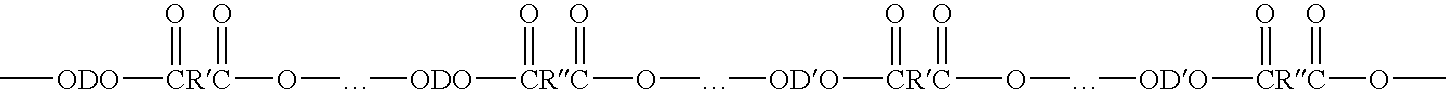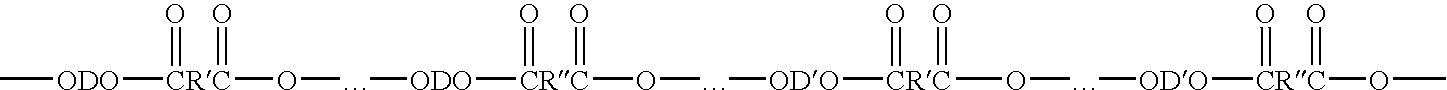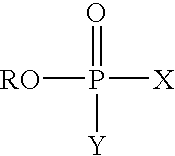Patents
Literature
2602 results about "Polybutylene terephthalate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
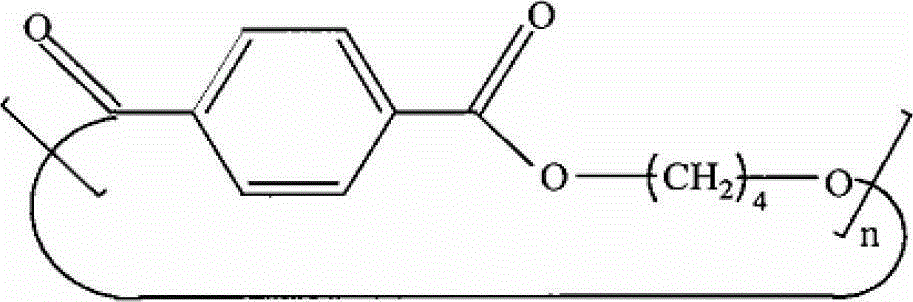
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic engineering polymer that is used as an insulator in the electrical and electronics industries. It is a thermoplastic (semi-)crystalline polymer, and a type of polyester. PBT is resistant to solvents, shrinks very little during forming, is mechanically strong, heat-resistant up to 150 °C (or 200 °C with glass-fibre reinforcement) and can be treated with flame retardants to make it noncombustible. It was developed by Britain's Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI).
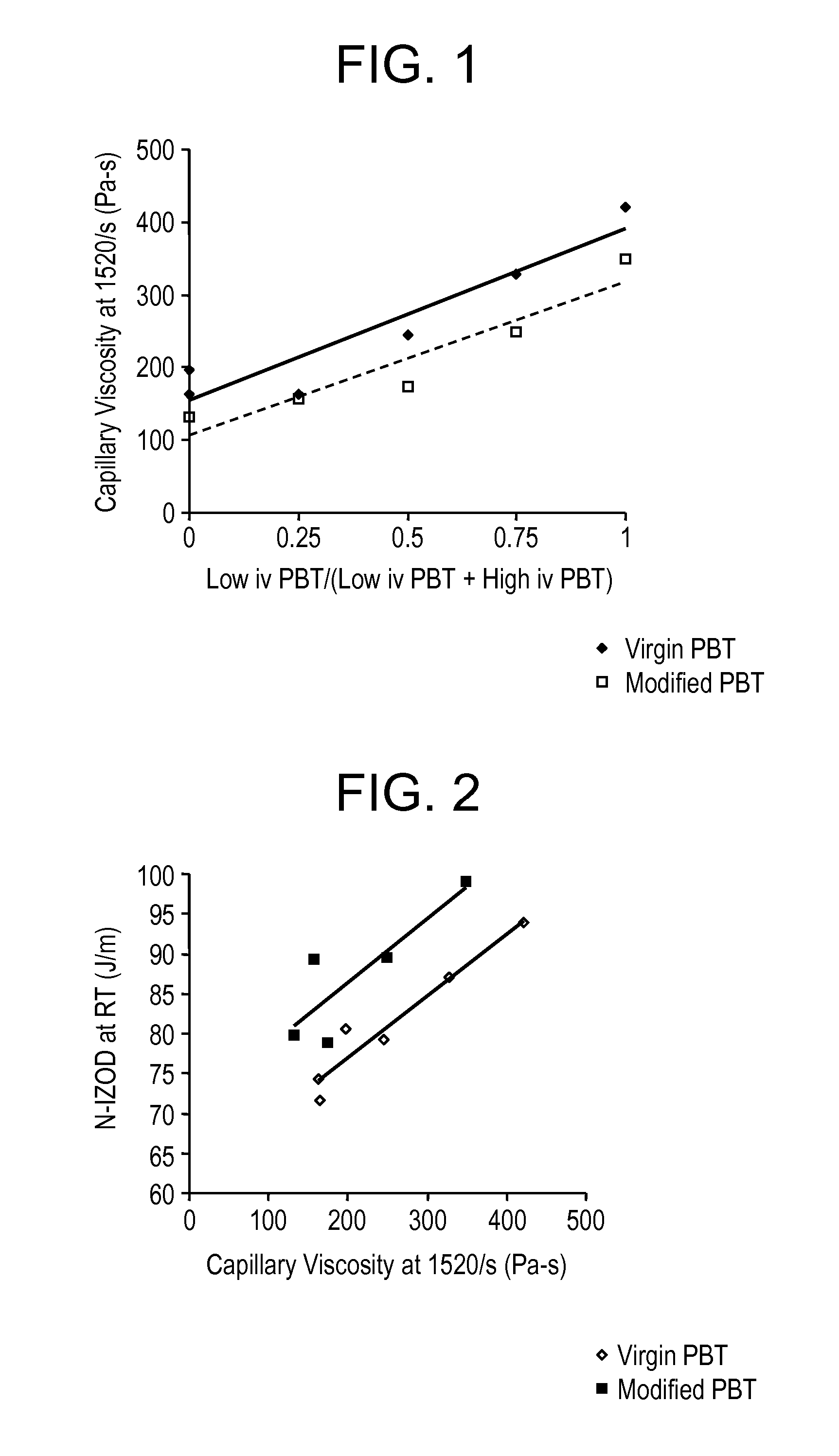
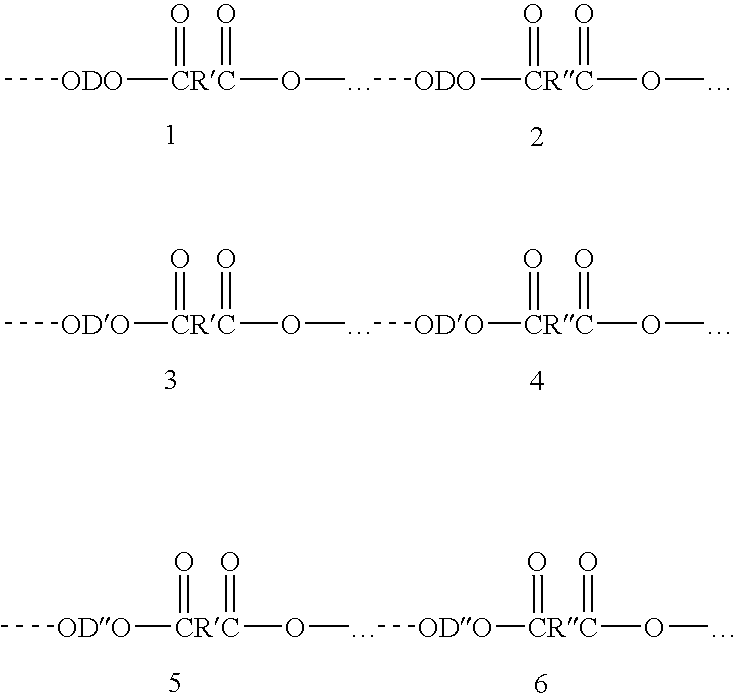
Articles derived from compositions containing modified polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) random copolymers derived from polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
ActiveUS20070275242A1Useful performance propertyPlastic recyclingSpecial tyresPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
Compositions of matter including articles derived from (a) from 5 to 99.99 wt % of a modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymer that (1) is derived from polyethylene terephthalate and (2) contains a at least one residue derived from polyethylene terephthalate selected from the group consisting of antimony, germanium, diethylene glycol groups, isophthalic acid groups, cis isomer of cyclohexane dimethanol, trans isomer of cyclohexane dimethanol, sodium benzoate, alkali salts, napthalane dicarboxylic acids, 1,3-propane diols, cobalt, cobalt-containing compounds, and combinations thereof, and (b) from 0.01 to 95 wt. % of a member selected from the group consisting of (1) fillers, (2) a carboxy reactive component, (3) polyethyelene terephthalate, (4) a component including a polycarbonate and an impact modifier. The articles may be derived from various conversion processes, e.g., injection molding processes, extrusion processes, thermoforming processes, melt-blown process.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Composite of aluminum alloy and resin composition and process for producing the same
InactiveCN1717323ASynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingPolytetramethylene terephthalateSurface roughness
The invention relates to a complex, which is characterized in that the complex consists of an aluminium alloy shape and a thermoplastic resin combination; the roughness of surface of the complex is more than 5 to 50 Mu m; the surface is provided with the aluminium alloy shape with minute recessed parts or raised parts, the diameter of which is less than 1 Mu m; the aluminium alloy shape is fixed through the recessed parts or raised parts; with the longitudinal and transverse average coefficientof linear expansion ranging from 2X<-5> DEG C<-1> to 4X<-5> DEG C<-1>, the thermoplastic resin combination is primarily made of polybutylene terephthalate resin or polyphenyl thioether; as the thermoplastic resin combination is not peeled off easily from the aluminium alloy shape, the invention has the advantages of metal enclosers and synthetic resin structures in electronic machines and electric appliances. The production efficiency is high, and the complex can be produced on large scale with shape and structure to be designed freely.
Owner:TAISEI PLAS CO LTD
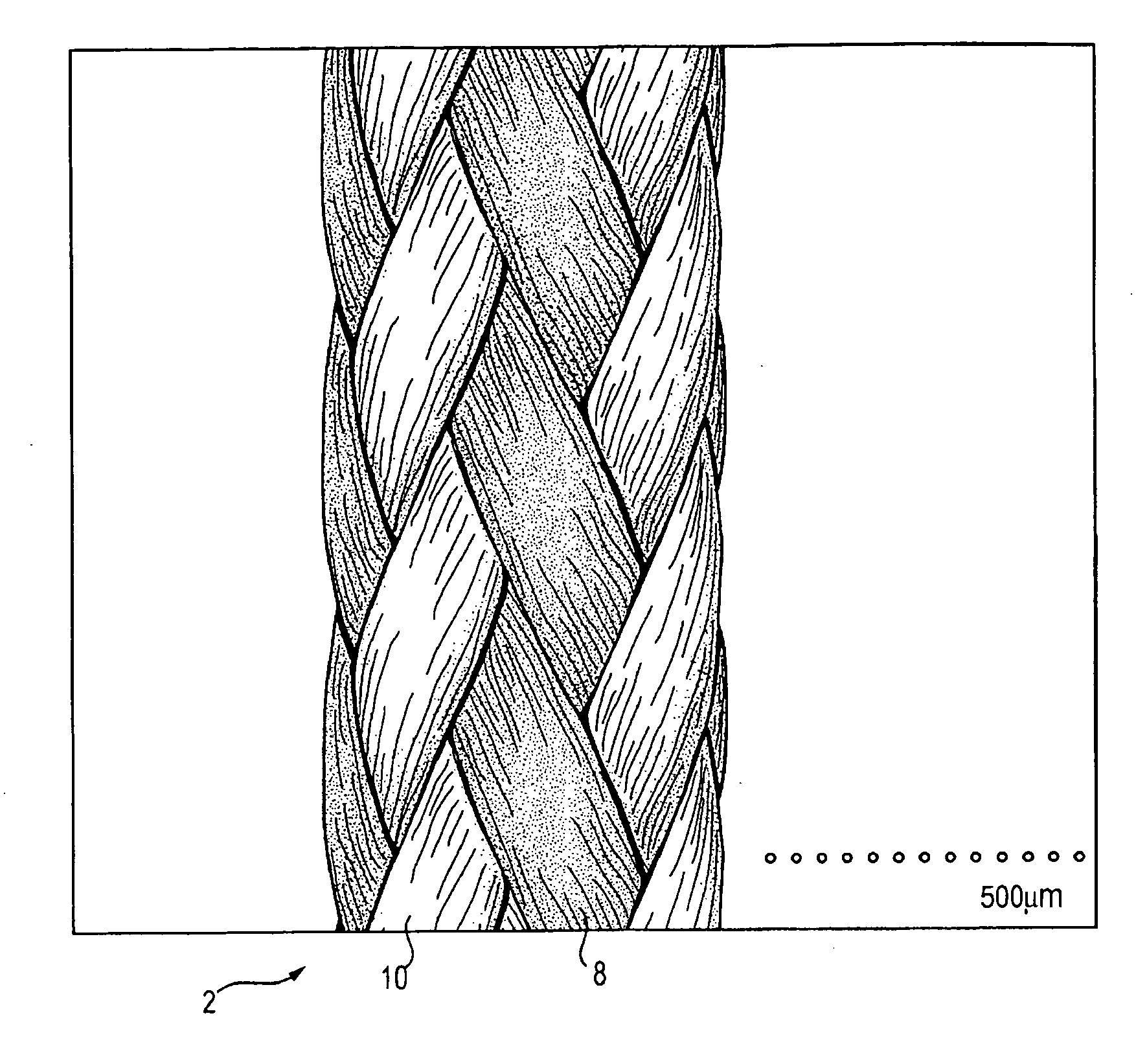
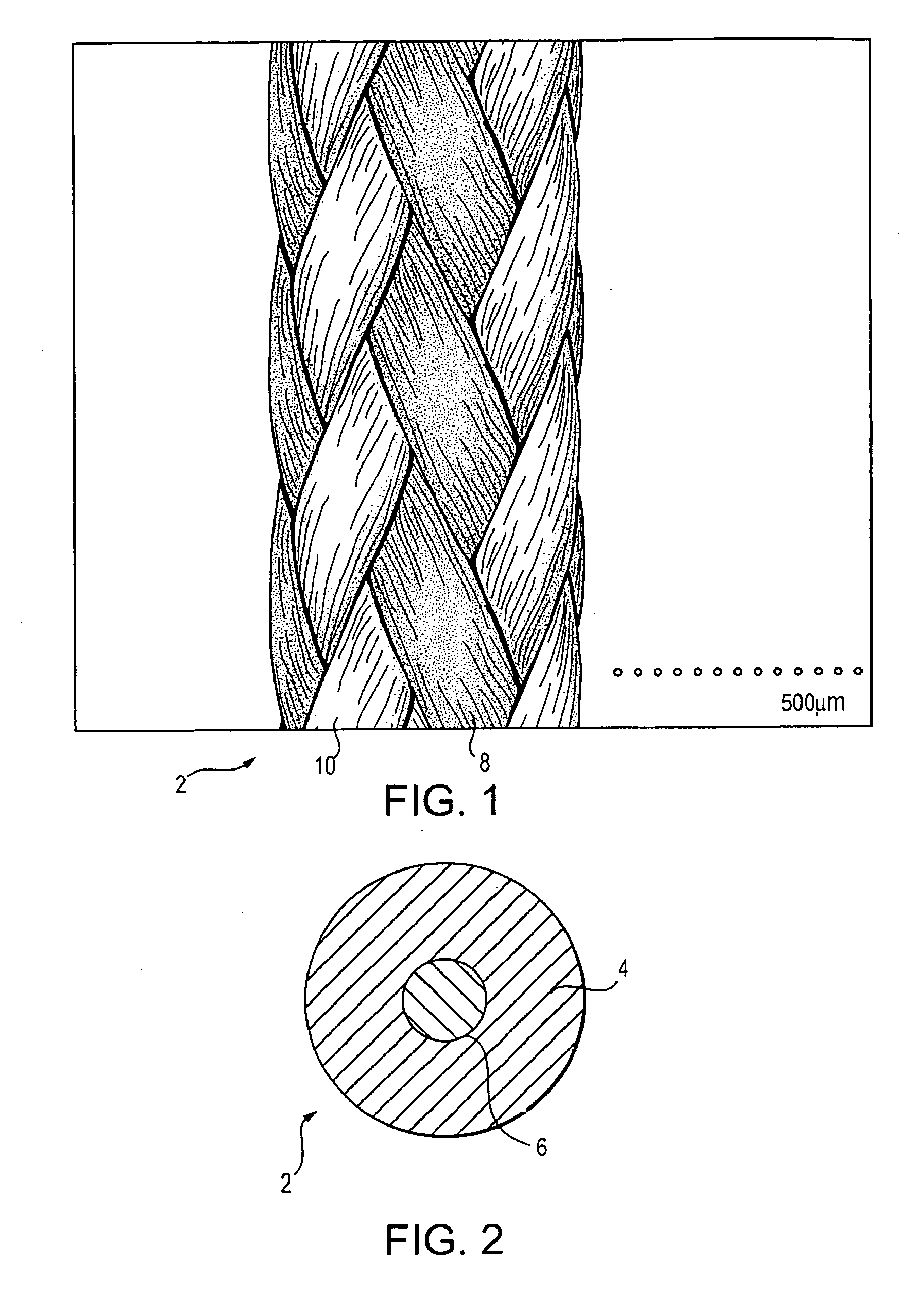
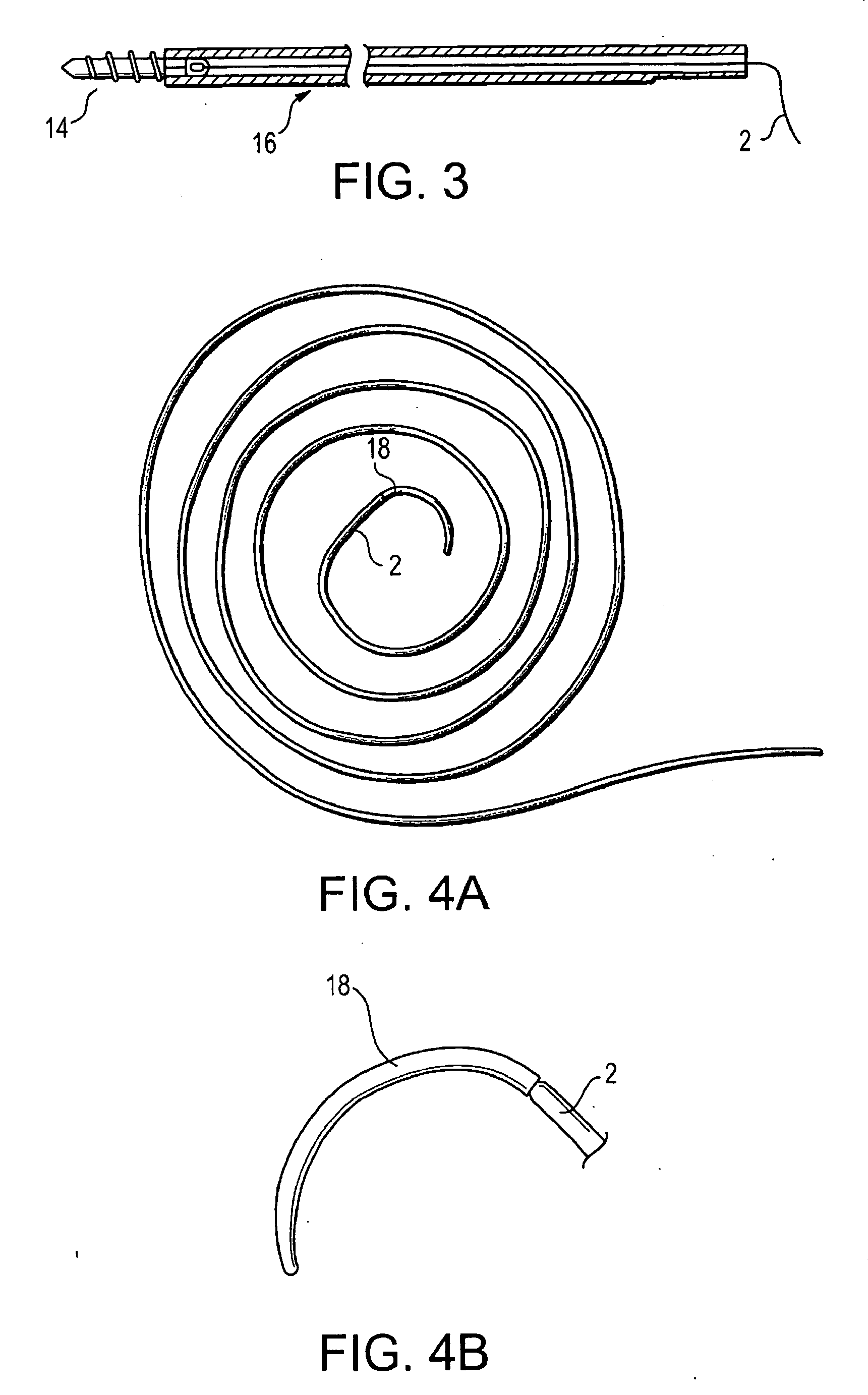
High strength suture formed of UHMWPE and PBT
InactiveUS20070135840A1High strengthImproved tie down characteristicSuture equipmentsBraidFiberPolytetramethylene terephthalate
A high strength abrasion resistant surgical suture material with improved tie down characteristics is color coded for visualization and identification purposes. The suture features a multifilament cover formed of strands of ultra high molecular weight long chain polyethylene braided with polybutylene terephthalate. Selected fibers in the cover may be provided in a color contrasting with the other cover fibers to provide an identifiable trace. The cover surrounds a core formed of twisted strands of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene. The suture, provided in a #2 size, has the strength of #5 Ethibond, is ideally suited for most orthopedic procedures, and can be attached to a suture anchor or a curved needle.
Owner:ARTHREX
Composite of aluminum alloy and resin composition and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20060257624A1Mass productivityMold shrinkage factor should be smallSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storagePolytetramethylene terephthalateHigh volume manufacturing
A composite characterized by comprising an aluminum alloy shaped item having a surface roughness of 5 to 50 μm or more, the surface provided with 1 μm or less fine depressions or protrusions, and a thermoplastic resin composition composed mainly of a polyphenylene sulfide or polybutylene terephthalate resin whose average of lengthwise and crosswise linear expansion coefficients is in the range of 2 to 4×10−5° C.−1, the thermoplastic resin composition penetrating and anchored in the depressions or protrusions. The thermoplastic resin composition is not easily detached from the aluminum alloy shaped item. Thus, in, for example, electronic equipments and household electrical appliances, the advantage of metallic cage body can be reconciled with the advantage of synthetic resin structure. This composite can ensure high production efficiency and is suitable for mass production. Further, morphology and structure designing thereof can be accomplished freely.
Owner:TAISEI PLAS CO LTD
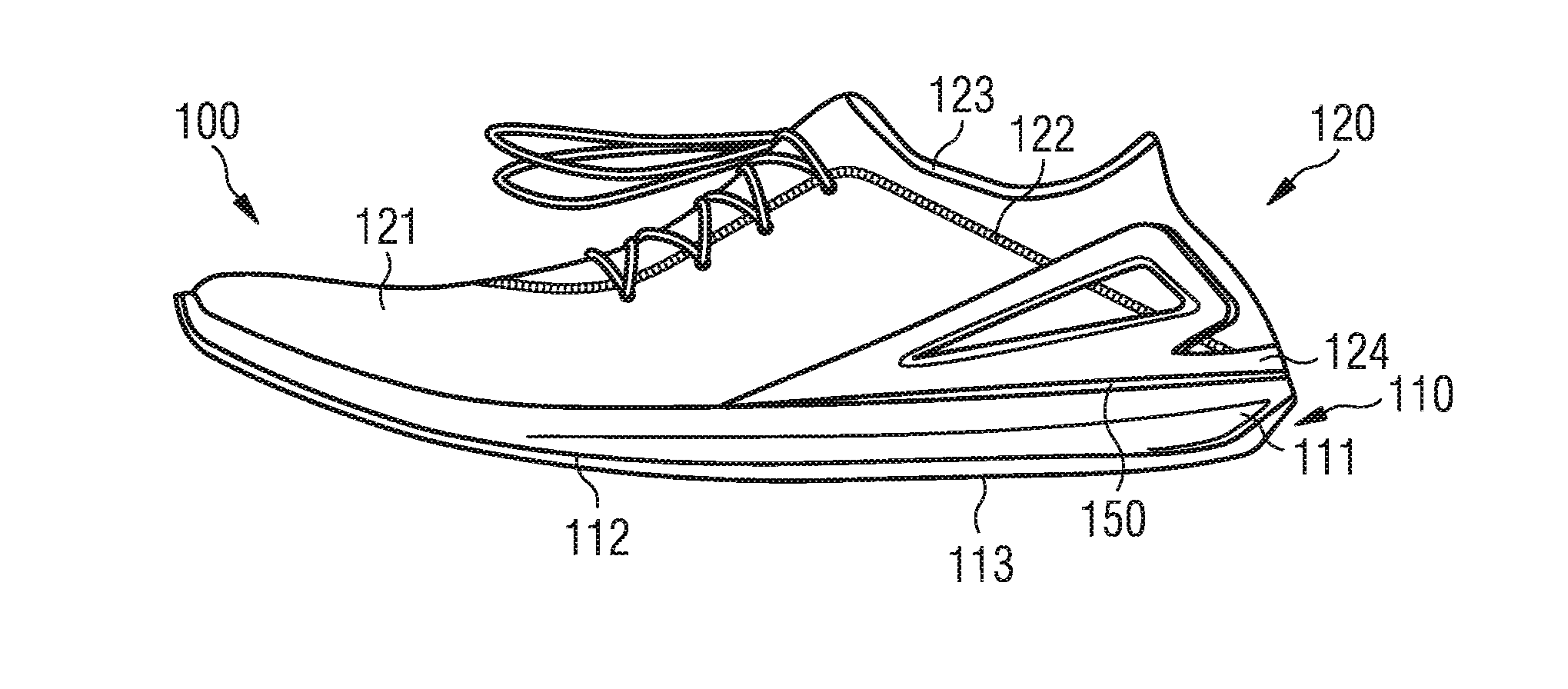
Sports Shoes and Methods for Manufacturing and Recycling of Sports Shoes
InactiveUS20160302508A1Easy to identifySolesInsolesPolyethylene terephthalatePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
A sports shoe includes an upper wherein a majority by weight of the upper is made from a thermoplastic base material and a sole wherein a majority by weight of the sole is made from the same thermoplastic base material. The sole and the upper are individually fabricated and joined to each other. The thermoplastic base material includes at least one of the following materials: thermoplastic polyurethane TPU, polyamide PA, polyethylene terephthalate PET, or polybutylene terephthalate PBT.
Owner:ADIDAS
Molding compositions containing fillers and modified polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) random copolymers derived from polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
The invention relates to a composition comprising (a) from 5 to 99 wt % of a modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymer that (1) is derived from polyethylene terephthalate component selected from the group consisting of polyethylene terephthalate and polyethylene terephthalate copolymers and (2) has at least one residue derived from the polyethylene terephthalate component, and (b) at least 1 wt % of a filler component. In one embodiment, the invention relates to an article molded from the above-mentioned molding composition. In another embodiment, the invention relates to methods for making and methods for using the molding composition.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Conversion of contaminated polyethylene terephthalate to decontaminated polybutylene terephthalate
InactiveUS6518322B1Fast reaction timeCost is removed entirelyPolytetramethylene terephthalate1,4-Butanediol
Decontaminated crushed polyethylene terephthalate is converted to decontaminated PBT withtout requiring a catalyst by mixing with 1,4-butanediol under reduced pressure, transeterifying at 120-190° C., distilling off ethanediol and tetrahydrofuran under sub-atomspheric pressure. The method lowers costs, and decreases wasteful by-products and removes contaminants present in post-consumer PET, (e.g. paper, pigments, plastics, dyes, mineral sands, and clays) and chemical and water insoluble contaminants.
Owner:ALPHAPET LTD +1
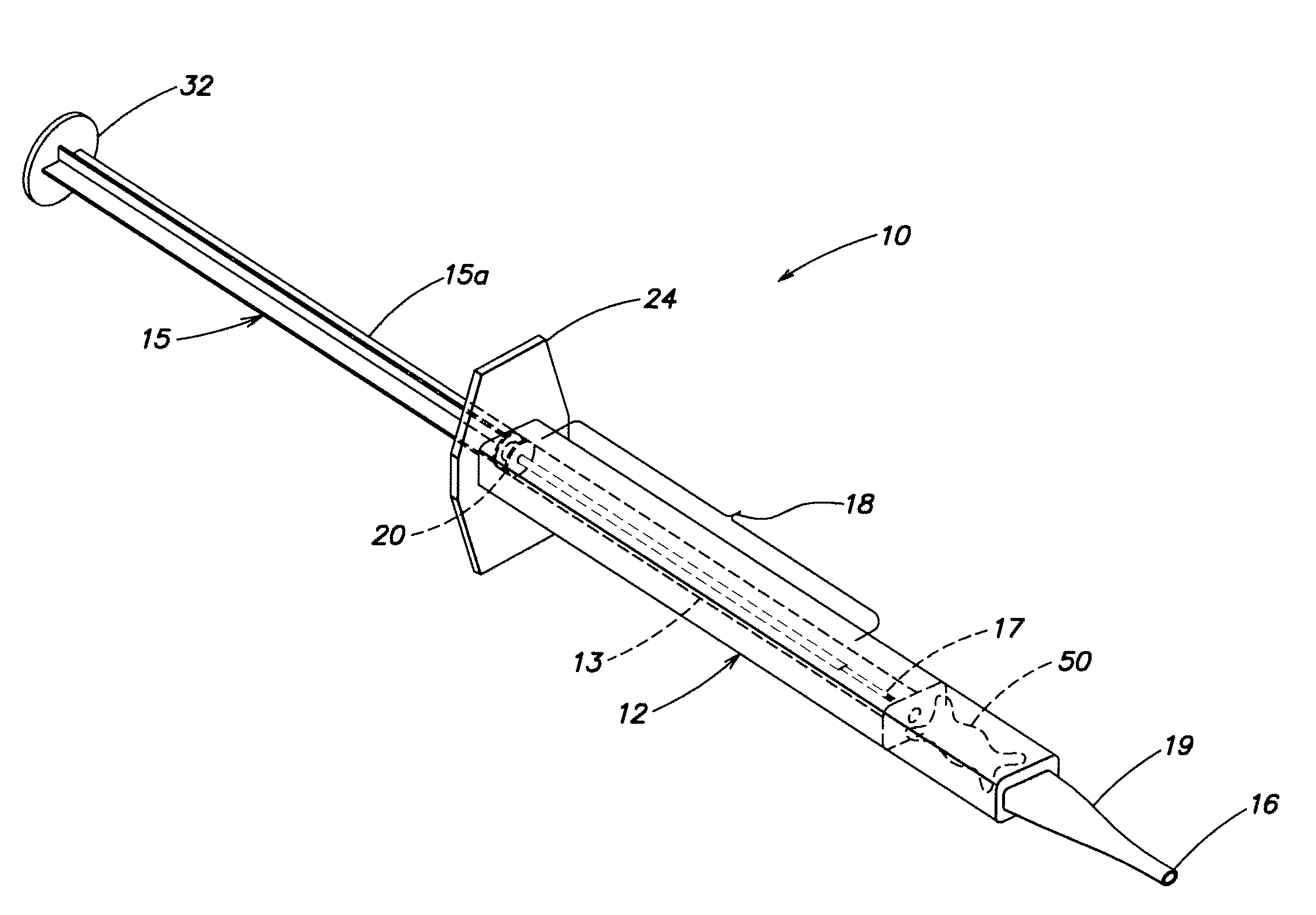
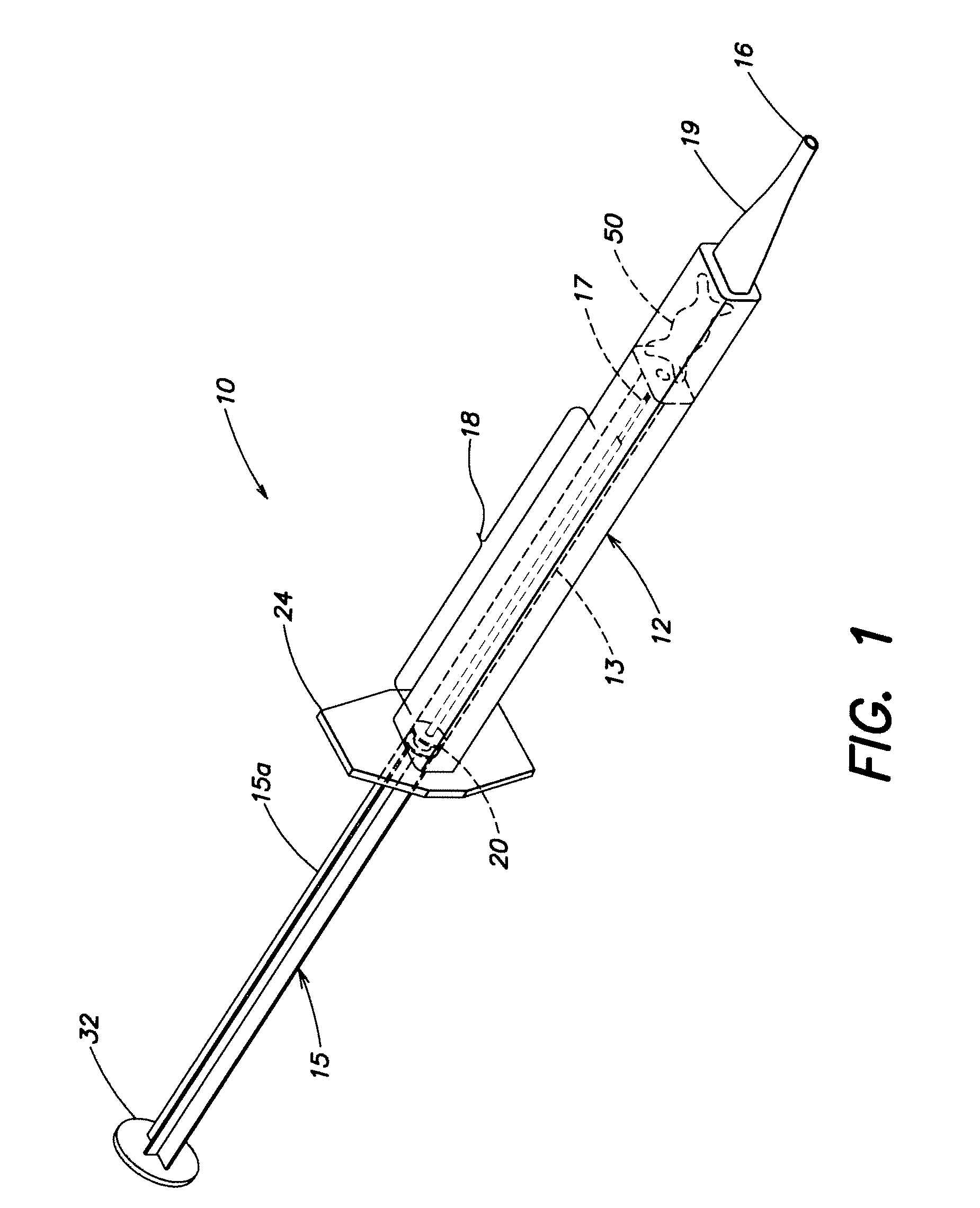
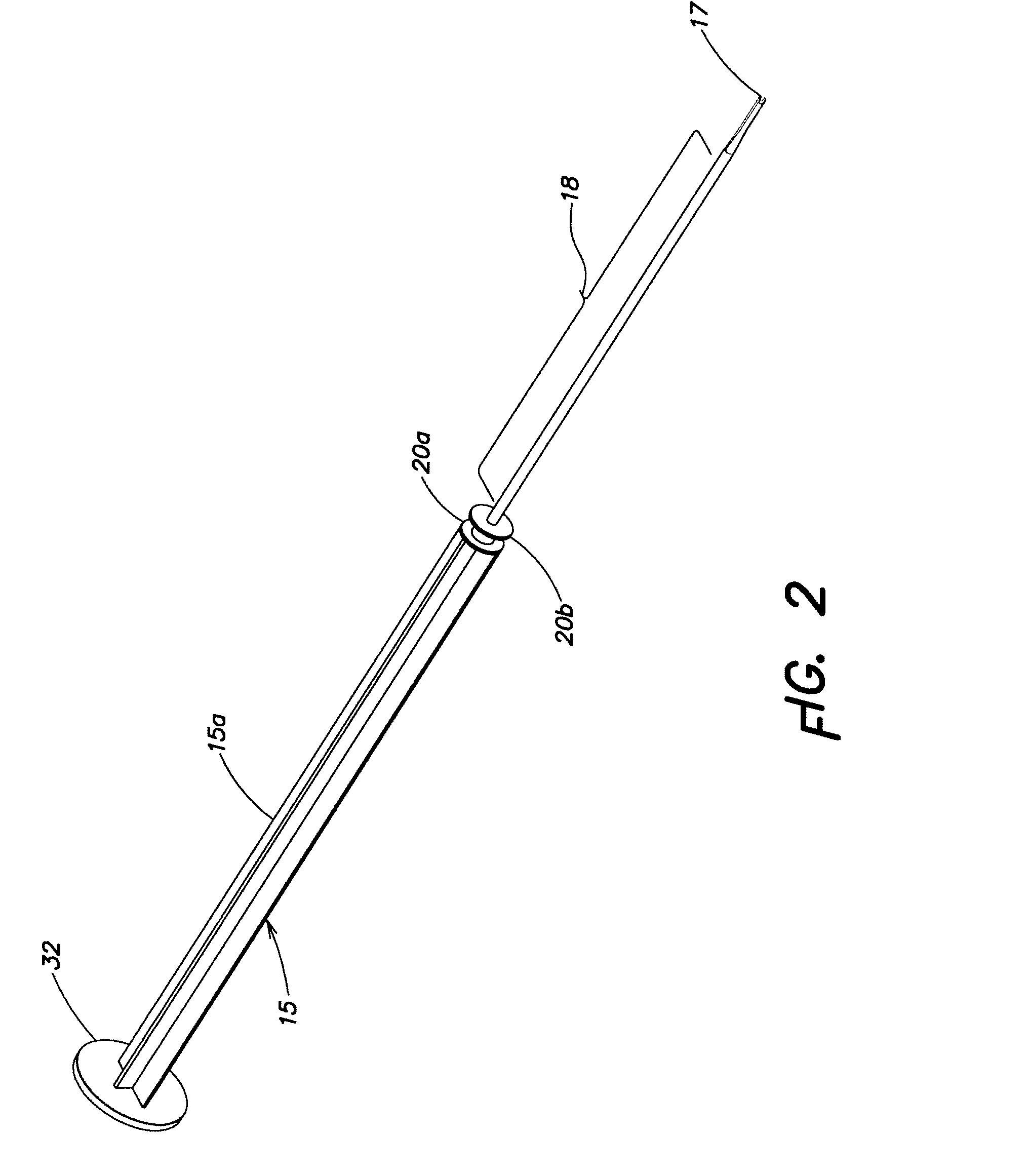
Intraocular Lens Inserter Plunger
InactiveUS20080027461A1Precise deliveryReduce deliveryEye surgeryIntraocular lensPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolyphthalamide
An IOL injector, comprising an injector body; and a plunger. The plunger comprises a shaft comprising a moldable material having a flexural modulus greater than 600 thousand psi, and a plunger tip. The moldable material may have a flexural modulus greater than 750 thousand psi or greater than 1 million psi. The plunger shaft may comprise, for example, Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT), Polyphthalamide (PPA) or liquid crystal polymer (LCP).
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Multi-layered foamed polymeric objects and related methods
ActiveUS20090104420A1Large levelIncrease in sizeClosuresClosure using stoppersPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention disclosed herein relates to relates to foamed thermoplastic material objects and articles of manufacture having an internal layered cellular structure, as well as to methods of making the same. In one embodiment, the invention is directed to a multi-layer foamed polymeric article of manufacture, comprising: a non-laminated multi-layer thermoplastic material sheet, wherein the multi-layer thermoplastic material sheet has first and second discrete outer layers sandwiching a plurality of discrete inner foamed layers, and wherein the two outer layers and plurality discrete inner foamed layers are integral with one another. The thermoplastic material may be a semi-crystalline polymer such as, for example, PET (polyethylene terephthalate), PEEK (polyetheretherketone), PEN (polyethylene napthalate), PBT (polybutylene terephthalate), PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate), PLA (polylactide), polyhydroxy acid (PHA), thermoplastic urethane (TPU), or blends thereof. The two outer layers may be unfoamed skin layers having smooth outer surfaces, and the discrete inner foamed layers may be microcellular.
Owner:DART CONTAINER +1
Method of Making Polybutylene Terephthalate and Compositions and Articles Comprising the Same
A process for making modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymers from a polyethylene terephthalate component includes reacting an oligomeric diol component selected from the group consisting of bis(hydroxybutyl)terephthalate, bis(hydroxybutyl)isophthalate, hydroxybutyl-hydroxyethyl terephthalate, and combinations thereof to a reactor; (i) a polyethylene terephthalate component selected from the group consisting of polyethylene terephthalate and polyethylene terephthalate copolymers with (ii) a diol component selected from the group consisting of 1,4-butanediol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, and combinations thereof, in the reactor under conditions sufficient to depolymerize the polyethylene terephthalate component into a first molten mixture; combining the first molten mixture is combined with 1,4-butanediol under conditions to form a second molten mixture; and placing the second molten mixture under conditions sufficient to produce the modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymers. Also described are compositions and articles made from the process.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Method for fabricating composite pressure vessels
InactiveUS6171423B1Speed up the processRatio is limitedVessel manufacturingCylinder headsPolytetramethylene terephthalateFiber
A process for fabricating a composite vessel includes the steps of: A) preforming (e.g., by winding fiber and at least one thermoplastic substance onto a thermoplastic liner) a thermoplastic shell which has at least one opening for access to the interior; B) extruding a circular cross section of a fluid parison of thermoplastic material (which preferably is chosen to have a melting point lower than that of the thermoplastic shell) into the interior of the thermoplastic shell through the opening; C) in a mold, applying at least one force (such as gas under pressure) which tends to urge the fluid parison toward the interior walls of the thermoplastic shell (which may be preheated prior to introduction into the mold) such that the fluid parison imparts heat to the thermoplastic shell; D) continuing step C) until the thermoplastic shell and the fluid parison consolidate to form a composite vessel; E) cooling the vessel until it is solidified; and F) removing the vessel from the mold. For some composite vessels, prior to step C), an insert may be introduced into the interior of the parison and positioned in alignment with the opening in the thermoplastic shell such that the insert is rendered integral with the composite vessel during step D). Suitable thermoplastic materials include polyethylene, polypropylene, polybutylene terephthalate and polyethylene terephthalate. The resulting composite vessel exhibits superior mechanical and aesthetic properties.
Owner:FLECK CONTROLS +1
Process for making polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) from polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
The invention relates to a process for making modified polybutylene terephththalate random copolymers from a polyethylene terephthalate component. The invention relates to a three step process in which a diol component selected from the group consisting of ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, and combinations thereof reacts with a polyethylene terephthalate component under conditions sufficient to depolymerize the polyethylene terephthalate component into a first molten mixture; and where the first molten mixture is combined with 1,4-butanediol under conditions that create a second molten mixture that is subsequently placed under subatmospheric conditions that produce the modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymers. The invention also relates to compositions made from the process.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Polymer Compositions, Method of Manufacture, and Articles Formed Therefrom
ActiveUS20080246181A1Improve ductilityIncrease modulusMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentPolytetramethylene terephthalateHeat deflection temperature
A composition comprises, based on the total weight of the composition: from 10 to 80 wt. % of a modified polybutylene terephthalate copolymer that (1) is derived from polyethylene terephthalate component selected from the group consisting of polyethylene terephthalate and polyethylene terephthalate copolymers and (2) has at least one residue derived from the polyethylene terephthalate component; from 10 to 80 wt. % of a polycarbonate; from 0 to 20 wt. % of an impact modifier; from 1 to less than 25 wt. % of a reinforcing filler; from 0.1 to less than 2.5 wt. % of a fibrillated fluoropolymer; from 0 to 5 wt. % of an additive selected from the group consisting of antioxidants, mold release agents, colorants, quenchers, stabilizers, and combinations thereof. The composition has a heat deflection temperature of at least 110° C., measured in accordance with to ASTM D648 on 3.2 mm thick molded bars at 0.455 MPa.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Hybrid impact modifiers and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20090018248A1Improve impact performanceGood effectNanotechnologyPigment pastesThermoplasticRecovery method
The present invention relates to hybrid impact modifiers prepared by:either spray drying, coagulation, freeze coagulation or other known recovery methods of a mixture of a latex or slurry of standard impact modifiers and a slurry of a mineral filler,either simultaneous drying (by spray-drying, coagulation other known recovery possible methods) of (i) a latex or slurry of standard impact modifiers and of (ii) a slurry of a mineral filler,further to the coagulation or freeze coagulation, if any, there is a filtration and drying step to recover these hybrid impact modifiers as a powder.The host polymers to be impact modified, can be any thermoplastic. Advantageously it can be polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyamide (PA), polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), polystyrene (PS), polycarbonate (PC), thermoplastic polyesters such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), polycyclohexanedimethanol terephthalate, and polyolefins such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and any other matrix polymer which can be improved by an impact modifier.The present invention also relates to the use of said hybrid impact modifiers in thermoplastic polymers.The present invention also relates to a thermoplastic polymer containing said hybrid impact modifiers.The present invention also relates to hybrid impact modifiers having improved powder properties (flowability, lumping / caking resistance, segregation between the organic and the mineral parts).The present invention also relates to a thermoplastic polymer containing said hybrid impact modifiers with better dispersion homogeneities.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Elastomer blends containing polycarbonates and copolyetheresters derived from polyethylene terephthalate, method of manufacture, and articles therefrom
ActiveUS20080027167A1Improve performanceOutstanding performance propertyFilm/foil adhesivesElastomerPolyethylene terephthalate
A composition comprising from 10 to 90 weight percent of a copolyetherester elastomer comprising: a modified, random polybutylene terephthalate copolymer block that is derived from a polyethylene terephthalate component selected from the group consisting of polyethylene terephthalate, polyethylene terephthalate copolymers, and combinations thereof; and that contains at least one residue derived from the polyethylene terephthalate component; and a polyalkylene oxide copolymer block that is derived from the polyethylene terephthalate component and a polyalkylene oxide glycol, and that contains polyalkylene oxide and at least one residue derived from the polyethylene terephthalate component; from 10 to 90 weight percent of a polycarbonate; and from 0 to 60 weight percent of a polyester.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Gas-barrier heat-seal composite films and vacuum insulation panels comprising the same
ActiveUS20120148785A1High gas barrierImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
A gas-barrier heat-seal composite film is provided. The gas-barrier heat-seal composite film includes a heat-seal layer including very low density polyethylene (VLDPE), low density polyethylene (LDPE), linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE), high density polyethylene (HDPE), metallocene polyethylene (mPE), metallocene linear low density polyethylene (mLLDPE), ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymer, ethylene-propylene (EP) copolymer or ethylene-propylene-butene (EPB) terpolymer, and a gas-barrier layer formed on the heat-seal layer, wherein the gas-barrier layer includes a plurality of composite layers, each including a polymer substrate and a single layer or multiple layers of metal or oxide thereof which is formed on one side or both sides of the polymer substrate, and the polymer substrate includes uniaxial-stretched or biaxial-stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), polyimide (PI), ethylene / vinyl alcohol (EVOH) copolymer or a combination thereof. The invention also provides a vacuum insulation panel including the composite film.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Multi-layered foamed polymeric objects and related methods
ActiveUS7807260B2ClosuresClosure using stoppersPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolyethylene terephthalate
Owner:DART CONTAINER +1
Molding compositions containing polycarbonate and modified polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) random copolymers derived from polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
ActiveUS20070276069A1Reduce the amount requiredFibre treatmentPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolymer science
A molding composition comprising: (a) from 5 to 90 wt. % of a modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymer that (1) is derived from polyethylene terephthalate component selected from the group consisting of polyethylene terephthalate and polyethylene terephthalate copolymers and (2) has at least one residue derived from the polyethylene terephthalate component, and (b) from 5 to 90 wt. % of a polycarbonate component; and from at least 1 wt. % of an impact modifier component, wherein the modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymer, the polycarbonate component, the impact modifier, and optionally at least one additive, have a combined weight % of 100 wt %. The invention also encompasses methods for making the composition and articles made from the composition.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Polybutylene terephthalate resin composition for fusion bonding with laser and molded article
InactiveUS20050165176A1Improve Laser Welding PerformanceImprove welding strengthPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolymer science
A laser weldable PBT-series resin composition comprises a polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)-series resin (A), and at least one resin (B) selected from the group consisting of a polycarbonate-series resin (b1), a styrenic resin (b2), a polyethylene terephthalate-series resin (b3) and an acrylic resin (b4). The PBT-series resin (A) may be a PBT homopolyester, or a PBT-series copolymer modified with not more than 30 mol % of a copolymerizable monomer (e.g., a bisphenol compound or an adduct thereof with an alkylene oxide, and an asymmetrical aromatic dicarboxylic acid). The ratio (weight ratio) of the resin (B) relative to the PBT-series resin (A) [the former / the latter] is about 0.1 / 1 to 1.5 / 1. The resin composition may comprise a glass fiber. The resin composition is excellent in laser weldability, and can improve in welding strength of a shaped article formed from the resin composition.
Owner:WIN TECH POLYMER LTD
Articles derived from compositions containing modified polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) random copolymers derived from polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
Compositions of matter including articles derived from (a) from 5 to 99.99 wt % of a modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymer that (1) is derived from polyethylene terephthalate and (2) contains a at least one residue derived from polyethylene terephthalate selected from the group consisting of antimony, germanium, diethylene glycol groups, isophthalic acid groups, cis isomer of cyclohexane dimethanol, trans isomer of cyclohexane dimethanol, sodium benzoate, alkali salts, napthalane dicarboxylic acids, 1,3-propane diols, cobalt, cobalt-containing compounds, and combinations thereof, and (b) from 0.01 to 95 wt. % of a member selected from the group consisting of (1) fillers, (2) a carboxy reactive component, (3) polyethyelene terephthalate, (4) a component including a polycarbonate and an impact modifier. The articles may be derived from various conversion processes, e.g., injection molding processes, extrusion processes, thermoforming processes, melt-blown process.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
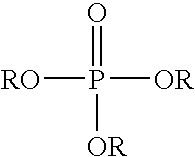
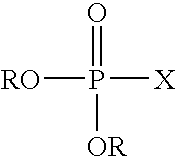
Esterification catalyst and process therewith
InactiveUS20050215425A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsTitanium organic compoundsPolytetramethylene terephthalateOligomer
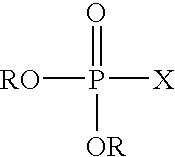
A process for producing polybutylene terephthalate comprises contacting terephthalic acid or its salt or its ester and butylenes glycol, in the presence of a catalyst composition, which comprises, or is produced from, titanium or a titanium compound, a complexing agent, a phosphorus-containing ester, and optionally a solvent. The process can also comprise contacting terephthalic acid or its salt or its ester and a glycol, in the presence of a catalyst composition to produce an oligomer and contacting the oligomer with a phosphorus-containing ester in which the catalyst composition can be one that catalyzes esterification or transesterification or polycondensation.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Molding compositions containing polyalkylene terephthalates and modified polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) random copolymers derived from pet
A molding composition comprising (a) from 5 to 90 wt % of a modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymer that (1) is derived from polyethylene terephthalate component selected from the group consisting of polyethylene terephthalate and polyethylene terephthalate copolymers and (2) at least one residue derived from the polyethylene terephthalate component, and (b) from 5 to 40 wt % of a polyalkylene terephthalate component; wherein the modified polybutylene terephthalate random copolymer, the polyalkylene terephthalate component, and optionally, at least one additive, have a combined weight % of 100 wt %. Methods for making the composition and articles made from the composition.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Preparation method of functional polyester fibers
ActiveCN102719932AHigh crystallinityImprove mechanical propertiesFilament forming substance formingMelt spinning methodsPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolyethylene glycol
The invention provides a preparation method of functional polyester fibers. The preparation method mainly comprises the following two steps of: firstly, mixing functional powders, polybutylene terephthalate cyclic oligomer (CBT) and a dispersing agent, performing reactive extrusion on the mixture by double screws to prepare a polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) functional master batch, wherein the functional powders are one of or several of a carbon nano tube, nano titanium dioxide, tourmaline powders, a nano-silver antibacterial agent, a nano silicon oxide and fluorescent powders; and secondly, blending and spinning the master batch, the PBT, polyethylene glycol terephthalate (PET) or polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) to prepare the functional polyester fibers. According to the method, the reactive extrusion process is adopted, the operation is simple and convenient, the process flow is shortened greatly, the obtained PBT functional master batch contains 30wt%-40wt% of the functional powders, and can be well dispersed in a base body, the compatibility of the obtained functional master batch and polyester polymer is good, and the fiber obtained by the method has an obvious functional effect.
Owner:ZHOUSHAN XINXIN CHEM FIBER
Combination piece of metal and plastic and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN101578018AHigh strengthEasy to integratePivotable antennasCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsPolytetramethylene terephthalateUltimate tensile strength
The invention provides a combination piece of metal and plastic, which comprises a metal body and a plastic part, wherein the metal body and the plastic part are formed integrally by adopting embedded forming technology; at least one positioning structure is formed on a combine part of the metal body and the plastic part; a material of the metal body is selected from one of a magnesium alloy, an aluminum alloy and a titanium alloy; and a material of the plastic part is selected from one of a liquid crystal high polymer, polyphenylene sulphide and polybutylene terephthalate. The invention also provides a manufacture method for the combination piece of the metal and the plastic. The combination piece of the metal and the plastic has the advantages of high strength, difficult deformation and cracking and adaptability in thinning design.
Owner:FU ZHUN PRECISION IND SHENZHEN +1
Shape-memory polybutylene terephthalate film, production process and use thereof, and process for production of polybutylene terephthalate film
InactiveUS20060051540A1Easy to shapeImprove stabilityStampsWrappersPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolymer science
A polybutylene terephthalate laminate film having excellent shape memory and high-temperature dimensional stability obtained by (1) subjecting a laminate film comprising a polybutylene terephthalate film and another film or film laminate to a shaping treatment at a temperature T1 equal to or lower than the glass transition temperature of said polybutylene terephthalate while maintaining a first shape; (2) deforming the shaped laminate film to a second shape at a temperature T2 higher than said glass transition temperature; and (3) cooling said laminate film to a temperature T3 equal to or lower than said glass transition temperature.
Owner:KAGAWA SEIJI
Preparation method of polybutylene terephthalate/adipate butanediol copolyester
The invention relates to a preparation method of polybutylene terephthalate / adipate butanediol copolyester, which utilizes a titanium compound and an antimony compound as the composite catalyst, the mole ratio of terephthalic acid to adipate is 3:7-8:2, the ratio of the total mole of the terephthalic acid and the adipate to the mole of 1,4-butanediol is 1:1.0-1.8, esterification is carried out at normal pressure and the temperature of 150-220 DEG C, the pressure is reduced to high vacuum 10-150 Pa for the reaction, the final temperature for the reaction is 265-280 DEG C, and inert gas is utilized to recover the pressure to be normal to obtain the copolyester. The reaction time is shortened, the production amount of tetrahydrofuran is small, the intrinsic viscosity of copolyester chips is 0.90-1.32 dL / g, the hue b value of the product is between 0 and 8, the L value is between 68 and 85, and the product of the polybutylene terephthalate / adipate butanediol copolyester can be used in the fields of various soft package plastic products.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
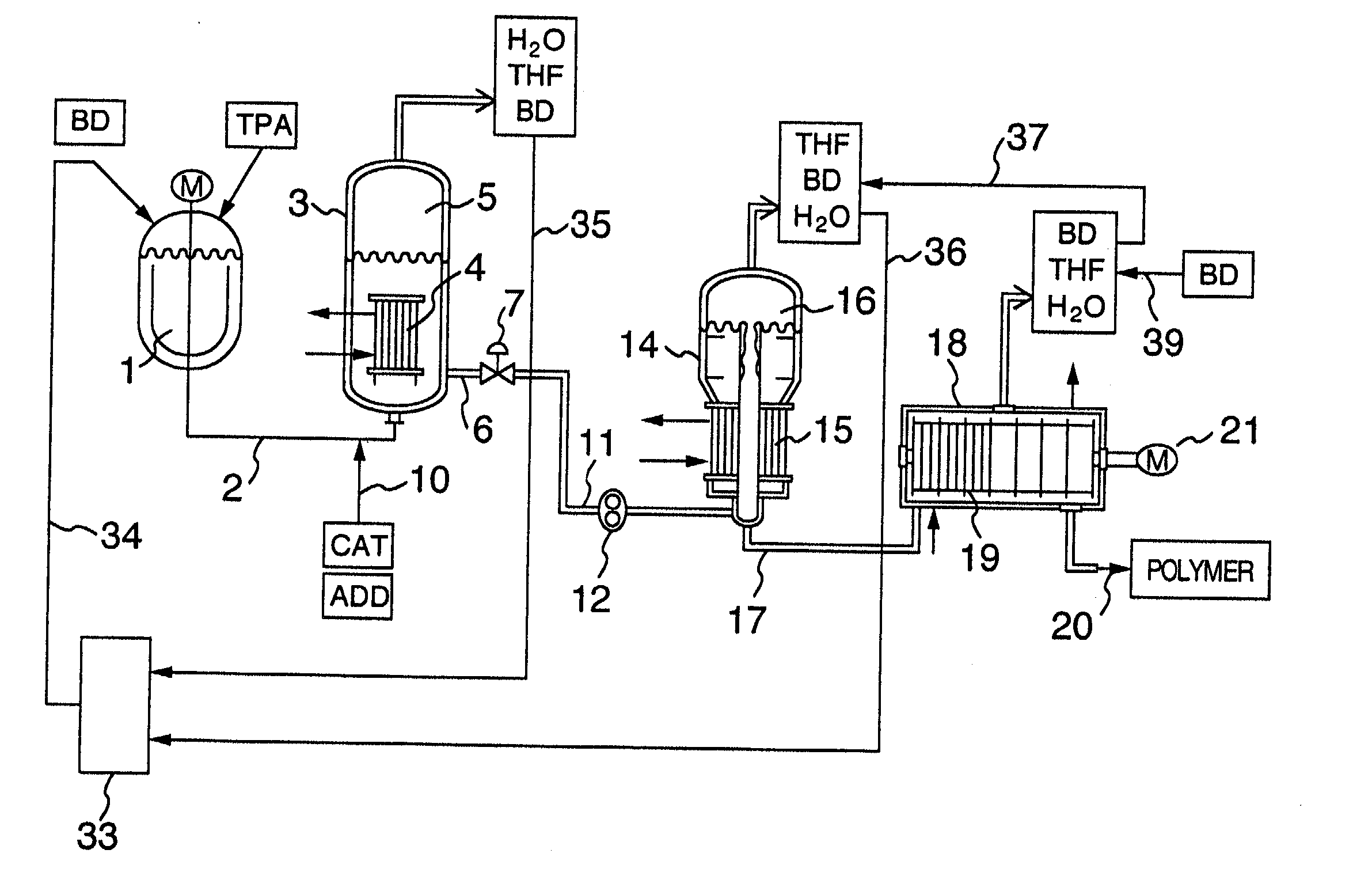
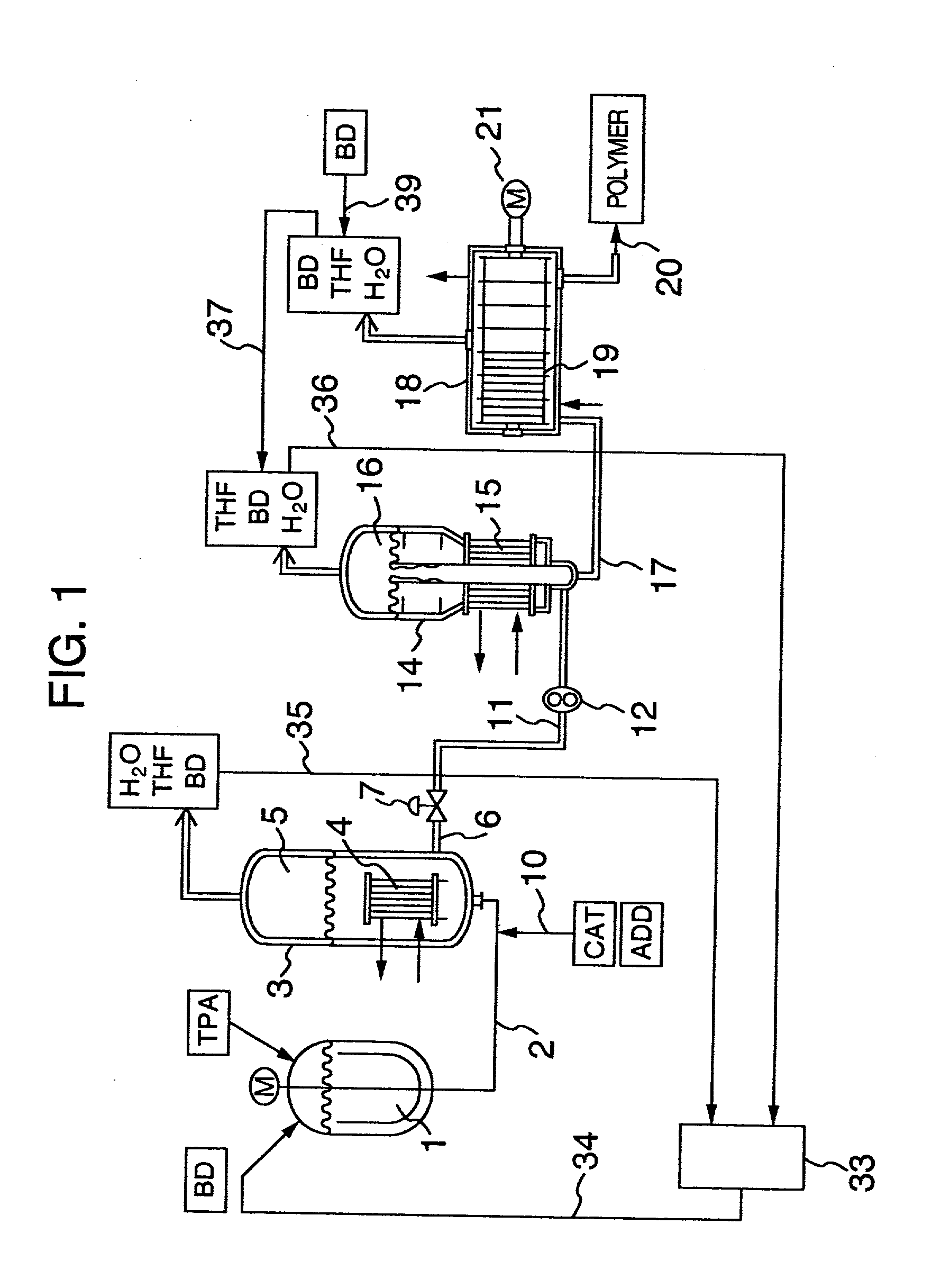
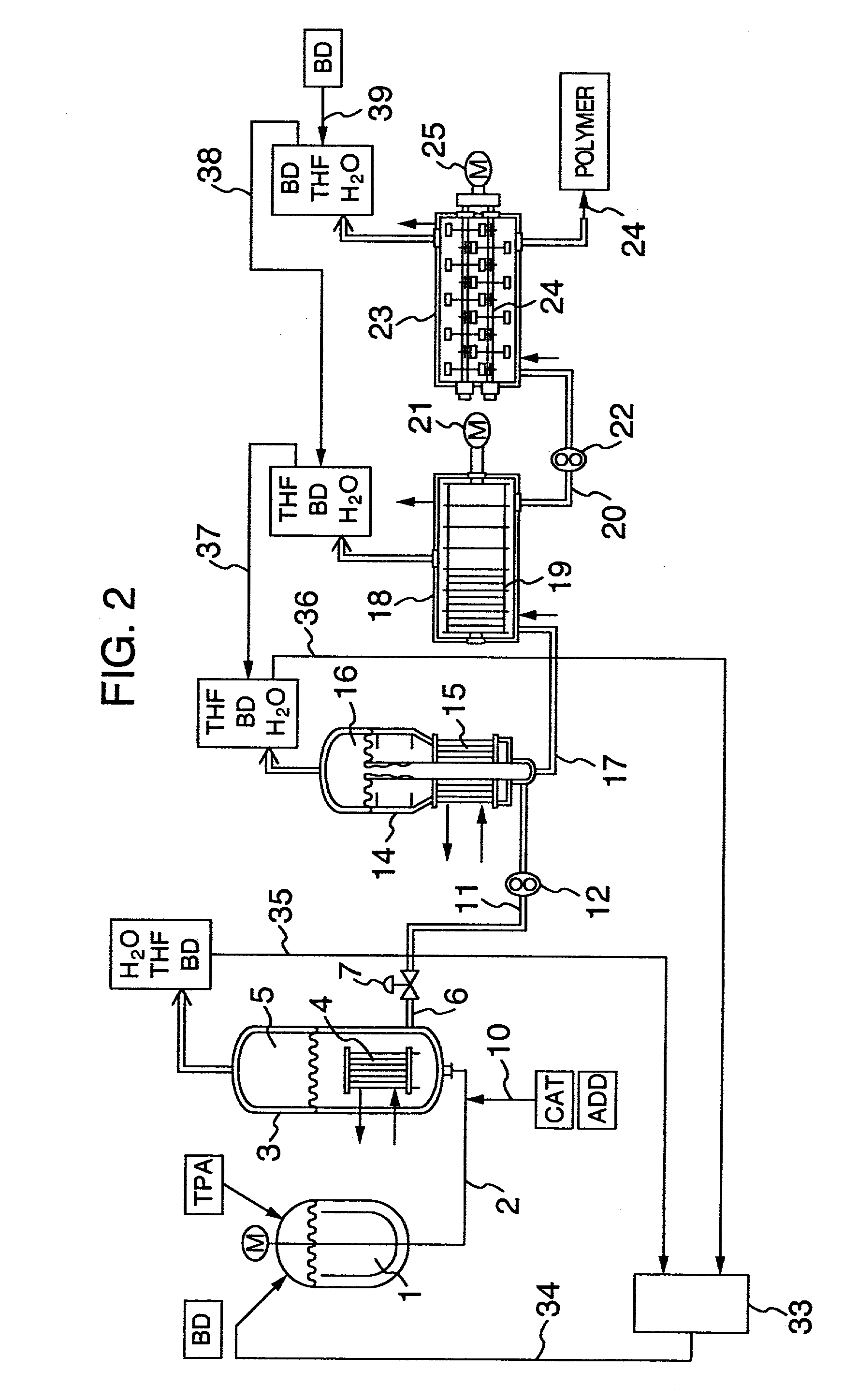
Process for continuously producing polybutylene terephthalate
InactiveUS20020128399A1Improve effectivelyGood molding effectChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsLiquid-gas reaction processesPolytetramethylene terephthalatePolybutylene
Polybutylene terephthalate having good heat stability and excellent hydrolysis resistance is continuously produced in a series of a first reactor for reacting an aromatic dicarboxylic acid comprising terephthalic acid as a main ingredient or a derivative thereof with a glycol comprising 1,4-butanediol as a main ingredient, thereby producing an oligomer with an average degree of polymerization of 2.2 to 5, a second reactor for polycondensating the oligomer from the first reactor, thereby preparing a low polymerization product with an average degree of polymerization of 25 to 40, and a third reactor for further polycondensating the low polymerization product from the second reactor, thereby producing a high molecular weight polyester with an average degree of polymerization of 70 to 130, or followed by a fourth reactor for further polycondensing the polyester from the third reactor to an average degree of polymerization of 150 to 200, thereby producing a high molecular weight polyester. Another third reactor or a plurality of third reactors can be provided in parallel to the third reactor, thereby producing different kinds of polybutylene phthalate with different degrees of polymerization from that produced in the main line of the third and fourth reactors or adjusting operating conditions of each of a plurality of the third reactors to increase kinds, precise quality.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Matrix tray with tacky surfaces
InactiveUS6926937B2Widen meansSufficient forceEnvelopes/bags making machinerySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPolyetherimidePolybutylene terephthalate
A tray for handling and retaining a plurality of small components comprising a rigid body portion with a plurality of pockets formed therein. Each of the pockets has an elastomeric contact surface for contacting and retaining a component. The contact surface may be formed from a thermoplastic material having a surface energy between 20 dyne / cm and 100 dyne / cm, and a surface electrical resistivity of between about 1×104 ohms / square and 1×1012 ohms / square. The material for the contact portion may be urethane, polybutylene terephthalate, polyolefin, polyethylene terephthalate, styrenic block co-polymer, styrene-butadiene rubber, polyether block polyamide, or polypropylene / crosslinked EDPM rubber. The body portion may be formed from acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene, polycarbonate, urethane, polyphenylene sulfide, polystyrene, polymethyl methacrylate, polyetherketone, polyetheretherketone, polyetherketoneketone, polyether imide, polysulfone, styrene acrylonitrile, polyethylene, polypropylene, fluoropolymer, polyolefin, or nylon. The body portion may have a peripheral border region and a downwardly projecting skirt portion to facilitate stacking of multiple trays.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Full-biodegradable material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a full-biodegradable material which is characterized by comprising the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 30-65% of starch, 5-15% of vegetable oil, 15-50% of polylactic acid, 10-20% of polybutylene adipate-polybutylene terephthalate copolymer and 5-30% of compatilizer. Preferably, the compatilizer accounts for 5-20% of the total weight of the raw materials. The full-biodegradable material has the advantages of excellent and stable properties and low cost, is biodegradable, well gives consideration to economic benefit and environmental benefit, and has wide application prospects. The invention also provides a preparation method of the full-biodegradable material. The preparation method is easy to implement, operate and control, can easily implement industrial production, and is beneficial to lowering the cost of the full-biodegradable material.
Owner:ECOTA ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Transparent flexible surface enhanced Raman active substrate and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a transparent flexible surface enhanced Raman active substrate and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the substrate comprises the following steps: taking a transparent flexible material such as polybutylene terephthalate (PET) plastics as a substrate, performing O2 plasma etching to form a nano wire array, loading gold, silver and other precious metal nanoparticles on the nano wire surface by virtue of a coating technology, and forming a three-dimensional nanometer structure array. The transparent flexible surface enhanced Raman active substrate provided by the invention is uniform in morphology and controllable in structure and has high-density electromagnetic hot spots in three-dimensional distribution. Therefore, the substrate has high sensitivity and reproducibility. The PET plastic film is high in flexibility and high in transparency, and incident laser and Raman scattered light easily penetrate through the substrate at low loss, so that the substrate can be used for in-situ detection of to-be-detected objects. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple in process, large-area preparation is easily realized, even roll-to-roll production process is permitted, and the cost is low.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com