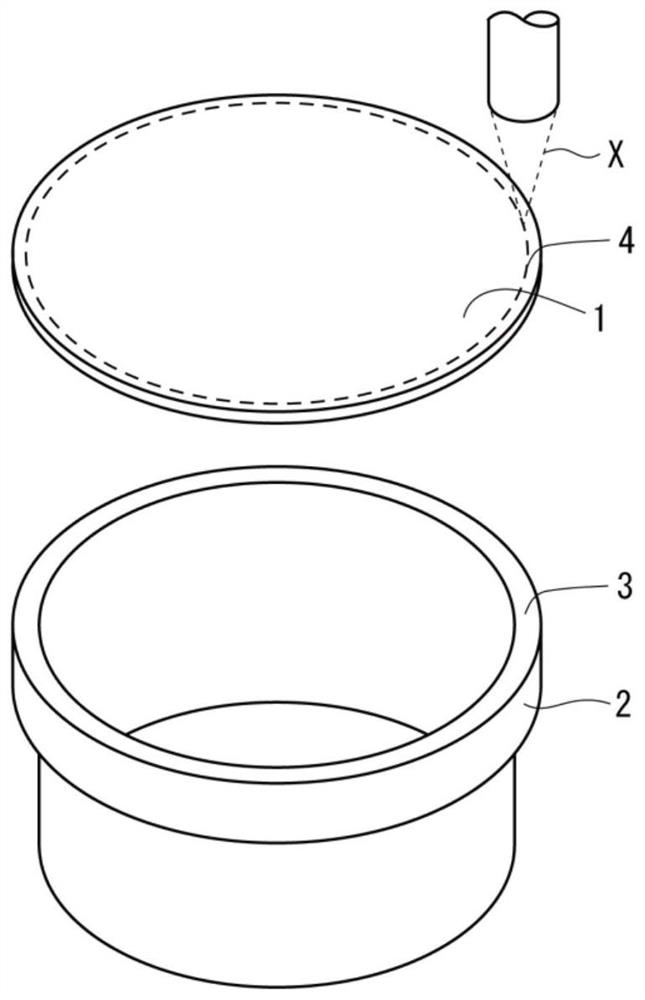
Thermoplastic resin composition for millimeter-wave radar members, molded article, and resin composition production method
A technology of thermoplastic resin and millimeter-wave radar, which is applied in the direction of radio wave reflection/re-radiation, use of re-radiation, radio wave measurement system, etc., can solve the problem of inability to realize the performance of millimeter-wave radar and the inability to accurately detect obstacles, mm Wave and reflected wave weakening and other problems, to achieve the effect of excellent laser welding, excellent low warpage and appearance, and stable deviation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 to 3 and comparative example 1
[0190] The pellets of the thermoplastic resin composition were obtained by uniformly mixing the components shown in the above Table 1 except the glass fibers using a drum mixer in the proportions (parts by mass) shown in the following Table 2, from a twin-screw The obtained mixture was fed into the main feed port of a kneading extruder (TEX30α manufactured by Japan Steel Works, L / D=42), the barrel temperature of the first kneading section was set at 270° C., plasticized, and from the side Feed glass fibers to the feed port at the ratio shown in Table 2. After adding glass fibers, set the barrel temperature to 270 ° C, melt and knead at a discharge rate of 40 kg / h and a screw speed of 200 rpm, and extrude The obtained kneaded product was taken out, rapidly cooled in a water bath, and then formed into pellets using a pelletizer. Except in Example 2, kneading was performed under the above-mentioned conditions, and the screw kneading temperature was 278°C.
[0191] In Example 2, ...
Embodiment 4 to 7 and comparative example 2
[0223] [table 3]
[0224]
[0225] The pellets of the thermoplastic resin composition were obtained by uniformly mixing the other components shown in the above Table 3 except the glass fibers using a drum mixer in the ratio (parts by mass) shown in the following Table 4, from the twin-screw The obtained mixture was fed into the main feed port of a kneading extruder (TEX30α manufactured by Japan Steel Works, L / D=42), the barrel temperature of the first kneading section was set at 270° C., plasticized, and from the side Feed glass fibers to the feed port at the ratio shown in Table 4. After adding glass fibers, set the cylinder temperature to 220 °C, melt and knead at a discharge rate of 40 kg / h and a screw speed of 200 rpm, and extrude The obtained kneaded product was taken out, rapidly cooled in a water bath, and then formed into pellets using a pelletizer, and these pellets were evaluated in the same manner as in Example 1, and were subjected to the following evaluations. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| epoxy equivalent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com