Method for randomly inserting DNA fragment into bacillus subtilis chromosome and application thereof
A Bacillus subtilis, random insertion technology, applied in the high biological field, can solve the problems of false positives, inactivation of temperature-sensitive proteins, multi-copy insertion, etc., and achieve the effect of optimizing the expression level
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Construction process of embodiment 1 plasmid pTMCZ and pUSIGH
[0024] Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis were cultured at 37°C with LB medium (peptone 1%, yeast powder 0.5%, sodium chloride 1%, pH 7.0). Transposon left repeat sequence ITR1 (Breton et al..2006.Appl EnvironMicrobiol.72:327-333.Doi:10.1128 / AEM.72.1.327-33.) and transcription terminator B0015 (http: / / parts .igem.org / Part:BBa_B0015) was entrusted to a biological company to synthesize, and then amplified by primers P1 / P2 to obtain the fragment ITR1-Transcription terminator. Using plasmid pNW33N (GenBank Number AY237122) as a template, primers P3 / P4 were used to amplify the chloramphenicol resistance gene. Using the plasmid pMarA (Breton et al..2006.Appl EnvironMicrobiol.72:327-333.Doi:10.1128 / AEM.72.1.327-33.) as a template, ITR2 was amplified using primers P5 / P6. Finally, using primers P1 / P6, ITR1-Transcription terminator, chloramphenicol resistance gene and ITR2 three fragments were connected by over...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2 Random insertion of transposon into Bacillus subtilis chromosome
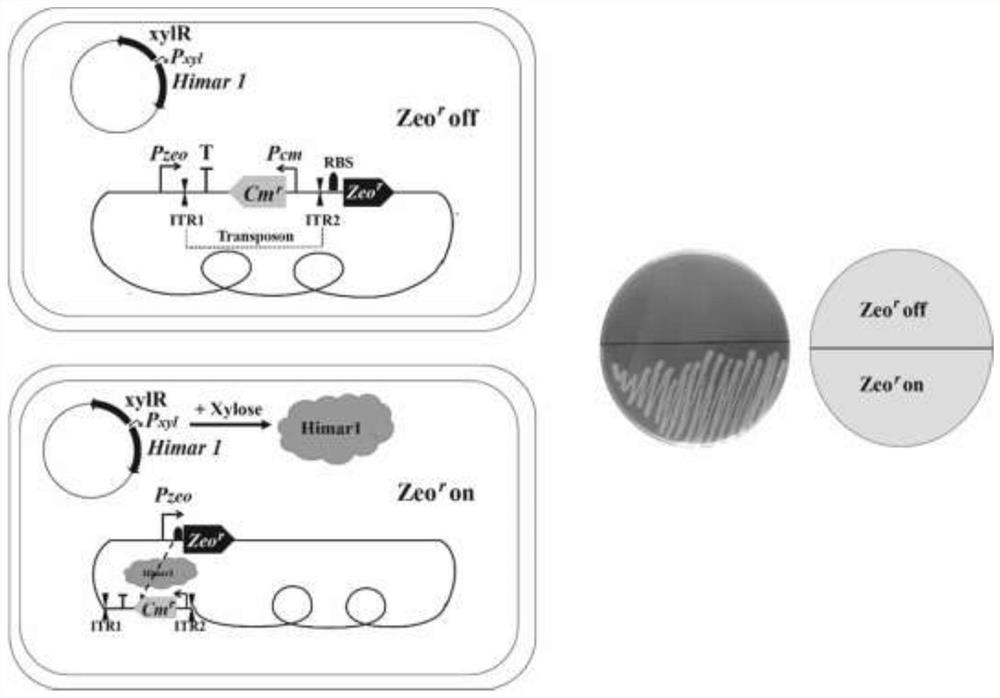
[0027] Such as figure 1 Plasmids pTMCZ and pUSIGH were co-transformed into B. subtilis 168 as indicated. The transformation of Bacillus subtilis was carried out with reference to the method established by Anagnostopoulos et al. (1961. J Bacteriol. 81:741-746.). After plasmid pTMCZ enters strain 168, fragment P zeo -ITR1-Transcription terminator-Cm-ITR2-Zeo will be inserted into the amyE site of the host chromosome through homologous recombination, and the plasmid pUSIGH can replicate independently after entering strain 168. Strain PDZC (pUSIGH) was obtained after resistance screening (10ppm chloramphenicol and 100ppm spectinomycin) and PCR verification. Culture strain PDZC(pUSIGH) to OD 600 After =1.0, add 1% xylose to induce the expression of the transposase gene Himar1 on the plasmid pUSIGH (induce 3 hours), and under the effect of transposase, the transposon ITR1-Transcription terminator...
Embodiment 3
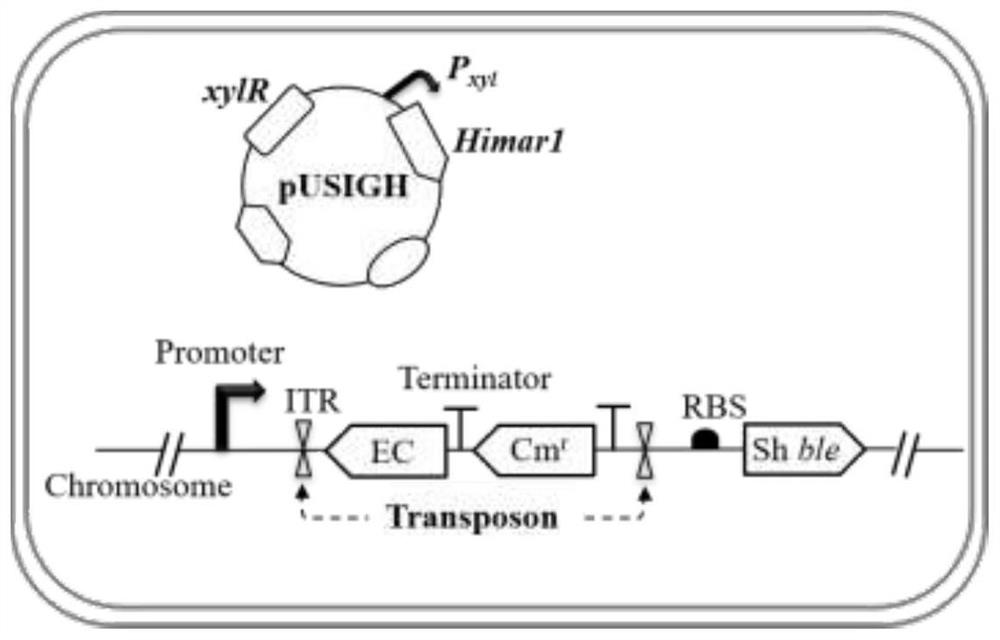
[0028] Example 3 random insertion of target DNA into Bacillus subtilis chromosome
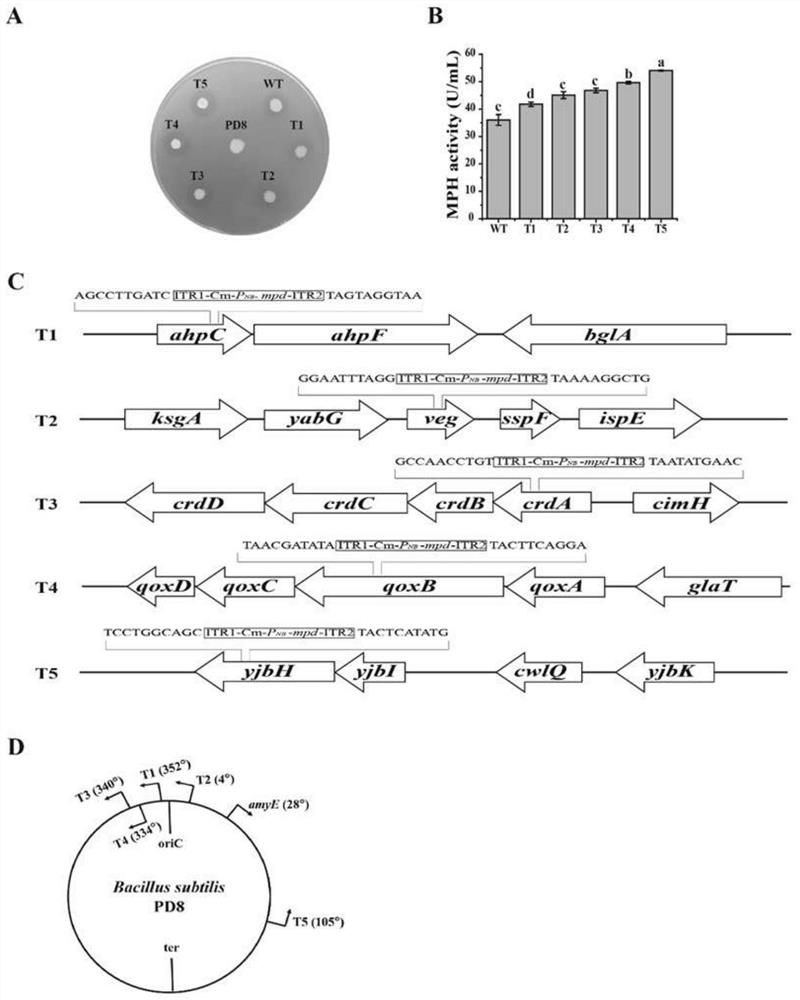
[0029] In order to use the transposon ITR1-Transcription terminator-Cm-ITR2 as a carrier, the target DNA is randomly inserted into the Bacillus subtilis chromosome, and the target DNA (such as figure 2 Middle EC) was inserted into the transposon by homologous recombination, and then xylose was used to induce transposon jumping (same as Example 2). In order to verify the feasibility, the expression cassette of methyl parathion hydrolase (MPH) P NBP3510 -mpd(Zhou et al..2019.Microb Cell Fact.18(1):111.Doi:10.1186 / s12934-019-1159-0) was inserted into the transposon ITR1-Transcription terminator-Cm-ITR2, and a strain was generated PDZCM (pUSIGH). The specific steps are: using the total DNA of the strain PDZC (pUSIGH) as a template, using primer pairs P20 / P21 and P22 / P23 to amplify LF-ITR1-Transcription terminator and ITR2-RF respectively; using the strain PD8NM (Zhou et al..2019.Microb Cell Fac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com