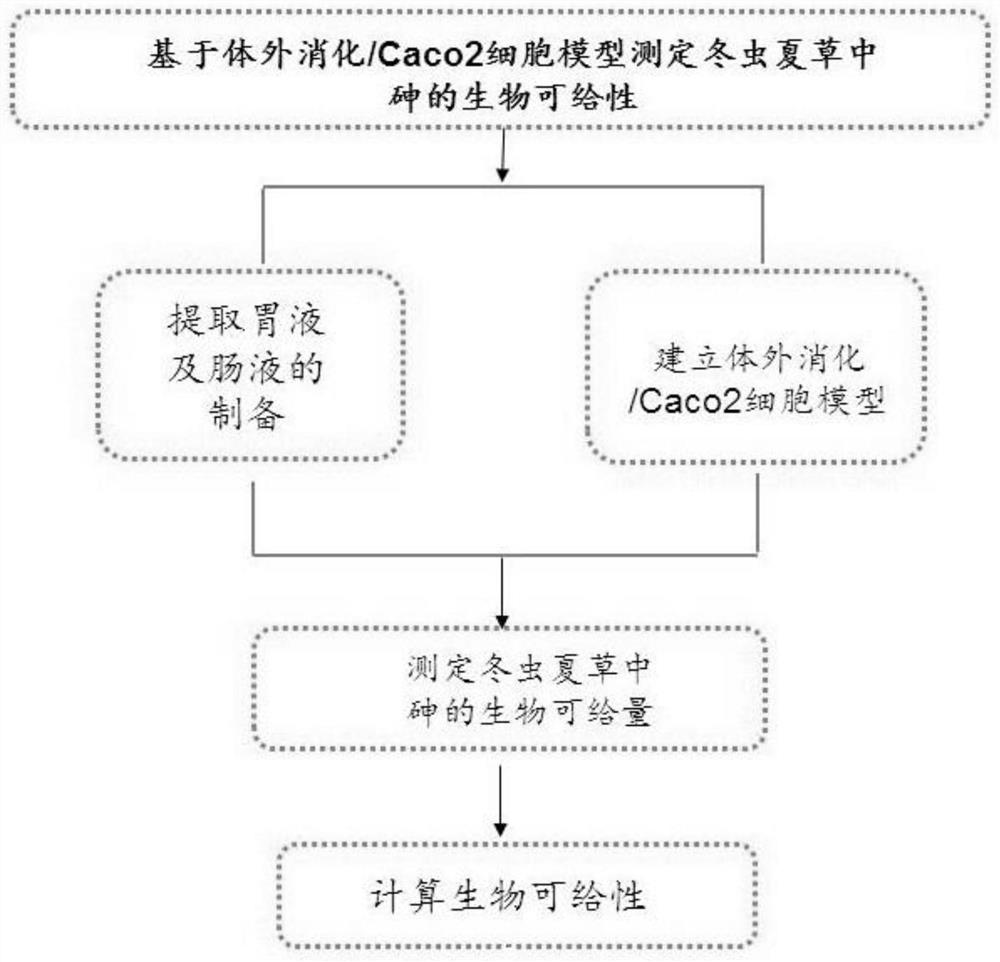
Method for determining bioavailability of arsenic in cordyceps sinensis based on in-vitro digestion/Caco2 cell model
A technology of cell model and Cordyceps sinensis, which is applied in the preparation of test samples, measuring devices, and material analysis through electromagnetic means, can solve the problems of different bioavailability detection methods, and achieve the effect of saving traditional Chinese medicine resources and promoting development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Cordyceps sinensis samples (purchased from the Tibet Lhasa Medicine Market) Crushing, 50 mesh sieve, precisely 0.5g Cordyceps sinensis powder, add 50 ml to simulate gastric fluid (from 1.25 g of gastric protease, 0.5 g sodium citrate, 0.5 g sodium maline, 420μL lactic acid It is formulated with 500 μl of acetic acid, and the dissolution is reached to 1 L, and the pH is adjusted to 1.5 by HCl). The argon gas is 1 to 2 minutes, and an anaerobic environment in the gastrointestinal tract is simulated. Evergings 1 h in a constant temperature water bath at 37 ° C (100R · min -1 ), Centrifugation 5 min (4000R · min -1 ), To obtain residue and supernatant layers. The precision amount was taken 25 ml, and the electric hot plate was concentrated to about 3 mL, and 5 ml of nitric acid was added, and the microwave digestometer was decomposed. After the elimination is cooled, the ultrapure water is set to 50 ml of volumetric flask to obtain "extraction gastric liquid" to be tested. The ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com