Solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of solar cells and manufacturing methods, applied in the field of solar cells, capable of solving problems such as inability to realize industrial mass production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
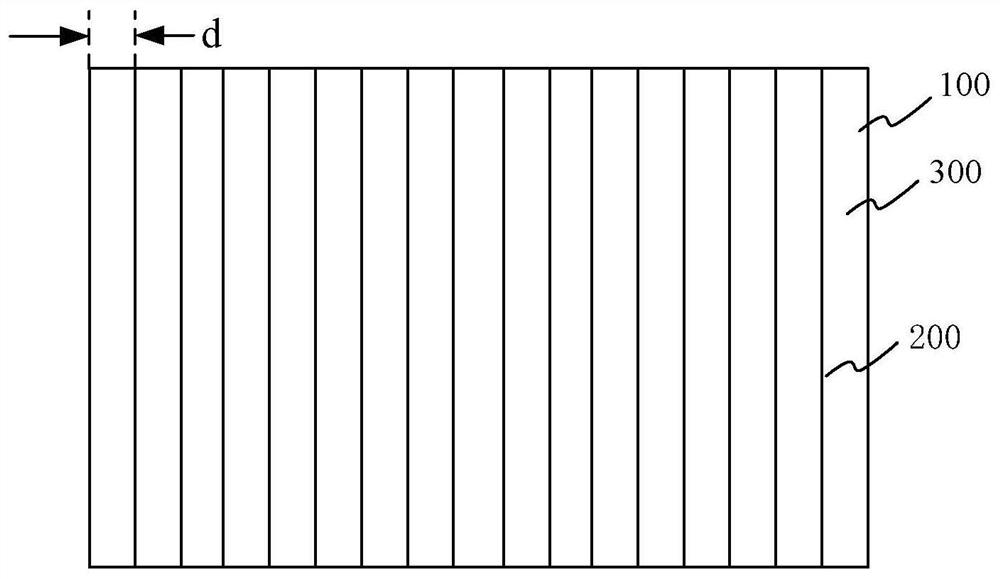
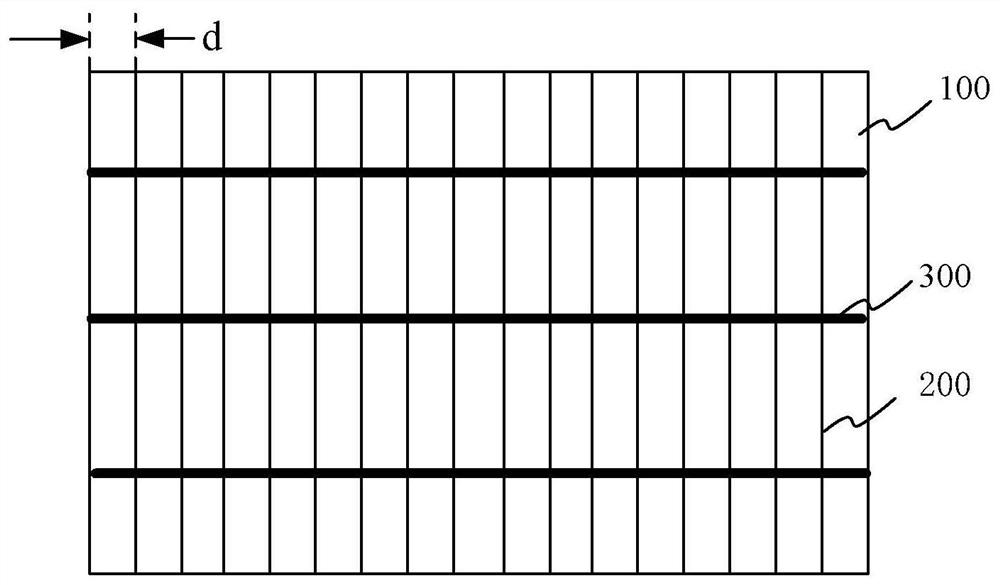
[0053] Figure 1A A schematic top view of a solar cell without a busbar provided by an embodiment of the present invention; Figure 1B A schematic top view of a solar cell provided by an embodiment of the present invention when there is a busbar. Such as Figure 1A and Figure 1B As shown, the solar cell provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes: a battery sheet 100 and a plurality of fine grids 200 formed on the surface of the battery sheet 100 . The number of these fine grids 200 can be set according to the size of the surface area of the battery sheet 100 . For example, for a battery sheet 100 with an opposite side length of 150 mm to 200 mm, the number of thin grids 200 may be 70 to 200, and the distance d between two adjacent thin grids 200 is 1 mm to 3 mm.
[0054] In one example, such as Figure 1A As shown, the surface of the plurality of fine grids 200 formed on the above-mentioned battery sheet 100 may not have a busbar. At this time, the solar...
Embodiment 2
[0089] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for manufacturing a solar cell, which can be realized by using a laser transfer printing system. The laser transfer printing system has a laser, a first transfer substrate and a second transfer substrate. The laser beam emitted by the laser can be various lasers such as infrared laser, green laser or ultraviolet laser. Specifically, carbon dioxide laser, excimer laser, titanium sapphire laser, semiconductor laser, dye laser, copper vapor laser and Nd:YAG solid can be selected. Lasers, etc., but not limited to. The first transfer substrate and the second transfer substrate may be non-bendable rigid transfer substrates, or may be bendable flexible substrates. The material of the transfer substrate can be selected from transparent materials, including but not limited to glass, quartz, and organic polymer materials. The organic polymer material can be a transparent polyimide film material, or polyvinyl chloride (PVC...
Embodiment 3
[0120] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for manufacturing a solar cell, comprising the following steps:
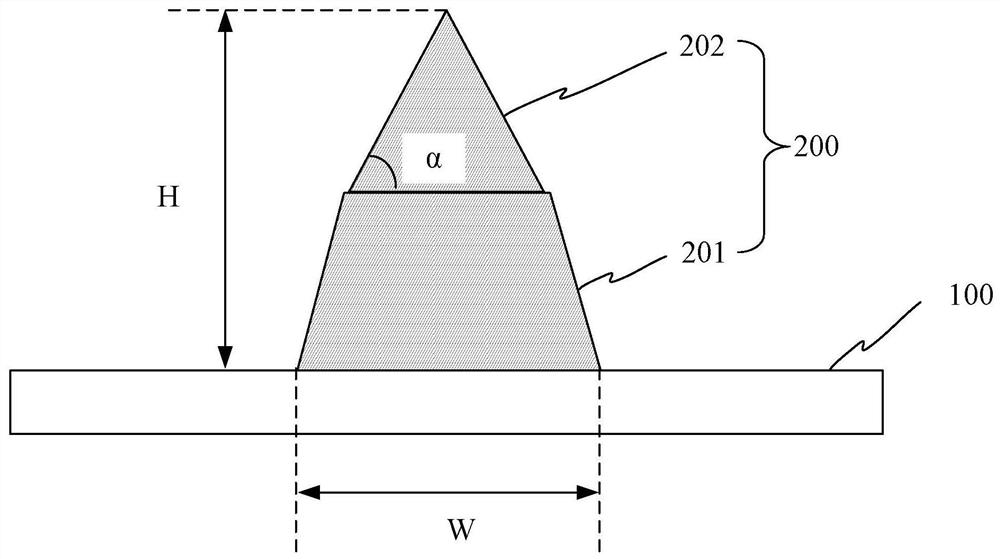
[0121] In the first step, the electrode material is laser-transferred on the surface of the battery sheet by using the preset grooves of the first transfer substrate to form 110 terrace-shaped transfer parts. The cross-section of the table-shaped transfer part is trapezoidal.
[0122] The above-mentioned first transfer substrate is a transparent polyimide substrate. The preset groove shape of the first transfer substrate is a trapezoidal groove, and the depth of the trapezoidal groove gradually decreases along the direction of increasing groove depth. The bottom width of the trapezoidal groove is 20 μm, the opening width is 28 μm, and the depth is 14 μm. The inner wall of the groove is coated with conductive glue. The electrode material fills the grooves by scraping. The conductive material contained in the electrode material is silver paste, an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com