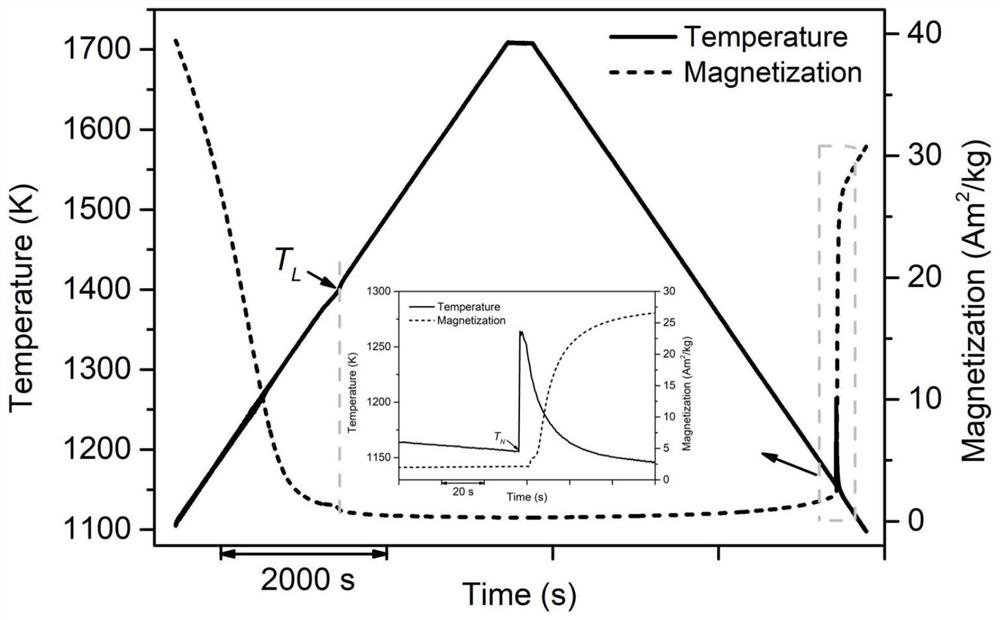
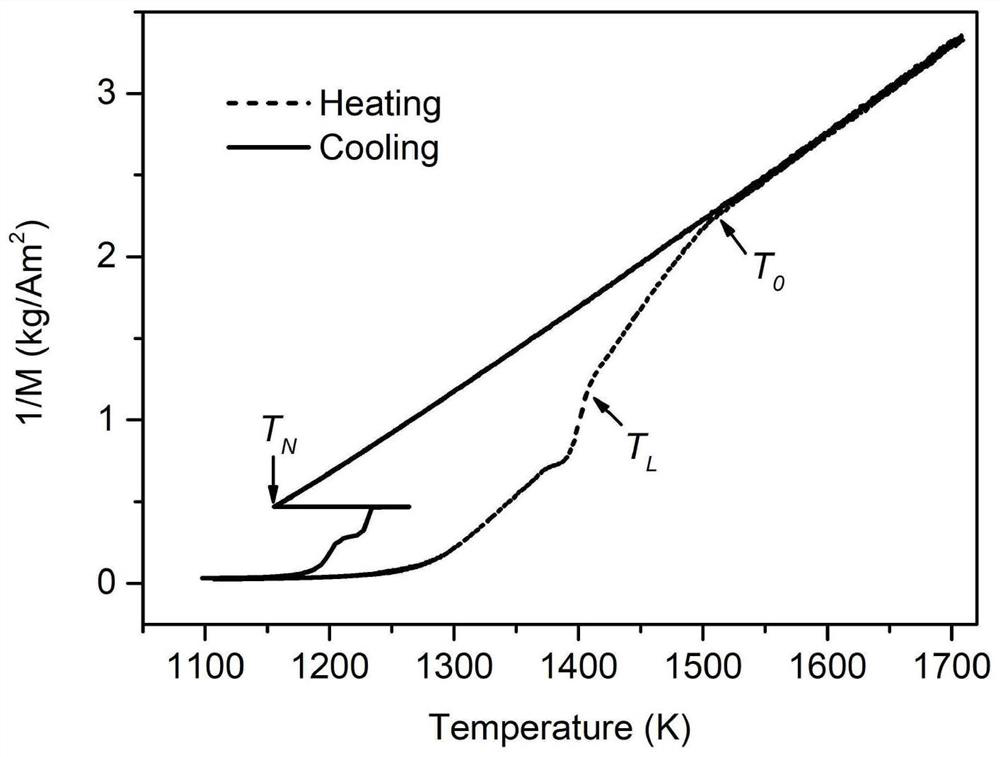
Method for regulating and controlling nucleation undercooling degree of cobalt-boron alloy through melt structure transition in high-intensity magnetic field
A magnetic field regulation and subcooling technology, applied in the field of alloy material preparation, can solve problems such as poor metallurgical quality, and achieve the effects of reducing equipment energy consumption, low subcooling, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] This embodiment is a method to regulate Co 81.5 B 18.5 The method of eutectic alloy melt structure and nucleation supercooling behavior, the specific process is:
[0059] The first step is raw material processing and batching. After the cobalt flakes and boron particles with a purity of more than 99.9% are polished off the surface oxide layer with a grinding wheel, they are soaked in 99.8% absolute ethanol, and surface impurities such as oil stains and abrasive debris are removed by ultrasonic vibration. According to the atomic percentage Co:B=81.5:18.5, the corresponding mass raw materials were weighed with an analytical balance, and used in the subsequent smelting process.
[0060] In the second step, the preparation of Co 81.5 B 18.5 Eutectic alloy ingot. The cobalt-boron raw materials obtained in the first step are put into a non-consumable vacuum arc melting furnace together, and the cobalt sheet is covered on the boron particles. First of all, vacuumize to k...
Embodiment 2
[0066] This embodiment is a method to regulate Co 81.5 B 18.5 The method of eutectic alloy melt structure and nucleation supercooling behavior, the specific process is:
[0067] The first step is raw material processing and batching. After the cobalt flakes and boron particles with a purity of more than 99.9% are polished off the surface oxide layer with a grinding wheel, they are soaked in 99.8% absolute ethanol, and surface impurities such as oil stains and abrasive debris are removed by ultrasonic vibration. According to the atomic percentage Co:B=81.5:18.5, the corresponding mass raw materials were weighed with an analytical balance, and used in the subsequent smelting process.
[0068] In the second step, the preparation of Co 81.5 B 18.5 Eutectic alloy ingot. The cobalt-boron raw materials obtained in the first step are put into a non-consumable vacuum arc melting furnace together, and the cobalt sheet is covered on the boron particles. First of all, vacuumize to k...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Vickers hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com