Model for simulating dermatophyte infection in vitro and establishment method and application thereof
A dermatophyte, in vitro simulation technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of dermatophyte reproduction, difficulty in triggering cell reactions, long and complicated construction process, etc., and achieve the effect of easy cellular immune response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Method of establishing an in vitro model simulating dermatophyte infection
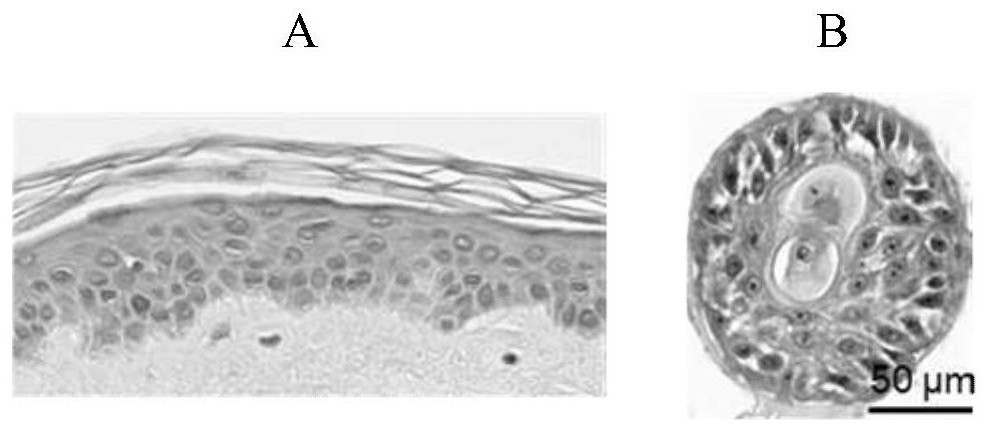
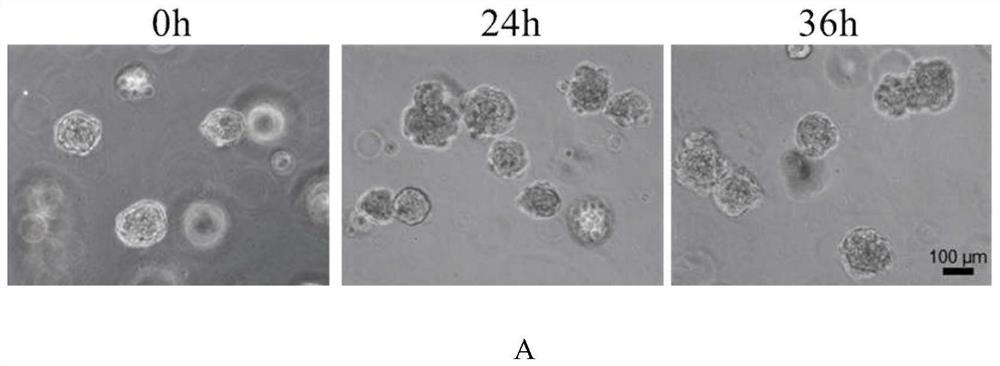
[0044] This embodiment establishes a kind of model that simulates dermatophyte infection in vitro, and the following description includes: the process of obtaining the cell spheres (also referred to as epidermis analogs herein) in the model, the process of obtaining dermatophyte conidia, and using the Infection of conidia with epidermal analogue cells to establish an in vitro model mimicking dermatophyte infection.
[0045] I. Acquisition of epidermis analogs
[0046] In this step, epidermal cells with differentiation function are cultured to obtain epidermal analogues. Epidermal stem / progenitor cells may be used from any commercial source or obtained using existing literature methods. The operation of culturing epidermal stem / progenitor cells isolated from human discarded foreskin tissue (the foreskin tissue comes from the Urology Department of the Fifth Medical Center of the Peop...
Embodiment 2
[0141] Example 2: Application of in vitro simulation of Trichophyton rubrum infection epidermis analog model in pathogenic mechanism research
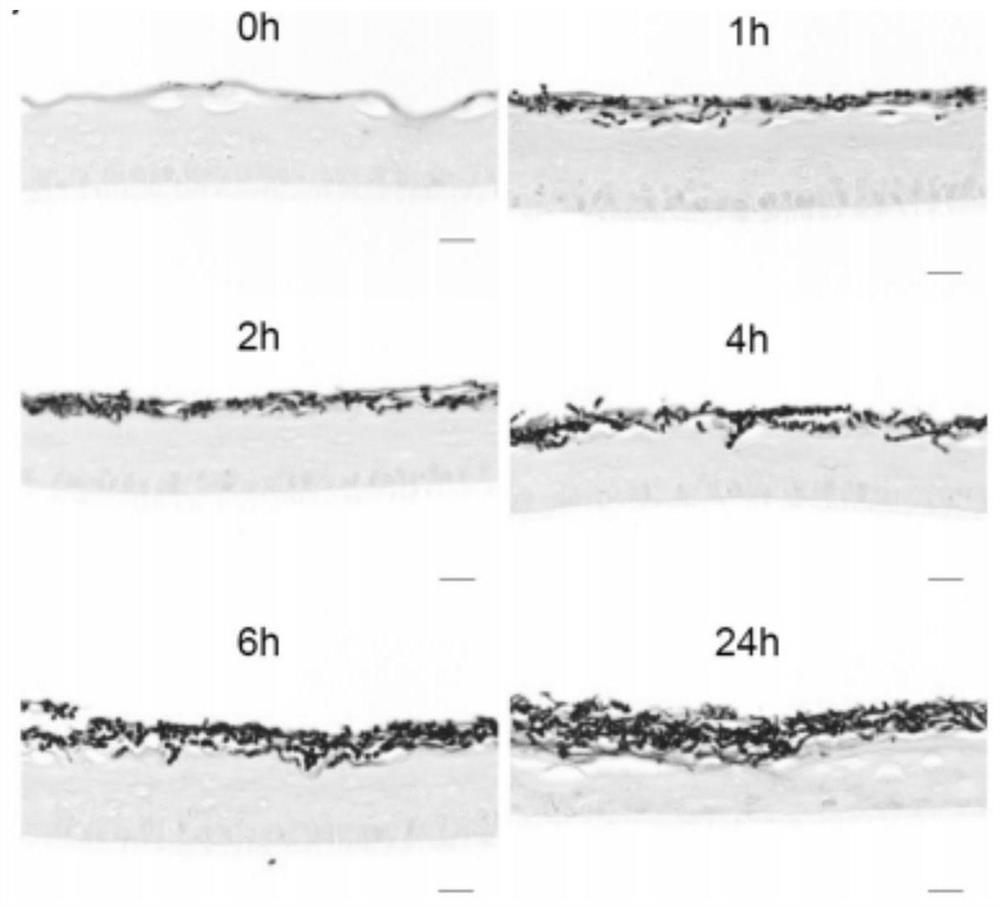
[0142] This embodiment utilizes the in vitro simulated Trichophyton rubrum infection model established in the above-mentioned Example 1 (use the third medium to co-culture the Trichophyton rubrum conidia embedded in solidified matrigel and the epidermis analog for 24 hours to establish ), as the infection group; the epidermis analog embedded in the solidified Matrigel was simultaneously cultivated with the third medium for 24 hours, as the control group; the epidermis analog samples in the infection group and the control group were detected, and the red hair was analyzed. Pathogenesis of ringworm.
[0143] (1) Genomic sequencing of epidermal analogues in infected and control groups
[0144] High-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) was performed on the epidermis analogs in the infection group and the control group, respectively, to stu...
Embodiment 3
[0183] Embodiment 3: the application of the model of simulating Trichophyton rubrum infection in vitro in the screening of anti-phytophyte drugs
[0184] This embodiment utilizes the in vitro simulated Trichophyton rubrum infection model established in the above-mentioned Example 1 (use the third medium to co-culture the Trichophyton rubrum conidia embedded in solidified matrigel and the epidermis analog for 24 hours to establish ) were tested for susceptibility to antiphytophyte drugs.
[0185] 1) The experimental group added amphotericin B (AmB) (a common anti-ringworm drug) to the model; the control group did not add amphotericin B to the model;
[0186] 2) After the experimental group and the control group were further cultured for 12 hours, the epidermal analogues of the experimental group and the control group were stained with glycogen granules (PAS) and observed under a transmission electron microscope according to operations 2.2 and 2.3 of Part III in the above-mentio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com