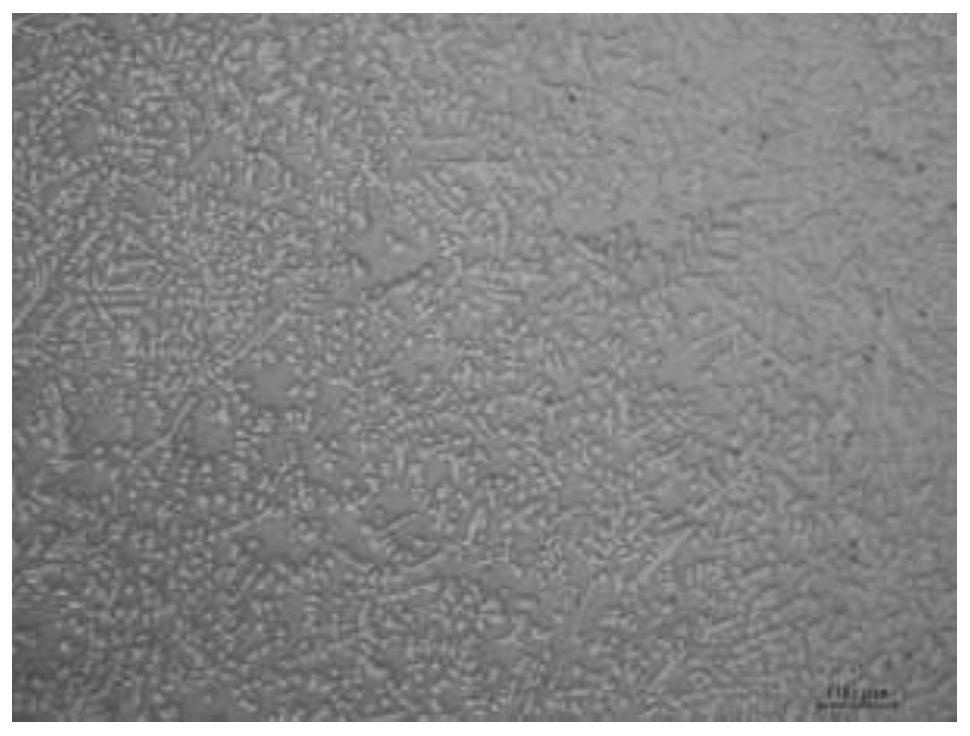
Structure optimization method for vacuum consumable electric arc smelting copper-chromium contact material
A vacuum consumable arc, copper-chromium contact technology, applied in the direction of contacts, circuits, electrical switches, etc., can solve the problems affecting the voltage resistance, breaking and anti-welding electrical properties of contact materials, and coarse metallographic structure. To achieve the effect of improving safety, reliability and protection, improving electrical performance, and promoting progress and development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
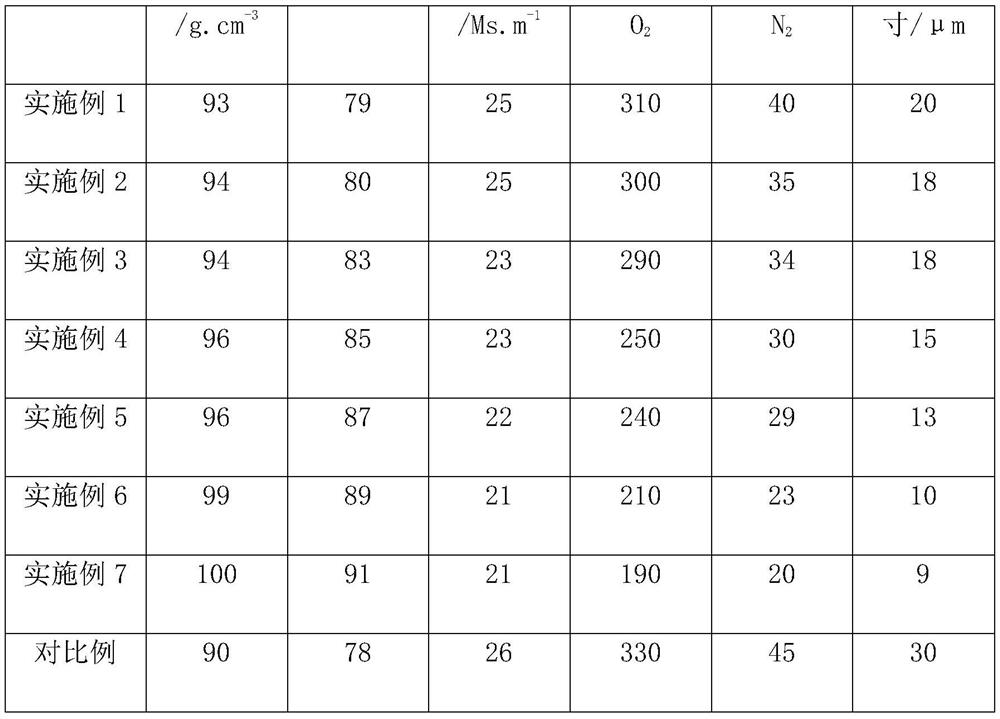
[0029] Embodiment 1: A method for optimizing the structure of copper-chromium contact material in vacuum consumable arc melting, comprising the following steps:
[0030] S1. Ingredients
[0031] According to the alloy composition of technological requirement, take by weight percentage respectively the copper powder of 45% and the chromium powder of 55%;
[0032] S2, sintering
[0033] S2-1. Fully mix the copper powder and chromium powder in step S1, and carry out compaction treatment under the condition of vacuum degree of 40Pa and pressure of 300KN, place the compacted alloy powder in a sintering furnace, and heat Sintering treatment under the conditions for 5h, to obtain the master alloy;
[0034] S2-2. Put the master alloy obtained in step S2-1 into the graphite crucible of the melting chamber, and fill the melting chamber with N 2 As a protective gas, heat the graphite crucible until the copper powder and chromium powder are completely melted, and after 10 minutes of he...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: A method for optimizing the structure of copper-chromium contact material in vacuum consumable arc melting, comprising the following steps:
[0040] S1. Ingredients
[0041] According to the alloy composition required by the process, 70% copper powder and 30% chromium powder were weighed in weight percentage; the copper powder is derived from electrolytic copper powder;
[0042] S2, sintering
[0043] S2-1. Fully mix the copper powder and chromium powder in step S1, and carry out compaction treatment under the conditions of vacuum degree of 70Pa and pressure of 400KN, place the compacted alloy powder in a sintering furnace, and heat Sintering treatment under the conditions for 7h to obtain the master alloy;
[0044] S2-2. Put the master alloy obtained in step S2-1 into the graphite crucible of the melting chamber, and fill the melting chamber with N 2 As a protective gas, heat the graphite crucible until the copper powder and chromium powder are complet...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3 A method for optimizing the microstructure of copper-chromium contact material in vacuum consumable arc melting, comprising the following steps:
[0050] S1. Ingredients
[0051] According to the alloy composition required by the process, 90% of the copper powder and 10% of the chromium powder are weighed in percentage by weight;
[0052] S2, sintering
[0053] S2-1. Fully mix the copper powder and chromium powder in step S1, and carry out compaction treatment under the conditions of vacuum degree of 90Pa and pressure of 500KN, place the compacted alloy powder in a sintering furnace, and heat Sintering treatment under conditions for 8 hours to obtain an intermediate alloy;
[0054] S2-2, put the master alloy obtained in step S2-1 into the graphite crucible of the melting chamber, and fill the melting chamber with N 2 As a protective gas, heat the graphite crucible until the copper powder and chromium powder are completely melted, and after heat preservat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com