Method for producing roadbed base material from low-calorific-value solid waste
A solid waste and basic material technology, applied in the field of low-calorific value solid waste to produce roadbed basic materials, can solve environmental problems, achieve simple process, reduce fuel consumption, and realize the effect of resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
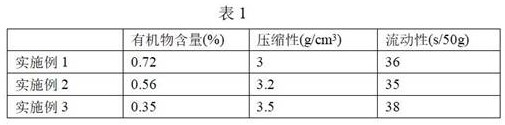
Embodiment 1
[0029] The raw material used is oil shale semi-coke, including the following components in mass percentage: moisture 10%, organic matter 25%, Al 2 o 3 14%, SiO 2 36%, Fe 2 o 3 6%, CaO 2%, MgO 1%, other 9%.
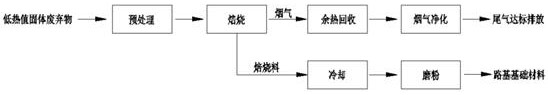
[0030] A method for producing roadbed basic materials from low calorific value solid waste, comprising the following steps:
[0031] A. Raw material pretreatment: A certain amount of oil shale semi-coke is air-dried after natural drying. After air-drying, the water content of the material is 5.8 wt.%, and then crushed and screened. The material discharge particle size is 1-5mm. To the powder silo for temporary storage;
[0032] B. Roasting: Add the material obtained after the treatment in step A to a roasting device, and roast it at a temperature of 400°C for 0.5h, and obtain a roasted material after roasting, and generate flue gas at about 350°C;
[0033] C. Cooling: the roasted material obtained in step B is cooled by water cooling, and a material with a temperat...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The raw material used is coal gangue, including the following mass percentage components: moisture 8%, organic matter 20%, Al 2 o 3 8%, SiO 2 41%, Fe 2 o 3 3%, CaO 10%, other 10%.
[0038] A method for producing roadbed basic materials from low calorific value solid waste, comprising the following steps:
[0039] A. Raw material pretreatment: Air-dry a certain amount of coal gangue after natural drying. After air-drying, the water content of the material is 5.6wt.%. Then, it is crushed and screened. The particle size of the material is 1-5mm. Warehouse temporary storage;
[0040] B. Roasting: add the material obtained after the treatment in step A to a roasting device, and roast it at a temperature of 500°C for 1.5h, and obtain a roasted material after roasting, and generate flue gas at about 400°C;
[0041] C. Cooling: the roasted material obtained in step B is cooled by water cooling, and a material with a temperature <60°C is obtained after cooling;
[0042]...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The raw material used is coal slag, including the following mass percentage components: moisture 7%, organic matter 10%, Al 2 o 3 30%, SiO 2 40%, Fe 2 o 3 6%, CaO 4%, other 3%.
[0046] A. Raw material pretreatment: Air-dry a certain amount of coal slag after natural drying. After air-drying, the water content of the material is 5wt.%. live;
[0047] B. Roasting: add the material obtained after the treatment in step A to a roasting device, and roast it at a temperature of 600°C for 3 hours, obtain a roasted material after roasting, and generate flue gas at about 500°C;
[0048] C. Cooling: the roasted material obtained in step B is cooled by water cooling, and a material with a temperature <60°C is obtained after cooling;
[0049] D, milling: add the material cooled in step C into the milling device and grind for 1 hour in a dry milling mode to obtain a roadbed base material with a particle size of 0.074-0.4mm;
[0050] E. After the waste heat is recovered by t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com