A preparation method of porous fluoroapatite ceramics for absorbing radionuclides
A technology for radionuclide and fluorapatite, which is applied in the field of preparing porous fluorapatite ceramics for adsorbing radionuclides, can solve the problem that the adsorption capacity of salt content is greatly affected, the adsorption capacity of radionuclides is reduced, and there is no porous structure and other issues, to achieve the effect of protecting human health, promoting sustainable development, and strong resistance to salt corrosion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
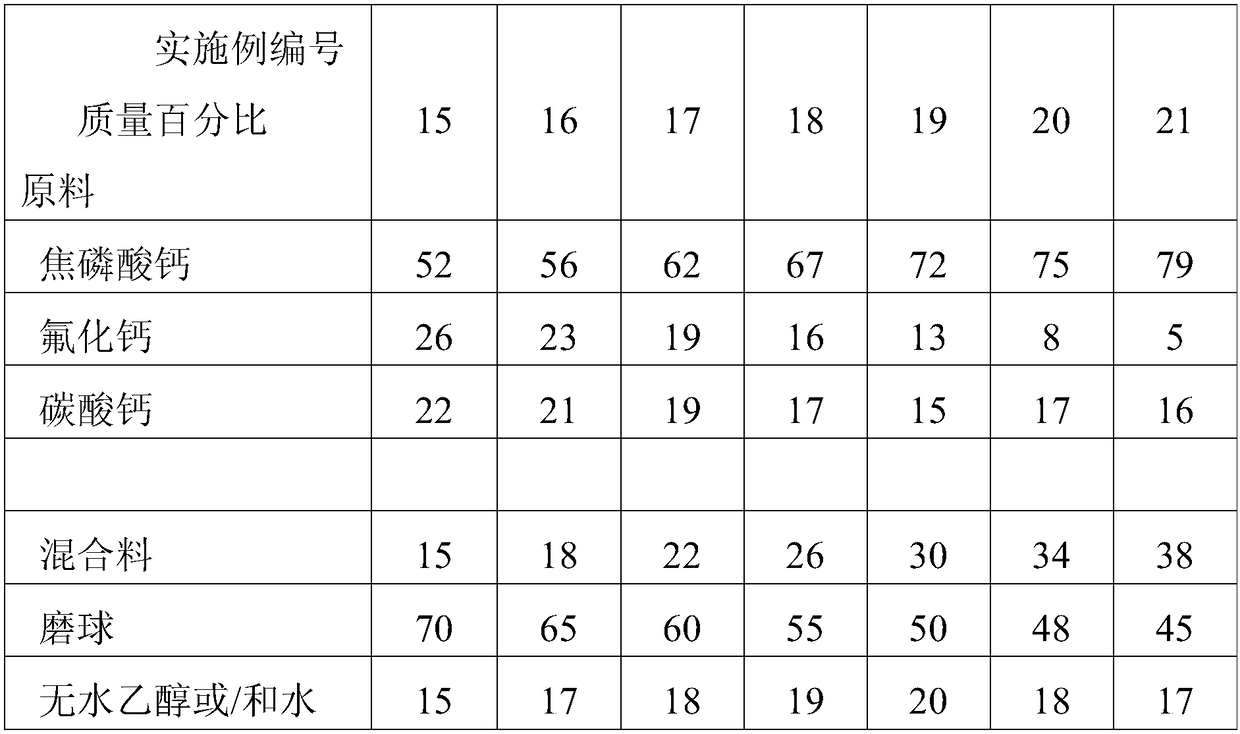
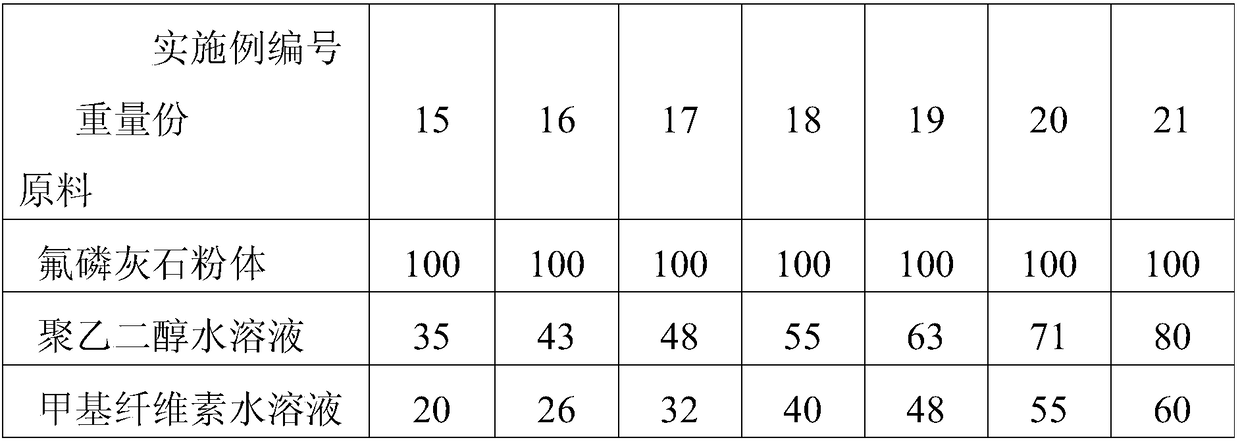
[0032] A method for preparing porous fluoroapatite ceramics for adsorbing radionuclides is to take the raw materials of each component according to the components and mass percentages of calcium pyrophosphate 50%, calcium fluoride 26%, and calcium carbonate 24%, and mix to obtain a mixture Material; After weighing the mass percentage of 12% of the mixture, 78% of the grinding balls, and 10% of anhydrous ethanol, the ball milled for 1 hour, the ball-milled material was dried at 50°C for 2 hours; the dried powder was dried at 2MPa Press for 1 minute; calcinate the pressed block in a box-type resistance furnace at 750°C for 2 hours; grind the calcined block for 20 minutes, and then use 40 mesh and 200 mesh sieve for sieving, and 40 mesh sieve The fluorapatite powder is obtained by adding 30 parts by weight of 1% polyethylene glycol aqueous solution and 20 parts by weight to 100 parts by weight of fluorapatite powder. Parts by weight of a methylcellulose aqueous solution with a con...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A preparation method of porous fluoroapatite ceramics for adsorbing radionuclides is: taking the components and mass percentages of calcium pyrophosphate 65%, calcium fluoride 17%, and calcium carbonate 18% and mixing them to obtain a mixture Material; weigh the mixture 26%, the grinding ball 52%, and the deionized water 22% mass percentage, then ball mill for 3 hours, the ball milled material is dried at 75 ℃ for 5 hours; the dried powder is 11MPa Press for 15 minutes; calcinate the pressed block in a box-type resistance furnace at 1175°C for 7 hours; grind the calcined block for 30 minutes, and then use 100 mesh and 270 mesh sieve for sieving, and 100 mesh sieve The raw material and the 270-mesh sieve are the prepared fluorapatite powder; in 100 parts by weight of fluorapatite powder, add 55 parts by weight of 10% polyethylene glycol aqueous solution and 40 parts by weight. Weight parts of methylcellulose aqueous solution with a concentration of 8% by mass, stirred for...
Embodiment 3
[0036] A method for preparing porous fluoroapatite ceramics capable of adsorbing radionuclides is to take the components and mass percentages of calcium pyrophosphate 80%, calcium fluoride 4%, and calcium carbonate 16%, and mix them. Material; After weighing the mixture 35%, grinding ball 35%, 30% absolute ethanol, ball milling for 6 hours, the ball milled material is dried at 80 ℃ for 8 hours; the dried powder is 20MPa Pressing for 30 minutes; calcining the pressed block in a box-type resistance furnace at 1600°C for 12 hours; grinding the calcined block for 40 minutes, and then sieving with 170 mesh and 400 mesh sieve successively, and 170 mesh under the sieve The raw material and the 400 mesh sieve are the prepared fluoroapatite powder; in 100 parts by weight of fluoroapatite powder, 80 parts by weight of 20% polyethylene glycol aqueous solution and 60% by weight are added. Part by weight of methyl cellulose aqueous solution with a concentration of 15% by weight was stirred ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com