Semiconductor device and crack detection method
A crack detection and semiconductor technology, which is applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, semiconductor/solid-state device components, etc., can solve problems such as undetectable cracks and achieve high-precision detection effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
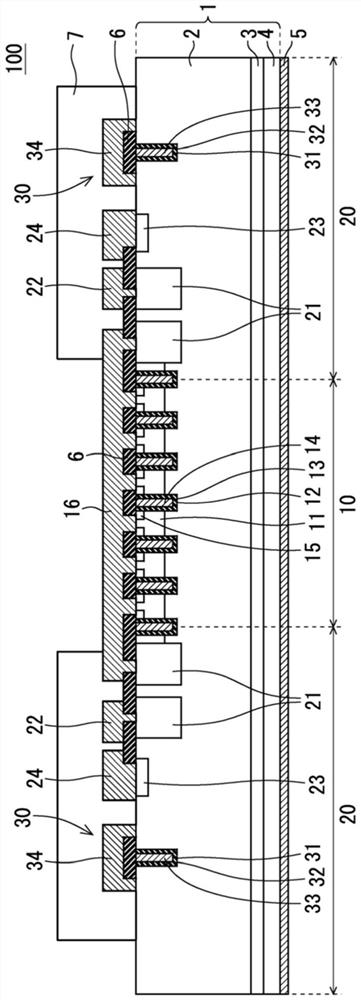
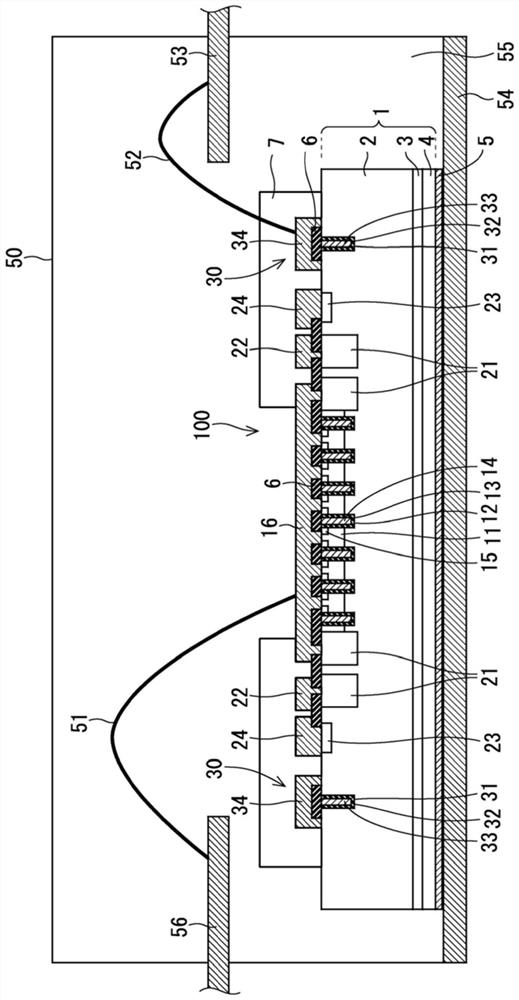
[0021] figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view showing the structure of the semiconductor device 100 according to the first embodiment. In the present embodiment, the semiconductor element included in the semiconductor device 100 is an insulated gate type, more specifically, a trench gate type IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor). However, the semiconductor element may be, for example, elements other than IGBTs such as MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors) and diodes. In addition, the IGBT and MOSFET may be of planar gate type. In addition, in the following description, the first conductivity type is referred to as N type, and the second conductivity type is referred to as P type, but it is also possible to reverse this, and the first conductivity type is referred to as P type, and the second conductivity type is referred to as N type. type.
[0022] The semiconductor device 100 is formed using a semiconductor substrate 1 as a semiconductor layer. ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0041] Figure 4 It is a cross-sectional view showing the structure of the semiconductor device 100 according to the second embodiment. Figure 4 The right half of the cross section of the semiconductor device 100 is enlarged in the middle. In addition, in Figure 4 in, right with figure 1 Components that are the same as those shown are assigned the same reference numerals, and therefore descriptions thereof will be omitted here.
[0042] In the semiconductor device 100 according to Embodiment 2, the additional inner wall insulating film 32 a made of, for example, a silicon oxide film is stacked on the inner wall insulating film 32 of the crack detection structure 30 . Therefore, the actual thickness of the inner wall insulating film 32 (including the thickness of the additional inner wall insulating film 32 a ) is larger than the thickness of the gate insulating film 13 . In the following description of Embodiment 2, "the thickness of the inner wall insulating film 32" me...
Embodiment approach 3
[0046] Figure 5 is a cross-sectional view showing the structure of the semiconductor device 100 according to the third embodiment. exist Figure 5 In , the right half of the cross section of the semiconductor device 100 is also enlarged and shown. In addition, in Figure 5 in, right with figure 1 Components that are the same as those shown are assigned the same reference numerals, and therefore descriptions thereof will be omitted here.
[0047] In the semiconductor device 100 according to Embodiment 3, the trench 31 of the crack detection structure 30 is formed in the N-type drift layer 2 , but the second conductivity type is formed in the vicinity of the trench 31 to cover the periphery of the trench 31 . The P-type region 36. By forming the PN junction formed by the N-type drift layer 2 and the P-type region 36 around the trench 31, it is possible to reduce the voltage applied to the inner wall insulating film 32 when a voltage is applied between the collector electro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com