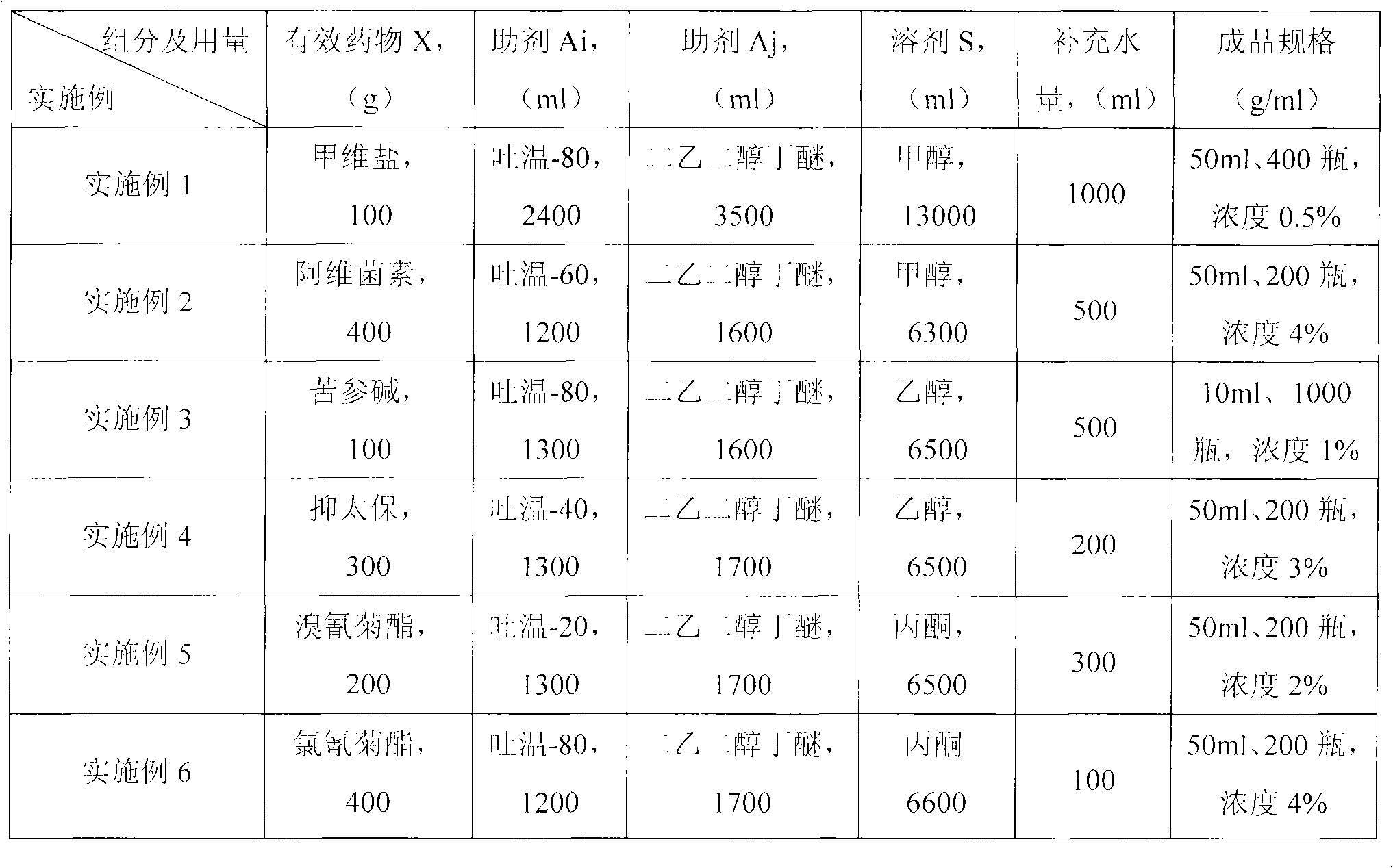Patents
Literature
38 results about "Xylophilus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Xylophilus is a species of proteobacteria, which causes plant disease. It is available from the NCPPB in the United Kingdom for legitimate researchers and plant disease diagnosticians working in premises licensed to hold it.
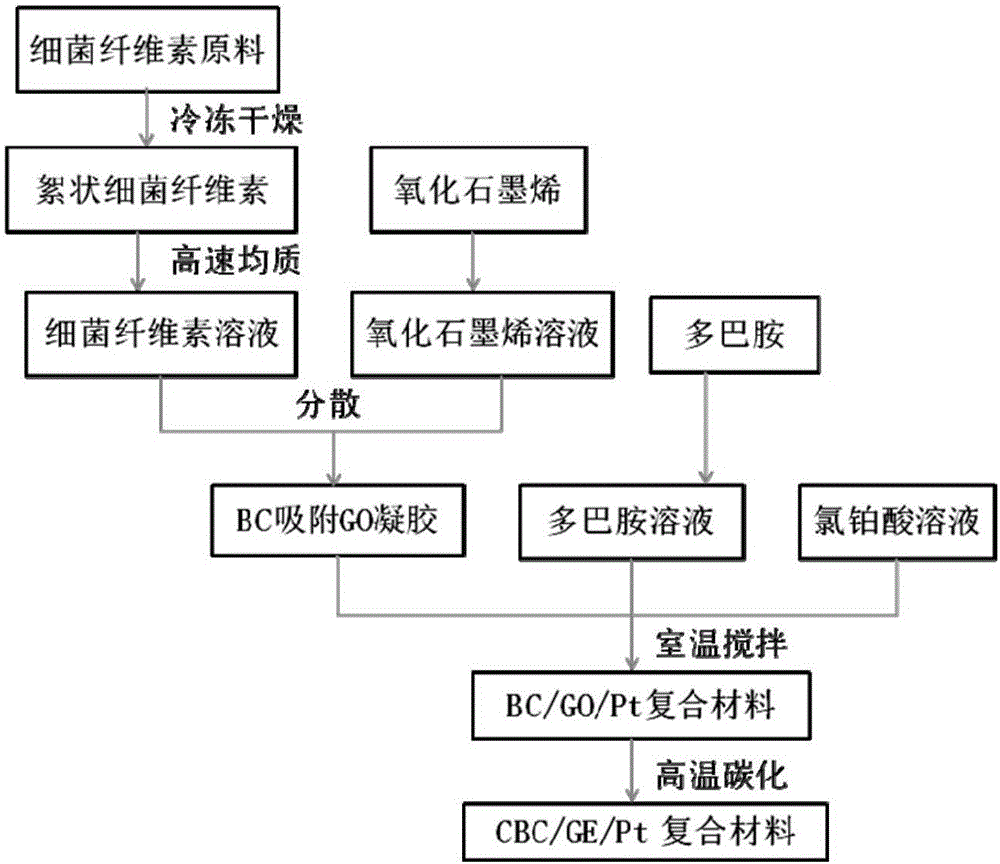
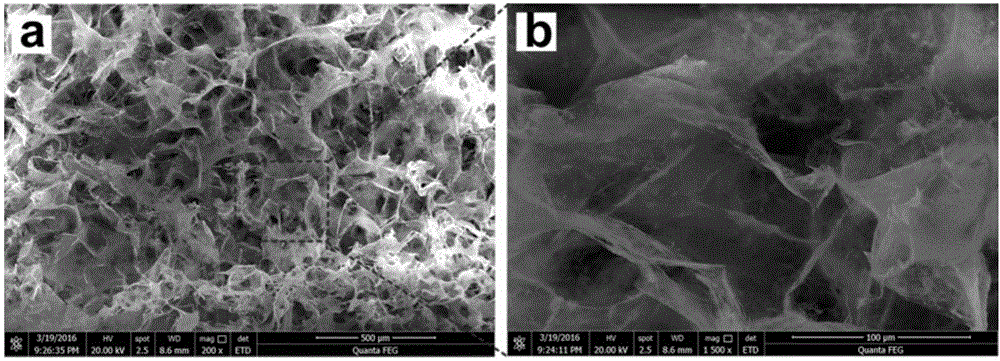
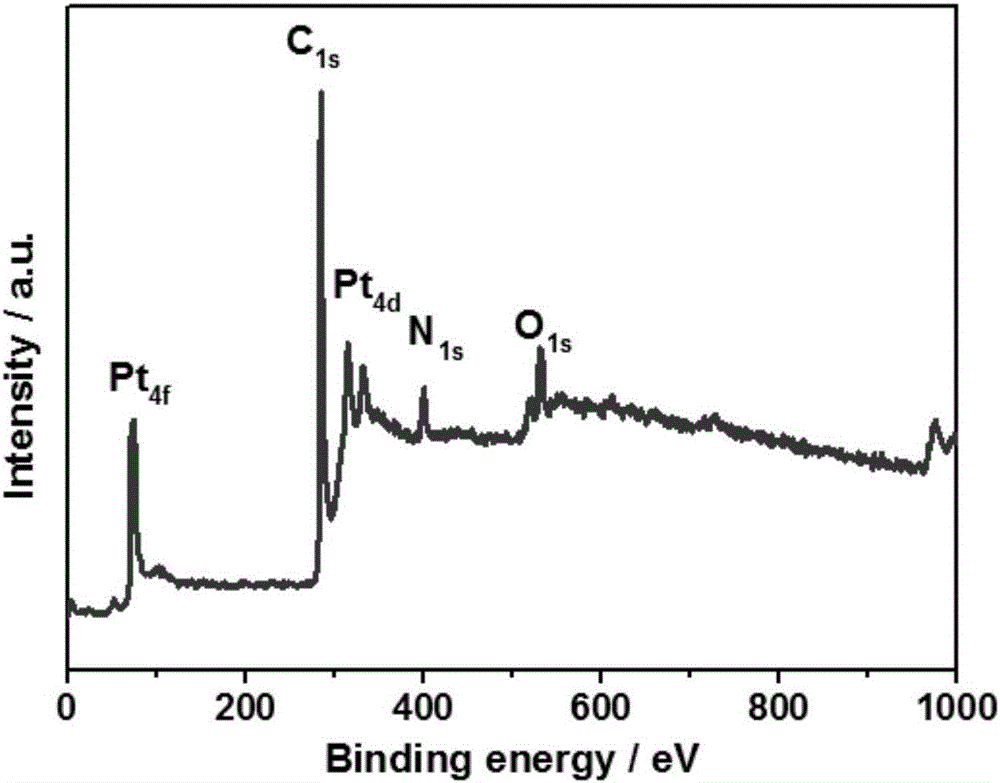
Nitrogen doping carbonized bacterial cellulose/graphene/platinum composite nanomaterial and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106410223AAvoid stackingImprove catalytic performanceMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesCross-linkCarbonization
The present invention discloses a preparation method of a nitrogen doping carbonized bacterial cellulose / graphene / platinum composite nanomaterial. The material is prepared according to the following steps of pre-treating flocculent bacterial cellulose generated in fermentation of acetobacter xylophilus, then refrigering and drying the flocculent bacterial cellulose so as to obtain flocculent bacterial cellulose; homogenizing at high speed so as to obtain a uniform solution, mixing the uniform solution with graphene oxide, and dispersing the mixture uniformly through ultrasonic; and adding a dopamine solution, stirring and mixing by using a machine, adding chloroplatinic acid finally, and carbonizing at high temperature so as to obtain the nitrogen doping carbonized bacterial cellulose / graphene / platinum composite nanomaterial. The composite nanomaterial prepared by the method uses a one-step method to carbonize, and the reaction process is easy. Under the action of the dopamine, the flocculent bacterial cellulose and the graphene oxide are bonded, so as to form a three-dimensional networked cross-linked skeleton structure. In carbonization, nitrogen doping and platinum reduction are realized, and the conductive nanometer composite system that has small and uniformly distributed particles is prepared. The nanomaterial prepared by the method can be applied to application fields such as fuel batteries and super capacitors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
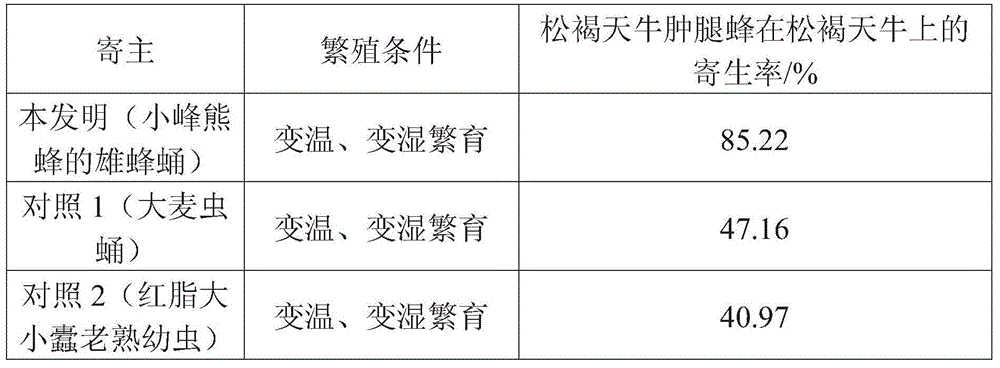
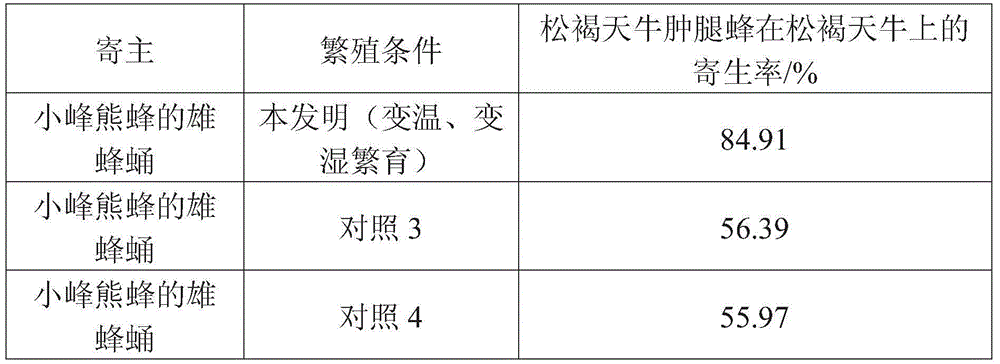
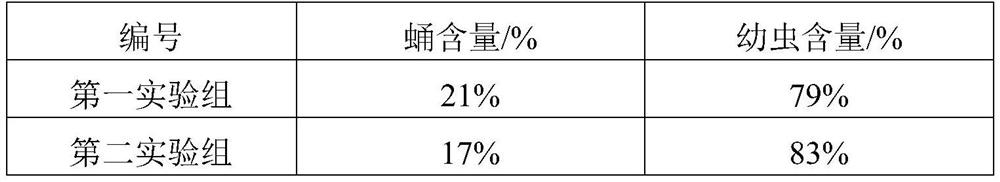
Technology for artificial domestication and breeding of sclerodermus and applied to prevention and treatment of pine sawyer beetles
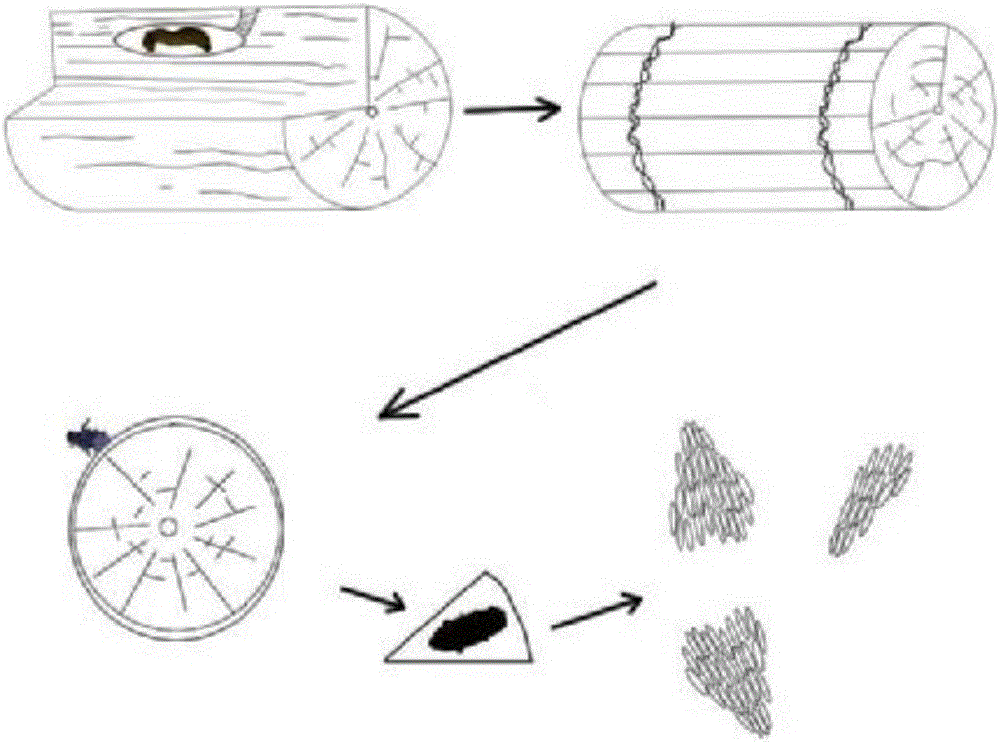
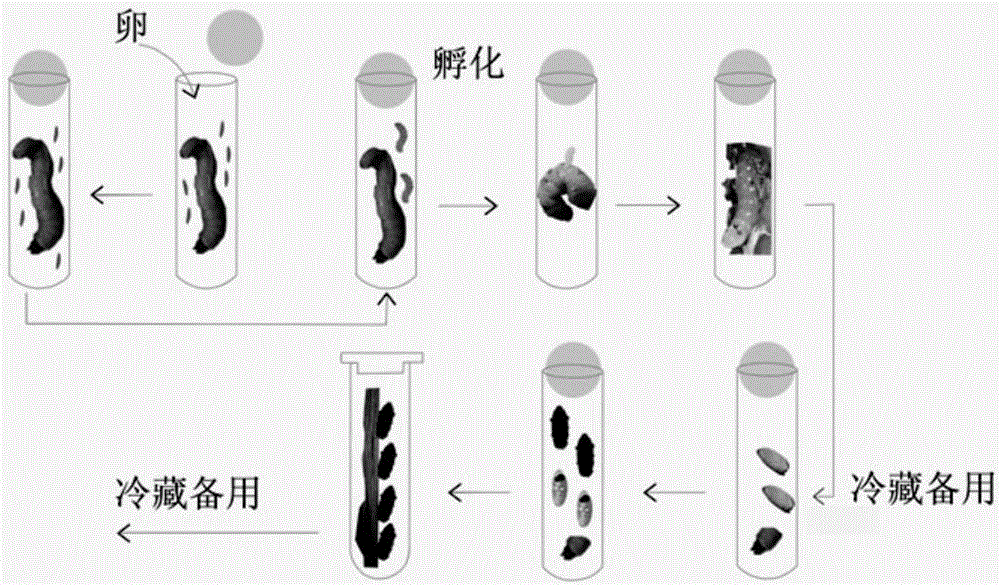
The invention discloses a technology for artificial domestication and breeding of sclerodermus and applied to prevention and treatment of pine sawyer beetles. The technology for artificial domestication and breeding of sclerodermus comprises the following steps of: firstly, feeding the sclerodermus to be substituted for the host of a barley pest; secondly, carrying out the selecting and refrigerating treatment of female sclerodermus; thirdly, packing the initiated pupa barley pest and the female sclerodermus into a finger-shaped tube, and plugging the tube with an ordered pine plug; and finally, neatly stacking and placing the tubes into a weather cultivation box with a cultivation temperature and conditions as well as prompts. In a bursaphelench xylophilus epidemic area, the throwing technology of sclerodermus comprises the following steps of: firstly, setting bait woods to induce the pine sawyer beetles to lay eggs; then examining the parasitic situation of the pine sawyer beetles in a pine tree section in an appropriate weather condition, and releasing the sclerodermus according to the groove number of the sawyer beetles; and finally investigating the parasitic situation of the sclerodermus. By the adoption of sawyer pests to prevent and treat the pine sawyer beetles so as to inhibit the occurrence of a bursaphelench xylophilus disease, the environment can not be polluted, the ecological balance is maintained, the biological diversity is kept, and the technology is an advanced technology for controlling the pine sawyer beetles and the bursaphelench xylophilus disease.
Owner:浙江森得保生物制品有限公司 +2
Bacillus pumilus and application thereof for killing bursaphelenchus xylophilus with poison
ActiveCN101899408ASimple cultivation conditionsEasy to storeBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismBacillus pumilus
The invention discloses a bacillus pumilus JK-SD001. Subclass thereof is named as Bacilluspumilus and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection CCTCC, preservation number thereof is M 209095, and preservation date is May 4th, 2009. The invention also discloses application of bacillus pumilus for killing bursaphelenchus xylophilus with poison. The invention also provides a micro organism bursaphelenchus xylophilus killing agent, obtained by the way that JK-SD001 is inoculated to a culture medium to be fermented and cultured and filtering is carried out by virtue of a filter with the aperture of 0.22Mum. The micro organism bursaphelenchus xylophilus killing agent of the invention has higher toxicity on bursaphelenchus xylophilus (B. xylophilus), and culture condition is simple and preservation is easy, thus being easy for industrialized production and having good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Pesticide for preventing and controlling Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and injection method thereof
ActiveCN101658176AGood control effectSimple injection methodBiocideNematocidesElectricityDendrolimus houi
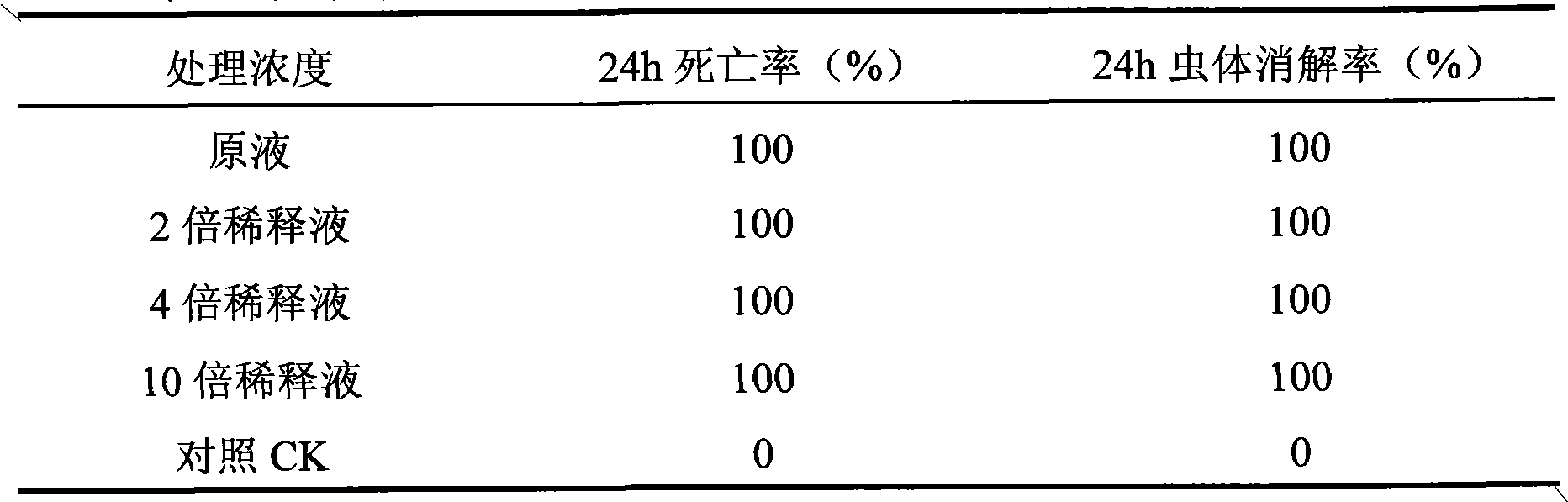
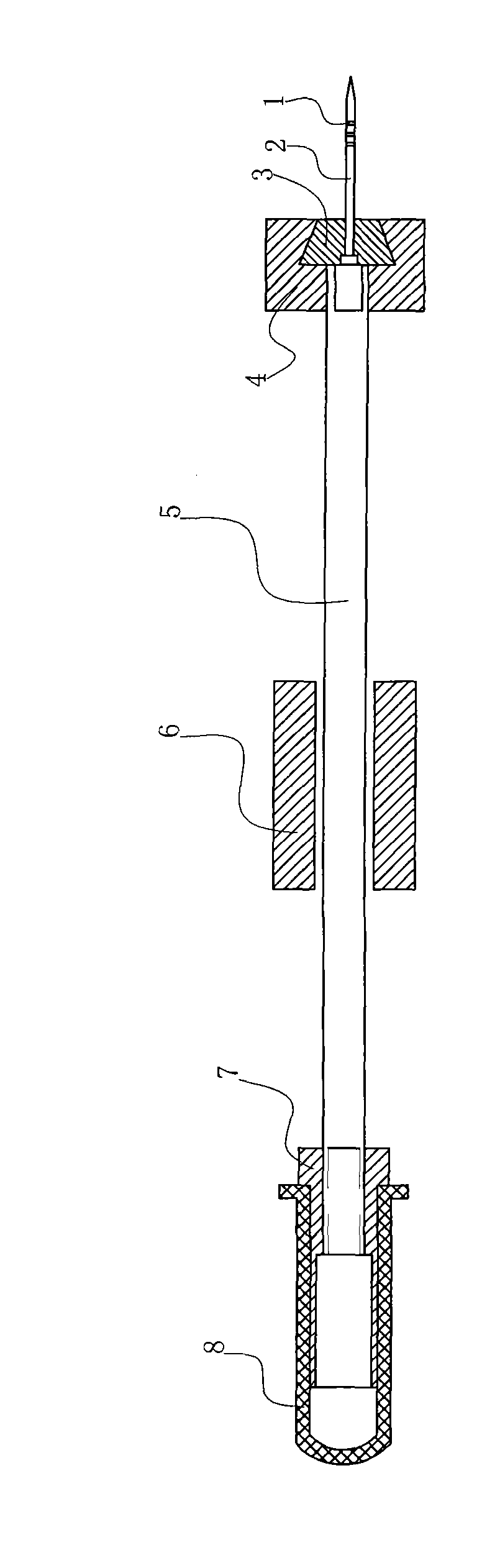
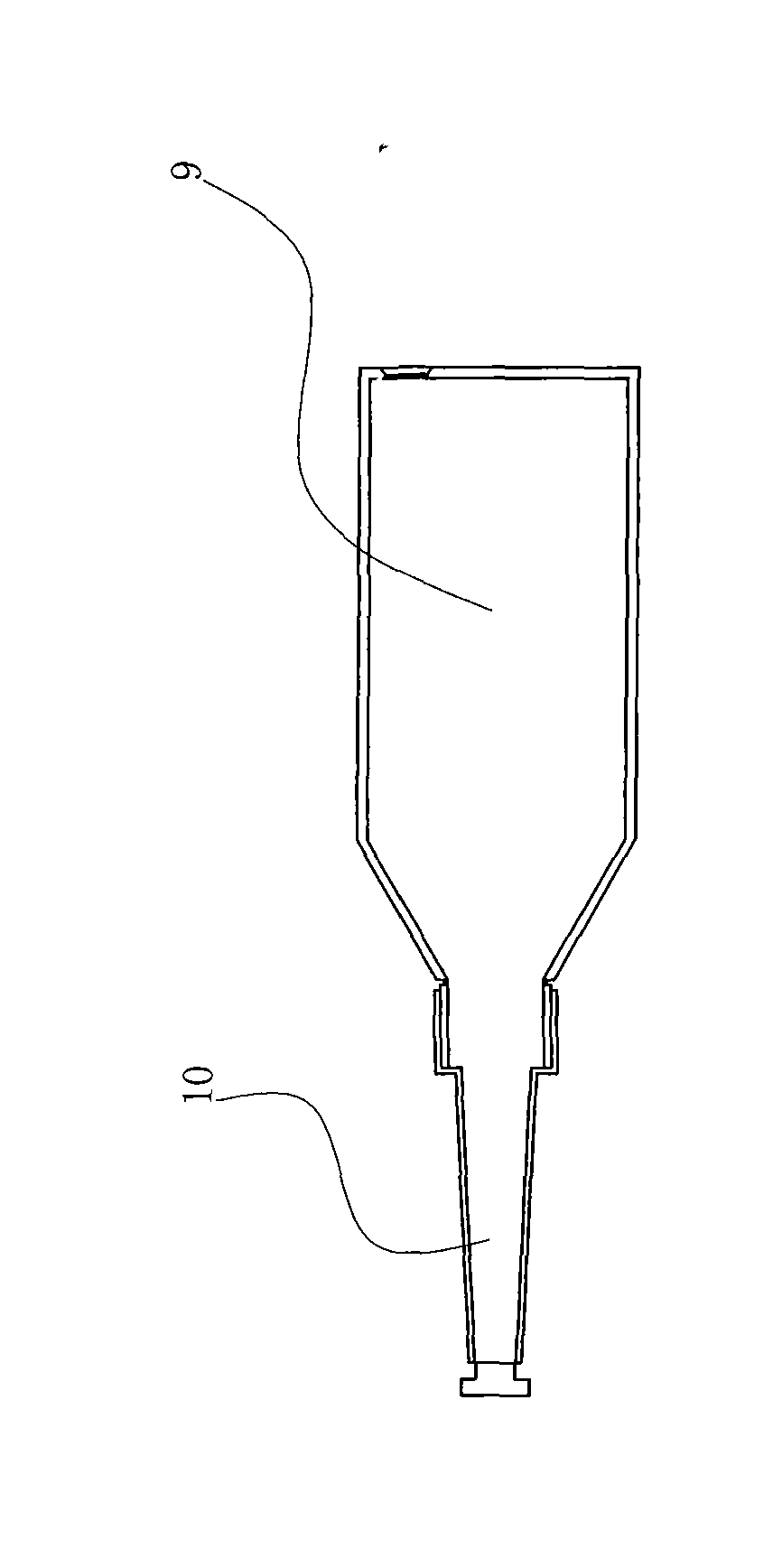
The invention provides a pesticide for preventing and controlling Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and an injection method thereof. The pesticide for preventing and controlling Bursaphelenchus xylophilus comprises an effective medicament X, compound auxiliaries Ai-Aj and solvent S which form an X-Ai-Aj-S system; based on preparing 1L of the pesticide, the consumption of the compositions is that: the consumption of the effective medicament X is 5 to 40g, the consumption of the auxiliary Ai is 100 to 150ml, the consumption of the auxiliary Aj is 150 to 200ml, the consumption of the solvent S is 600 to700ml, and the balance is water; and the concentration of the prepared pesticide is 0.5-4g / ml. Through experiments, the pesticide has good effect of preventing and controlling the Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, and also has good effect of preventing and controlling Monochamus alternatus Hope, Atysa marginata cinnamomi Chen, sweetgum palmerworms, Dendrolimus houi Lajonquiere, Hylobius abietis, pine bark beetles and the like; and drilling machinery provided by the invention and the injection method adopting the drilling machinery are simple and practical, do not consume fuel or electricity, and are particularly suitable to meet the requirement of preventing and controlling plant diseases and insect pests in mountain woods and forests.
Owner:来燕学
Method for effectively controlling bursaphelenchus xylophilus by biologically controlling monochamus alternatus
InactiveCN104871886AIncreased parasitic abilityAnimal huntingPlant protectionBombus hypocritaZoology
The invention discloses a method by the adoption of biological control. According to the method, the populations of the monochamus alternatus of pine forests are obviously reduced and controlled, and the number of pines which die from bursaphelenchus xylophilus is also obviously reduced. Drone pupae of bombus hypocrita are adopted as hosts of sclerodermus sp., meanwhile proliferation conditions are regulated and controlled, and therefore the parasitic ability of the sclerodermus sp. obtained through proliferation is remarkably improved.
Owner:INST OF FOREST ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT & PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
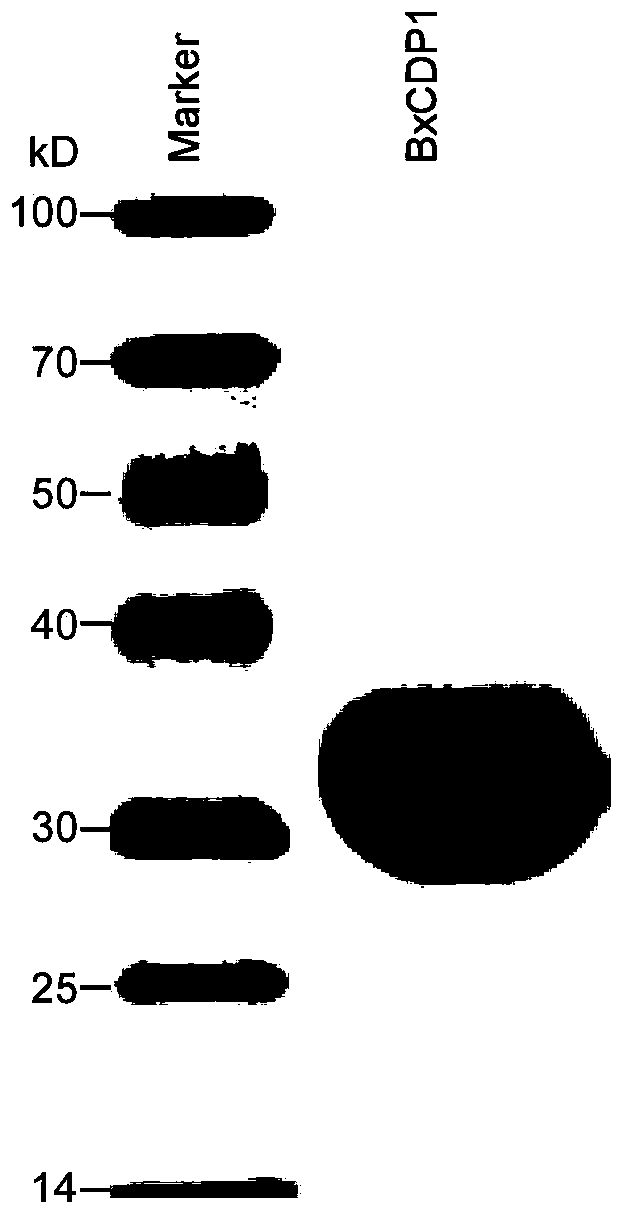
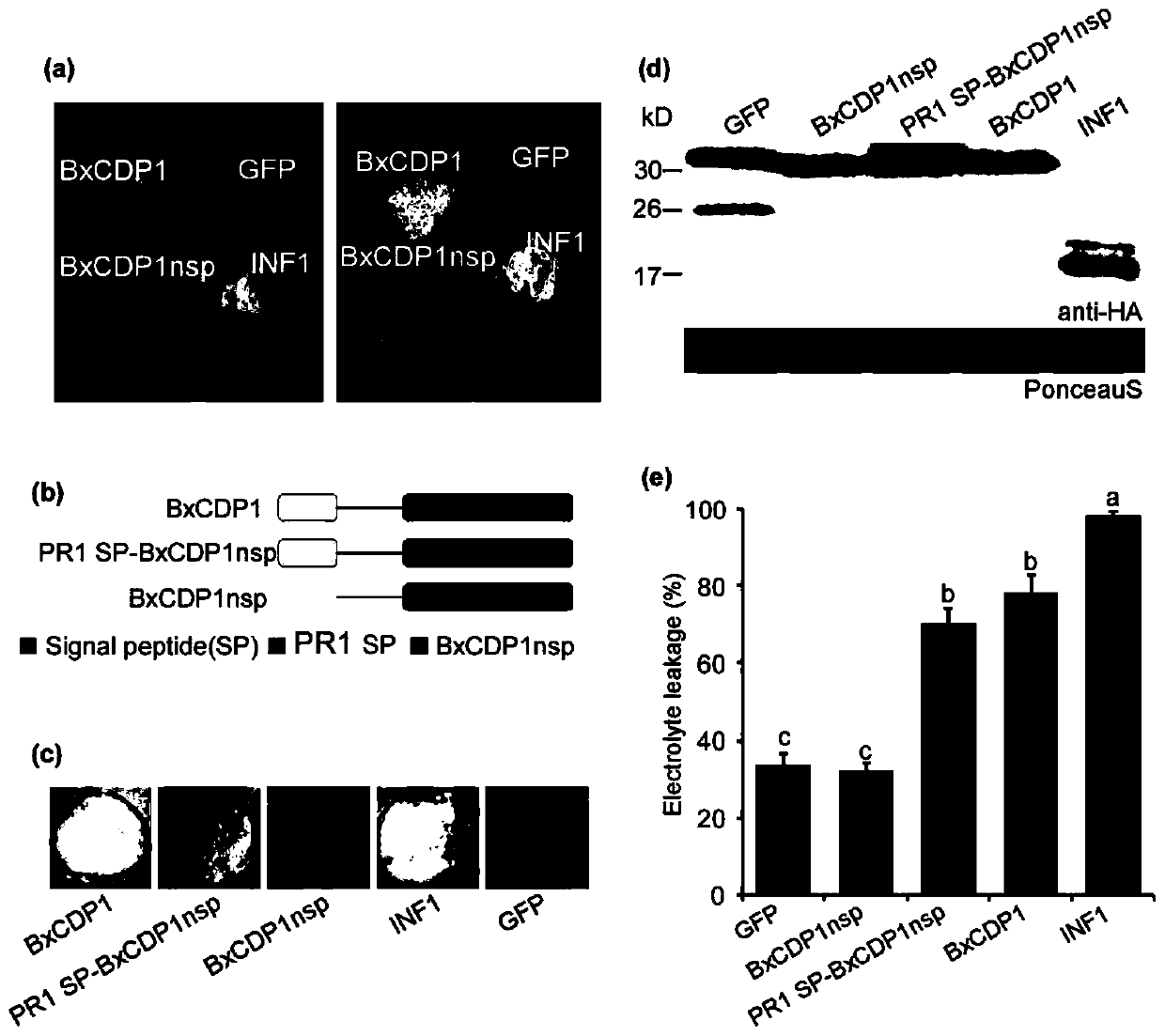
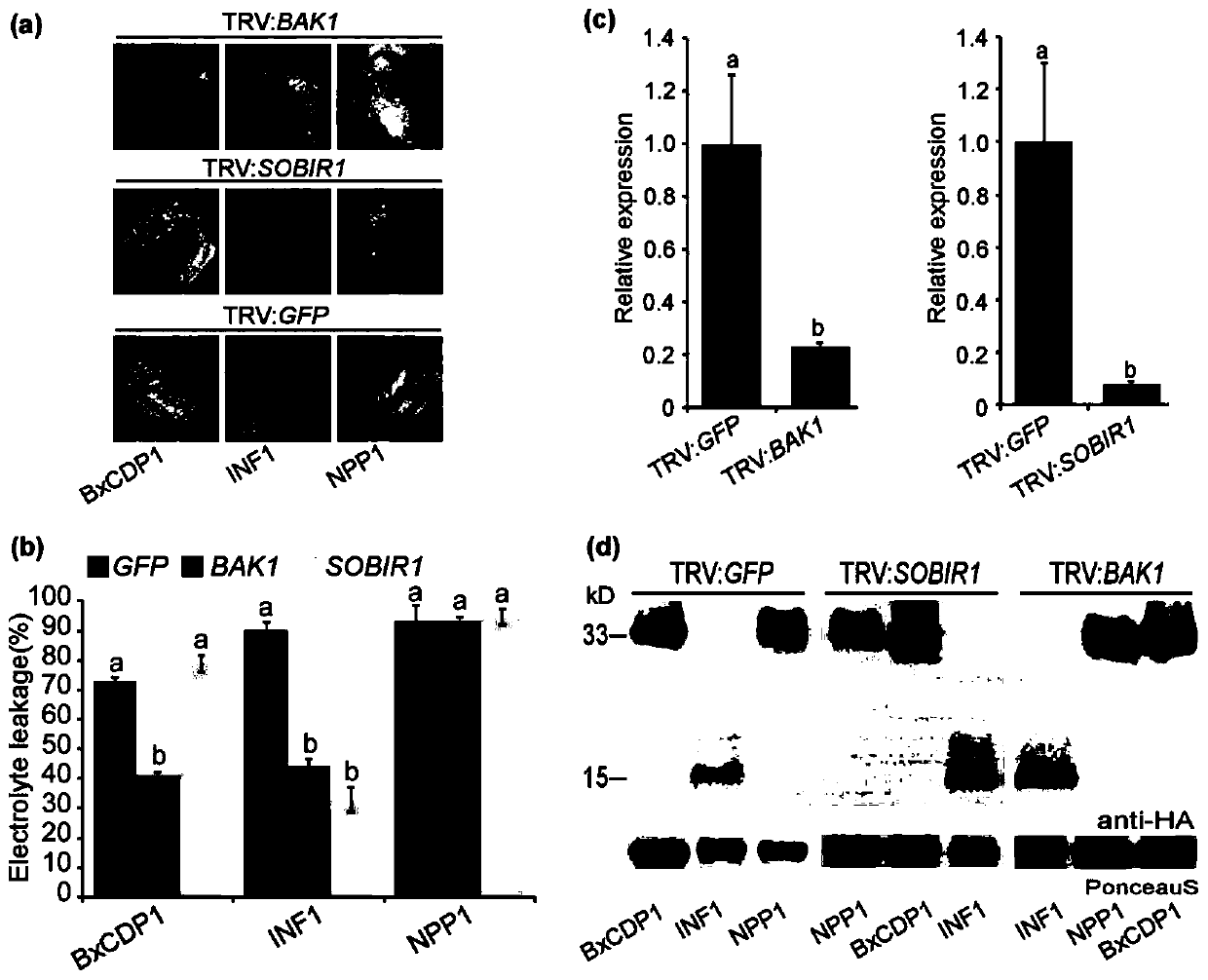
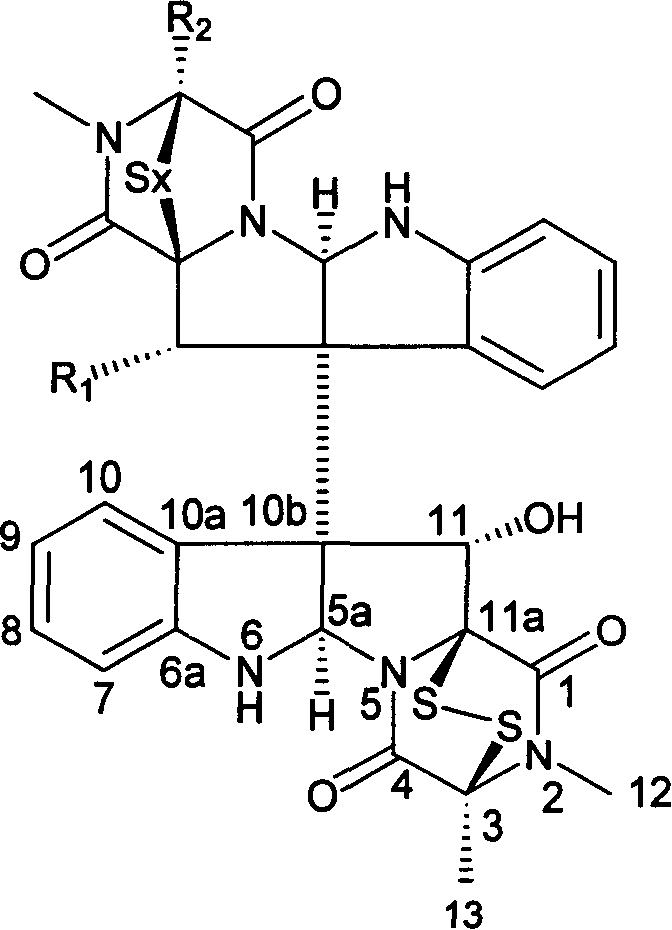
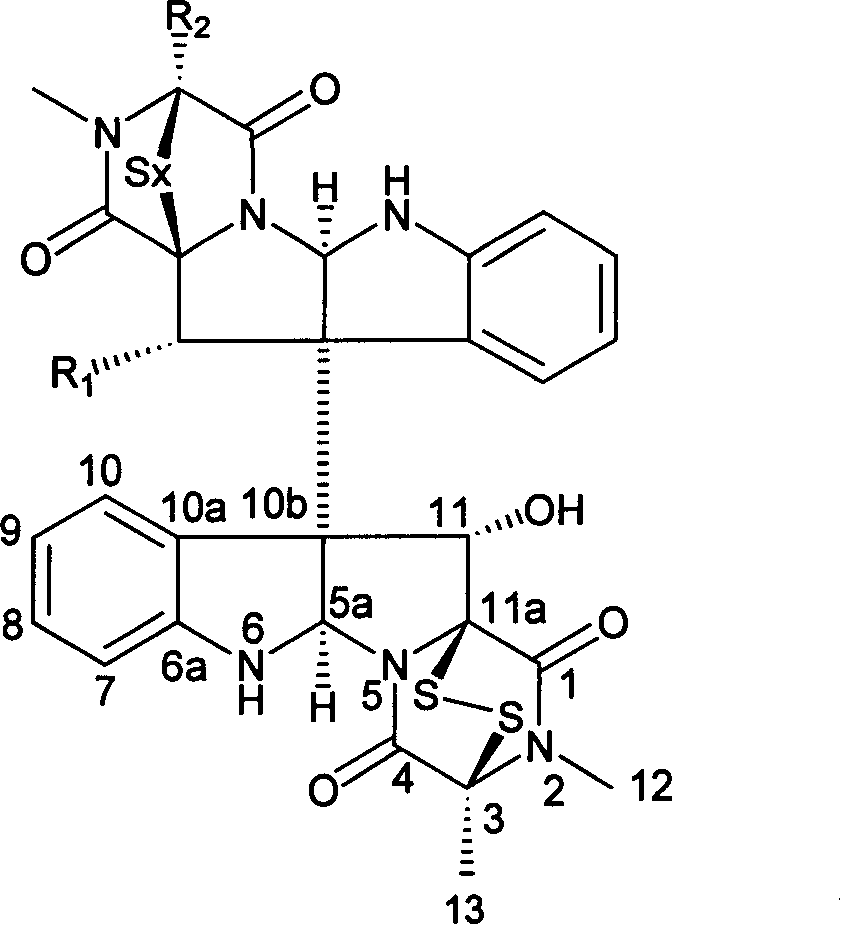
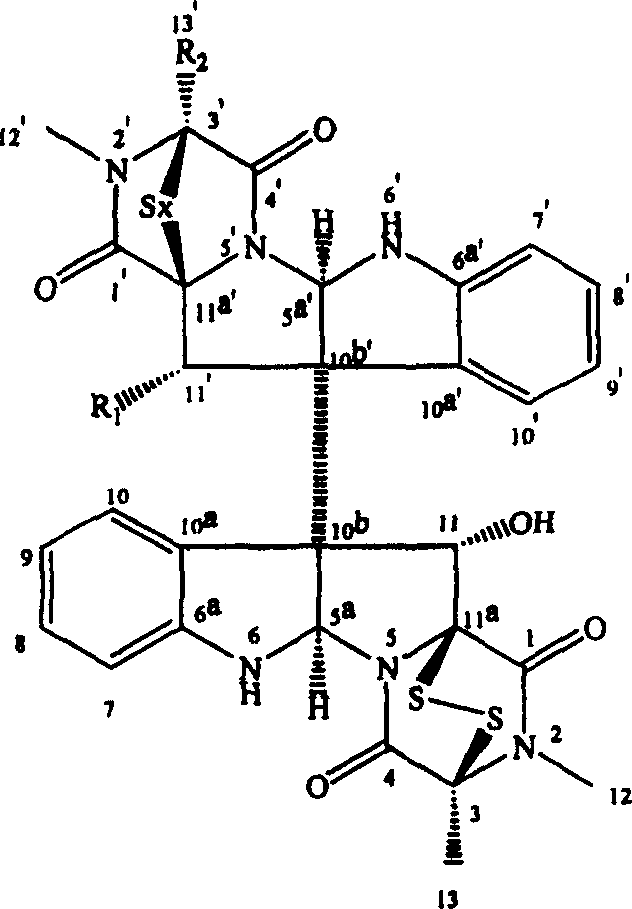
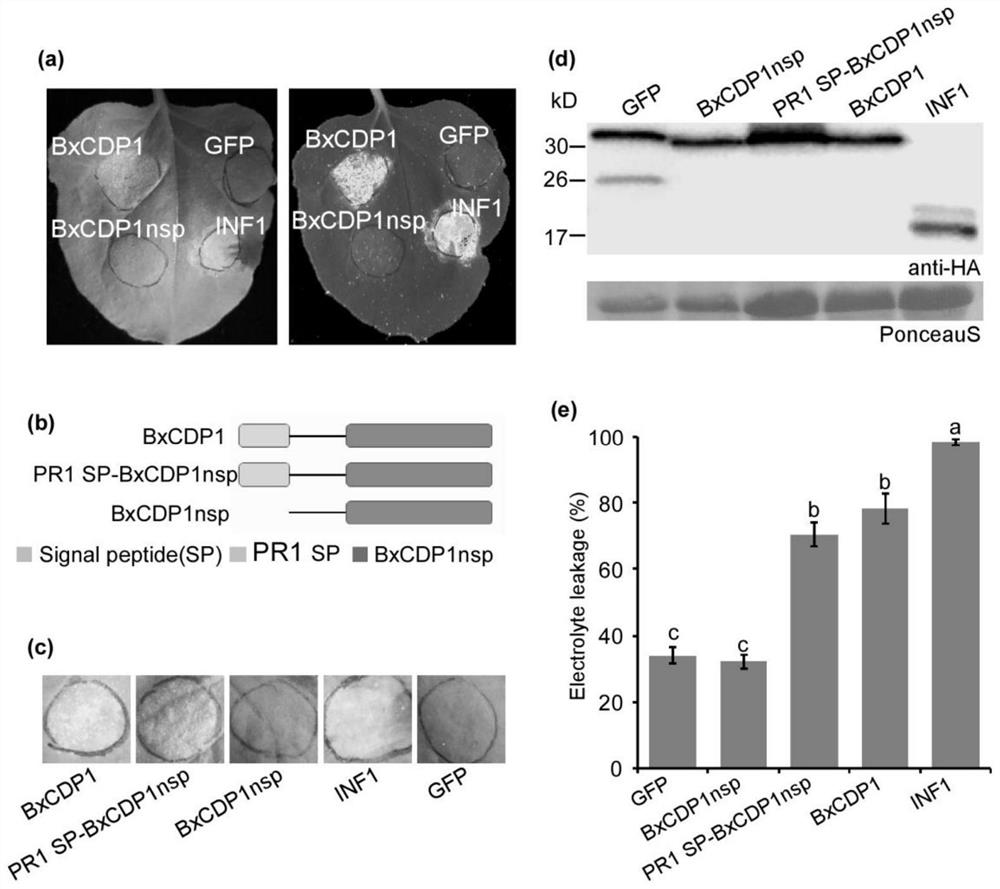
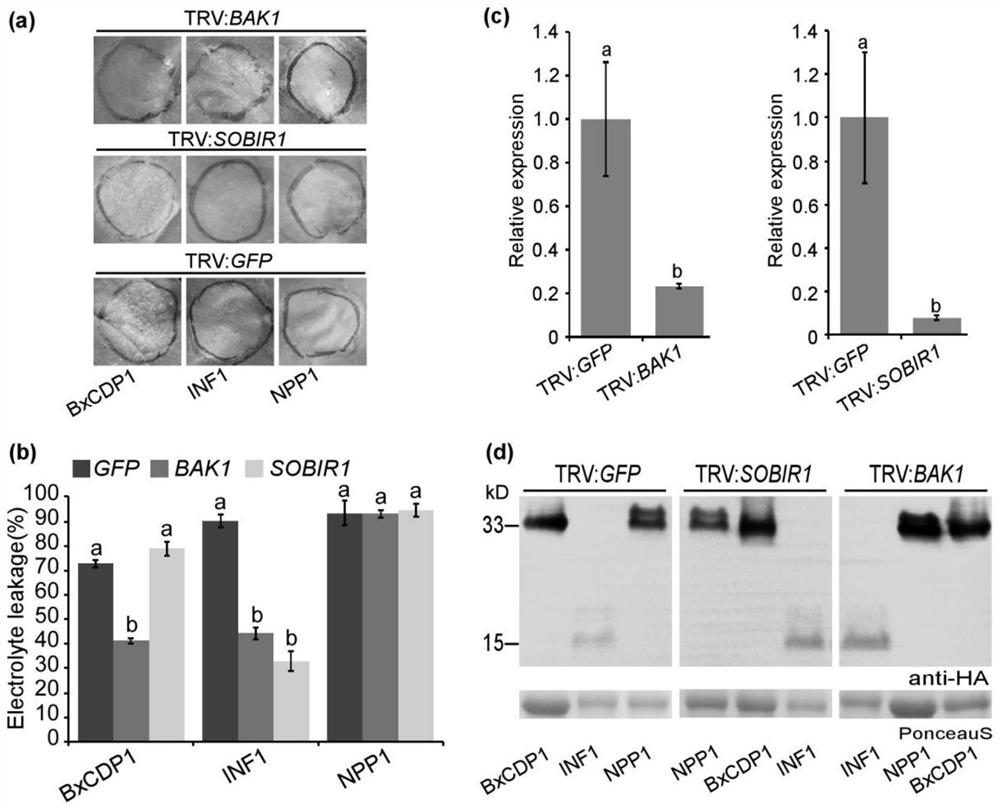
Protein BxCDP1 of bursaphelenchus-xylophilus pathogen-associated molecular patterns and application thereof
ActiveCN110156885AIncrease resistanceActivate immune responseFermentationAnimals/human peptidesHost plantsAmino acid
The invention discloses protein BxCDP1 of bursaphelenchus-xylophilus pathogen-associated molecular patterns and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the protein BxCDP1 of the pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPS) is shown in SEQID NO.2. From effectors secreted by bursaphelenchus xylophilus and the PAMP, the defensive responses of a host plant, namely, a pine tree, to bursaphelenchus xylophilus invasion are studied, the protein BxCDP1 of the pathogen-associated molecular patterns is obtained from the bursaphelenchus xylophilus, it is proven through experiments that the protein BxCDP1 can trigger cell necrosis of various plants including the host plant, has a certain broad spectrum in cell necrosis triggering, and stimulates the defensive response of the host plant. The BxCDP1 triggered cell necrosis depends on a co-receptor BAK1 of pattern recognition receptors, the BxCDP1 can stimulate the accumulation of nicotiana benthamiana ROS and up regulation of PTI Marker genes, and the immunoreaction of the nicotiana benthamiana is stimulated. It can be seen that the BxCDP1 is a PAMP secreted by the bursaphelenchus xylophilus, and has important theoretical and practicalsignificance for revealing the pathogenic mechanism of the bursaphelenchus xylophilus and improving the resistance of the pine tree to the bursaphelenchus xylophilus in a targeted mode.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Preparation method for trunk injecting microcapsule pesticide for controlling Bursaphelenchus xylophilus
InactiveCN106035356AEfficient killingReduce the cost of prevention and treatmentBiocideDead animal preservationCompound aEmulsion
The invention discloses a preparation method for a trunk injecting microcapsule pesticide for controlling Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and aims to prepare a pesticide capable of controlling occurrence of the Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. A microcapsule technology is adopted to compound a chitinase inhibitor pesticide with an abamectin biopesticide, and the preparation method comprises the specific flow as follows: (1) the chitinase inhibitor pesticide is ground with diesel oil as an assistant, and ointment is prepared; (2) the biopesticide is dissolved with a solvent and mixed with the ointment, and the mixture is stirred uniformly; a synergist, a surfactant and water are added, the materials are heated and stirred to be emulsified and dispersed, and an emulsion is prepared; (3) a wall material aqueous solution is added to the emulsion and stirred at the constant temperature of 55-65 DEG C, a microcapsule forming reaction is performed, a product is cooled after the reaction, and the trunk injecting microcapsule pesticide is prepared. The pesticide prepared with the method can kill the Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and larvae of monochamus alternatus. The period of validity of the pesticide in a trunk can be 2 years or longer, and the Bursaphelenchus xylophilus killing rate can be 100%.
Owner:南通伟德动力电池研究所(普通合伙)
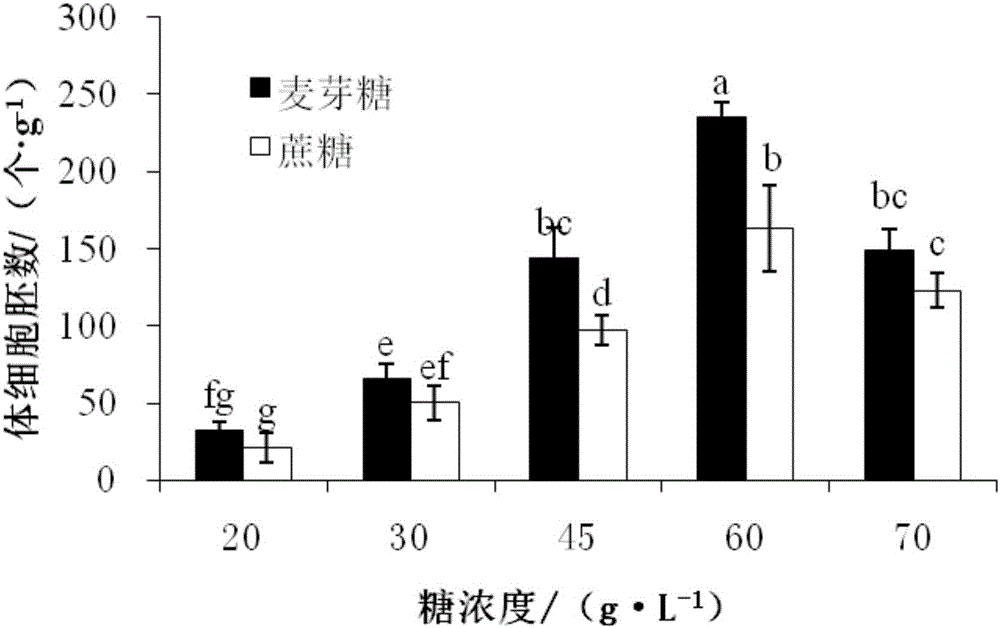
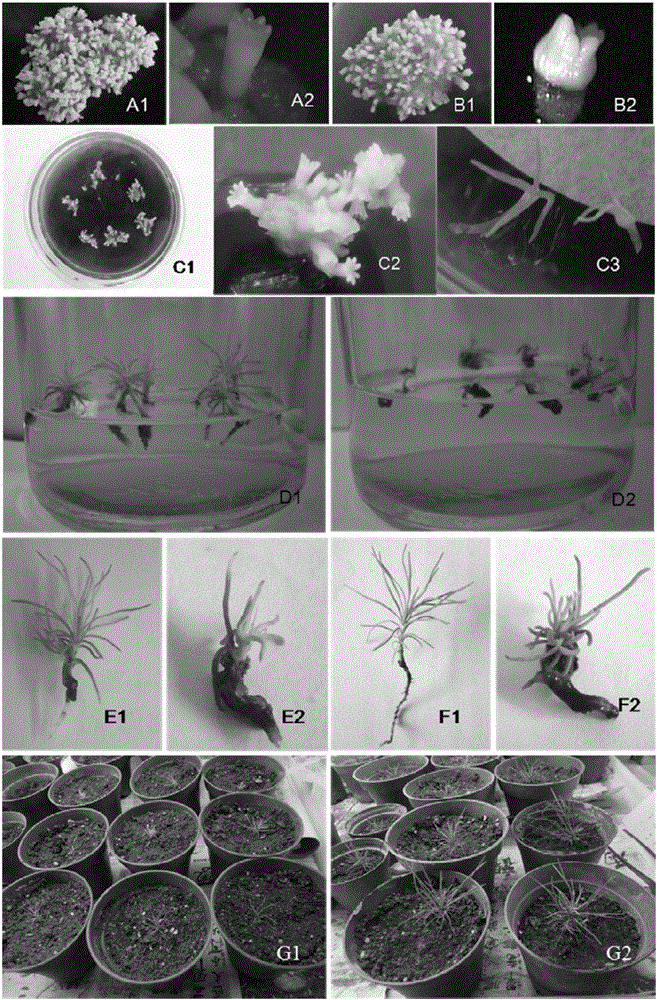
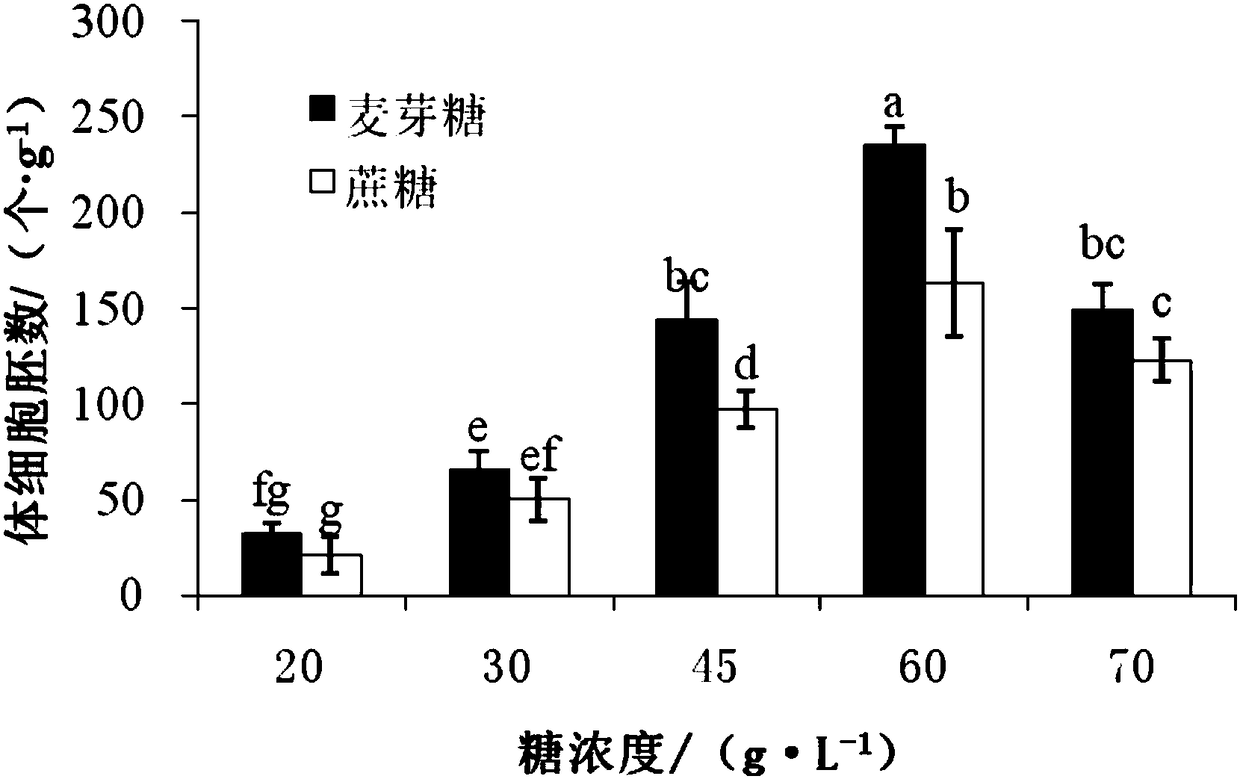
High-synchronization bursaphelenchus xylophilus resistant pinus densiflora somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration method
ActiveCN106718889AImprove germination rateImprove conversion rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSomatic embryogenesisXylophilus
The invention discloses a high-synchronization bursaphelenchus xylophilus resistant pinus densiflora somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration method. The high-synchronization bursaphelenchus xylophilus resistant pinus densiflora somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration method comprises the steps of inducement and proliferation of embryonic callus as well as maturation, germination and transformation of somatic embryos; and the maturation culture of the somatic embryos is carried out by using a liquid-solid proliferation-solid maturation method. According to the high-synchronization bursaphelenchus xylophilus resistant pinus densiflora somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration method, with immature zygotic embryos of bursaphelenchus xylophilus resistant pinus densiflora as explants, mature somatic embryos and regenerated plants are successfully obtained by carrying out tests, such as somatic embryo maturation, germination and plant regeneration, on the embryonic callus obtained by successfully inducing the immature zygotic embryos of bursaphelenchus xylophilus resistant pinus densiflora; the mature somatic embryos and the regenerated plants are transplanted and survive; and the germination rate and plant transformation rate of the somatic embryos generated on a maturation culture medium are high and are respectively 67.2% and 46.5%; therefore, the high-synchronization bursaphelenchus xylophilus resistant pinus densiflora somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration method provides an important scientific basis and technical support for large-scale propagation and factory production of the bursaphelenchus xylophilus resistant pinus densiflora.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
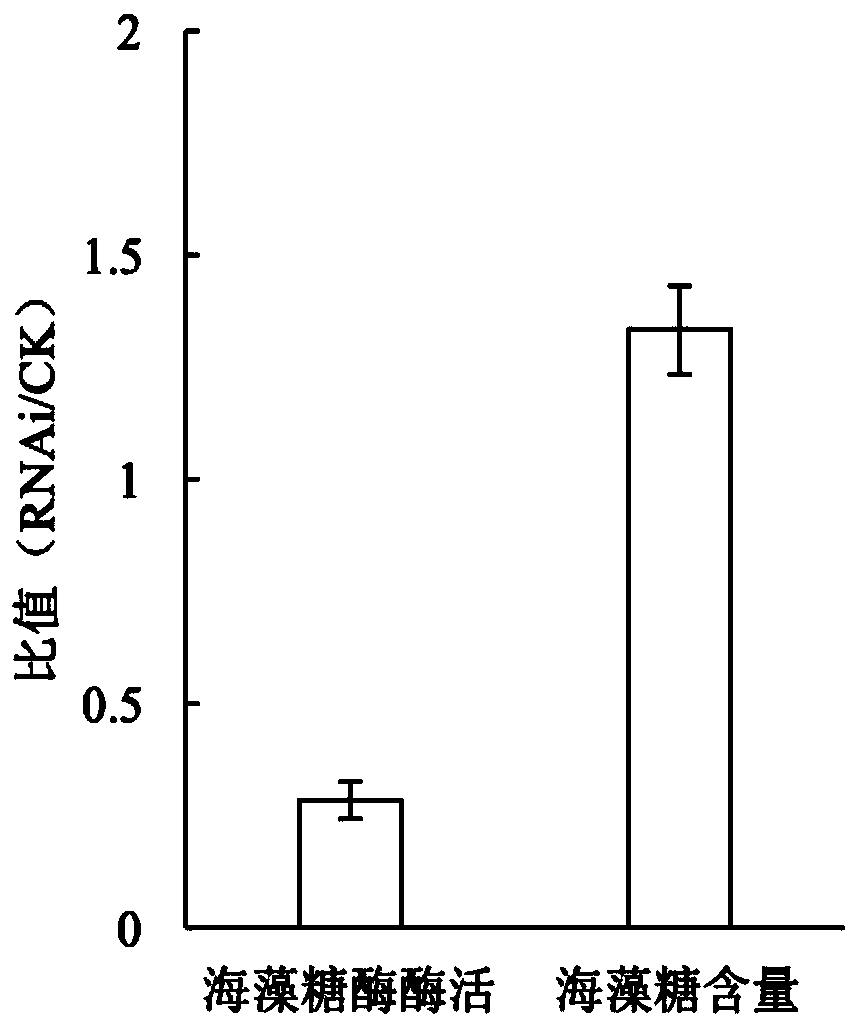
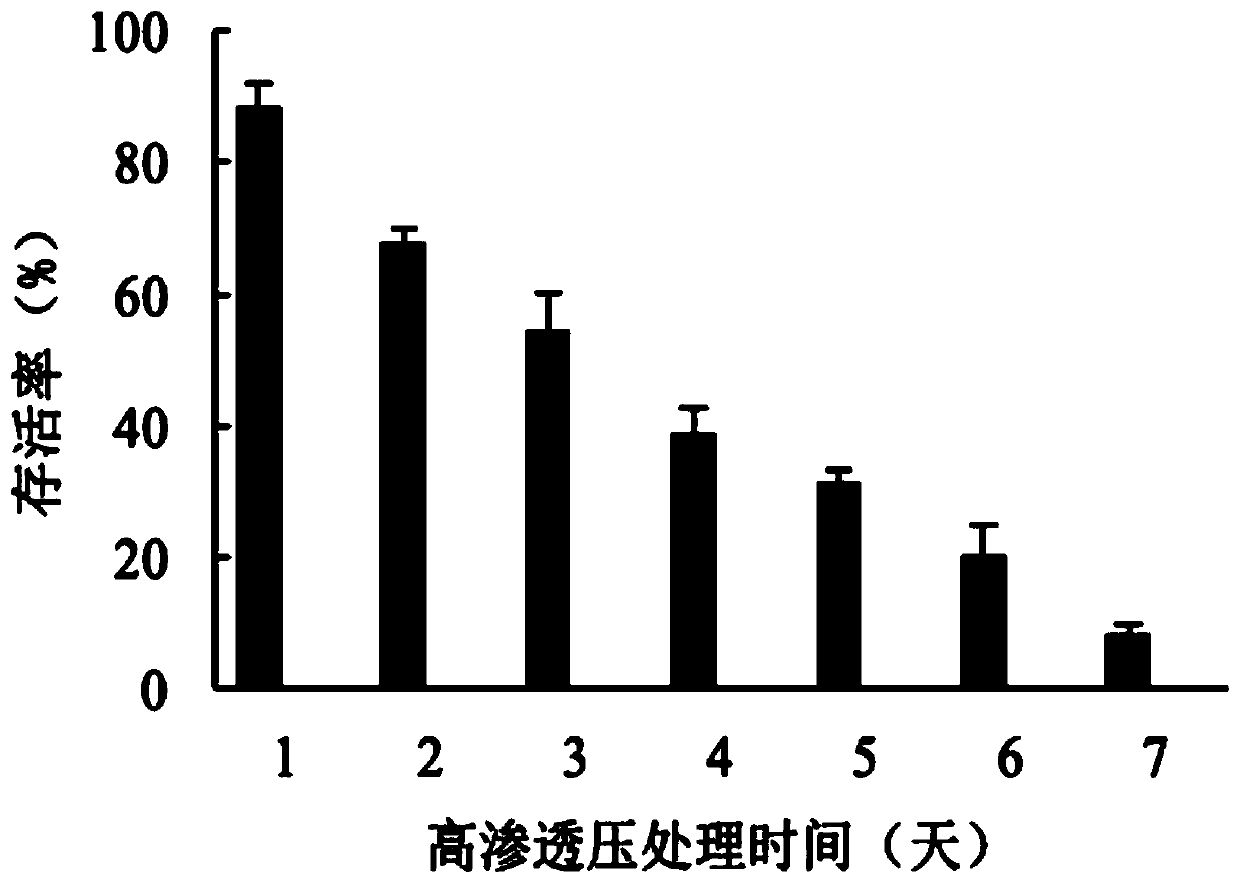
Trehalase gene Bx-tre1 and application thereof
ActiveCN110257407ABlock metabolic pathwayReduced survival rateBiocideNematocidesLarva currensGene silencing
The invention relates to trehalase gene Bx-tre1 and application thereof and aims to solve the problem of bursaphelenchus xylophilus spread due to the fact that stress-resistant larvae of bursaphelenchus xylophilus are capable of starting a variable percolation state to survive in a high-permeation-pressure environment. The trehalase gene Bx-tre1 is applied to pine tree disease and pest prevention and control. A nucleotide sequence of the trehalase gene Bx-tre1 is shown as Seq ID NO:1 in a sequence table. By gene silencing, the expression quantity of the trehalase gene in male bursaphelenchus xylophilus can be reduced, trehalase activity can be effectively lowered, a trehalose metabolism path is blocked, and accordingly the survival rate of the male bursaphelenchus xylophilus under high-permeation-pressure stress is remarkably decreased, and sexual propagation is further inhibited. The trehalase gene Bx-tre1 is applied to the field of bursaphelenchus xylophilus prevention and control.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Biological control method for bursaphelenchus?xylophilus
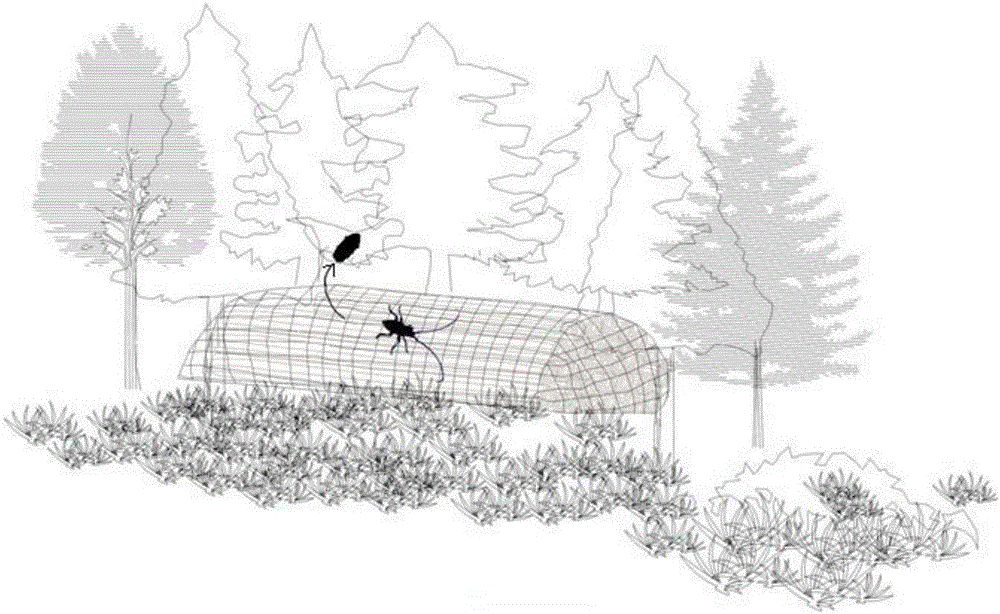
The invention discloses a biological control method for bursaphelenchus?xylophilus. The biological control method comprises the following steps: firstly, taking a manually set device for trapping dastarcus helophoroide eggs to collect eggs of dastarcus helophoroides so as to obtain egg cards; placing part of the egg cards in a culture box, and performing cultivation to obtain chrysalises; and after the chrysalises emerge into bursaphelenchus xylophilus imagoes in 20-30 days, collecting the imagoes into a container to obtain imagoes. Pine disease wood piles are arranged in each bursaphelenchus xylophilus affected area, the egg cards or imagoes are put into the pine disease wood piles in March and April every year and the pine disease wood piles are enwrapped by an isolation material for isolation. Compared with the prior art, according to the biological control method disclosed by the invention, epidemic situations are controlled on the spot, and an affected area is changed into a place for naturally breeding dastarcus helophoroides, so that the labor intensity of epidemic prevention is greatly reduced, the epidemic prevention efficiency is improved, the epidemic prevention effect can be ensured for many years after the residence of the dastarcus helophoroides, and the biological control method is suitable for controlling bursaphelenchus xylophilus in mountain woods and forests.
Owner:来燕学
Pesticide application method for handling monochamus alternatus in bursaphelench xylophilus diseased wood
In a bursaphelench xylophilus disease area, dead and dying trees whose forest stand is not cleared and pines around houses of farmers are collected on the spot before the eclosion and migration of monochamus alternatu imagoes, and are cut into wood segments with length less than 2 cm, thiamethoxam moiety powder is sprayed on the wood segments, and the wood segments are tightly covered by plastic films. The handled wood segments can be used as fuel wood whenever being taken, and after being used, the handled wood segments are covered tightly. By the next summer, monochamus alternatus in the forest stand of the handled wood segments died, and the monochamus alternatu imagoes cannot lay eggs on the wood segments and decompose and decay voluntarily after the plastic films are opened. The pesticide application method for handling the monochamus alternatus in the bursaphelench xylophilus diseased wood can effectively reduce the amount of the monochamus alternatus, and thereby the spreading of the bursaphelench xylophilus disease is controlled, people and livestocks cannot be damaged, time and labor are saved, and the cost is low.
Owner:ZUNYI INST OF FORESTRY
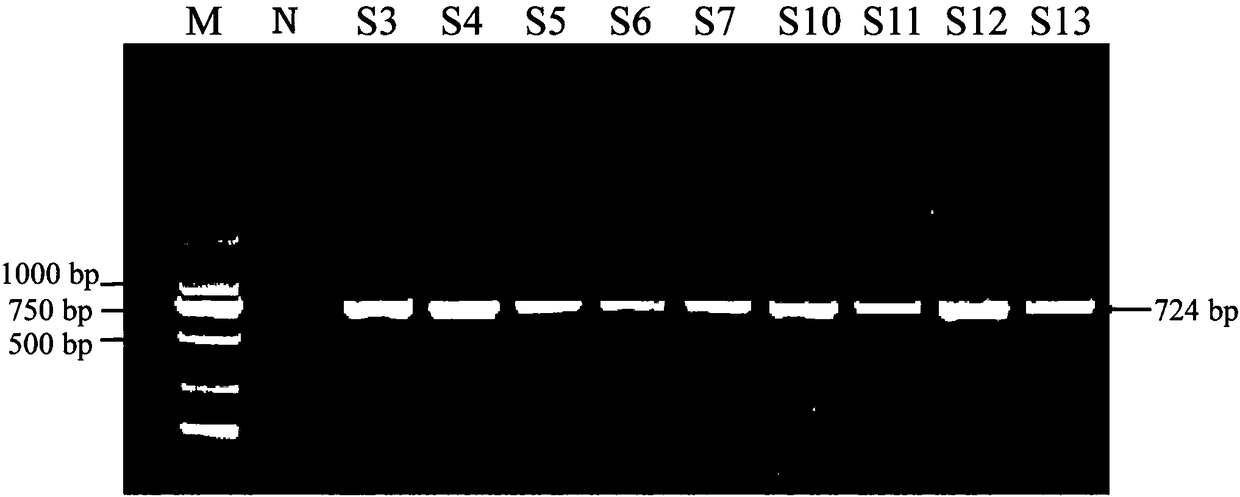
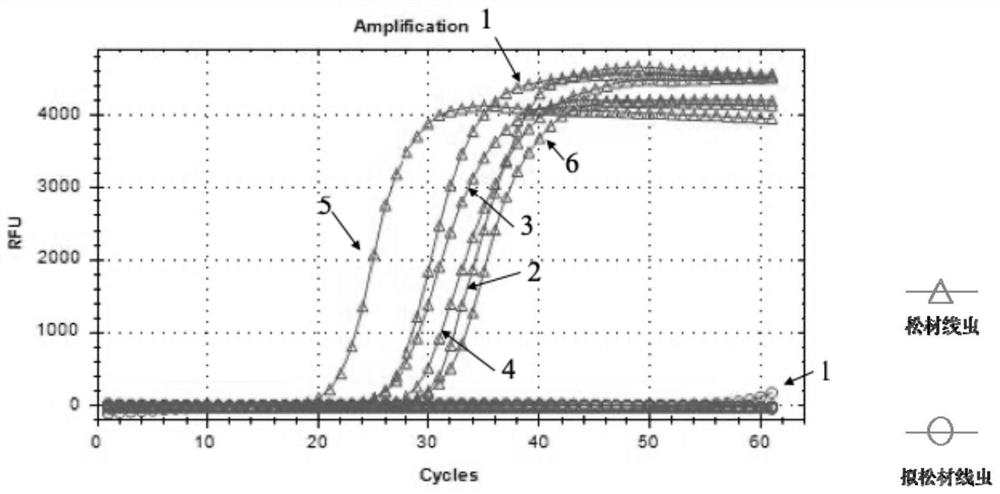
Molecular detection kit and method for detecting trace of bursaphelenchus xylophilus in pine wood
PendingCN108384860AImprove detection accuracyAvoid judgmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseGenetics
The invention relates to a molecular detection kit for detecting trace of bursaphelenchus xylophilus in pine wood, and a method for detecting the bursaphelenchus xylophilus in pine wood by adopting the molecular detection kit. Specific amplification primers comprise a primary PCR specific primer and a nest PCR ITS specific primer, wherein the sequences of the nest PCR ITS specific primer are as follows: the upstream primer: 5'-ATGCGATTGGTGACTTCGGTT-3', and the downstream primer: 5'-CCCGCAAGGCTTCACGACGA-3'. The molecular detection kit and the method have the beneficial effects that the kit candetect trace of bursaphelenchus xylophilus from pine wood infected with diseases at the early stage, so that the judgment of the false negative result is avoided, and the detection accuracy for the trace of B. xylophilus in the pine wood is obviously improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY ACAD
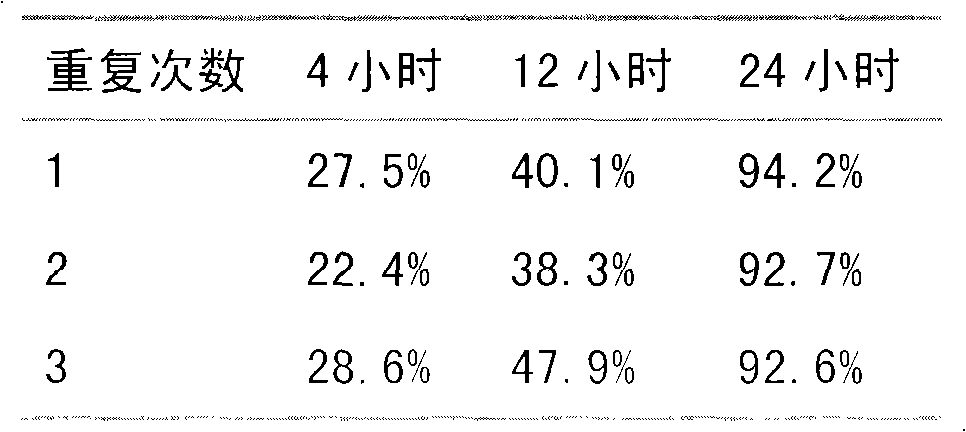
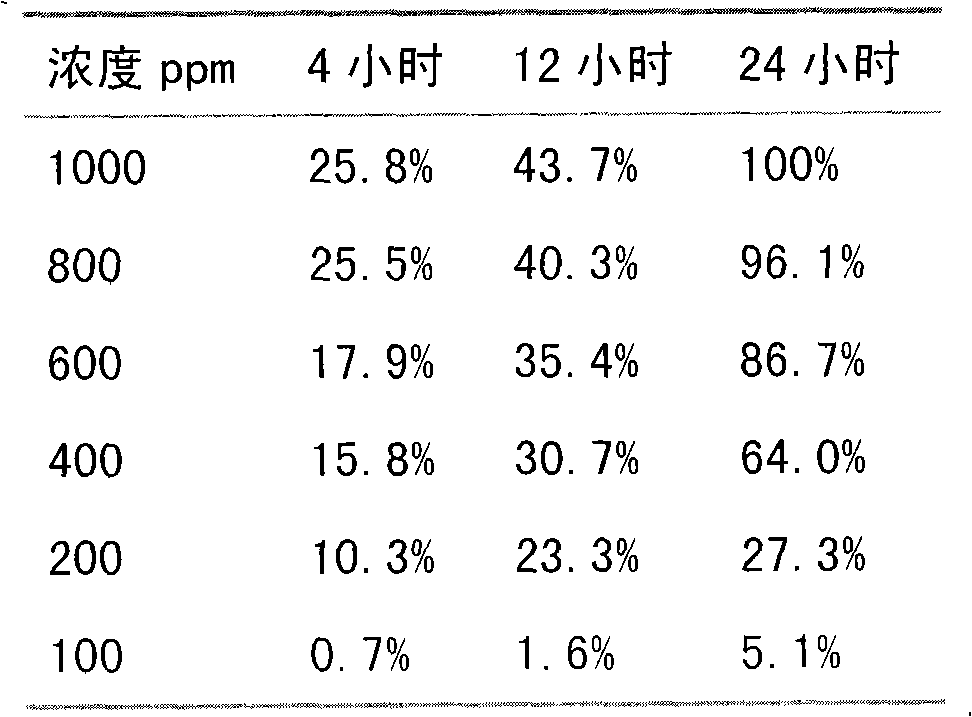
Paecilomyces metabolite and application thereof
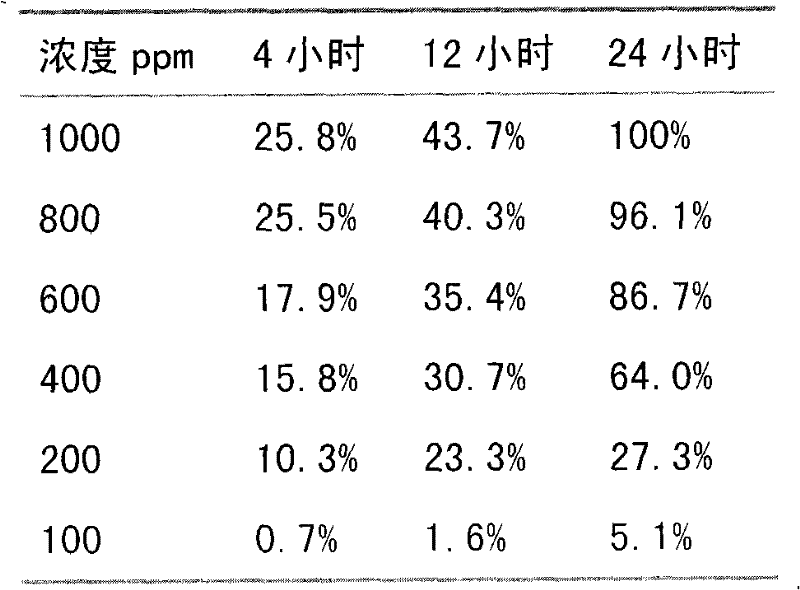
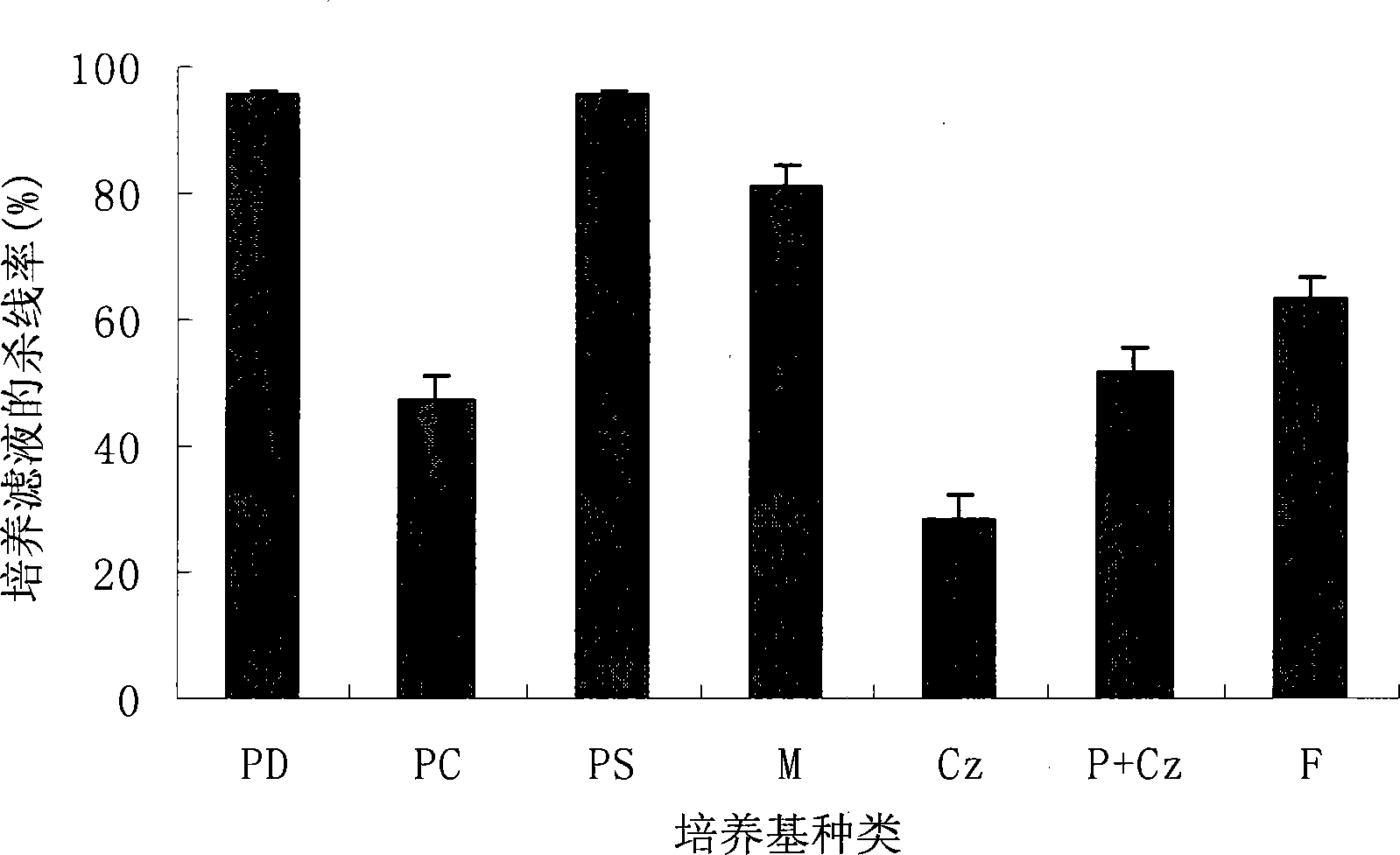
The invention relates to a paecilomyces metabolite and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of microbial medicine screening. The invention is realized by the following steps that: a production strain is paecilomyces sp.1788, and the preservation code is CGMCCNo. 3422; the paecilomyces sp.1788 is fermented and cultured by czapek culture medium conventional liquid, the fermentation fluid is concentrated at low pressure, column chromatography is carried out to water phase repeatedly, and the paecilomyces metabolite of the invention is prepared after elution. The paecilomyces metabolite of the invention has the function of killing bursaphelenchuh xylophilus, the lethal rate (ED50) in 24h is 299.5ppm, and the ED95 is 796.2ppm, and can be applied to bursaphelenchuh xylophilus preparations. Compared with the traditional bursaphelenchuh xylophilus chemical, the invention is characterized by high efficiency, low toxin, water solubility, easy preparation and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
A kind of pine xylophilus RNAi regulation gene and its application
The invention provides a pine xylophilus RNAi regulation gene, the full-length sequence of the RNAi regulation gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and the full-length cDNA sequence of the RNAi regulation gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The present invention also provides the application of the pine wood nematode RNAi regulation gene in the preparation of pine wood nematode control bacteria agent. The present invention screens out a highly efficient RNAi regulation gene segment, and feeds the positive fungal transformants containing the gene segment to pine wood nematodes to obtain an obvious RNAi phenotype, the gene expression of pine wood nematode Bx-etr-1 is significantly down-regulated, and the pine wood nematode The nematodes have abnormal embryonic development, high larval mortality, changed trajectory, slowed movement speed, and significantly decreased population.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of punicalagin in killing pine xylophilus
InactiveCN104542646BWide variety of sourcesLow costBiocideNematocidesBiotechnologyAcetylcholine esterase
The invention relates to the application of punicalagin in killing of pine wood nematodes; the concentration of the punicalagin is 200-1000micro-g / mL, the punicalagin is capable of effectively killing the pine wood nematodes, the punicalagin has the median lethal concentration of 332.88micro-g / mL within 72 hours for the pine wood nematodes; the punicalagin is capable of effectively inhibiting the activity of acetylcholine esterase of the pine wood nematodes so as to kill the pine wood nematodes; the punicalagin has the half inhibiting concentration of 654.92micro-g / mL. The punicalagin is obtained by being separated from pomegranate bark. The punicalagin is simple in operation method, wide in raw material source, low in cost, high in efficiency and low in toxicity, safe and environmentally friendly; the punicalagin has a good application prospect in the aspect of controlling pine wilt diseases, thus being applied to pesticide preparations for killing the pine wood nematodes.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Polypeptides and nucleic acids that mediate endocytosis of exogenous proteins and their applications and methods for gene editing in Neopodia prawns
The invention discloses polypeptides and nucleic acids that mediate the endocytosis of exogenous proteins and their application, and a method for gene editing in Neocaridina heteropoda. The invention finds a length of A polypeptide of only 40aa, the polypeptide has an unexpected effect of mediating the endocytosis of exogenous proteins, so it is easy to express, purify, form RNP complexes and be endocytosed, and has a good effect in the gene editing of Neopodia prawn Application prospects. This technology can be widely applied to non-model organisms that are not yet proficient in embryonic microinjection technology, and is of great significance for Cas9-mediated gene editing.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
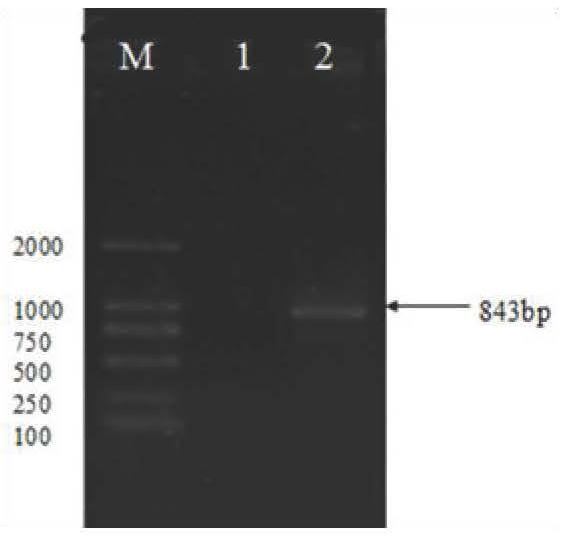
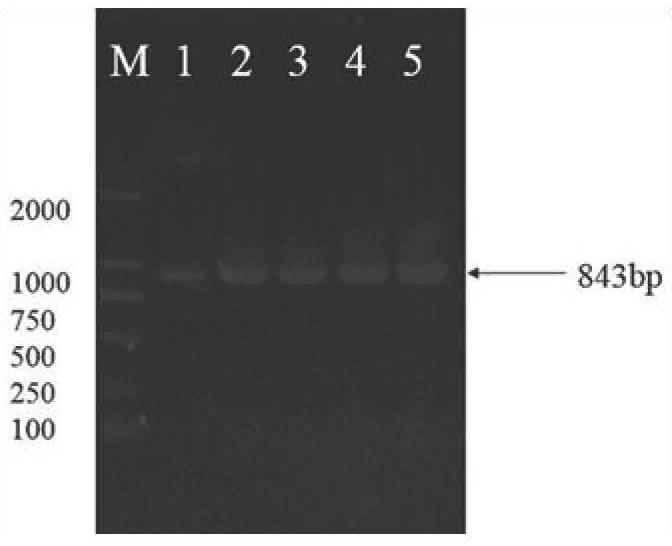
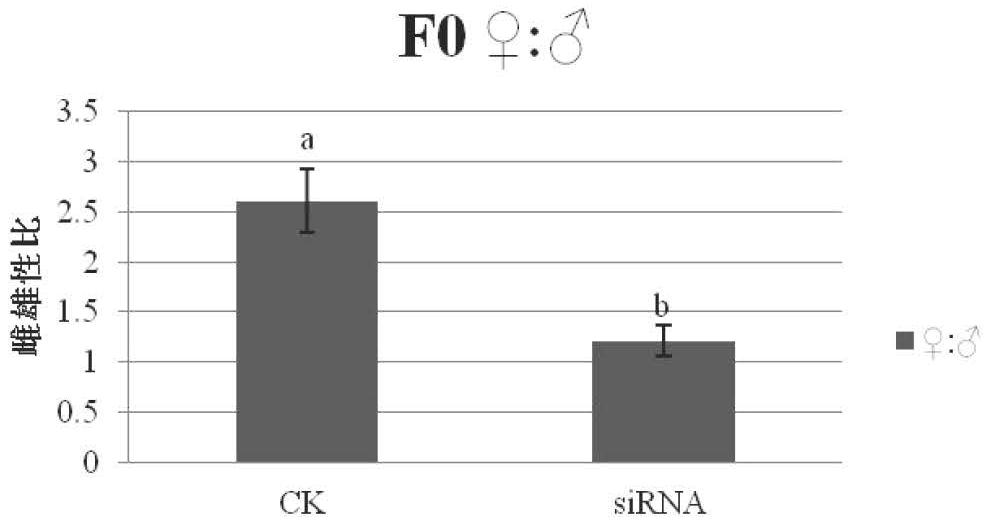
Mog-2 Gene of Pine Xylophilus and Its Application in Developmental Disturbance
The invention relates to the technical field of nematode disease prevention and control, in particular to the mog-2 gene of pine xylophilus, and a patent application for using the gene to interfere with the development of pine xylophilus to prevent and control pine xylophilus disease. The full-length DNA sequence of mog‑2 gene of pine wood nematode is 953bp, including 3 introns and 4 exons, and the start codon and stop codon of the DNA sequence are ATG and TGA, respectively. The length of CDS sequence of mog-2 gene of B. xylophilus composed of exons is 843bp. This application has cloned the mog‑2 gene of pine wood nematode and analyzed its function. It is believed that the gene is closely related to the growth and development of pine wood nematode, especially sex determination; using siRNA to interfere with the development of pine wood nematode can cause pine wood nematode Nematodes are obviously masculinized and their population fecundity is reduced. The siRNA can be used to interfere with development to prevent and control pine wood nematode disease.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
LAMP primer group and LAMP detection kit for detecting bursaphelenchus xylophilus by taking Bx-tlp-2 as target gene
InactiveCN113862377AStrong specificityImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMicrobiology
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
A kind of biological control method for effectively controlling pine wood nematode disease in monochamus
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural pest control, and in particular relates to a biological control method for effectively controlling pine wood nematode disease by biological control of monochamus. The method for effectively controlling pine wood nematode disease by the biological control of Monochamus alternata described in the present invention is to apply Cornus officinalis extract in pine trees containing Monochamus larvae before the pupation of Monochamus alternata at the end of April and the beginning of May each year The method of / morroniside can effectively block the pupation of monochamus alternatus, stop the development of monochamus larvae, reduce the population density of pine xylophilus pupae and adults, and then reduce the mortality of pine trees. At the same time, it also effectively prevents Subsequent pine wood nematodes formed a diffuse fourth-instar nematode with the eclosion of Monochamus alternatus, which effectively blocked the spread of pine wood nematodes, thereby reducing the mortality rate and spread speed of pine trees in areas where pine wood nematodes occurred, and preventing the spread of pine wood nematodes in forests. The prevention and control goal of further spread and expansion in the region can solve the problem of large-scale reproduction and rapid spread of pine wood nematode in the place where the pine wood nematode epidemic occurs.
Owner:HEZE UNIV
A method for highly synchronized somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of pine wood nematode-resistant Pinus pine
ActiveCN106718889BImprove germination rateImprove conversion rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureDiseaseSomatic embryogenesis
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Chitosan nanoparticle, biopesticide preparation for controlling pine wood nematode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103081928BConforms to embeddingImprove the stability of active ingredientsBiocideNematocidesChitosan nanoparticlesNematode
The invention discloses a chitosan nanoparticle which is formed by raw materials in percentage by weight: 0.5-5% of chitosan, 1-10% of a cosolvent, 0-5% of an anti-freezing agent, 0.1-1% of a surfactant, 0.1-0.5% of an emulsifying agent, 40-60% of buffering liquid and of the balance of water. The invention further provides a biological pesticide preparation and a preparation method thereof. The biological pesticide preparation is mainly prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: (A) 0.05-15% of an effective component, (B) 19.95-55% of a solvent, and (C) 30-80% of the chitosan nanoparticle, wherein in the effective component, siRNA (small interfering Ribonucleic Acid) is synthesized aiming at pine wood nematode efficient lethal target genes and the siRNA is 15-50nt double-chain RNA. According to the chitosan nanoparticle, the stability of the biological pesticide preparation is better and the effect of preventing and treating pine wood nematodes is better.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RIBOBIO
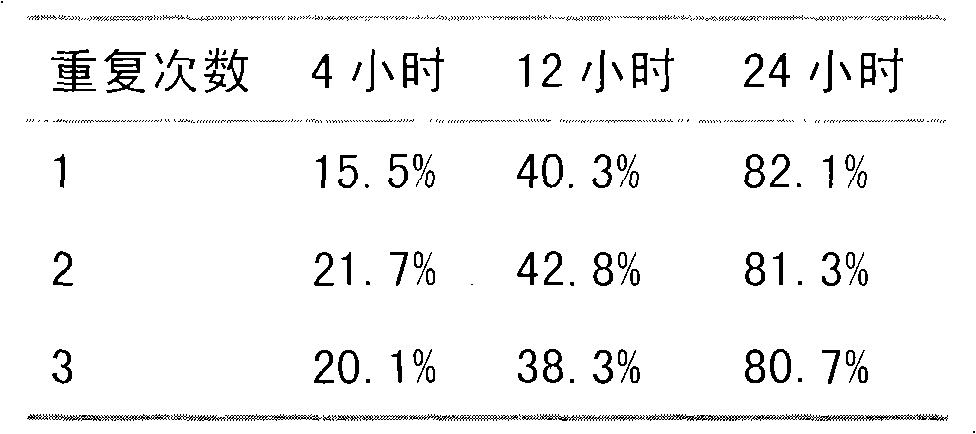
Paecilomyces metabolite and application thereof
InactiveCN101787376BEasy to manufactureBiocideMicroorganism based processesSolubilityPinewood nematode
The invention relates to a paecilomyces metabolite and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of microbial medicine screening. The invention is realized by the following steps that: a production strain is paecilomyces sp.1788, and the preservation code is CGMCCNo. 3422; the paecilomyces sp.1788 is fermented and cultured by czapek culture medium conventional liquid, the fermentation fluid is concentrated at low pressure, column chromatography is carried out to water phase repeatedly, and the paecilomyces metabolite of the invention is prepared after elution. The paecilomyces metabolite of the invention has the function of killing bursaphelenchuh xylophilus, the lethal rate (ED50) in 24h is 299.5ppm, and the ED95 is 796.2ppm, and can be applied to bursaphelenchuh xylophilus preparations. Compared with the traditional bursaphelenchuh xylophilus chemical, the invention is characterized by high efficiency, low toxin, water solubility, easy preparation and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
gRNAs, kits and vector systems for detection of pine xylophilus
ActiveCN113528678BHigh detection specificityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVector systemNucleotide
The invention discloses a gRNA for detecting pine xylophilus, comprising a) a guide sequence such as SEQ ID NO: 1, which can hybridize to a target nucleotide sequence, and b) a framework nucleic acid fragment interacting with Cas nuclease . The invention also discloses a kit for detecting pine xylophilus, which comprises the gRNA or the DNA that can be transcribed into the gRNA. The present invention also discloses a vector system, which comprises one or more vectors, the vector comprising: a first regulatory element and a second regulatory element, the first regulatory element is operably linked to a nucleoside encoding Cas nuclease An acid fragment, the second regulatory element is operably linked to the nucleotide fragment encoding the gRNA.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Active material extracted from euphorbia lathyris and application thereof
The invention relates to an active material extracted from euphorbia lathyris and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological pesticides. The active material extracted from euphorbia lathyris is characterized in that a method for obtaining the active material comprises the following steps of: a, cleaning collected branches or leaves of the euphorbia lathyris by tap water, putting the cleaned branches or leaves in an oven for roasting at the temperature of 50 DEG C for 10 hours, cutting 10g of dried branches or leaves into pieces, and putting the cut branches or leaves in a triangular flask, soaking the branches or leaves by 80 percent ethanol, wherein the time for the first soaking extraction is 4 hours, and the time for the second and the third soaking extractions is 12 hours and 24 hours respectively; b, mixing extraction solution obtained by the extractions at the third time, condensing the obtained solution until the solvent is vaporized to obtain coarse extracts of the branches or leaves, dissolving the coarse extracts in methanol to prepare the solution of which the concentration is 0.1g / ml, and putting the obtained solution in a refrigerator for later use. The active material can be used for preparing a biological reagent of killing B.xylophilus. The active material has the advantages of low cost, simple and convenient preparation method, high efficiency and low toxicity, which can be used for preparing the biological reagent of killing B.xylophilus.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
A kind of biopesticide for controlling pine wood nematode and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a biological pesticide capable of preventing and treating bursaphelenchus xylophilus and a preparation method thereof as well as application of the biological pesticide to prevention and treatment of the bursaphelenchus xylophilus. A dosage form of the pesticide is powder; an active component of the powder is Trichoderma virens T43 fermented liquid n-butanol extract; the preparation method of the powder comprises the following steps: filtering and centrifuging fermented liquid, taking supernatant liquid, adding n-butanol, mixing and extracting, removing a water layer,and evaporating and concentrating an n-butanol layer to obtain the powder.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
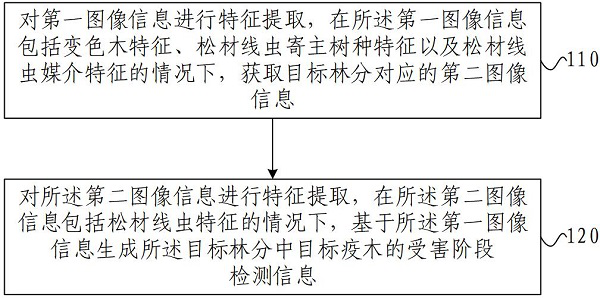
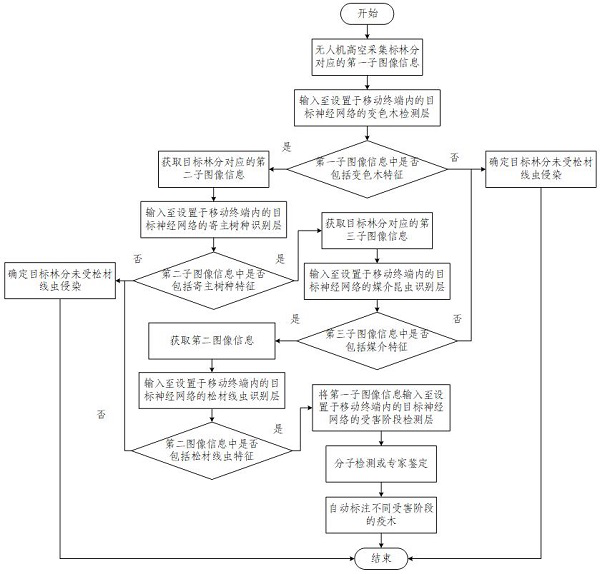
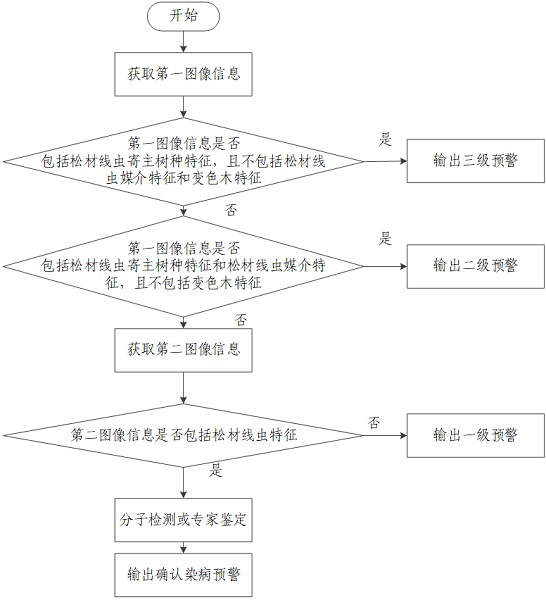
Mobile-based integrated early warning and detection method and device for pine wood nematode disease
ActiveCN114550017BPrevent proliferationAvoid spreadingImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionMobile end
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Compound with pine wood nematode killing activity with poison and use thereof
The invention relates to a class of compounds with the activity of poisoning and killing pine xylophilus and applications thereof, belonging to the technical field of biological pesticides. Such active compounds are obtained from production strains by conventional solid fermentation and extraction and separation methods. Its production strain is Gliocladium roseum (Gliocladium roseum) Gr87, which has been preserved in the China Committee for the Preservation of Microorganisms on October 9, 2002, with a preservation number of CGMCC No.0807; this type of active compound consists of 6 compounds The composition can effectively poison and kill pine xylophilus, and can be used alone or in combination to prepare nematicidal biopesticides.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Epiphyte Xylaria sp.FDYS-1, biological agent prepared from the same and application thereof in preventing and curing bursaphenchus xylophilus nickle
InactiveCN101260370BHighly lethal activityImprove thermal stabilityBiocideFungiBiotechnologyEcological environment
The invention discloses a fungi Xylaria sp.FDYS-1, biological agents prepared by the fungi Xylaria sp.FDYS-1 and application of the fungi Xylaria sp.FDYS-1 in prevention and cure of pine wood nematodes. The fungi Xylaria sp.FDYS-1 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on February 25th, 2008 and the preservation No. is CCTCC NO:M 208025. The invention inoculates the Xylaria sp.FDYS-1 into a potato glucose liquid medium or a potato sugar liquid medium; the pH of the liquid medium is 5 to 8; the culture temperature is 26 DEG C to 29 DEG C; after cultivation of 3 to 5 days under nonluminous conditions, the culture medium is centrifugally filtered, and the biological agents are obtained by collection of filtrate. The biological agents have high killing activity on the pine wood nematodes, good thermal stability, environment-friendly source without toxity, strong selectivity and small ecological environmental influence. The fungi Xylaria sp.FDYS-1 has low culture condition requirements, basically maintains stable inheritance of the capacity for generation of active materials, and has good development and application prospect.
Owner:ZHONGKAI UNIV OF AGRI & ENG
PCR primer, PCR detection kit and detection method for detecting B.xylophilus
InactiveCN113699251AStrong specificityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMedicine
The invention discloses a PCR primer, a PCR detection kit and a detection method for detecting B.xylophilus. A PCR primer pair capable of specifically amplifying B.xylophilus is designed and screened by taking a conserved Bx-cpi gene in a B.xylophilus species as a target gene, and the PCR primer pair consists of two primers with nucleotide sequences shown as SEQ ID No.9 and SEQ ID No.10. According to the invention, the specific PCR primer pair is further utilized to establish a PCR detection method for B.xylophilus. The method can rapidly detect whether a sample to be detected carries the B.xylophilus. or not, and the detection method has the advantages of strong specificity, high accuracy, simple operation, short time consumption, low cost and the like. The method has application value for monitoring occurrence and spreading of the Pine Wilt Disease, overall early warning and control strategies of the Pine Wilt Disease and the like.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Pathogen-related model molecular protein bxcdp1 of pine wood nematode and its application
ActiveCN110156885BIncrease resistanceActivate immune responseFermentationAnimals/human peptidesBiotechnologyXylophilus
The invention discloses protein BxCDP1 of bursaphelenchus-xylophilus pathogen-associated molecular patterns and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the protein BxCDP1 of the pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPS) is shown in SEQID NO.2. From effectors secreted by bursaphelenchus xylophilus and the PAMP, the defensive responses of a host plant, namely, a pine tree, to bursaphelenchus xylophilus invasion are studied, the protein BxCDP1 of the pathogen-associated molecular patterns is obtained from the bursaphelenchus xylophilus, it is proven through experiments that the protein BxCDP1 can trigger cell necrosis of various plants including the host plant, has a certain broad spectrum in cell necrosis triggering, and stimulates the defensive response of the host plant. The BxCDP1 triggered cell necrosis depends on a co-receptor BAK1 of pattern recognition receptors, the BxCDP1 can stimulate the accumulation of nicotiana benthamiana ROS and up regulation of PTI Marker genes, and the immunoreaction of the nicotiana benthamiana is stimulated. It can be seen that the BxCDP1 is a PAMP secreted by the bursaphelenchus xylophilus, and has important theoretical and practicalsignificance for revealing the pathogenic mechanism of the bursaphelenchus xylophilus and improving the resistance of the pine tree to the bursaphelenchus xylophilus in a targeted mode.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com