Preparation method of low-melting-point quinary gallium-based liquid alloy
A liquid alloy, low melting point technology, applied in the field of material metallurgy, can solve problems such as the gap between gallium-based liquid alloys, achieve the effect of simple preparation method, wide application prospects, and solve the threat of environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
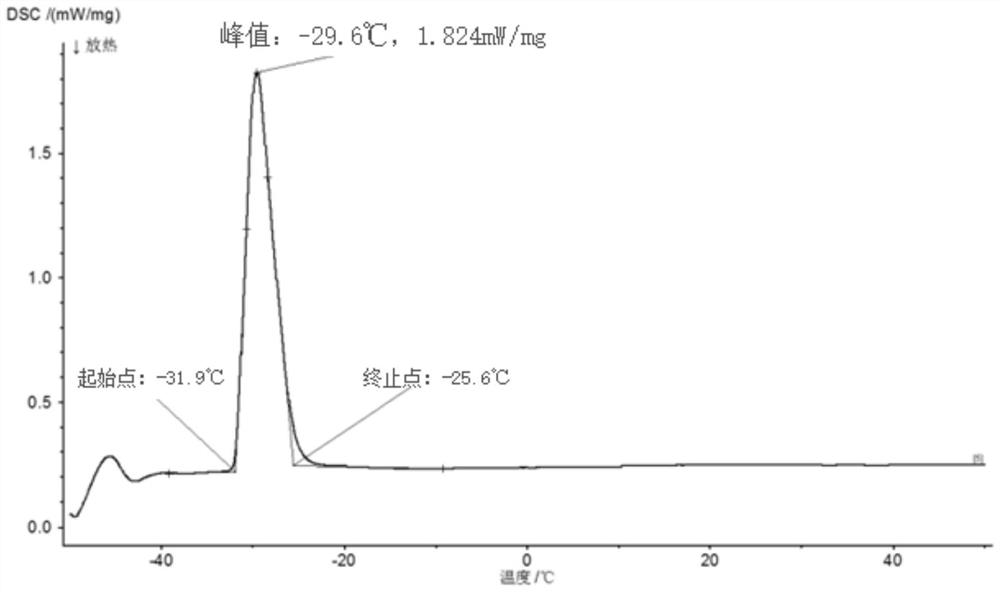
[0017] Accurately weigh gallium 16.7742g, indium 2.4420g, tin 0.7235g, zinc 0.0403g and aluminum 0.0200g (the aluminum content is about 0.1%) with an analytical balance. Gallium, indium, tin, and zinc were added first to the graphite crucible, followed by the aluminum. The graphite crucible is moved into the atmosphere furnace, and after vacuuming, it is protected by high-purity argon. Raise the temperature to 700°C and keep it warm for 1h. The graphite crucible was taken out with the furnace cooling to room temperature. After standing for 2 hours and removing the oxide film on the surface, a gallium-based liquid alloy with a low melting point is obtained.
Embodiment 2
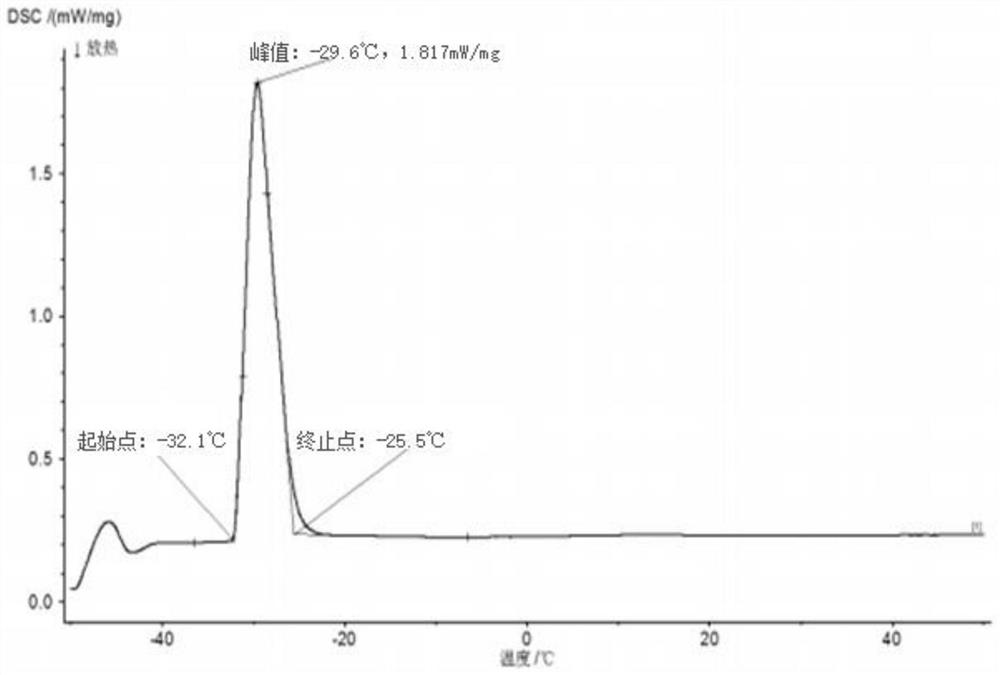
[0019] First place the whole bottle of raw gallium in a blast drying oven, heat up to 60°C until it is completely melted, weigh 50.3360g of liquid gallium, and add it to a polytetrafluoroethylene crucible. Then, accurately weigh 7.3210g of indium, 2.1610g of tin, 0.1201g of zinc and 0.0620g of aluminum (about 0.1% of aluminum content) with an analytical balance, and add them into a polytetrafluoroethylene crucible filled with molten gallium. The graphite rod was stirred until the solid metal material was completely dissolved in the molten gallium at 60°C, and the oxide film was removed after standing for 4 hours to obtain a gallium-based liquid alloy with an ultra-low melting point.
Embodiment 3
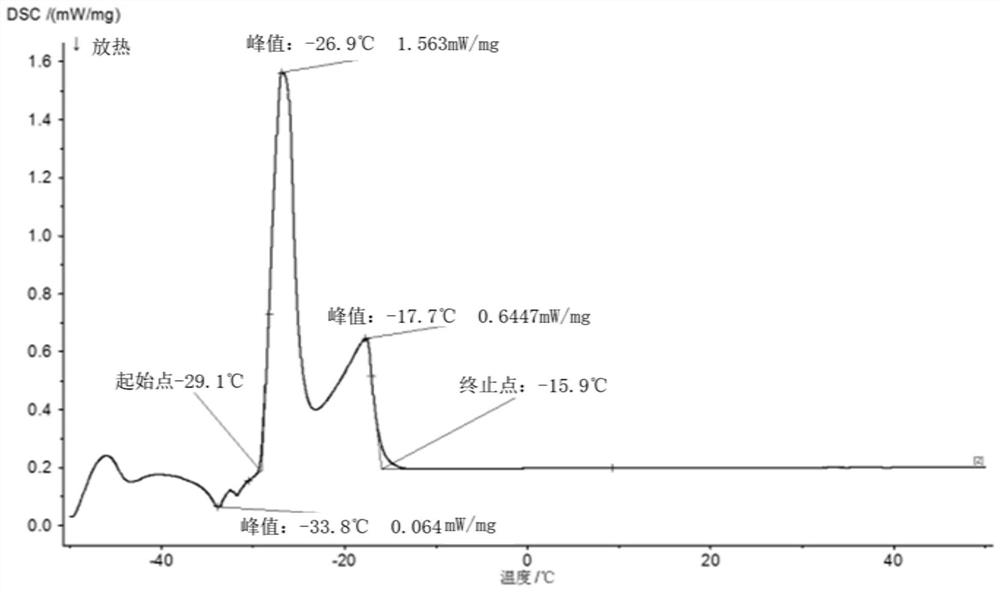
[0021] Accurately weigh 50.2780g of gallium, 7.3210g of indium, 2.1610g of tin, 0.1200g of zinc and 0.1200g of aluminum (the aluminum content is about 0.2%) with an analytical balance. Gallium, indium, tin, and zinc were added first to the graphite crucible, followed by the aluminum. The graphite crucible is moved into the atmosphere furnace, and after vacuuming, it is protected by high-purity argon. Raise the temperature to 700°C and keep it warm for 1h. The graphite crucible was taken out with the furnace cooling to room temperature. After standing for 2 hours and removing the oxide film on the surface, a gallium-based liquid alloy with a low melting point is obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com