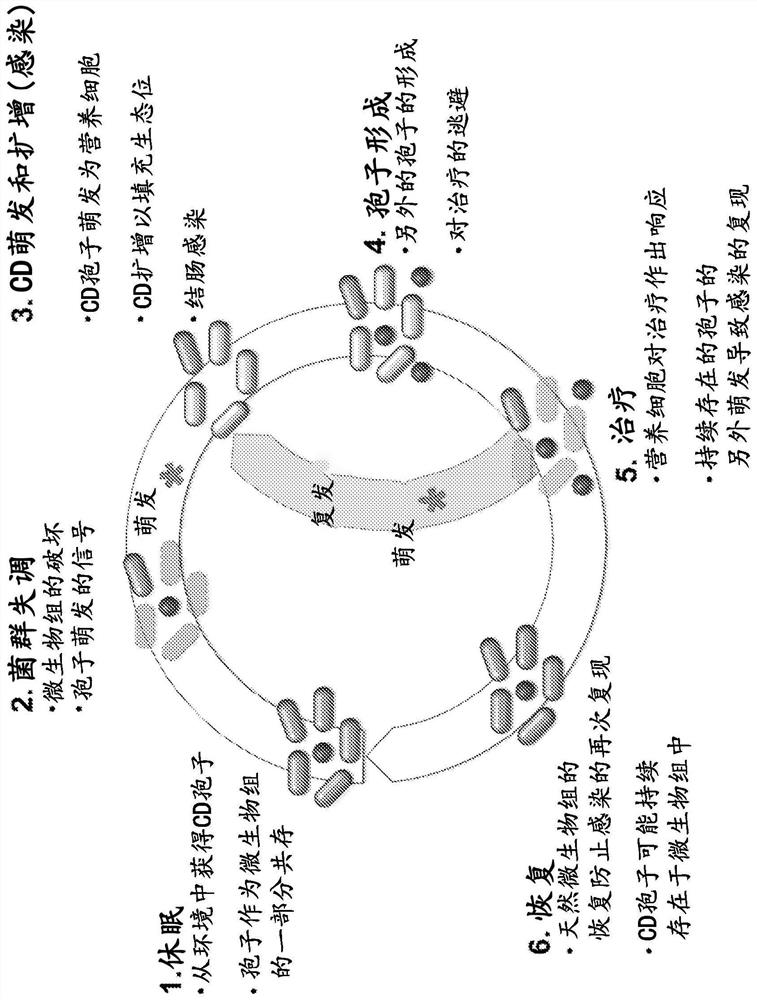
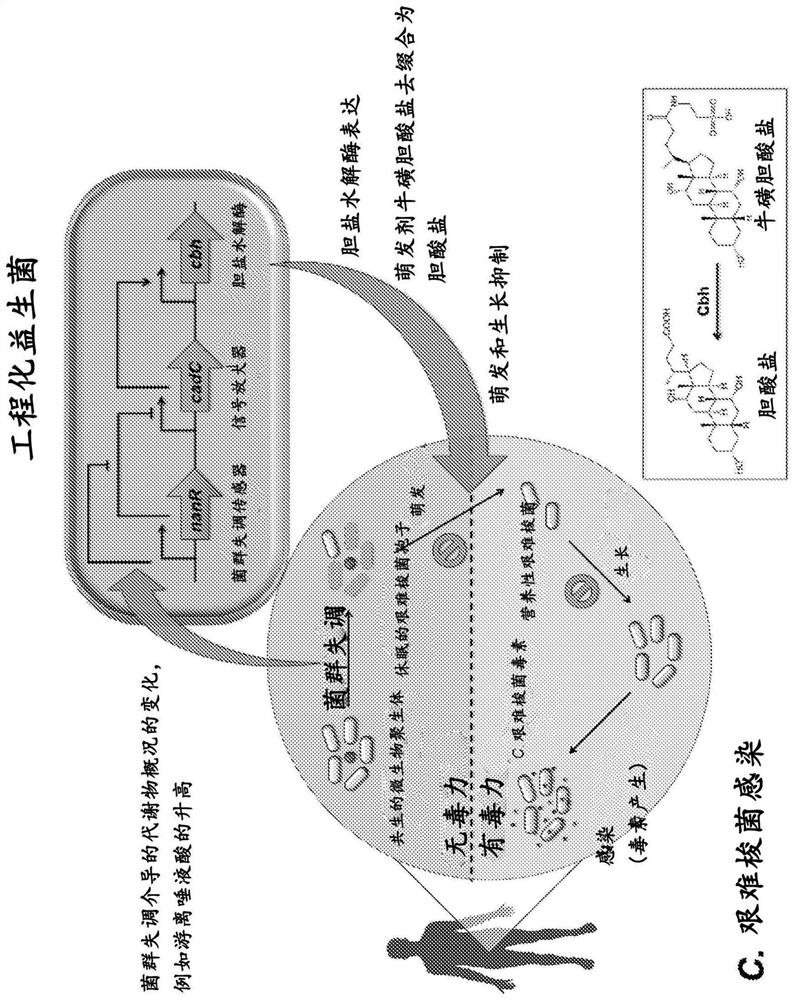
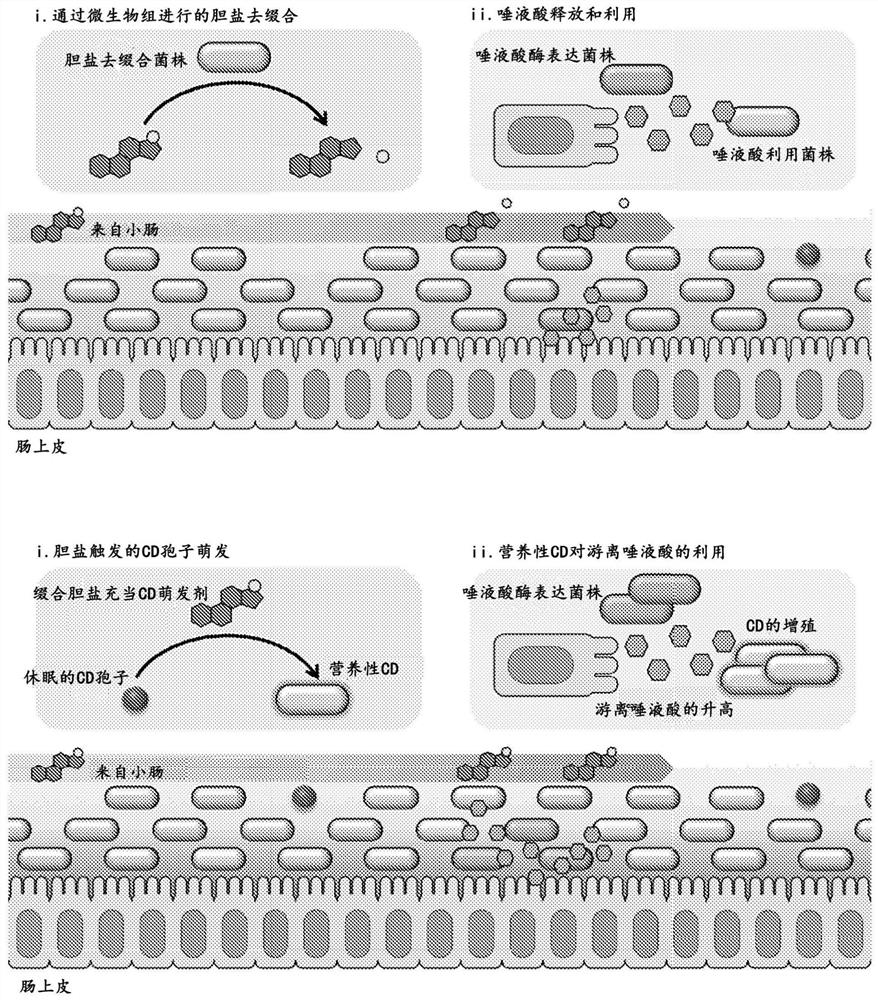
Engineered flora disorder sensing probiotics for clostridium difficile infection and recurrent infection management
A probiotics and expression cassette technology, applied in the field of engineered dysbacteriosis sensing probiotics for management of Clostridium difficile infection and recurrent infection, can solve problems such as unidentified specific species, unknown, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] Engineering of a probiotic chassis without antibiotic selection
[0074] One of the challenges in implementing engineered probiotics in vivo is ensuring the long-term stability of the genetic circuits in the chassis. Engineered genetic circuits are often engineered on plasmids and maintained by antibiotic selection, but such techniques are not feasible for in vivo applications. For colonizing probiotics in the gastrointestinal tract, maintenance of plasmid stability by continuous antibiotic selection cannot be conveniently achieved.
[0075] To achieve a plasmid chassis system that does not require antibiotic maintenance, an auxotrophic phenotype was generated in the E. coli Nissle wild-type strain. The alanine racemase gene essential for D-alanine biosynthesis was deleted from the E. coli Nissle genome to generate strain EcN( Figure 5 A). D-alanine is required for bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. Deletion of D-alanine prevents further division of the bacteria, re...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Optimization of NanR-dependent sialic acid-inducible promoters
[0080] The sequence of the sialic acid-inducible promoter pNanA (SEQ ID NO:4) from the MG1655 E. coli genome was obtained from the EcoCyc database [Keseler, I.M. et al. Nuc.Acids.Res.41:605-12 (2013)]. The promoter Subcloned upstream of the gfp gene in the pEaat plasmid (pEaat-pNanA-gfp), and then transformed into T10 and EcN for expression characterization ( Image 6 A). Unexpectedly, the two E. coli strains showed different responses to sialic acid induction ( Image 6 B). Induction of sialic acid results in positive activation of the T10 pNanA promoter, resulting in GFP expression. On the other hand, GFP under the pNanA promoter in EcN was strongly expressed in the absence of sialic acid, but repressed when induced by high concentrations of sialic acid.
[0081] The difference in response indicates that pNanA is regulated differently between T10 and EcN. NanR (SEQ ID NO:5) was previously identified...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Characterization of engineered sialic acid biosensors under gastrointestinal-specific conditions
[0087]The parental strain of EcN preferentially colonizes the lower gastrointestinal tract, especially the colon and rectum [Sonnenborn, U. and Schulze, J. Micob. Ecol. Health Dis. 21:122-58 (2009); Schultz, M. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 14(7):1012-8(2008)]. This makes it ideal as a biosensor for dysbiosis in the lower gastrointestinal tract. Selected constructs were characterized under a range of conditions specific to the lower gastrointestinal tract to assess their suitability.
[0088] Note that the pNanA sequence contains a catabolite-activating protein (CAP) binding site at position 4→8. CAP is a transcriptional activator protein that initiates the transcription process when bound to circulating AMP (cAMP). cAMP levels are elevated in the absence of glucose, thereby effectively acting as a transcriptional activator in response to low glucose. EcNs containing inducible (p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com