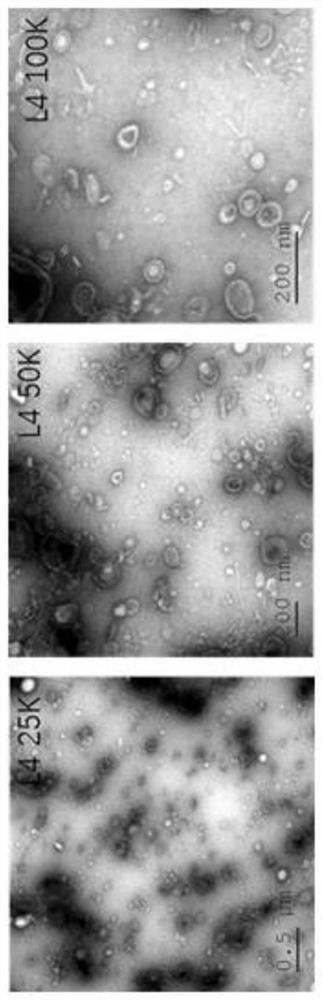
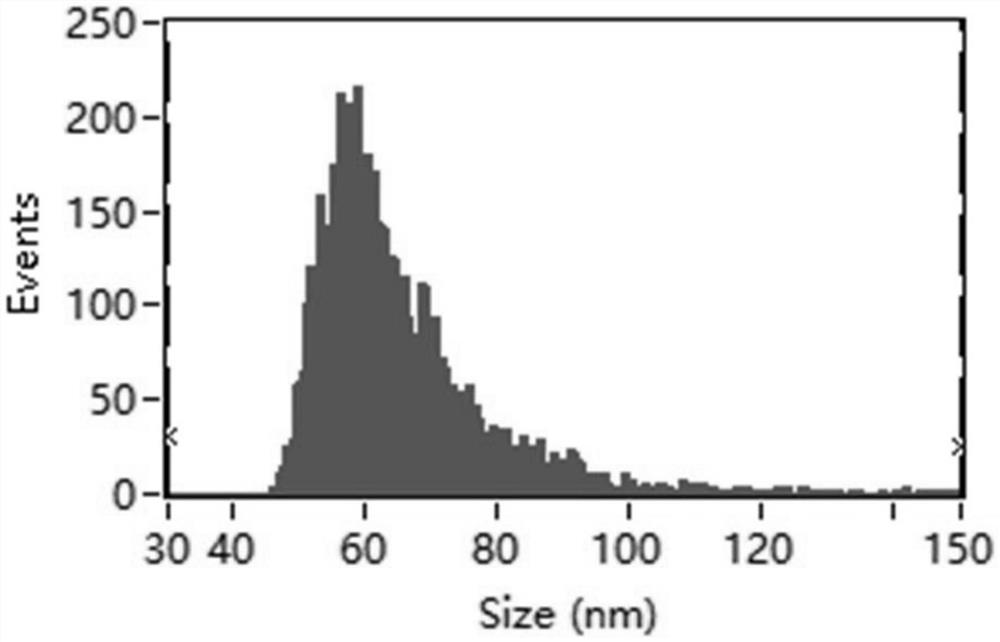
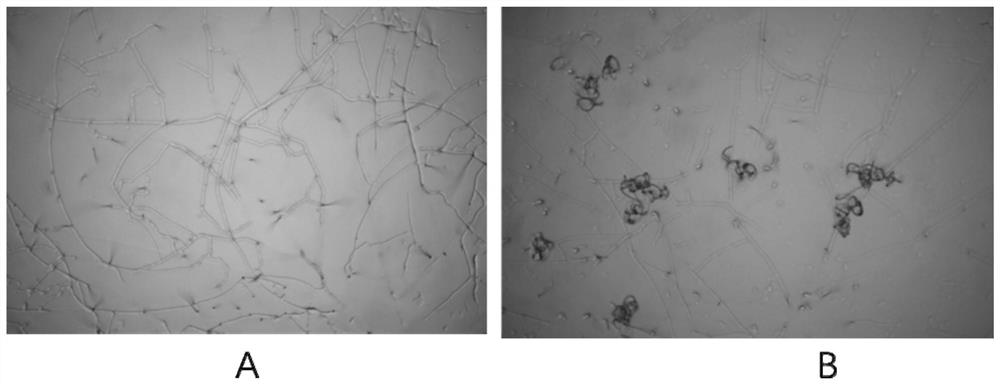
Method for inducing nematode-trapping fungi to generate trapping organ by using nematode extracellular vesicles
A technology for nematode-predating fungi and predatory organs, which is applied in the field of nematode-predating fungi induced by nematode extracellular vesicles to produce predatory organs, can solve the problems such as oligospore Arthrobush and achieve important application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] A method of using extracellular vesicles secreted by nematodes of the present invention to induce nematode-predating fungi to produce predatory organs, comprising the following steps:
[0048] (1) Cultivation of nematodes:
[0049] Medium and buffer of step1 nematodes: NGM solid medium and S Medium liquid medium are used to cultivate nematodes; M9 buffer is used to wash worms and hatch eggs; NGM solid medium 1L: weigh 2.5g of bacto-peptone, chloride Sodium chloride 3g, agar powder 20g, the remaining reagents except agar powder were dissolved in 800mL deionized water, after being completely dissolved, the volume was adjusted to 1L, and 250mL was divided into 500mL conical flasks, and agar powder was added in proportion to each bottle, 121 ℃ autoclave for 20 minutes, when cooled to about 55 ℃, add filter-sterilized 1mL 1M CaCl 2 , 1mL 1M MgSO 4 , 25mL 1M KPO 4 Buffer, 1mL 5mg / mL cholesterol (dissolved in 95% ethanol), mix well, divide into plates, dry and set aside; ...
Embodiment 2
[0076] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is:
[0077] In step (1), the nematodes are synchronized: observe the nematodes cultured for 2 days under a microscope. The eggs in the mother body are arranged in a straight line, and there are fewer larvae in the petri dish. This is the best period for synchronization, and M9 buffer is used. Wash the nematodes off the solid medium. During the cleaning process, repeated vigorous washing should be avoided to cause the agar in the medium to be washed down, which will affect the efficiency of the nematodes in the lysis process. Put the washed nematodes into a 15mL centrifuge tube, add an appropriate amount of M9 buffer to 15mL, let it settle naturally for 3-5min, remove the supernatant, and re-add M9 buffer to 15mL to wash the nematodes; this step needs to be repeated 4-6 times, top Wash the bacteria as far as possible until the clear liquid becomes clear; after removing the excess supernatant, add 2 mL of nematode lysa...
Embodiment 3
[0082] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is: embodiment 2
[0083] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is:
[0084]In step (1), the nematodes are synchronized: put the nematodes cultured for 2.5 days under a microscope, and the eggs in the mother body are arranged in a straight line, and there are fewer larvae in the petri dish. This is the best period for synchronization, and M9 buffer is used. Wash the nematodes off the solid medium. During the cleaning process, repeated vigorous washing should be avoided to cause the agar in the medium to be washed down, which will affect the efficiency of the nematodes in the lysis process. Put the washed nematodes into a 15mL centrifuge tube, add an appropriate amount of M9 buffer to 15mL, let it settle naturally for 3-5min, remove the supernatant, and re-add M9 buffer to 15mL to wash the nematodes; this step needs to be repeated 4-6 times, top Clean the bacteria as much as possible until the liquid tu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com