Channel and asynchronous impulse noise joint estimation method in OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) system
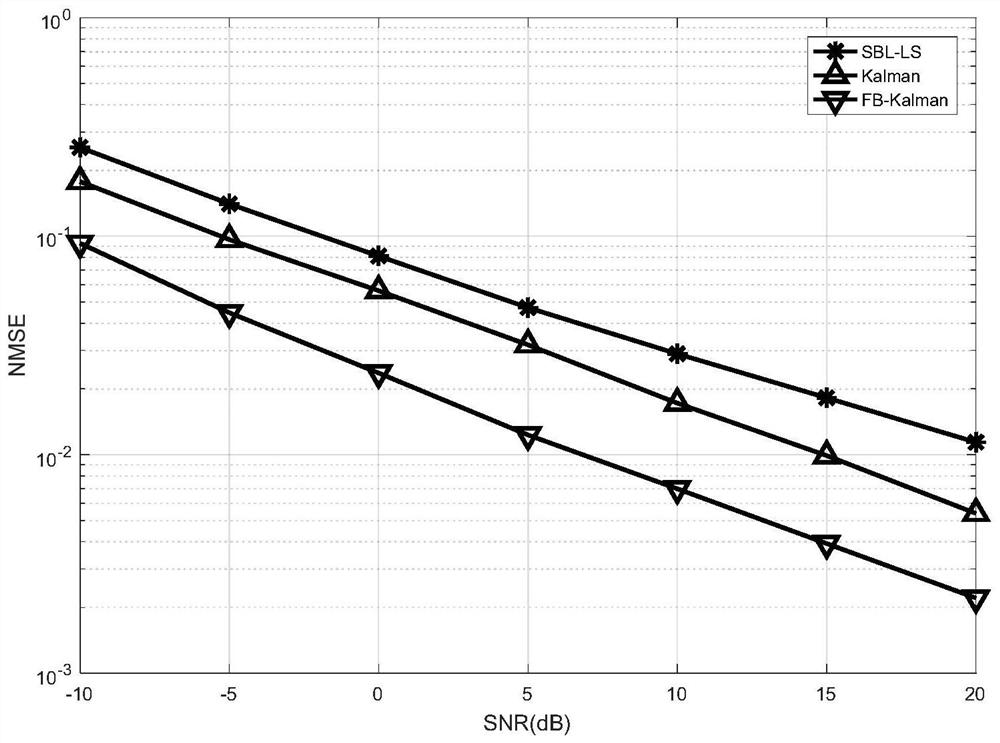
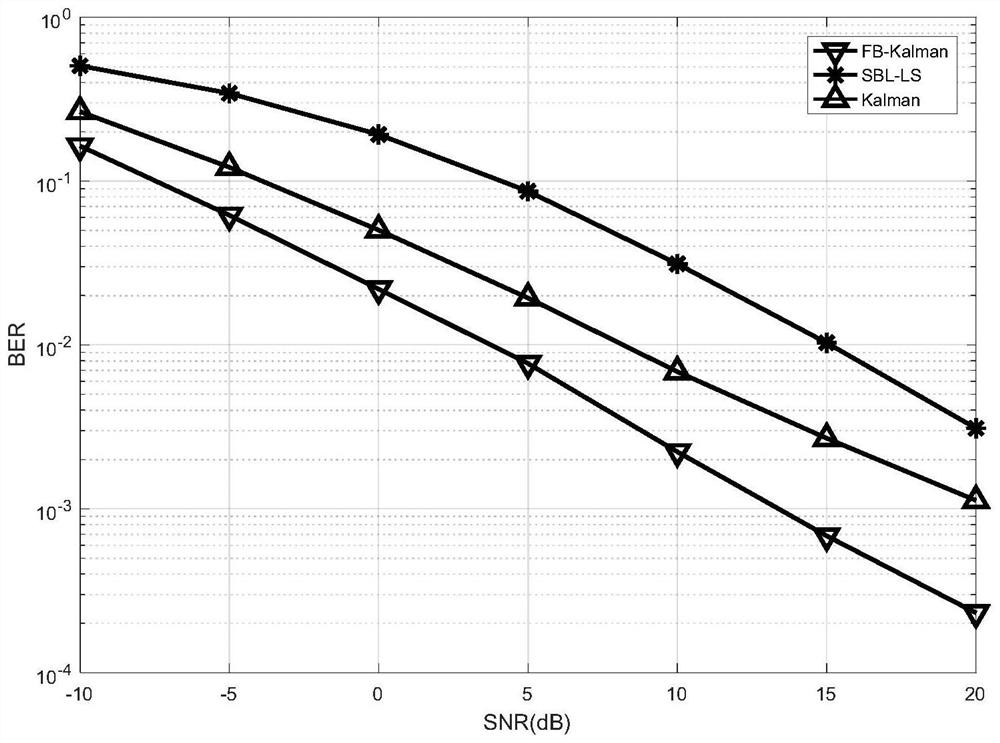
An impulse noise and joint estimation technology, applied in the field of channel and impulse noise joint estimation, can solve problems such as performance degradation, carrier interference, and performance empty sub-carrier number limitation, achieve good performance advantages, improve accuracy, and improve channel estimation performance. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
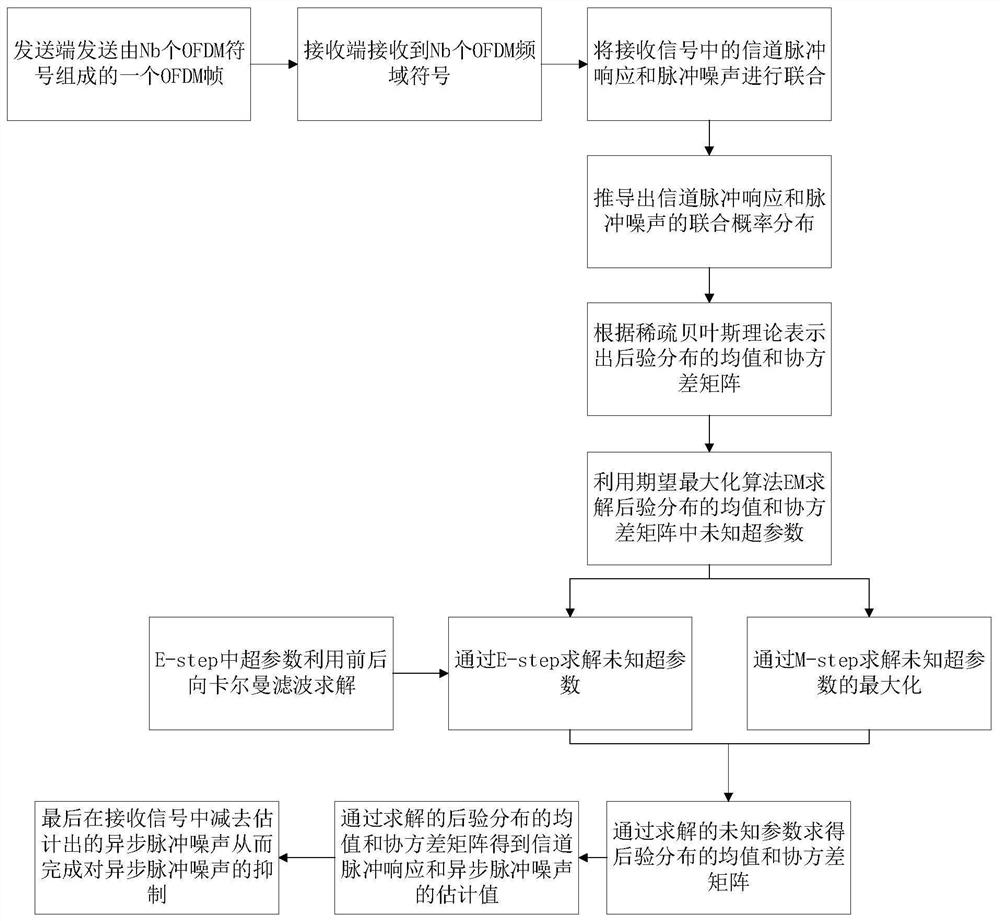
[0025] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0026] A method for joint estimation of channel and asynchronous impulse noise in an OFDM system proposed by the present invention, its overall realization block diagram is as follows figure 1 As shown, it includes the following steps:
[0027] Step 1: set the OFDM system to have N subcarriers, and the channel of the OFDM system is a slow time-varying channel; b An OFDM frame consisting of OFDM symbols; at the receiving end of the OFDM system, N is received on each subcarrier b frequency domain signals, the mth frequency domain signal received on any subcarrier is denoted as r m , r m =D m f L h m +Fi m +w m; among them, N, N b , m are positive integers, N≥1, such as taking N=256, N b ≥1, if take N b =7, the initial value of m is 1, 1≤m≤N b ,D m Represents a diagonal matrix of dimension N×N, D m =diag(d m ), d m Represents the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com