Method for determining related impurities I of atorvastatin calcium
A technology of atorvastatin calcium and related impurities, which is applied in the detection field of pharmaceutical impurities to achieve the effect of improving the purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
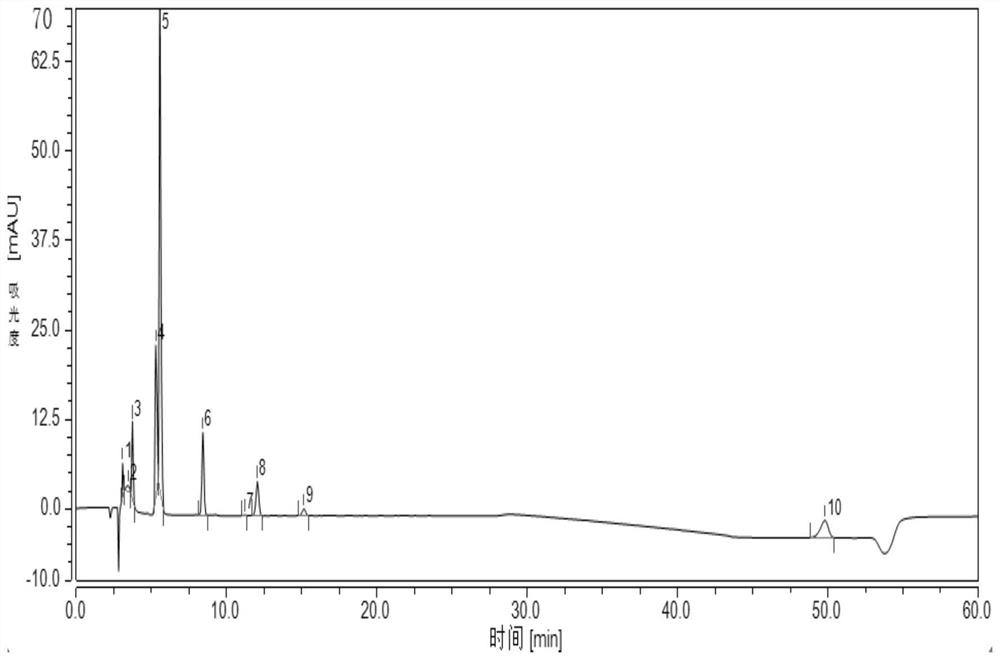
Embodiment 1
[0031] 1. HPLC chromatographic conditions Chromatographic column: Wondasil C18 (4.6mm×250mm, 5μm);
[0032] Mobile phase: mobile phase A is acetonitrile-tetrahydrofuran-acetate buffer, wherein the volume ratio of acetonitrile: tetrahydrofuran: acetate buffer is 35:3:62;
[0033] Mobile phase B is acetonitrile-tetrahydrofuran-acetate buffer, wherein the volume ratio of acetonitrile: tetrahydrofuran: acetate buffer is 82:3:15;
[0034] The preparation method of the acetic acid buffer solution is: take 1.50g of ammonium acetate, add 700mL of water to dissolve, after dissolving, adjust the pH to 4.0 with glacial acetic acid, then add water to 1000mL;
[0035] Flow rate: 1.0ml / min;
[0036] Detection wavelength: 244nm, column temperature 30°C;
[0037] Injection volume: 20μL;
[0038] The mobile phase gradient elution conditions are shown in Table 1.1.
[0039] Table 1.1 Mobile phase gradient elution conditions
[0040] time / min Mobile phase A / % Mobile phase B / % ...
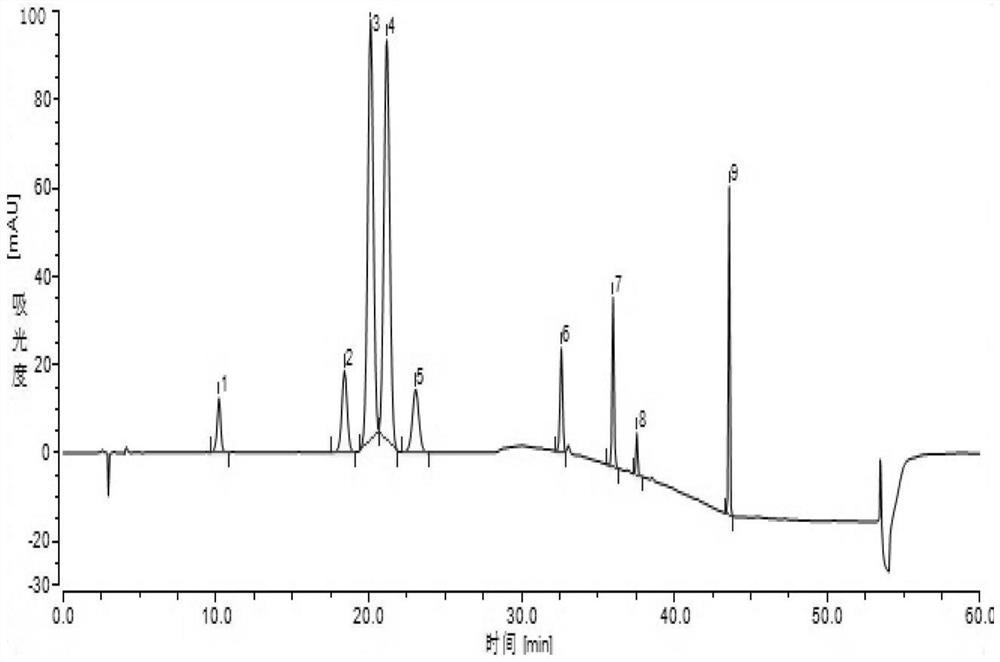
Embodiment 2
[0052] 1. HPLC chromatographic conditions Chromatographic column: Wondasil C18 (4.6mm×250mm, 5μm);
[0053] Mobile phase: mobile phase A is acetonitrile-tetrahydrofuran-acetate buffer, wherein the volume ratio of acetonitrile: tetrahydrofuran: acetate buffer is 40:5:55;
[0054] Mobile phase B is acetonitrile-tetrahydrofuran-acetate buffer, wherein the volume ratio of acetonitrile: tetrahydrofuran: acetate buffer is 85:5:10;
[0055] The preparation method of the acetic acid buffer solution is: take 1.55g of ammonium acetate, add 800mL of water to dissolve, after dissolving, adjust the pH to 4.0 with glacial acetic acid, then add water to 1000mL;
[0056] Flow rate: 1.0ml / min;
[0057] Detection wavelength: 244nm, column temperature 30°C;
[0058] Injection volume: 20μL;
[0059] The mobile phase gradient elution conditions are shown in Table 2.1.
[0060] Table 2.1 Mobile phase gradient elution conditions
[0061] time / min Mobile phase A / % Mobile phase B / % ...
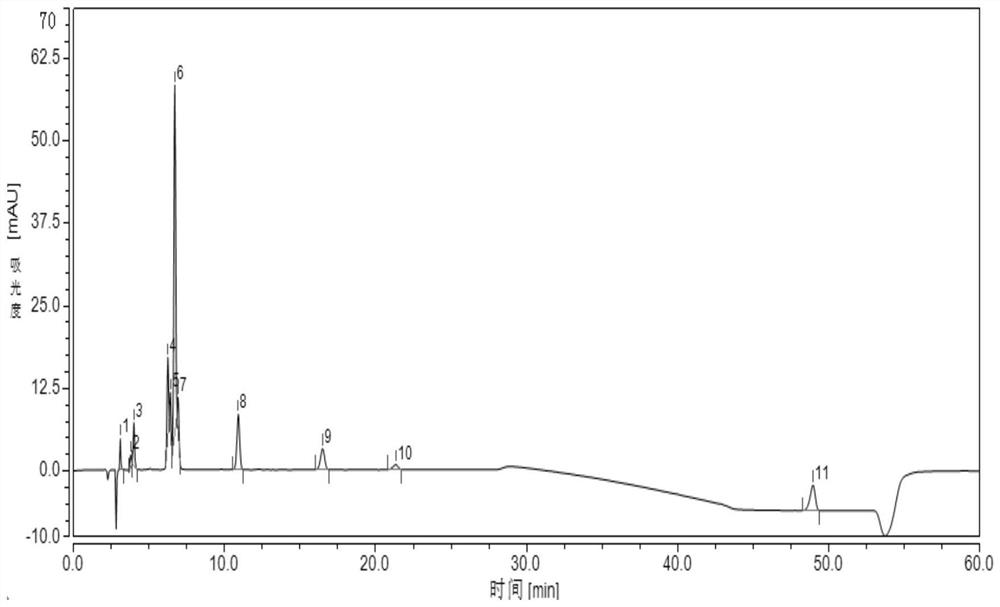
Embodiment 3
[0096] 1. HPLC chromatographic conditions Chromatographic column: Wondasil C18 (4.6mm×250mm, 5μm);
[0097] Mobile phase: mobile phase A is acetonitrile-tetrahydrofuran-acetate buffer, wherein the volume ratio of acetonitrile: tetrahydrofuran: acetate buffer is 45:7:48;
[0098] Mobile phase B is acetonitrile-tetrahydrofuran-acetate buffer solution, wherein the volume ratio of acetonitrile: tetrahydrofuran: acetate buffer solution is 87:7:6; the preparation method of acetate buffer solution is: take 1.58g ammonium acetate, add 900mL water for Dissolve, after dissolving, adjust the pH to 4.0 with glacial acetic acid, then add water to 1000mL;
[0099] Flow rate: 1.0ml / min;
[0100] Detection wavelength: 244nm, column temperature 30°C;
[0101] Injection volume: 20μL;
[0102] The mobile phase gradient elution conditions are shown in Table 3.1.
[0103] Table 3.1 Mobile phase gradient elution conditions
[0104] time / min Mobile phase A / % Mobile phase B / % 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com