Distributed non-smooth saturation consistency control method of discontinuous multi-agent system
A technology of a multi-agent system and a control method, applied in the information field, can solve the problems of communication bandwidth and transmission congestion, discontinuous dynamic behavior of multi-agent system and time-varying time delay, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing control costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] The finite-time global consistency and distributed non-smooth saturation control method of the discontinuous multi-agent system of the present invention, the steps are as follows:
[0072] Step 1: Establish a multi-agent system with discontinuous dynamics and time-varying time-delay and determine its consistency goal.
[0073]
[0074] in Represents the state variable of the i-th agent. The inline matrices D and B are positive definite and negative definite respectively, f(·):R n →R n is a nonlinear discontinuous vector-valued function. The time-varying delay τ(t) is a bounded positive function, 0≤τ(t)≤τ,
[0075] Due to limited communication bandwidth and transmission congestion, the multi-agent system considered in the present invention has discontinuous dynamic behavior and time-varying time delay, so traditional methods for dealing with nonlinear functions, such as Lipschitz conditions (Lipschitz continuous conditions) , sector conditions, QUAD conditions...
Embodiment 2
[0154] This embodiment describes the specific implementation methods of the above two types of controllers in conjunction with a specific multi-agent system, including the following steps:
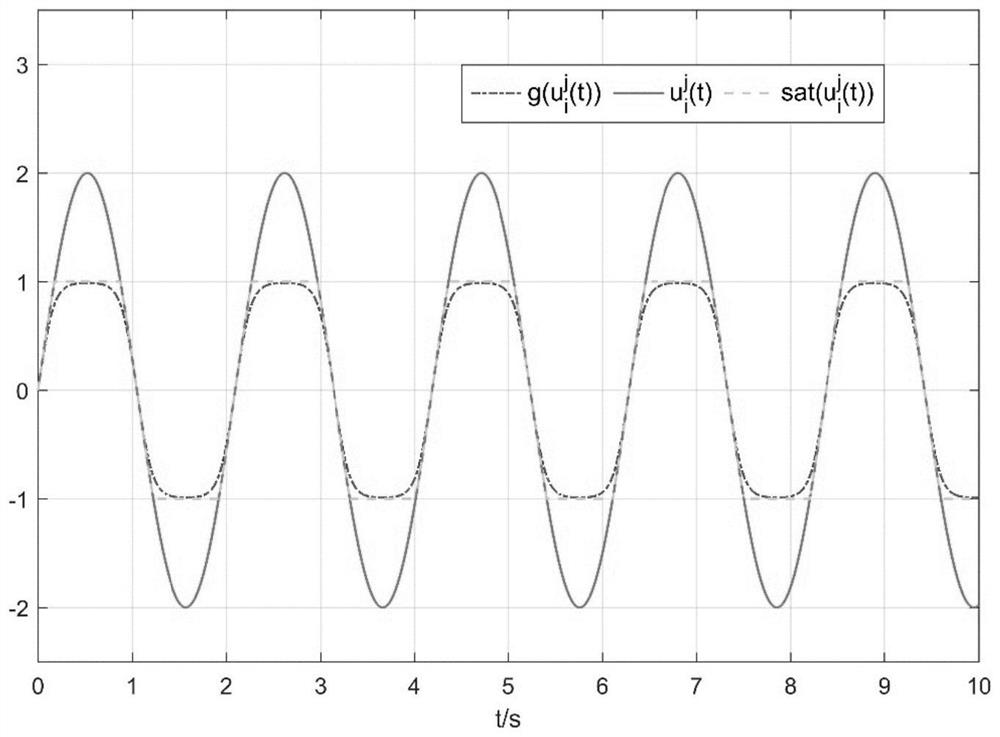
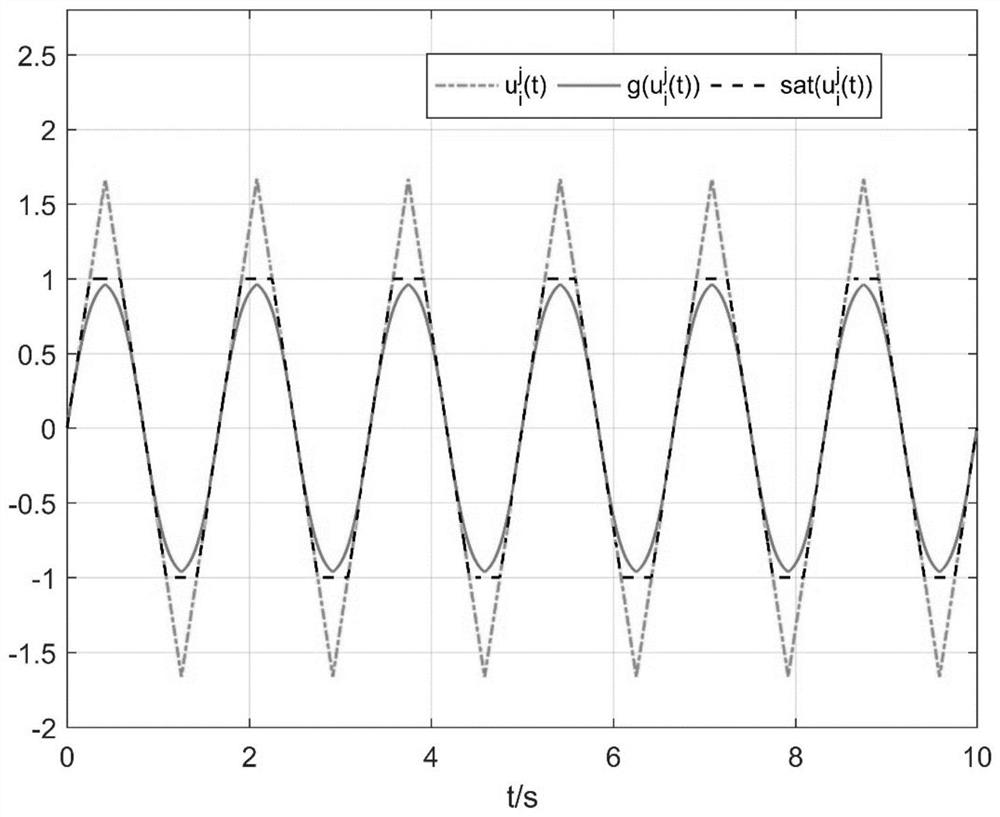
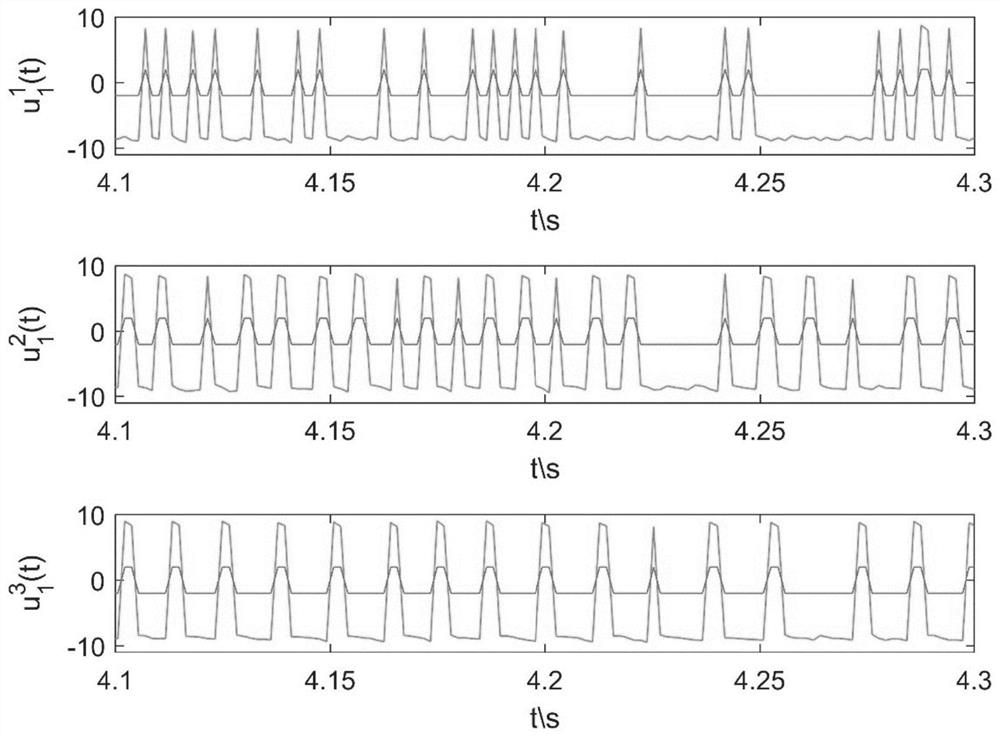
[0155] Step 1: Select system parameters. In order to be close to the actual working conditions, 4 agents are selected to form a multi-agent system, and each agent has 3 state components, ie N=4, n=3. According to the dynamic function f(·)∈B 2 , without loss of generality, choose f(z)=0.3z+2sign(z), thus q=0.3, w=4; make B=diag[-1,-1.2,-1.4], D=[ 0.1,0.2,0.3], time-varying delay τ(t)=0.03+sin 0.2t. The state evolution graph of an uncontrolled discontinuous multi-agent system is shown in Figure 3(a)-Figure 3(c) shown.
[0156] Step 2: Select Control Configuration Matrix Parameters. To implement distributed control, the following control coupling matrix is chosen:
[0157]
[0158] This means that the communication strength between each agent is different, divided into four levels...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com