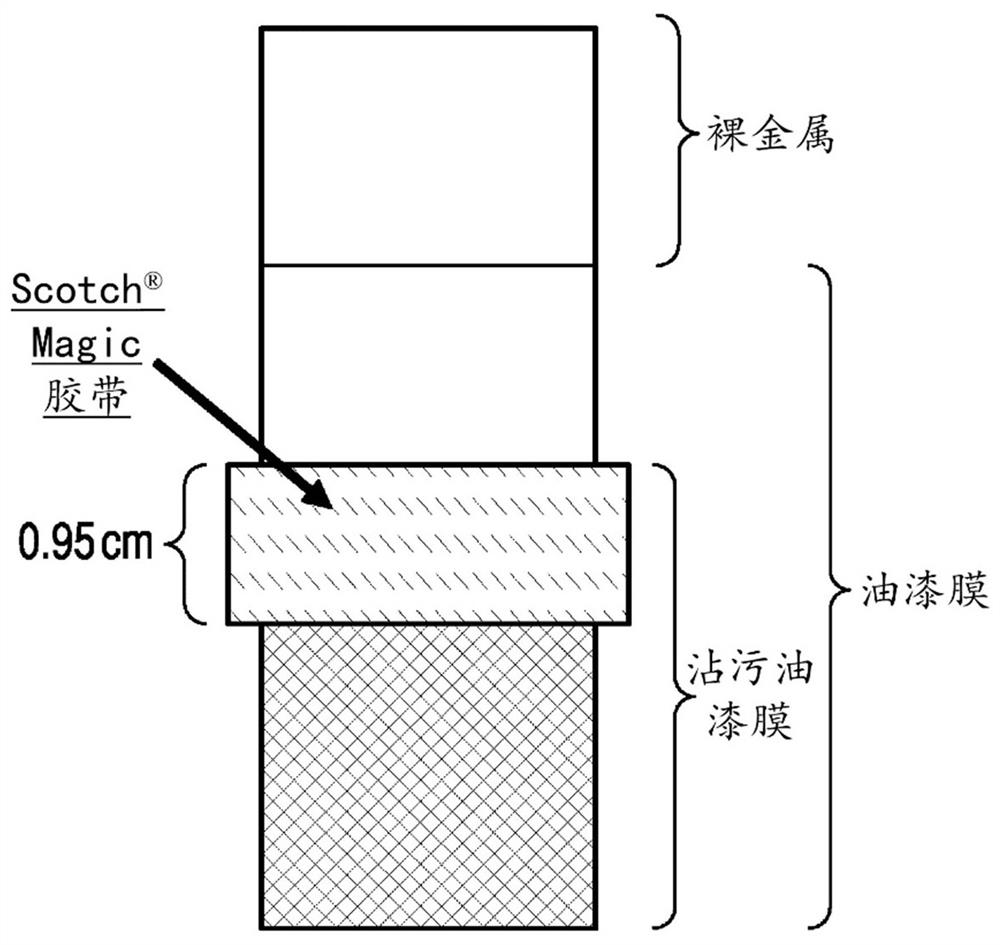
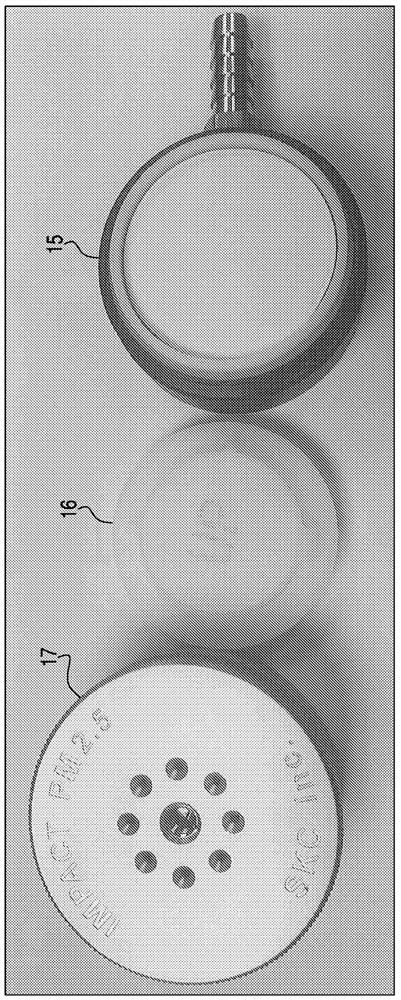
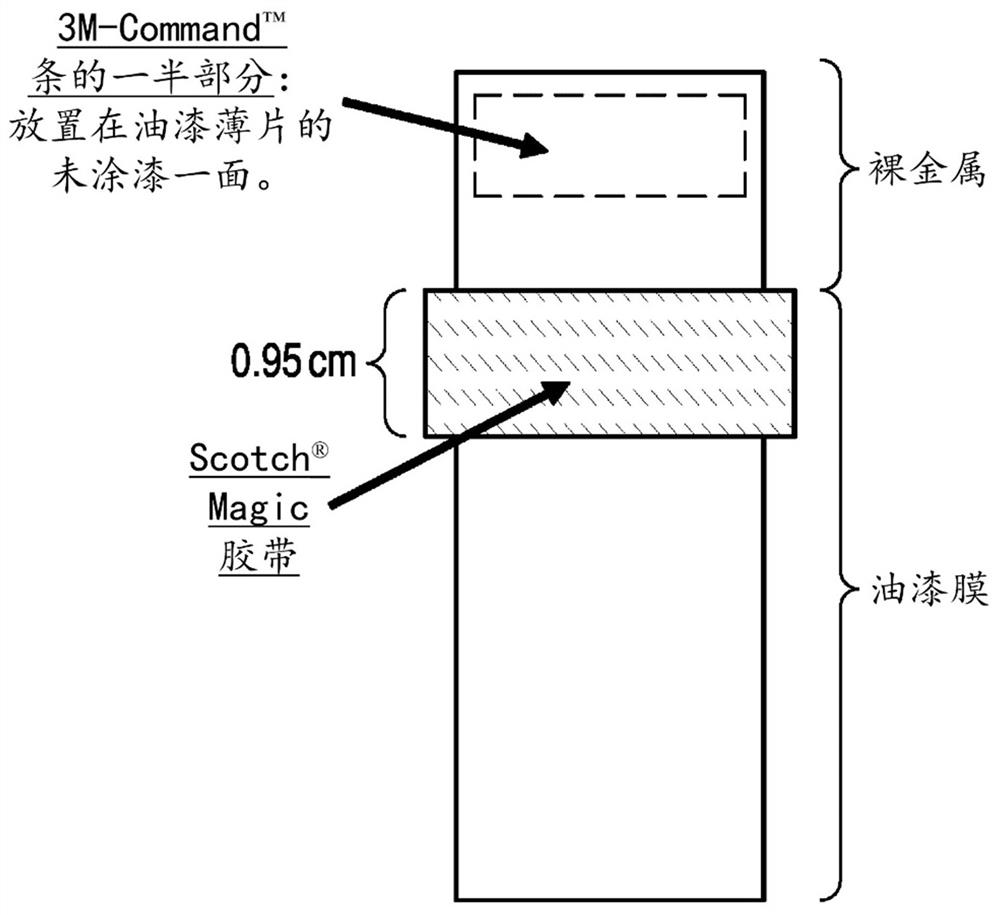
Process and apparatus for quantifying solid residue on a substrate
A substrate and solid technology, applied in measurement devices, suspension and porous material analysis, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to accurately simulate natural particle deposition processes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0103] Embodiment 1. Accelerated Testing of Commercial Paints
[0104] Using Preparation A, an additional replicate set of the seven paint film coated panels highlighted in Comparative Example 1 was prepared. Using the procedure described in Preparations B and C, the panels were then cut into thin slices, and two of the thin slices were evaluated simultaneously for accelerated dusting resistance for each paint type. During the evaluation period, a total of 6 continuously running carbon black (Flamrus 101 ) dusting channels were employed. The average delta gray value derived from each paint type flake pair is provided in Table 5.
[0105] table 5. The average Δ gray value of Example 1
[0106] 7 in 1 FutureColor Shield-1 NanoSemi-Gloss Shield-1 NanoSheen Super-shieldSemi-Gloss Super-shield Sheen Aquis Façade Novasil 26.6 7.2 1 4.6 0.8 3.4 3.9
[0107] For each non-zero outdoor exposure time at the Guangzhou test site highlighted in Table...
Embodiment 2
[0114] Embodiment 2. with different T g Accelerated Testing of Paints with Polymeric Binders of Value
[0115] Using emulsion polymerization techniques known to those skilled in the art, four unique polymer bonds were prepared using methyl methacrylate (MMA), methacrylic acid (MAA) and butyl acrylate (BA) monomers in varying amounts agent as an aqueous emulsion. The amount (in mmol) of each monomer used for each polymer binder synthesis is shown in Table 8. Also shown in Table 8 are the weight % solids of each prepared emulsion and the glass transition temperature (T g ). Emulsion wt % solids were determined gravimetrically by drying a sample of the emulsion in a standard vacuum oven at 110°C for 2 hours. The glass transition temperature of dry solid samples of the polymeric binder was measured using a TA Instruments Q100 Differential Scanning Calorimeter (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE) and associated software.
[0116] Table 8. Composition and characterization of poly...
Embodiment 3
[0126] Embodiment 3. Accelerated testing of paints with different pigment volume concentrations
[0127]Five paints with different pigment volume concentrations (PVC) were prepared according to the formulations provided in Table 11 using paint manufacturing techniques known to those skilled in the art.
[0128] Table 11. Composition of paints with different PVC values
[0129]
[0130] Two replicate sets of five paint film coated panels derived from the five resulting test paints were prepared using the procedure described in Preparation A. Using the procedure described in Preparations B and C, a set of panels was then cut into thin slices, and two of the thin slices were evaluated simultaneously for accelerated dusting resistance for each test paint. During the evaluation period, a total of 24 continuously running carbon black dusting channels were employed. The average delta gray values derived from each paint flake pair are provided in Table 12.
[0131] The remai...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com