loaded on the porous layer of the electrolyte. In the pores, a porous / dense composite structure ceramic loaded with active substances is formed. The obtained porous / dense composite structure ceramics loaded with active materials were used as the positive electrode and electrolyte, the so...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com