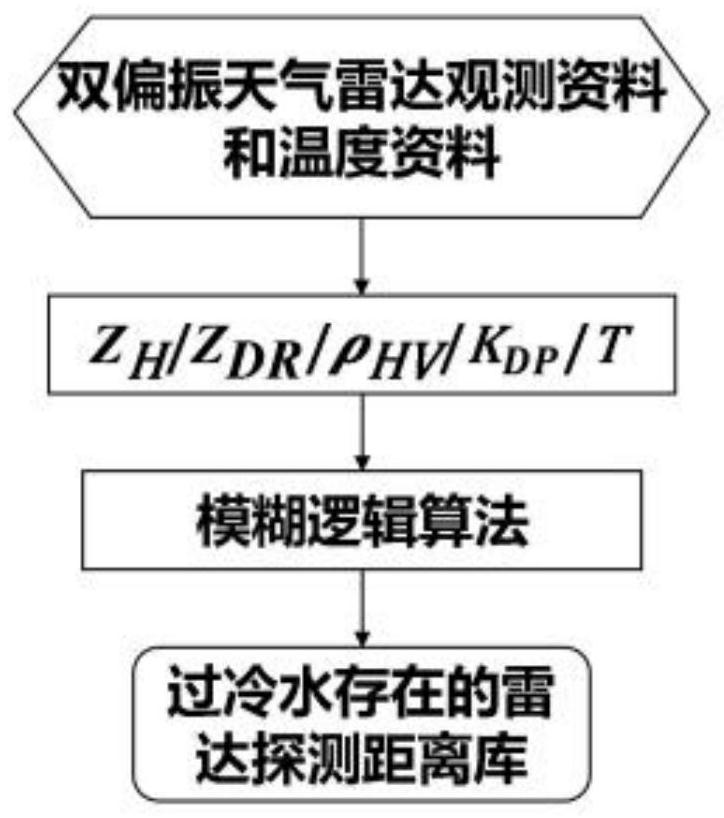
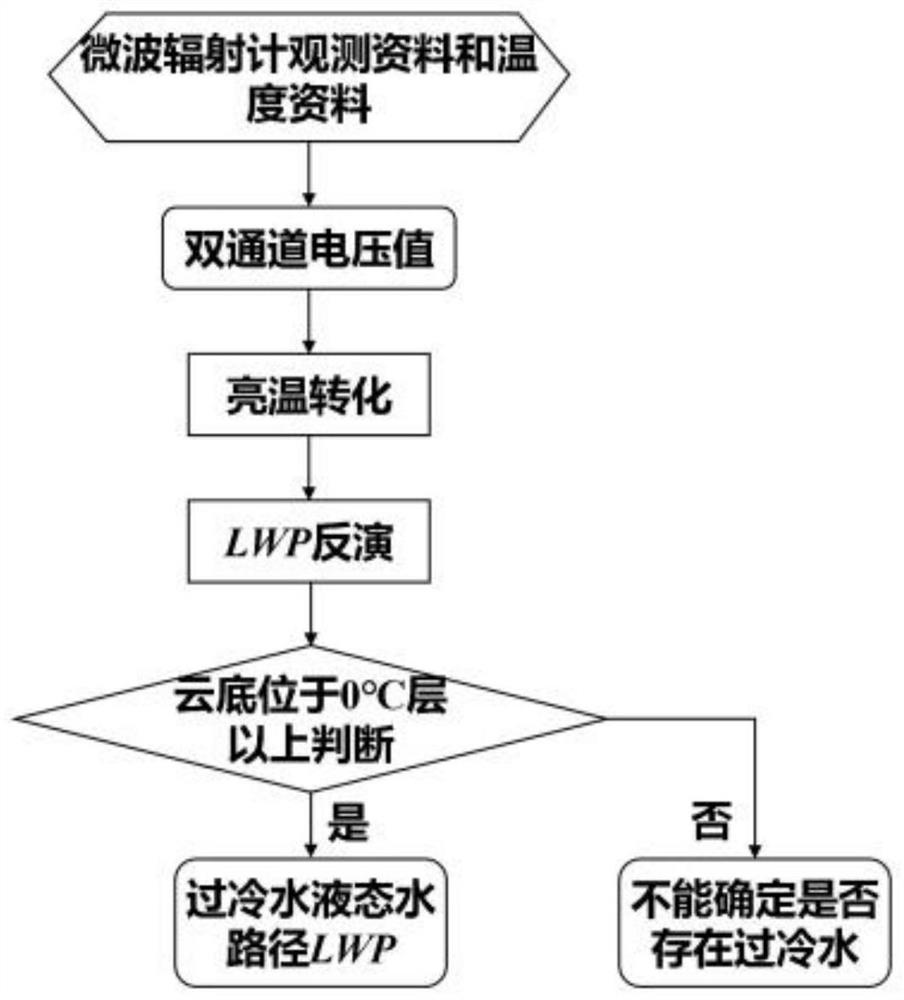
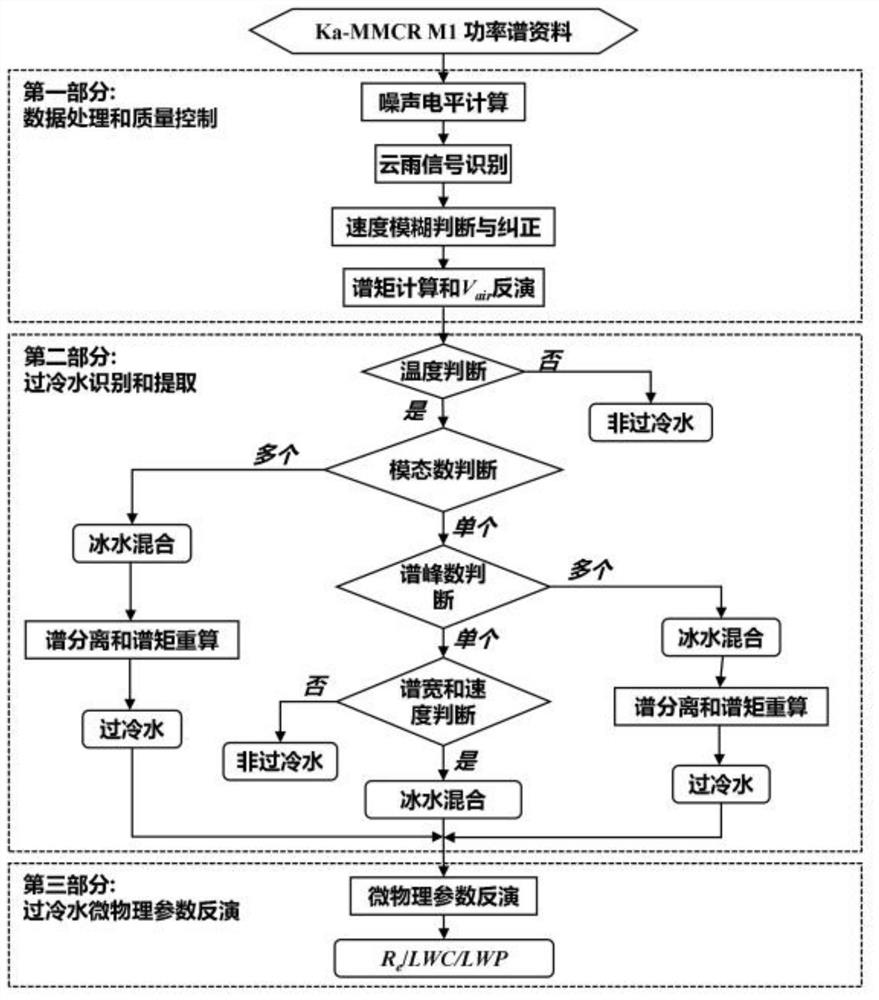
Method and device for detecting supercooled water by utilizing millimeter wave cloud radar and application
A supercooled water and millimeter wave technology, applied in measurement devices, re-radiation, radio wave measurement systems, etc., can solve problems such as inability to detect supercooled water, and achieve the effect of high speed resolution and high spatial and temporal resolution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0200] Using the observation data obtained by the Ka-band millimeter-wave cloud radar and microwave radiometer installed in a certain place during the TIPEX-III test, combined with the sounding temperature data of the station, the stratification of a certain day at 22:45-01:00 Supercooled water in clouds is detected using the method of the present invention.
[0201] available:
[0202] as attached Figure 4 The spatio-temporal distribution results of radar parameters of cloud particles in convective clouds detected by millimeter-wave cloud radar are shown, where (a)-(d) are the reflectivity factors Z e , spectral width σ v , Atmospheric vertical velocity V air and the average particle falling velocity From this figure, it can be seen that: from the Z of the global spectrum e According to the echo, the stratocumulus cloud lasted for 2 hours and 15 minutes over the station, the cloud top was about 4.5km high, and the fluctuation was small, but the echo intensity gradient ...
Embodiment 2
[0205] Using the observation data obtained by the Ka-band millimeter-wave cloud radar and microwave radiometer installed in a certain place during the TIPEX-III test, combined with the sounding temperature data of the station, the cumulus congestus on a certain day from 15:45 to 17:30 The supercooled water in cumulus, cumulus and altocumulus is detected using the method of the present invention.
[0206] available:
[0207] as attached Figure 6 The spatio-temporal distribution results of radar parameters of cloud particles in convective clouds detected by millimeter-wave cloud radar are shown, where (a)-(d) are the reflectivity factors Z e , spectral width σ v , Atmospheric vertical velocity V air and the average particle falling velocity It can be seen that from the global spectrum Z e It can be seen that cumulus congestus appeared from 15:50 to 16:40 and lasted for nearly 50 minutes. The cloud layer developed relatively high, and the highest cloud top could exceed 7.5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com