Preparation method of rhodium catalyst
A rhodium catalyst, rhodium ethylene dimer technology, applied in catalyst activation/preparation, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve problems such as high risk factor, high equipment requirements, and easy-to-corrosion reactors. Achieve the effects of low equipment requirements, shortened reaction time, and reduced toxic waste gas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] One embodiment of the present invention provides a kind of preparation method of rhodium catalyst, comprises the steps:
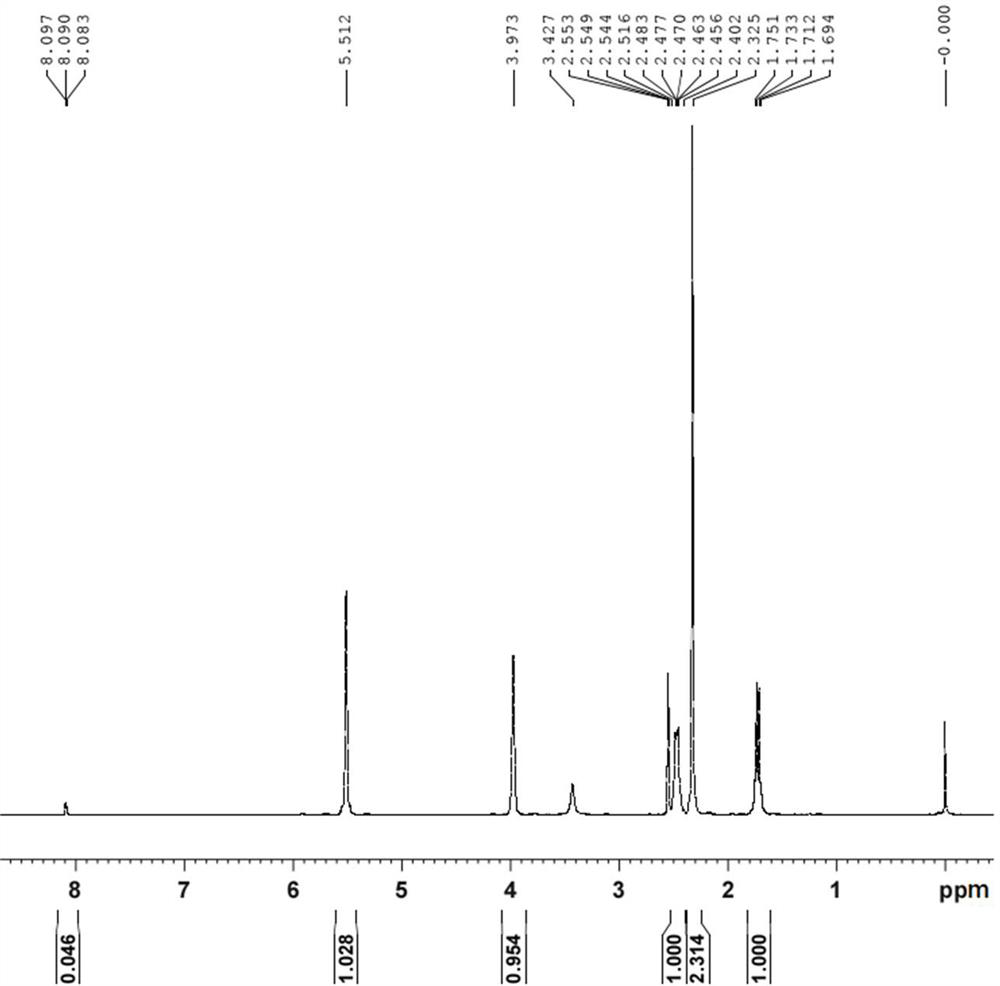
[0031] Introduce ethylene or diene into the aqueous solution of trivalent rhodium salt, and add zinc powder under protective atmosphere to carry out reduction reaction to obtain rhodium catalyst, which is monovalent rhodium ethylene dimer or monovalent rhodium diene diolefin Polymer.
[0032] In the process of the above-mentioned reduction reaction, the zinc powder gradually dissolves, trivalent rhodium is reduced to monovalent rhodium, and at the same time coordinates with ethylene or diene to form a water-insoluble rhodium catalyst, which is then precipitated from the reaction solution, while by-products such as zinc chloride The product is soluble in water, easy to separate, and the yield of the product is high.
[0033] The preparation method of above-mentioned rhodium catalyst adopts zinc powder to reduce trivalent rhodium salt under protective...
Embodiment 1
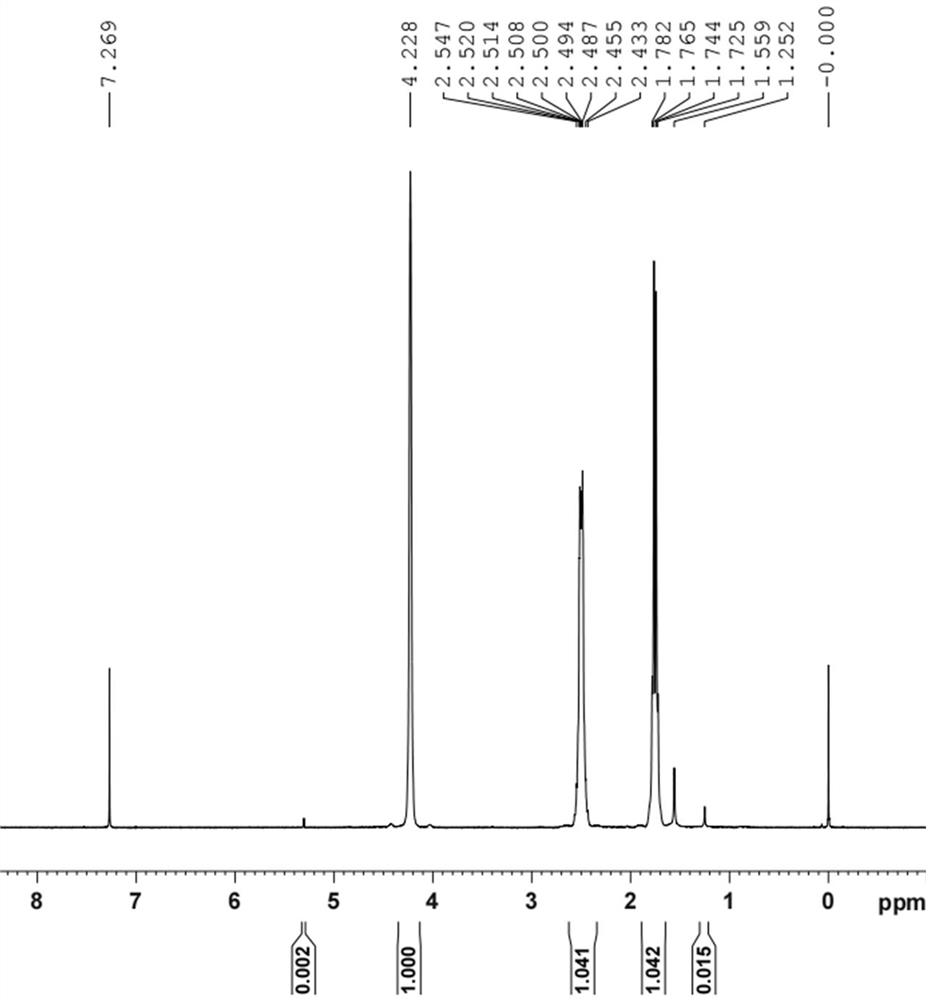
[0059] Example 1: Add 10.0 g of rhodium trichloride trihydrate and 150 mL of deionized water into a 250 mL three-necked flask, stir at room temperature for 30 minutes to completely dissolve the rhodium trichloride; first replace the atmosphere with argon gas three times, and then replace it with ethylene gas Three times, and ethylene gas was passed into the reaction solution at a ventilation rate of 0.5L / min; 2.4g of zinc powder was added in batches under stirring conditions at room temperature (in this invention, 25°C±5°C, the same below); the pH meter was online Check the pH value. When the pH value is 2.1, orange-red precipitation begins to appear in the reaction solution. When the pH value is 3.8, the zinc powder is added, and the color of the reaction solution gradually fades. When the pH value is 4.1, it remains unchanged within 1-2 minutes. Stop ventilation. The precipitate was filtered anaerobically, washed with weakly acidic deionized water, and dried to obtain 6.3 g ...
Embodiment 2
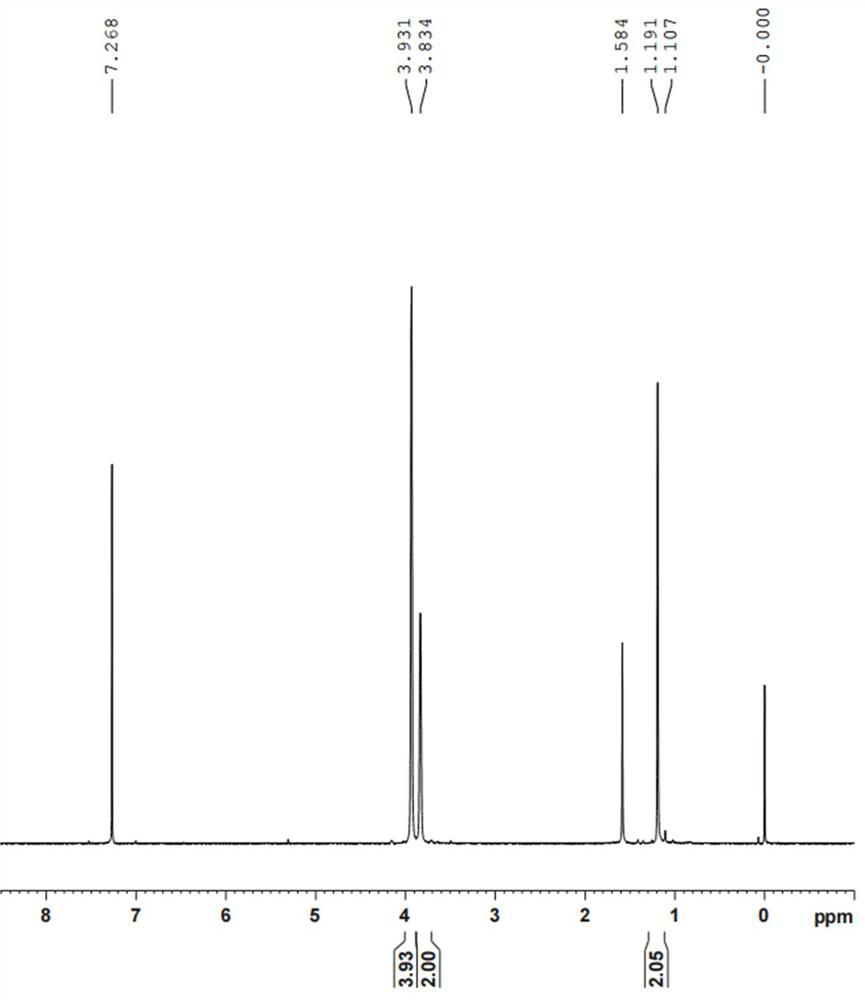
[0064] Example 2: Add 10.0 g of rhodium trichloride trihydrate and 150 mL of deionized water into a 250 mL three-necked flask, stir at room temperature for 30 minutes to completely dissolve the rhodium trichloride; first replace the atmosphere with argon gas three times, and then replace it with ethylene gas Three times, and ethylene gas was passed into the reaction solution at a ventilation rate of 0.5L / min; 2.7g of zinc powder was added in batches under stirring at room temperature; the pH value was detected online with a pH meter, and orange began to appear in the reaction solution when the pH value was 2.2. Red precipitation, when the pH value is 3.8, the zinc powder is added, the color of the reaction solution gradually fades, when the pH value is 4.3, it remains unchanged within 1-2 minutes, and the aeration is stopped. The precipitate was filtered anaerobically, washed with weakly acidic deionized water, and dried to obtain 6.7 g of orange-red powder.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com