Construction method of animal model of rat with compressive injury of nerve roots
A construction method and animal model technology, applied in the field of medical animal model construction, can solve problems such as no animal models, and achieve the effects of high success rate, unique construction method, and simple technical operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] 120 male SD rats (2 months old) were randomly divided into four groups: normal group (normal), sham operation group (shamsurgery), nerve root exposed group (nerve root exposed) and nerve root compressed group (nerve root compressed), in
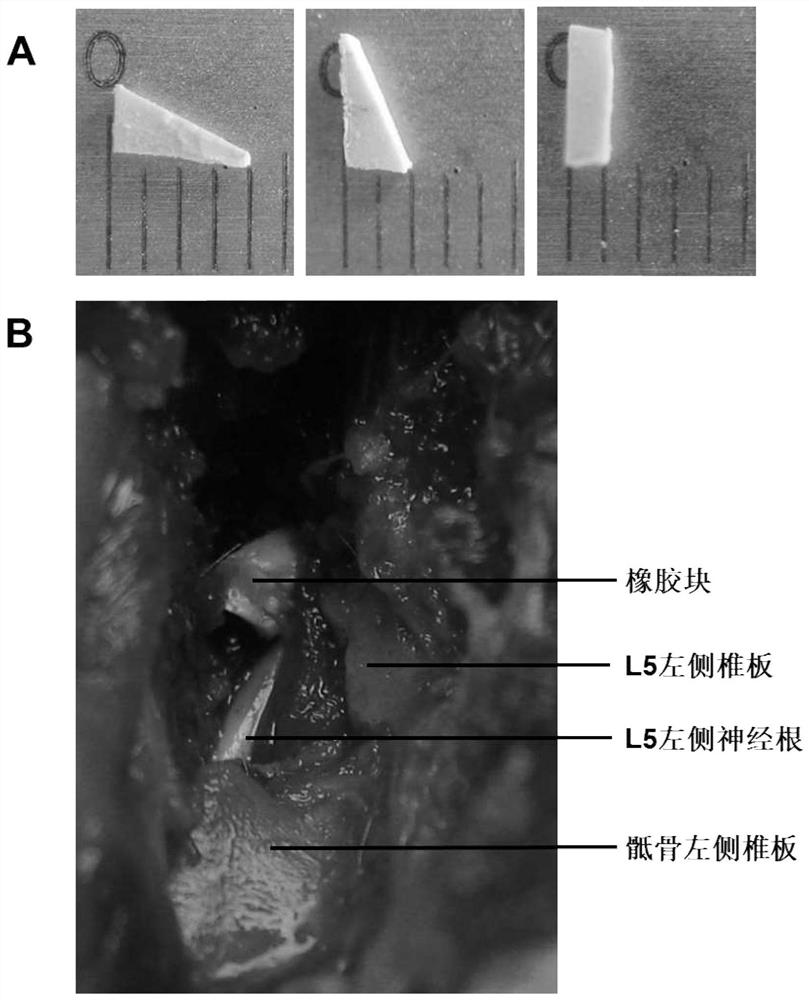
[0035] In the nerve root compression group, the rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of ketamine, and a 4 cm midline incision was made with a scalpel as a reference. The left paraspinal muscles were dissected and contracted to expose the left lamina of L5. Part of the left lamina and articular process of L5 was gradually dissected to expose the intact nerve root. will be like figure 1 A rubber block shown in A (a right-angled triangle, the lengths of the two right-angled sides are 4 μm and 2 μm respectively, and the thickness is 1 μm) is inserted into the spinal canal and pressed on the L5 nerve root (such as figure 1 shown in B). When the rubber block can no longer be inserted, the incision is stitched layer by laye...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The DRG obtained in Example 1 was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 8 hours, dehydrated with gradient sucrose, embedded in OCT gel, sectioned at 6 μm, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and then analyzed with the imaging analysis system with CMIAS-99B Histological analysis was performed by conventional light microscopy.
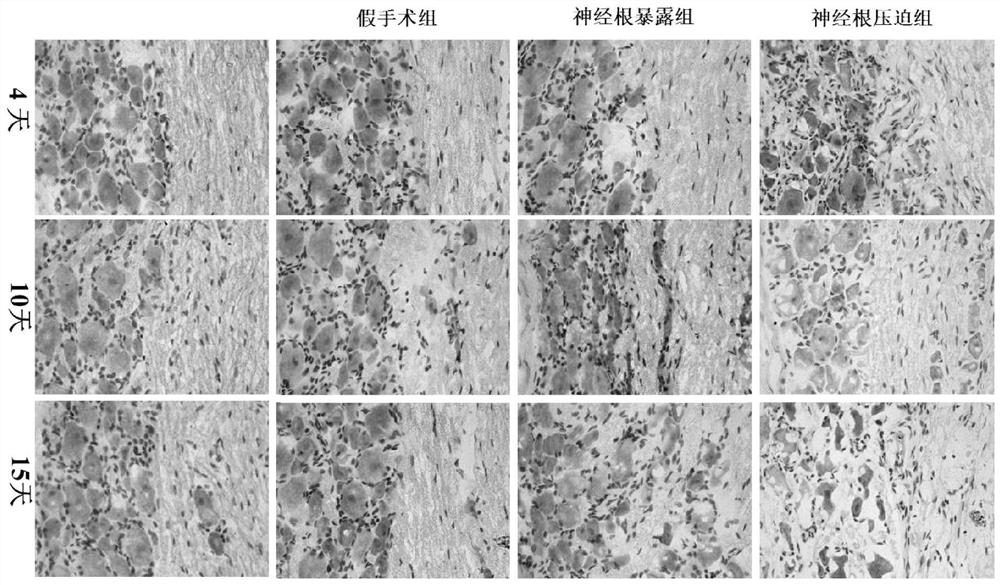
[0042] The experimental results of this example are as figure 2 (400 times) as shown:
[0043] At each time point, DRG neurons from the normal group, the sham group, the nerve root exposure group, and the 4-day nerve root compression group presented large, round shapes with intact structures. The cytoplasm of each group showed prominent Nissl bodies and the nuclei were slightly stained. Neurons are surrounded by satellite cells and arranged regularly;
[0044] 10 days after nerve root compression injury, DRG neurons of the surgically operated group exhibited irregular arrangements and vacuoles formed in their cytoplasm.
[0045] When the compres...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The DRG slices were stained with TUNEL reagent, and the TUNEL staining in this example used an in situ cell death detection kit (MBL, 8445, Japan). Specifically, the DRG slices were washed with PBS (twice, 5 min each), and incubated in 50 μL TdT buffer II at room temperature for 10 min. After removing TdT buffer II, the DRG slices were incubated in 50 μL TdT solution at 37°C for 60 min, and then soaked in TB solution and incubated at room temperature for 15 min. Nuclei were counterstained with 1 μg / mL DAPI (BioChemica). After labeling, the stained DRG sections were washed with PBS. Analysis was then performed using an immunofluorescence microscope (Olympus).
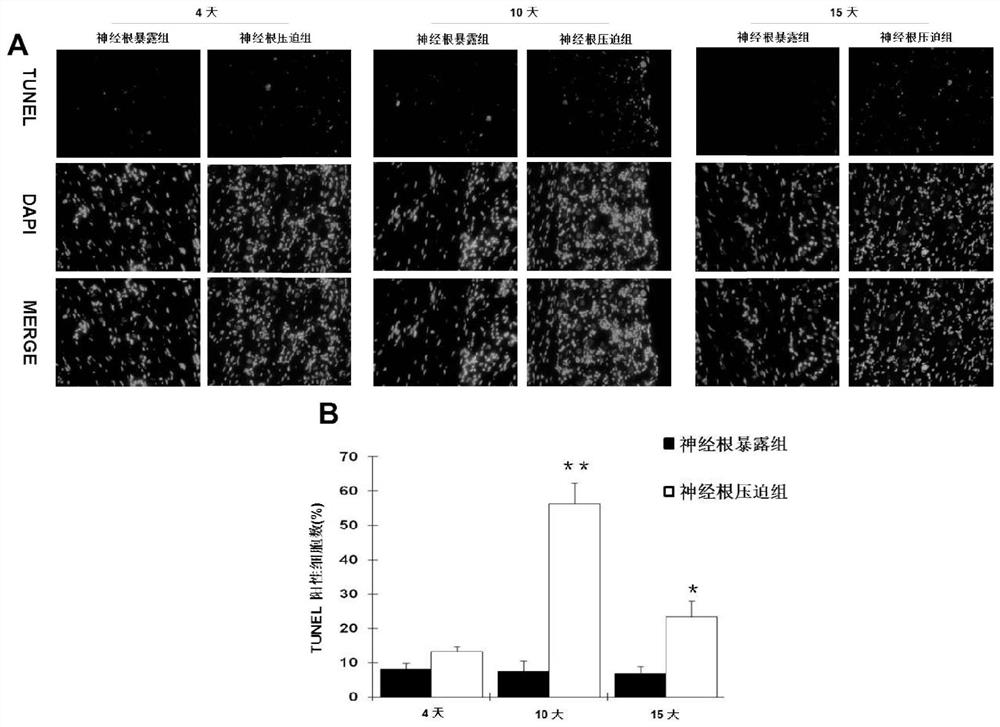
[0048] The experimental results of this example are as image 3 Shown:
[0049] In order to confirm the occurrence of apoptosis, this example uses TUNEL analysis to detect DNA strand breaks. image 3 In situ TUNEL staining of DRGs from control and operated animals is shown ( image 3 A, 400 times) and the pe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com