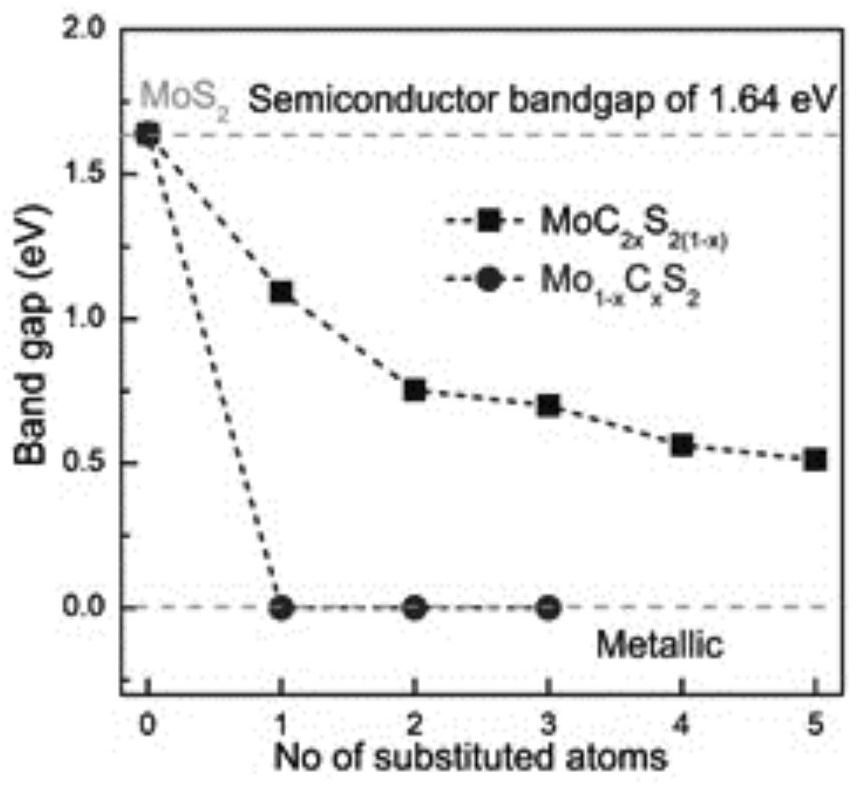
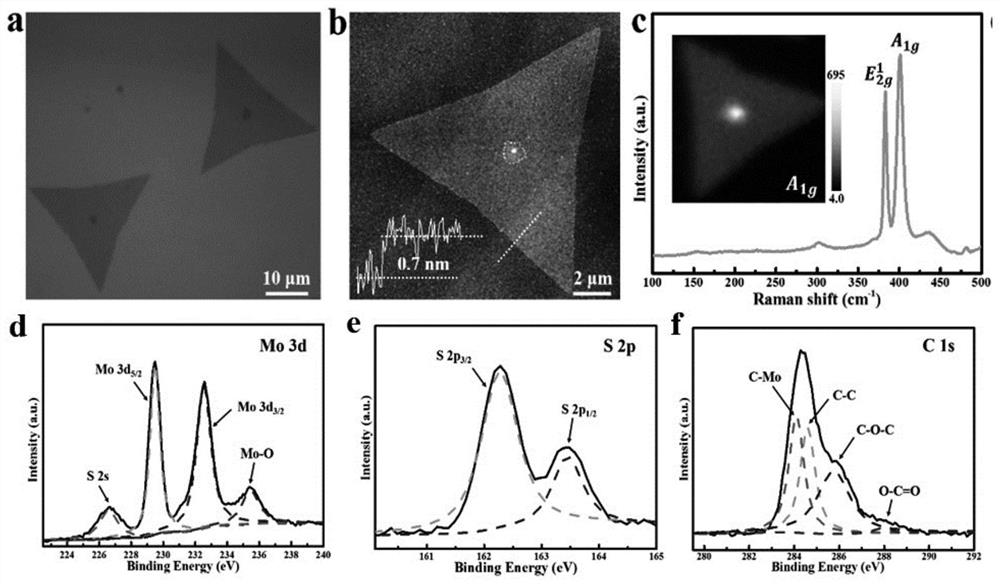
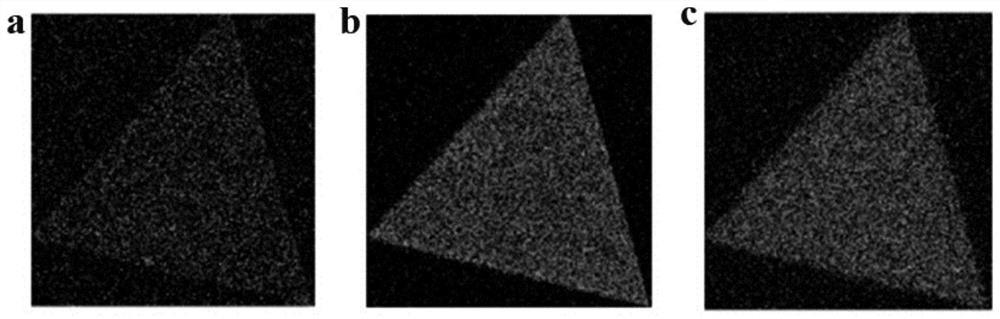
A kind of preparation method of carbon-doped molybdenum disulfide nanometer material
A technology of molybdenum disulfide and nanomaterials, applied in the field of two-dimensional nanomaterials, can solve the problems of complex and difficult preparation parameters, and achieve the effect of simple preparation technology and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] In this embodiment, quartz tube chemical vapor deposition equipment is used. MoO with 0.5% carbon 3 powder (approximately 10 mg) laid on Si / SiO 2 On the target substrate, this substrate is loaded into quartz tube furnace together with elemental sulfur, and this substrate and elemental sulfur are separated certain distances such as 12cm. Vacuum the quartz tube furnace, then heat the substrate area to 750°C within 60 minutes, and keep the reaction at a constant temperature for 10 minutes; while heating the substrate area, heat the S source to 130°C. After the reaction, it was naturally cooled to room temperature. In this way, carbon-doped 2D MoS 2 film. The high-temperature furnace is kept at low pressure (for example, the pressure is about 0.1 Pa) throughout the whole process, and an inert gas such as argon is introduced as a carrier gas during the whole process, and the flow rate is about 100 sccm.
[0028] For the carbon-doped MoS prepared in Example 1 2 Thin fil...
Embodiment 2
[0031] In this example, MoO containing 0.1% carbon 3 The powder (about 15 mg) is laid on the mica target substrate, which is charged into the high temperature furnace together with the elemental sulfur, and the substrate is separated from the elemental sulfur by a certain distance such as 10 cm. Vacuum the high-temperature furnace, then heat the substrate area, first raise the temperature to 500°C at a rate of 20°C per minute, and then keep it for 5 minutes; then raise the temperature to 850°C within 10 minutes, and keep the reaction at a constant temperature for 20 minutes; while heating the substrate region, the S source is heated to 120°C. After the reaction, it was naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain carbon-doped 2D MoS 2 film. The high-temperature furnace is maintained at normal pressure throughout the process, and an inert gas such as argon is introduced as a carrier gas during the entire process, and the flow rate is about 50 sccm.
[0032] For the carbon-...
Embodiment 3
[0035] In this example, MoO containing 2.0% carbon 3 The powder (about 20 mg) is laid on the sapphire target substrate, and this substrate is loaded into the high temperature furnace together with the elemental sulfur, and the substrate is separated from the elemental sulfur by a certain distance, such as 18cm. Vacuum the high-temperature furnace, then heat the substrate area, first raise the temperature to 400°C at a rate of 10°C per minute, and then keep it for 10 minutes; then raise the temperature to 650°C within 15 minutes, and maintain a constant temperature for 30 minutes; while heating the substrate region, the S source is heated to 150°C. After the reaction, it was naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain carbon-doped 2D MoS 2 film. The high-temperature furnace is kept at a low pressure of 2000 Pa during the whole process, and an inert gas such as nitrogen is introduced as a carrier gas during the whole process, and the flow rate is about 200 sccm.
[0036] F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com