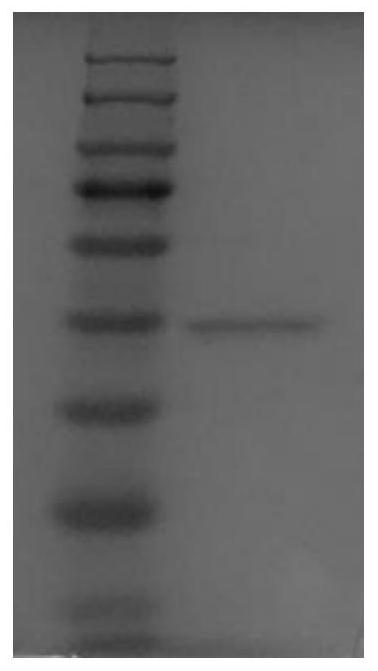
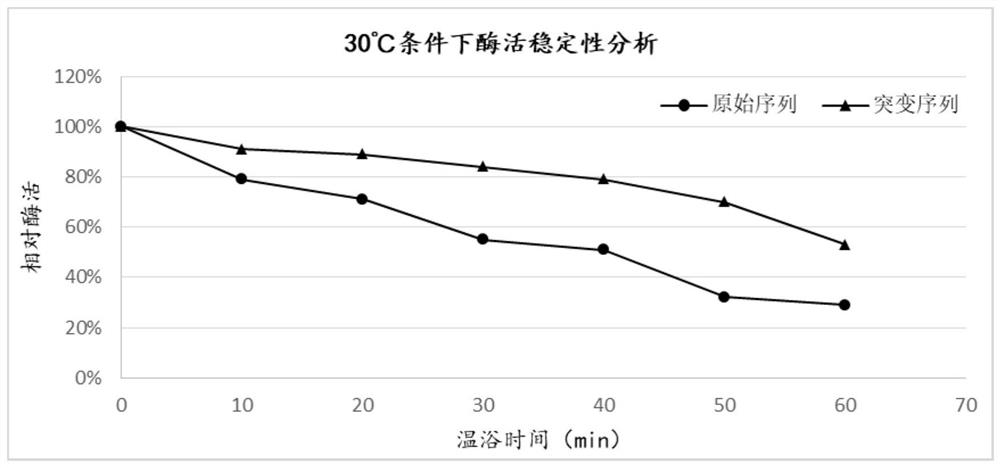
Heparinase I
A technology of heparinase and recombinant vector, which is applied in the field of biological genetic engineering and fermentation engineering, can solve the problems of large loss of enzyme activity, complex process, high cost, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the stability of enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0049] The present invention provides a preparation method of heparanase I, the preparation method comprising the following steps: first synthesizing the nucleotide sequence encoding the heparanase I involved in this paper, and then recombining the nucleotide sequence with eukaryotic cells to express The vectors are combined to obtain a recombinant vector; the recombinant vector is transformed into a host cell, then induced to express, and then purified to obtain heparanase I.
[0050] In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, in the above preparation method, the steps of synthesizing the nucleotide sequence encoding the heparanase I involved in this paper are as follows:
[0051] First, reverse-translate the amino acid sequence of the original heparanase I into a nucleotide sequence. Preferably, the obtained nucleotide sequence should be preferred by the selected host cell. In the present invention, the translated nucleotide sequence is The nucleotide sequence obtai...
Embodiment 1
[0076] Example 1 Improves the nucleotide sequence optimization of heparanase I and constructs an expression vector
[0077] (a) The amino acid sequence of the original heparanase I is derived from the published sequence of heparanase I in the NCBI database. The URL of the NCBI database is: https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / protein / ACB38160.1 .
[0078] (b) Suzhou Jinweizhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. reverse-translated the protein sequence into a DNA sequence according to the codon usage preference of Pichia pastoris in the Pichia pastoris codon preference data table, so that the codons of the DNA sequence Preferred by Pichia pastoris.
[0079] (c) Perform mutation modification on potential protease cleavage sites, and perform full sequence synthesis of the modified sequences respectively to obtain mutant nucleotide sequences.
[0080] (d) On the pPink-HC recombinant expression vector, two restriction sites, EcoRI and EcoRV, were selected to disconnect the expression vector, and the...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2 Competent preparation and electrotransformation
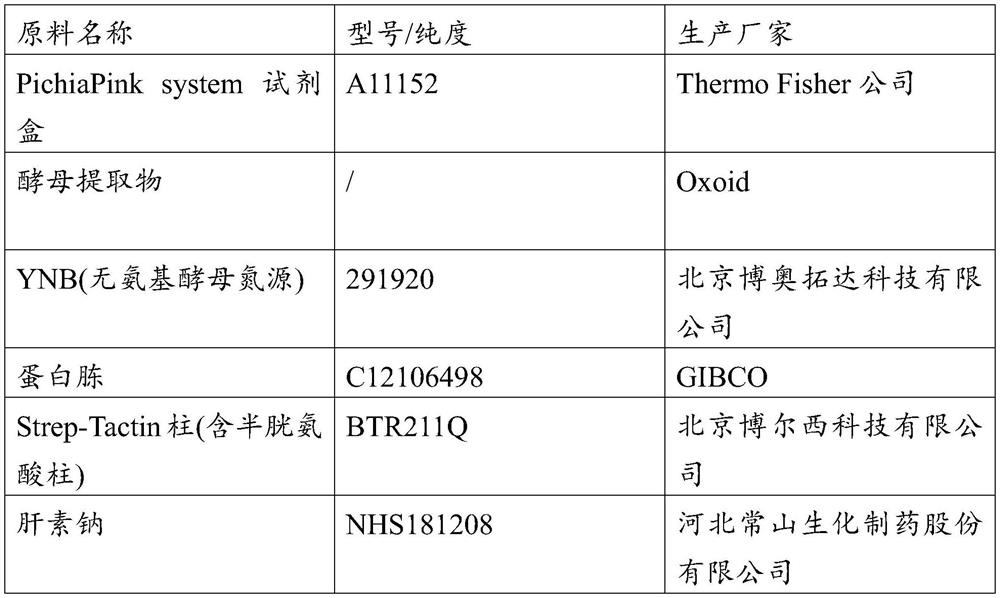
[0082] Follow the operating instructions of the PichiaPink system kit.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com