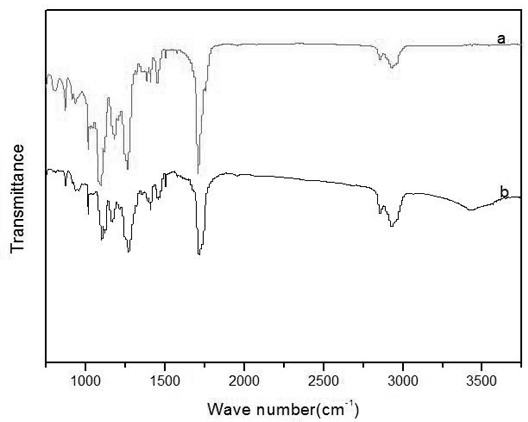
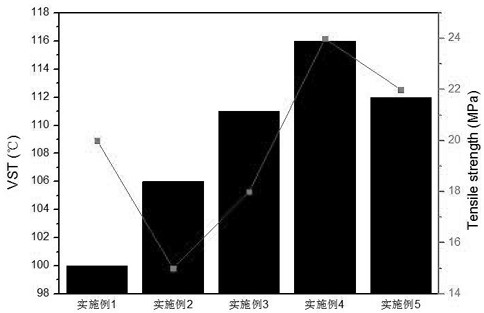
Preparation method of degradable heat-resistant copolyester
A technology of copolyester and heat resistance, which is applied in the field of preparation of degradable heat-resistant copolyester, can solve the problems of poor heat resistance and low mechanical strength, and achieve improved thermodynamic performance, high mechanical strength and heat resistance Improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (a) Put 1.5kgBDO, 976gTPA, and 791gSeA into the reaction kettle, mix evenly under the stirring of a low-speed motor, then add a titanium-based catalyst at a temperature of 210 °C, and carry out esterification at normal pressure, and the fraction collected after the reaction reaches the theoretical value or is greater than the theoretical value , can start to enter the polycondensation stage.
[0026] (b) The temperature rises to 240 ° C, and the vacuum pump is turned on to slowly reduce the vacuum degree of the system to about 700 Pa, and the polycondensation catalyst is added to observe the change of the motor torque value. The polycondensation is completed when the torque reaches a maximum value and remains constant. The pure material PBSeT was obtained. Nitrogen protection discharges the material, obtains the sample after water-cooling granulation and drying.
Embodiment 2
[0028] (a) Put 1.5kgBDO, 976gTPA, and 791gSeA into the reaction kettle, mix evenly under the stirring of a low-speed motor, then add a titanium-based catalyst at a temperature of 220°C, and carry out esterification at normal pressure, and the fraction collected after the reaction reaches the theoretical value or is greater than the theoretical value , can start to enter the polycondensation stage.
[0029] (b) The temperature rises to 240°C, and the vacuum pump is turned on to slowly reduce the vacuum degree of the system to about 700Pa, then a polycondensation catalyst is added, and the torque value of the motor is observed. The polycondensation is completed when the torque reaches a maximum value and remains constant. The vacuum of the system was stopped, and nitrogen gas was blown in to cool down. When the temperature drops to 180-200°C, add PLA to melt, and the mass ratio of PLA to PBSeT is 2:8. Then add the chain extender hexamethylene diisocyanate HDI dropwise, n(NCO):...
Embodiment 3
[0031] (a) Put 1.5kgBDO, 976gTPA, and 791gSeA into the reaction kettle, mix evenly under the stirring of a low-speed motor, then add a titanium-based catalyst at a temperature of 220°C, and carry out esterification at normal pressure, and the fraction collected after the reaction reaches the theoretical value or is greater than the theoretical value , can start to enter the polycondensation stage.
[0032] (b) The temperature rises to 250°C, and the vacuum pump is turned on to slowly reduce the vacuum degree of the system to about 700Pa. Add a polycondensation catalyst and observe the change of the motor torque value. The polycondensation is completed when the torque reaches a maximum value and remains constant. The vacuum of the system was stopped, and nitrogen gas was blown in to cool down. When the temperature drops to 180-200°C, add PLA to melt, the mass ratio of PLA to PBSeT is 2:8, and then start to drop the chain extender hexamethylene diisocyanate HDI, n(NCO):n(OH) is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com