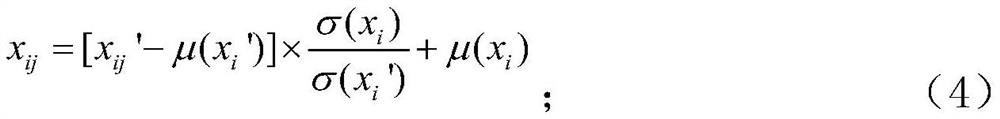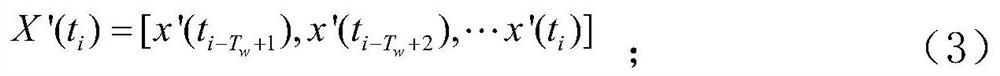Power distribution network abnormity identification method based on data driving
An anomaly identification, data-driven technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, digital data information retrieval, special data processing application, etc. The effect of recognition accuracy and fast calculation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
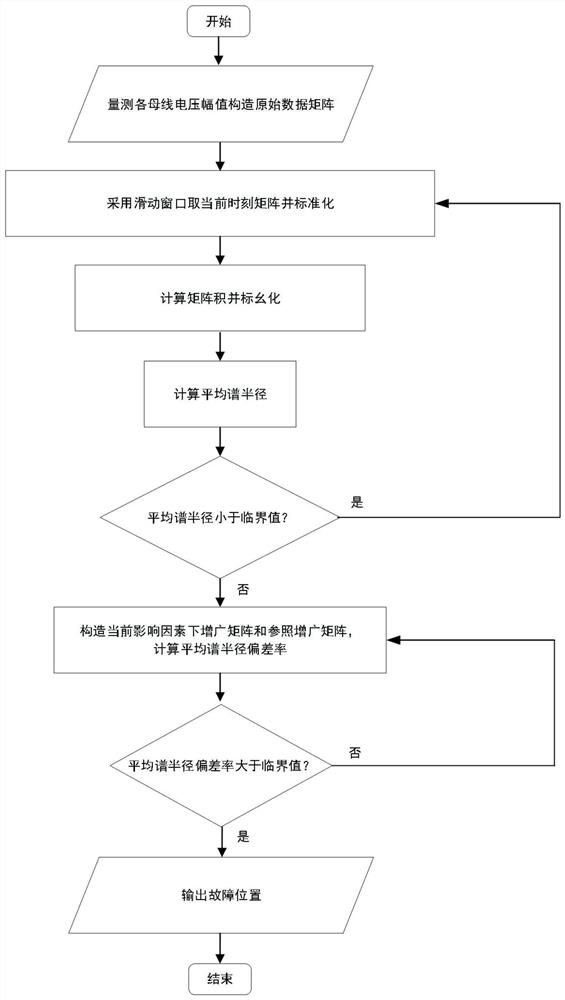
[0056] A data-driven distribution network anomaly identification method, which establishes a high-dimensional matrix model composed of voltage measurement data of each node, selects the average spectral radius as the linear eigenvalue statistic, and determines the time when the fault occurs; applies the augmented matrix theory to analyze the data Correlation analysis, the average spectrum radius deviation rate is constructed as a quantitative index, and the influence degree of each node voltage on the system operation state is measured.
Embodiment 2
[0058] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the construction and standardization process of the high-dimensional matrix model is as follows: select N state quantities in the distribution network to represent the operating state of the system, including the amplitude of the three-phase voltage or current of the node and phase angle, active power and reactive power; at sampling time t i Form an N-dimensional sample column vector at a time:
[0059] x'(t i ) = (x 1 ',x 2 ',...x N ') T ;
[0060] The data vectors of all sampling moments in T samples are concatenated in time order to form a large matrix of N×T dimensions:
[0061] X'=[x'(t 1 ), x'(t 2 ),…,x’(t i ),…];
[0062] This matrix contains the time and space information of the system, and is the original data source for applying the big data-driven method. The sliding time window technology can separate the measurement data of the current moment and the historical moment, and analyze the operating status of th...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Difference with embodiment two is: comprise matrix product and per unitization process thereof, specifically as follows: first obtain the singular value equivalence matrix of X by following formula
[0069]
[0070] in is a Haar unitary matrix; now consider the product of L independent non-Hermitian matrices:
[0071]
[0072] The matrix Z is per unitized by formula (6):
[0073]
[0074] Finally, a matrix element with expectation and variance satisfying The standard matrix product of According to the random matrix theory, when the number of rows and columns of the matrix X is N,T→∞ and the ratio of rows and columns c=N / T∈(0,1], The empirical spectrum of eigenvalues is almost all distributed within the ring, The probability density of is as follows:
[0075]
[0076] In the formula: λ is eigenvalues, L is the number of matrices; from formula (8), we can see that the standard matrix product on the complex plane The eigenvalues have a high ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com