Xanthobacter sp. T21 and application thereof
A bacillus and yellow technology, applied in bacteria, microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as refractory degradation, and achieve the effect of strong environmental adaptability, huge potential for ecological restoration, and efficient degradation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
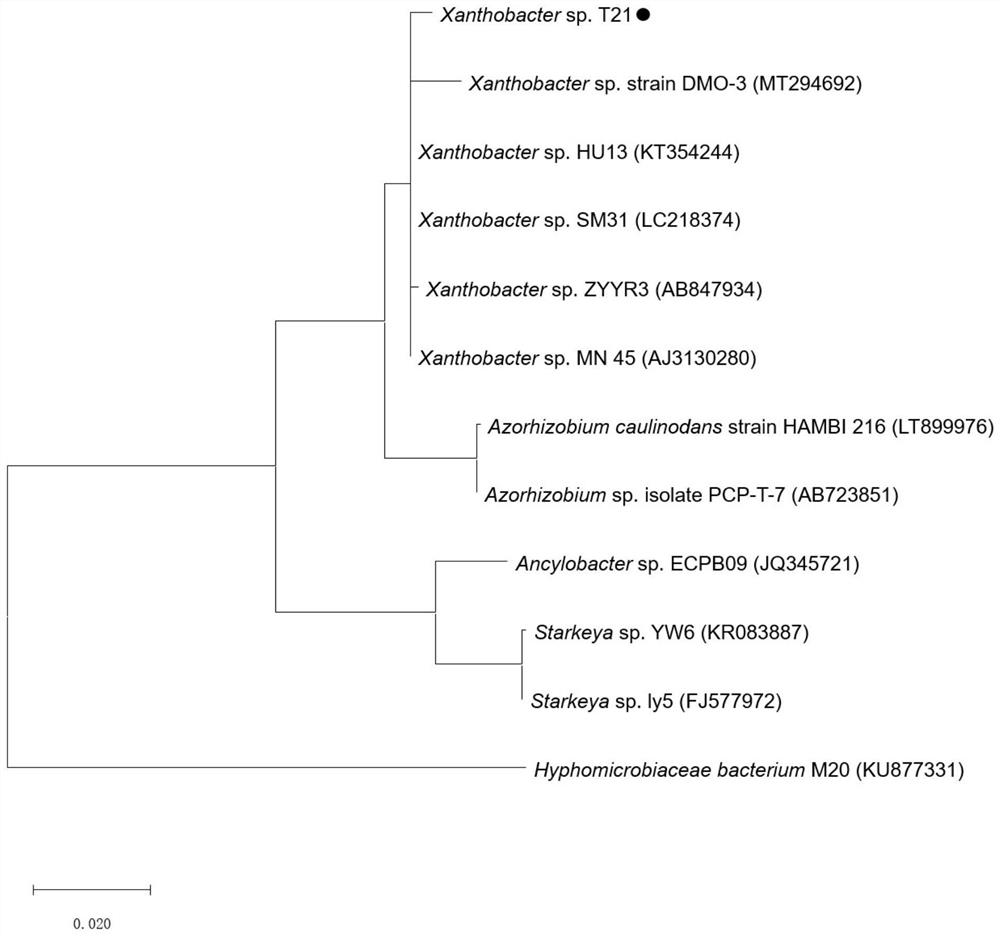
[0020] 1. Isolation and purification of strain T21
[0021] The sediment samples (ie, sediments) used for the isolation of microorganisms were obtained near an organophosphate flame retardant manufacturer in Hebei.
[0022] First, the sediment was enriched and cultured with mineral salt medium (MSM), and the specific steps were as follows: 10 g of sediment was added to a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with 90 mL of inorganic salt medium, and 5 mg / L TCEP was added as the only carbon source. Place a shaker, culture at 25°C, 120rpm. After TCEP is completely degraded, add TCEP to a concentration of 50 mg / L to continue culturing. After TCEP is completely degraded, transfer it to a new inorganic salt medium at a ratio of 1% by volume. After the transfer, add 50 mg / L TCEP as the sole carbon source, place on a shaker, and culture at 25°C and 120rpm. After TCEP is completely degraded, add 50mg / L TCEP to continue the cultivation, repeat the cultivation, and after TCEP is completely de...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2 Efficiency Measurement of Flavobacterium T21 Degradation TCEP
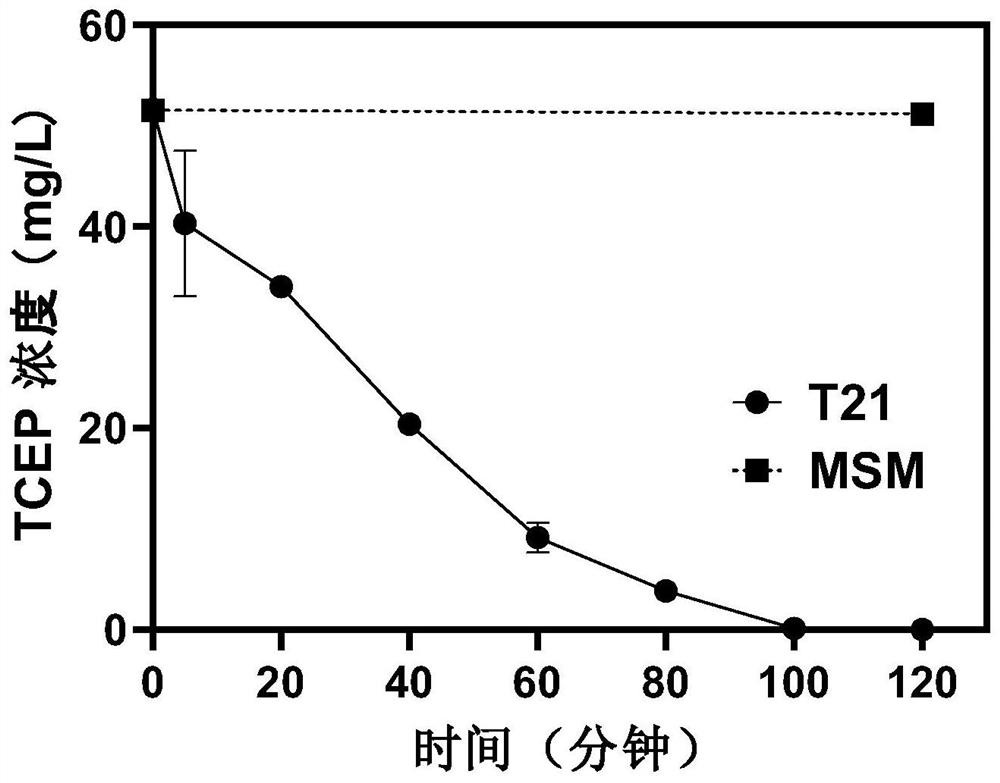
[0029] Inoculate Xanthobacterium T21 into LB medium, culture at 25°C and 120rpm until OD600 is about 0.1, obtain bacterial liquid, collect bacterial cells by centrifugation, wash 3 times with inorganic salt medium (same as Example 1), and resuspend in two Inorganic salt culture medium (same as Example 1) with double the bacterial liquid volume, add 50mg / L TCEP, 25 ℃, 120rpm culture. A control group without addition of Xanthobacterium T21 was also set up. Each experimental group contained three replicate samples. The results showed that the degradation rate of 50mg / L TCEP was 100% within 120 minutes, and the half rate constant was 22.4 minutes. TCEP degradation did not occur in the control group without strain T21. The degradation kinetics curve is as figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
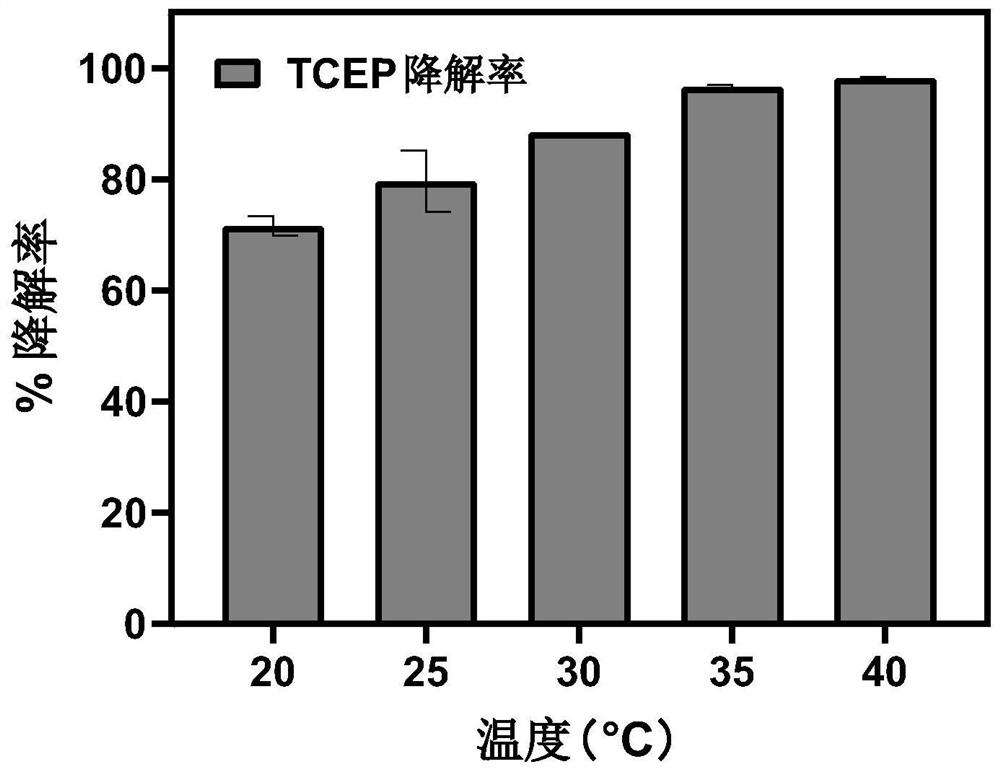
[0030] The influence of embodiment 3 temperature and pH on the degradation rate of Xanthobacterium T21
[0031] Inoculate Xanthobacterium T21 into LB medium, culture at 25°C, 120rpm until OD600 is about 0.1, obtain bacterial liquid, collect bacterial cells by centrifugation, wash 3 times with inorganic salt medium (same as Example 1), and resuspend in bacterial The same volume of inorganic salt culture medium (same as Example 1), add 50mg / L TCEP, set different gradient culture temperatures (20°C, 25°C, 30°C, 35°C, 40°C), and take samples after 30 minutes of shaking at 120rpm Determine the remaining TCEP concentration. Each culture condition contained three replicate samples.
[0032]Inoculate Xanthobacterium T21 into LB medium, culture at 25°C, 120rpm until OD600 is about 0.1, obtain bacterial liquid, collect bacterial cells by centrifugation, wash with inorganic salt medium (same as Example 1) for 3 times, and resuspend in bacterial The same volume of inorganic salt culture...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com