Monooxygenase MpdA, coding gene mpdA thereof and application of monooxygenase MpdA and coding gene mpdA thereof in synthesis of vitamin E precursor
A monooxygenase, encoding gene technology, applied in the high field of biology, can solve problems such as incompetent specific synthesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The cloning of embodiment 1 gene mpdA
[0032] (1) Extraction and sequencing of bacterial genome total DNA
[0033]The strain Mycobacterium neoaurum B5-4 and its mutant strain Mycobacterium neoaurum B5-4M were respectively cultured in large quantities in liquid LB medium (30°C, 200rpm, 48h), and then the total genomic DNA of the two strains with high purity and large fragments was extracted by CTAB method. Dissolve them in deionized water respectively and store them at -20°C. For specific methods, refer to the "Refined Molecular Biology Experiment Guide" edited by F. Osper et al. The genomic DNA of the obtained two bacterial strains was entrusted to a sequencing company for sequencing.
[0034] (2) Functional identification of gene mpdA
[0035] By comparing and analyzing the genomes of the strain Mycobacterium neoaurum B5-4 and its mutant strains, it was found that a DNA fragment of about 23kb was missing in the mutant strain. This fragment was analyzed in combinatio...
Embodiment 2
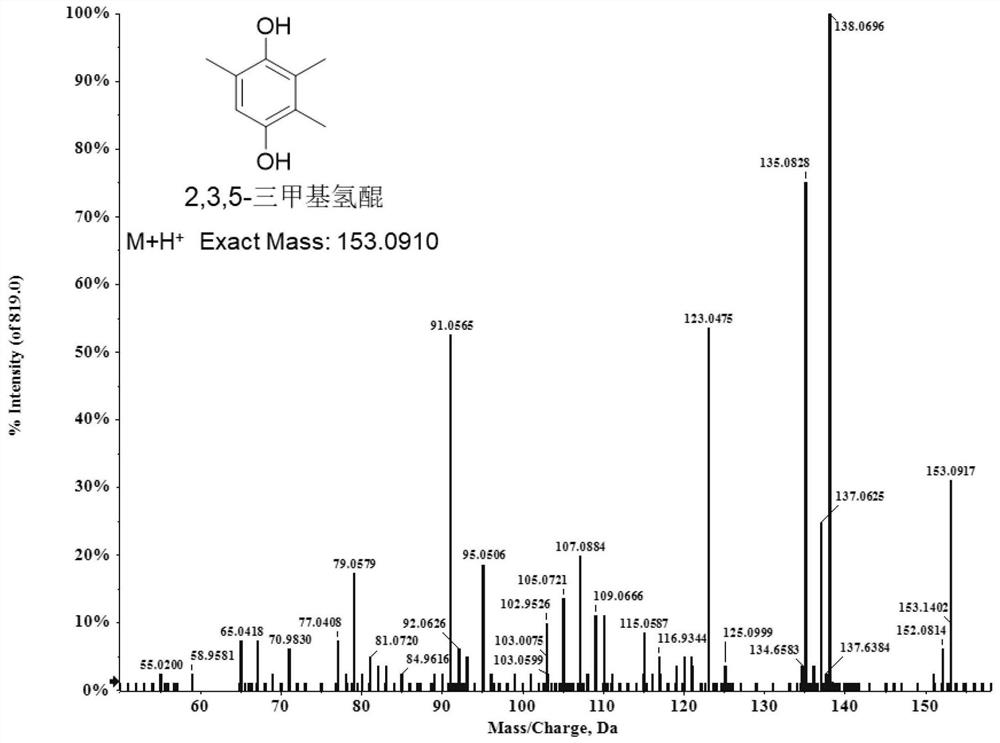
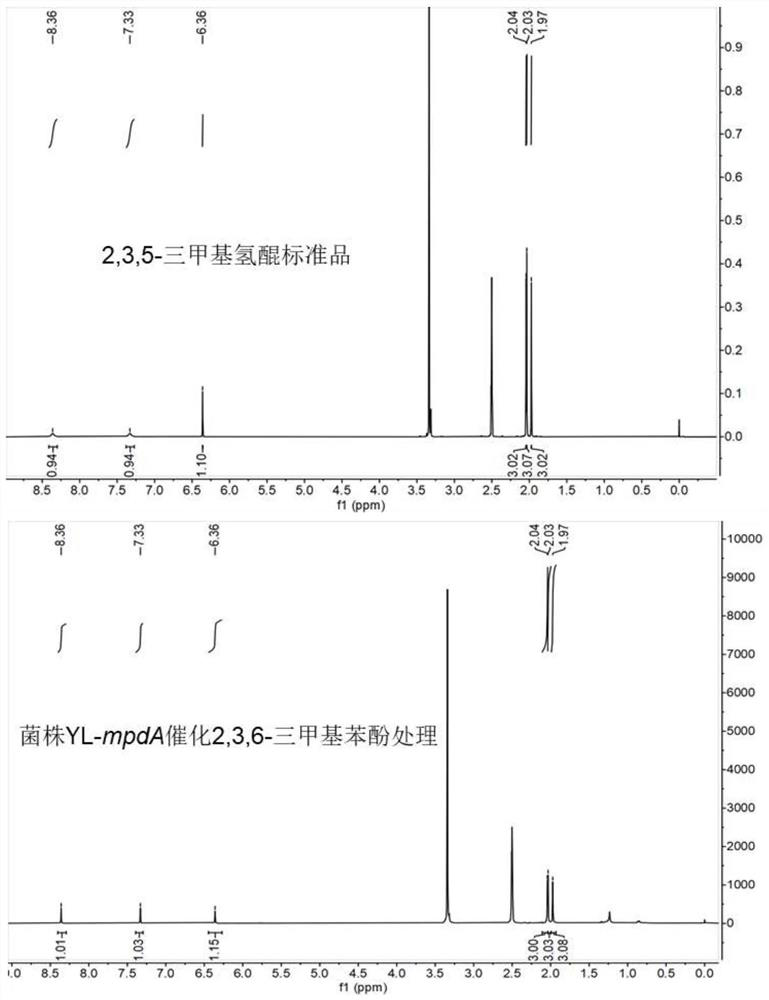
[0037] Example 2 The whole cell catalytic method synthesis of 2,3,5-trimethylhydroquinone
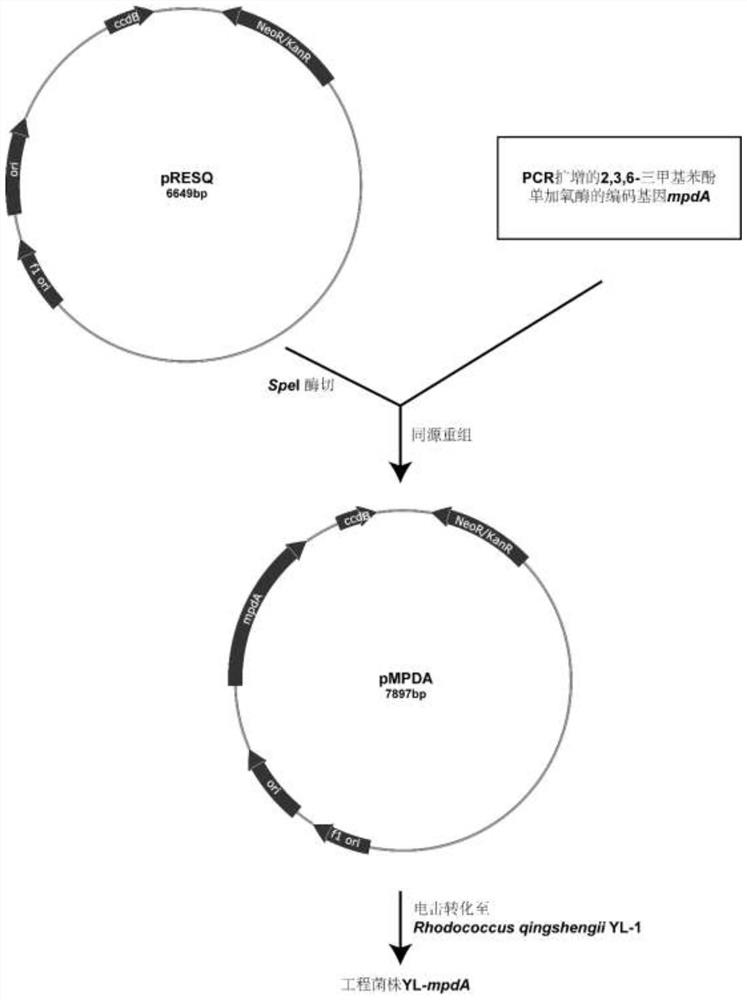
[0038] (1) Construction of engineering strains
[0039] Using the total DNA of strain B5-4 as a template, use forward primer (SEQ ID NO.3): 5'-ACCGAGCTCAGATCTACTAGTATGCAATTTTCCAAAGTTGG-3' and reverse primer (SEQ ID NO.4): 5'-ACACTGGCGGCCGTTACTAGTTCACAGCCACGGGGTATTCGG-3' to amplify out of the gene mpdA. PCR amplification program: denaturation at 95°C for 3 min; denaturation at 95°C for 1.5 min, annealing at 53°C for 0.5 min, extension at 72°C for 1.5 min, and 25 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 min, and cooling to room temperature. The obtained gene mpdA fragment was introduced into the SpeI restriction site of the plasmid pRESQ to construct the recombinant plasmid pMPDA; then, the recombinant plasmid was transformed into the strain Rhodococcus qingshengii YL-1 (CCTCC AB 2017132) (Li C, Zhang J, WuZG, Cao L, Yan X, Li SP.2012.Biodegr adation of buprofezin by Rhodococcussp.strain YL-1is...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3 The enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of 2,3,5-trimethylhydroquinone
[0043] (1) Preparation of crude enzyme solution
[0044] Strain YL-mpdA was cultured to the logarithmic phase in LB medium, collected by centrifugation at 5000rpm for 10min, washed twice with PBS buffer, resuspended in 10ml of PBS buffer, and ultrasonically broken in an ice-water bath for 10-15 minutes (AutoScience, UH-650B ultrasonic processor, 30% intensity), centrifuged at 12000rpm for 30min, and collected the supernatant, which was the prepared crude enzyme solution.
[0045] (2) Functional determination of 2,3,6-trimethylphenol catalyzed by crude enzyme solution
[0046] The reaction system of 2,3,6-trimethylphenol catalyzed by crude enzyme solution is: 0.5mM 2,3,6-trimethylphenol, 0.2mM NADH, 0.02mM FAD, 10ml of crude enzyme solution is added. After reacting at 30°C for 2 hours, an equal volume of dichloromethane was added to terminate the reaction and the product was extracted by vigorous...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com