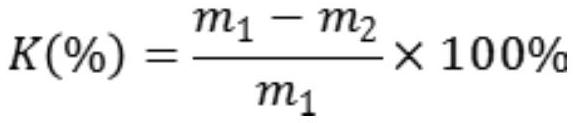Modified polyhydroxyethyl methacrylate gel and preparation method thereof, drug excipient and external gel
A technology of poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) and excipient, which is applied in the field of colloid gel and medicine, can solve the problems of application limitation, bleeding water, poor water retention performance, easy shrinkage of colloid, etc., and achieves an increase in the pore volume of the gel , good bioadhesion, enhance the effect of stimulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1 prepares pharmaceutical excipient
[0026] The preparation of the pharmaceutical excipient of the present invention is carried out according to the following steps: Weigh each component according to the weight percentage of each component, add carboxymethylated modified polyhydroxyethyl methacrylate and initiator in the container, stir, Fully swell the carboxymethylated poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate), then add λ-type carrageenan, osmotic pressure regulator, humectant, and preservative to mix, add water and stir well, and adjust the pH to 6-8 with a pH regulator , stirred for 30-45 minutes, that is.
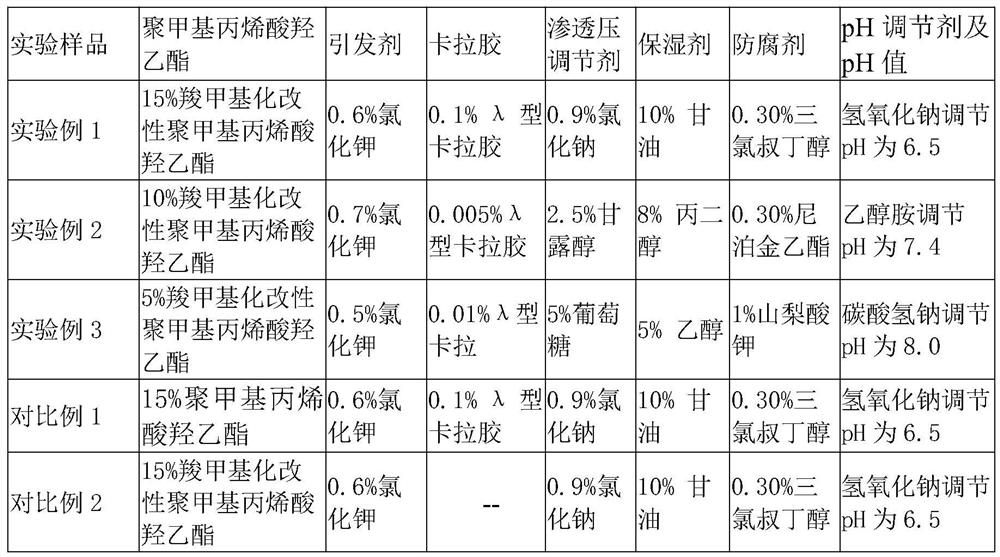
[0027] Prepare the pharmaceutical excipient gel samples of Experimental Examples 1, 2, and 3 according to this method, and prepare Comparative Examples 1 and 2 according to this method, and the specific components and proportioning of each sample are as shown in Table 1 (each component in the table The content is mass percent, and the balance is water). The ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 Determination of gel water separation rate
[0035] Accurately weigh 5 g of the pharmaceutical excipients just prepared in Experimental Examples 1-3 respectively, blot the water droplets on the surface of the gel with filter paper, and then accurately weigh again.
[0036] Calculation formula of water analysis rate:
[0037]
[0038] In the formula, K is the water separation rate of the gel;
[0039] m 1 is the initial gel mass;
[0040] m 2 is the gel mass after removal of surface moisture.
[0041] The results of the calculated water separation rate are shown in Table 2: the gel obtained in Experimental Example 1-3 does not have a water separation rate, indicating that the gel will not shrink in size due to dehydration, and the gel has better stability; , the water absorption rate of Comparative Example 1 was too high.
[0042] Table 2 Water analysis rate
[0043]
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3 texture property analysis
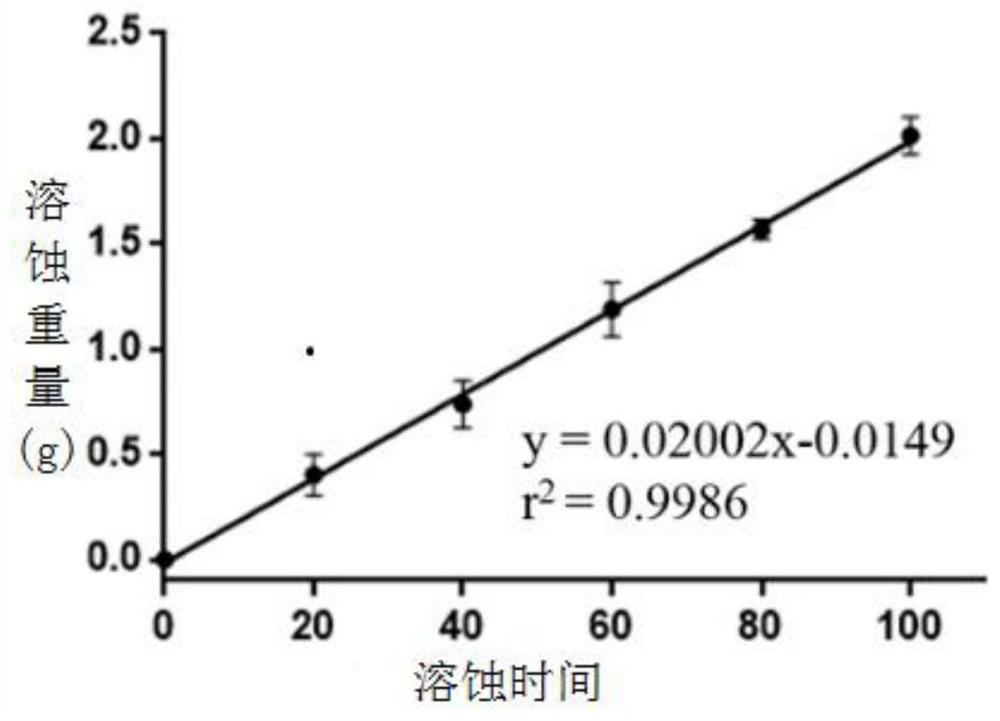
[0045] The gel strength and cohesiveness of pharmaceutical excipients were investigated by Brookfield CT3 texture analyzer. Select the cylindrical P / 0.5 probe, set the test to the push-down mode, lower the probe at a speed of 1mm / s, and the trigger force is 5g. When the probe touches the surface of the sample, the probe is pressed down to 10mm at 2mm / s, and then rises at a speed of 10mm / s. Record the stress-time curve and process the graph to obtain the maximum value of the positive peak of gel strength and the area of negative peak of adhesiveness.
[0046] The gel strength and adhesiveness test results of Experimental Examples 1-3 are shown in Table 3: the pharmaceutical excipient gel of the present invention has a softer texture and higher gel strength and adhesiveness. The strength and adhesion of the gel in Comparative Example 1 are relatively weak, which affects the quality of the gel and the use effect.
[0047] Table...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com