Genetic engineering high-yield strain streptomyces diastatochromogenes and production method and application of epsilon-polylysine
A technology for producing Streptomyces chromogenes and polylysine, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as less reports, and achieve the effects of increasing concentration, increasing yield, and improving fermentation level
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
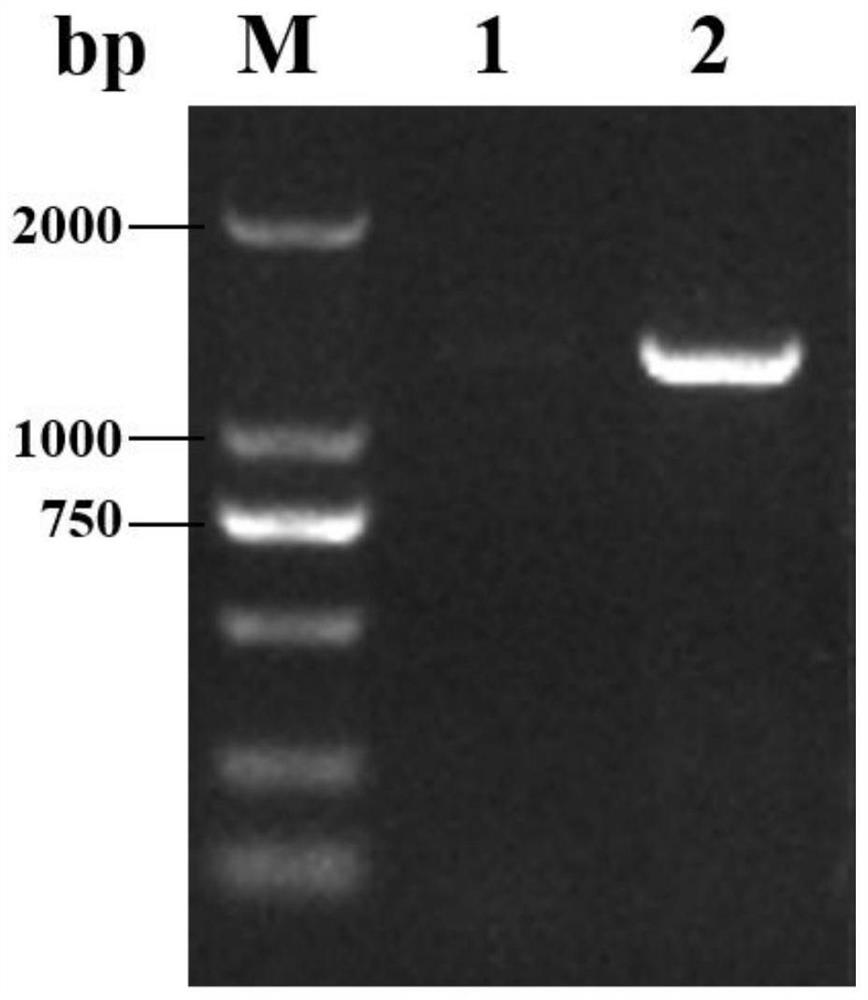
[0084] A genetic engineering high-yield amylase strain Streptomyces chromogenes ΔfabF1 (Streptomyces diastatochromogenes ΔfabF1), the construction steps are as follows:
[0085] (1) Obtaining the knockout component: the knockout component contains the allelic site of the fabF1 gene, that is, the upstream homologous fragment and the downstream homologous fragment of the gene, as well as the resistance fragment (apramycin resistance) as a selection marker.
[0086] Using the genome of S.diastatochromogenes 6#-7 as a template, the upstream and downstream homologous fragment primer sequences fabF1-L-F / fabF1-L-R and fabF1-R-F / fabF1-R-R were designed according to the fabF1 gene; The primer sequence fabF1-apr-F / fabF1-apr-R was designed for the mycin resistance gene (Apr).
[0087] Add 8 nucleotides at the upstream and downstream ends of the knockout module to form the restriction endonuclease EcoRI cutting site.
[0088] The sequence of the primers is:
[0089] fabF1-L-F: SEQ No.2...
Embodiment 2
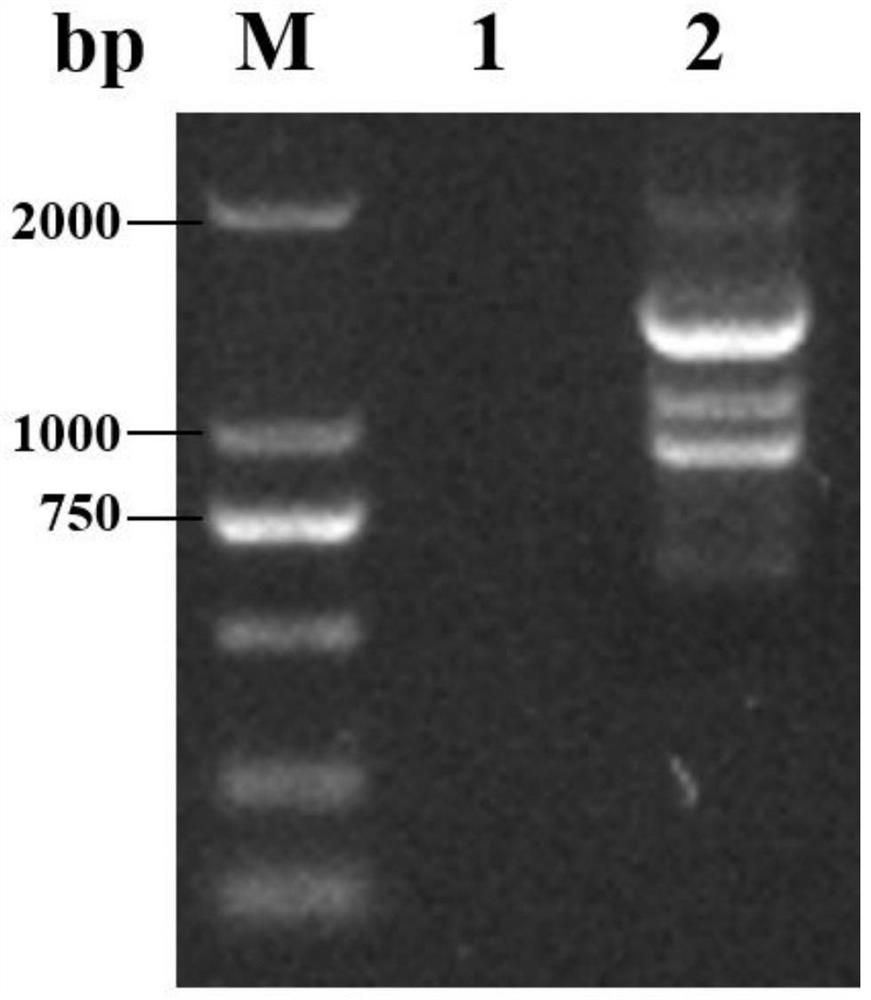
[0105] A genetic engineering high-yield amylase strain Streptomyces chromogenes ΔfabF2 (Streptomyces diastatochromogenes ΔfabF2), the construction steps are as follows:
[0106] (1) Obtaining the knockout component: the knockout component contains the allelic site of the fabF2 gene, that is, the upstream homologous fragment and the downstream homologous fragment of the gene, and the resistance fragment (apramycin resistance) as a selection marker.
[0107] Using the genome of S.diastatochromogenes 6#-7 as a template, the upstream and downstream homologous fragment primer sequences fabF2-L-F / fabF2-L-R and fabF2-R-F / fabF2-R-R were designed according to the fabF2 gene; The primer sequence fabF2-apr-F / fabF2-apr-R was designed for the mycin resistance gene (Apr).
[0108] Add 8 nucleotides at the upstream and downstream ends of the knockout module to form the restriction endonuclease EcoRI cutting site.
[0109] The sequence of the primers is:
[0110] fabF2-L-F: SEQ No.13, name...
Embodiment 3
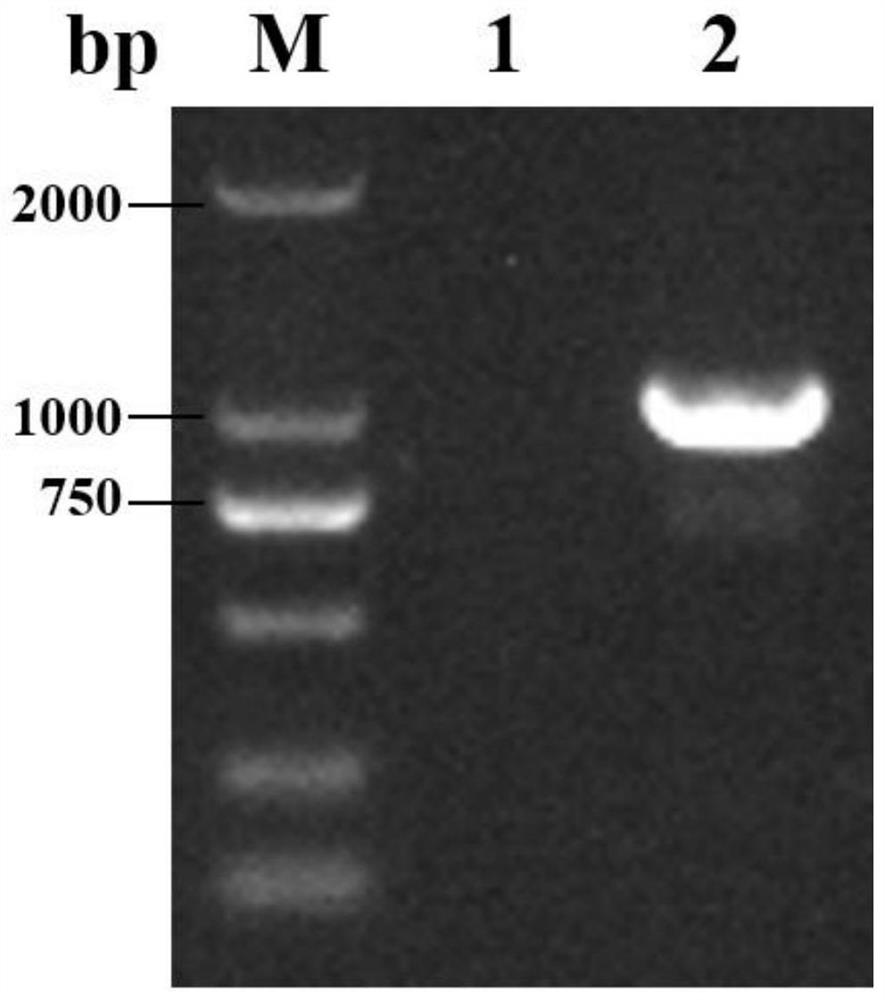
[0126] A genetic engineering high-yield amylase strain Streptomyces chromogenes ΔfabF3 (Streptomyces diastatochromogenes ΔfabF3), the construction steps are as follows:
[0127] (1) Obtaining the knockout component: the knockout component contains the allelic site of the fabF3 gene, that is, the upstream homologous fragment and the downstream homologous fragment of the gene, and the resistance fragment (apramycin resistance) as a selection marker.
[0128] Using the genome of S.diastatochromogenes6#-7 as a template, the upstream and downstream homologous fragment primer sequences fabF3-L-F / fabF3-L-R and fabF3-R-F / fabF3-R-R were respectively designed according to the fabF3 gene; using the pSET152 plasmid as a template, according to Apramycin Primer sequence fabF3-apr-F / fabF3-apr-R was designed for the protein resistance gene (Apr).
[0129] Add 8 nucleotides at the upstream and downstream ends of the knockout module to form the restriction endonuclease EcoRI cutting site.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com