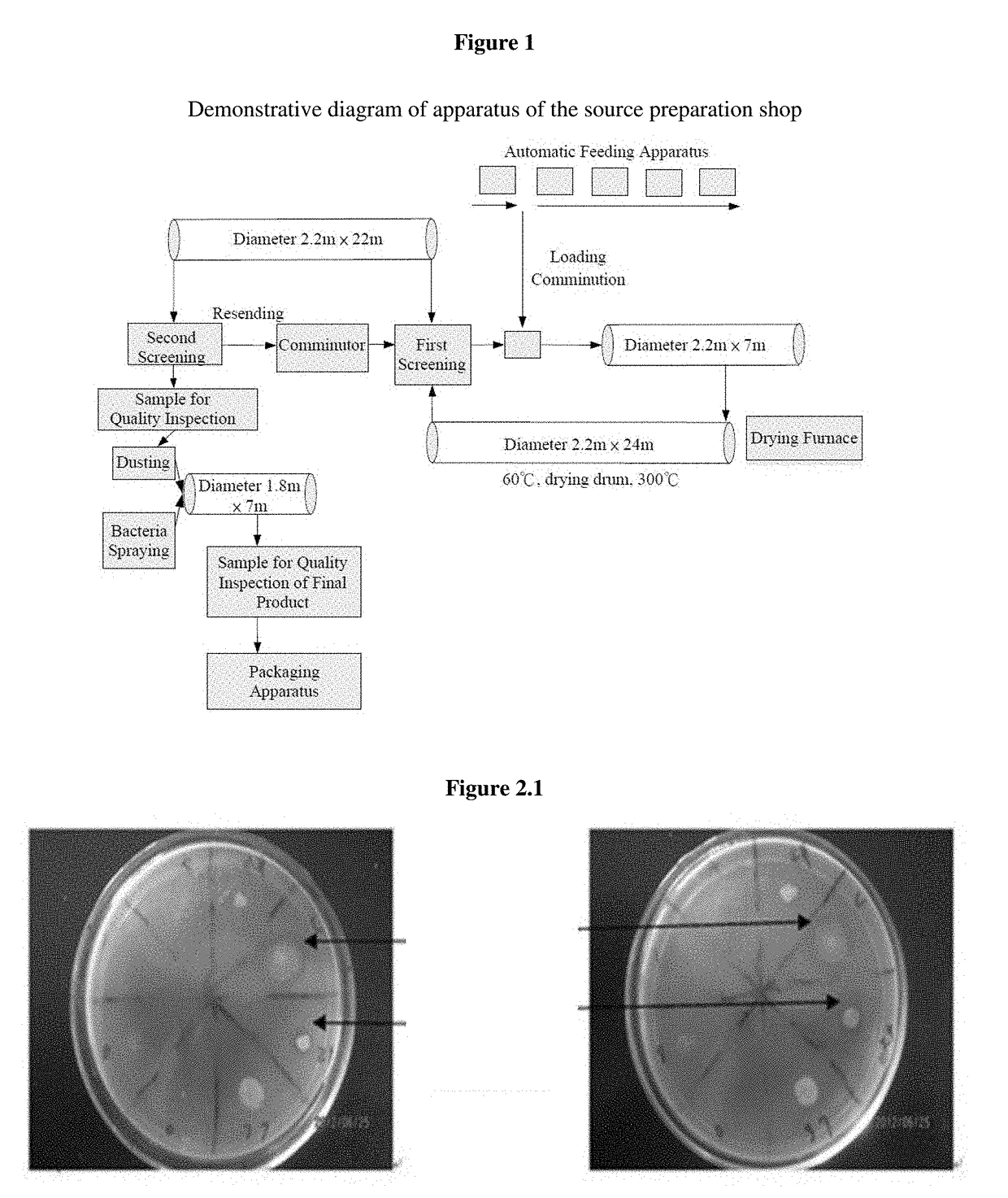
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Endospore Forming Bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
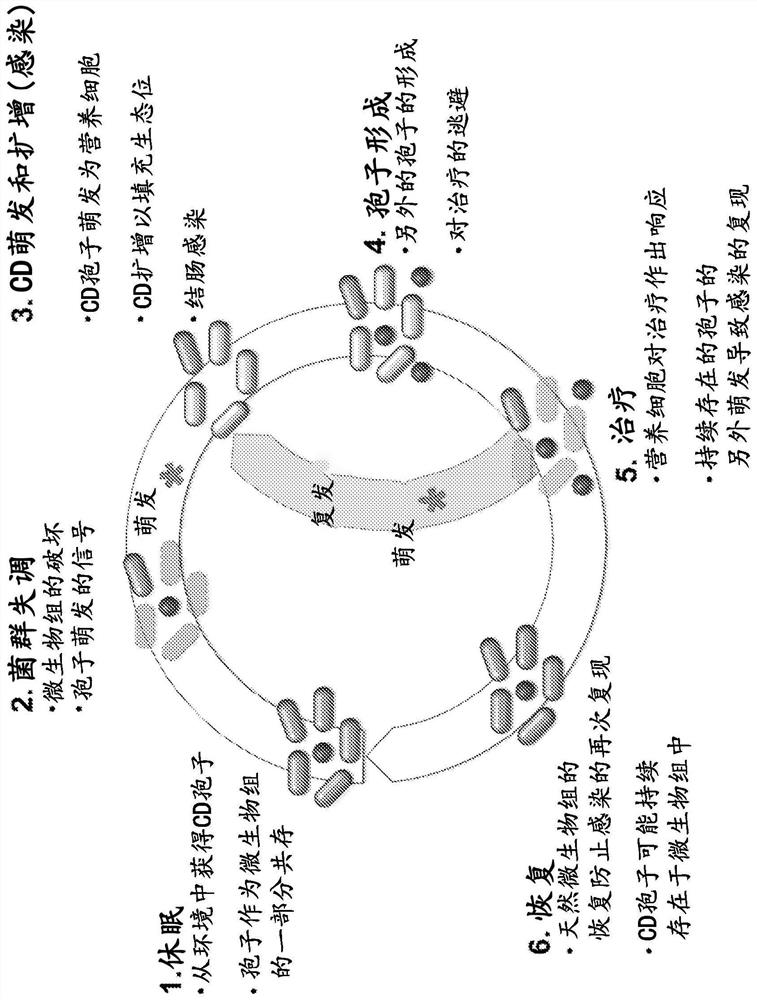
Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients, and usually occurs in gram-positive bacteria. In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall. One side then engulfs the other. Endospores enable bacteria to lie dormant for extended periods, even centuries.
Method and a product for the rapid decontamination and sterilization of bacterial endospores
The present invention is directed to a method for the disinfection and sterilization of material and surfaces contaminated with one or more members selected from the group consisting of bacteria and bacterial spores, comprising the steps of: (a) providing a biocidal fluid containing a mixture of effective amounts of a germinant and a germicide; and (b) contacting the material and surfaces contaminated with one or more members selected from the group consisting of bacteria and bacterial spores, with the biocidal fluid of step (a) for a time sufficient for disinfecting and sterilizing said material. The invention also provides a sterilizing composition suitable for killing and rendering spores lifeless comprising: (a) an effective amount of a germinating agent; (b) an effective amount of a germicide.
Owner:BAUGH CLARENCE L +2
Method for effecting the rapid release of a signature chemical from bacterial endospores, and for detection thereof
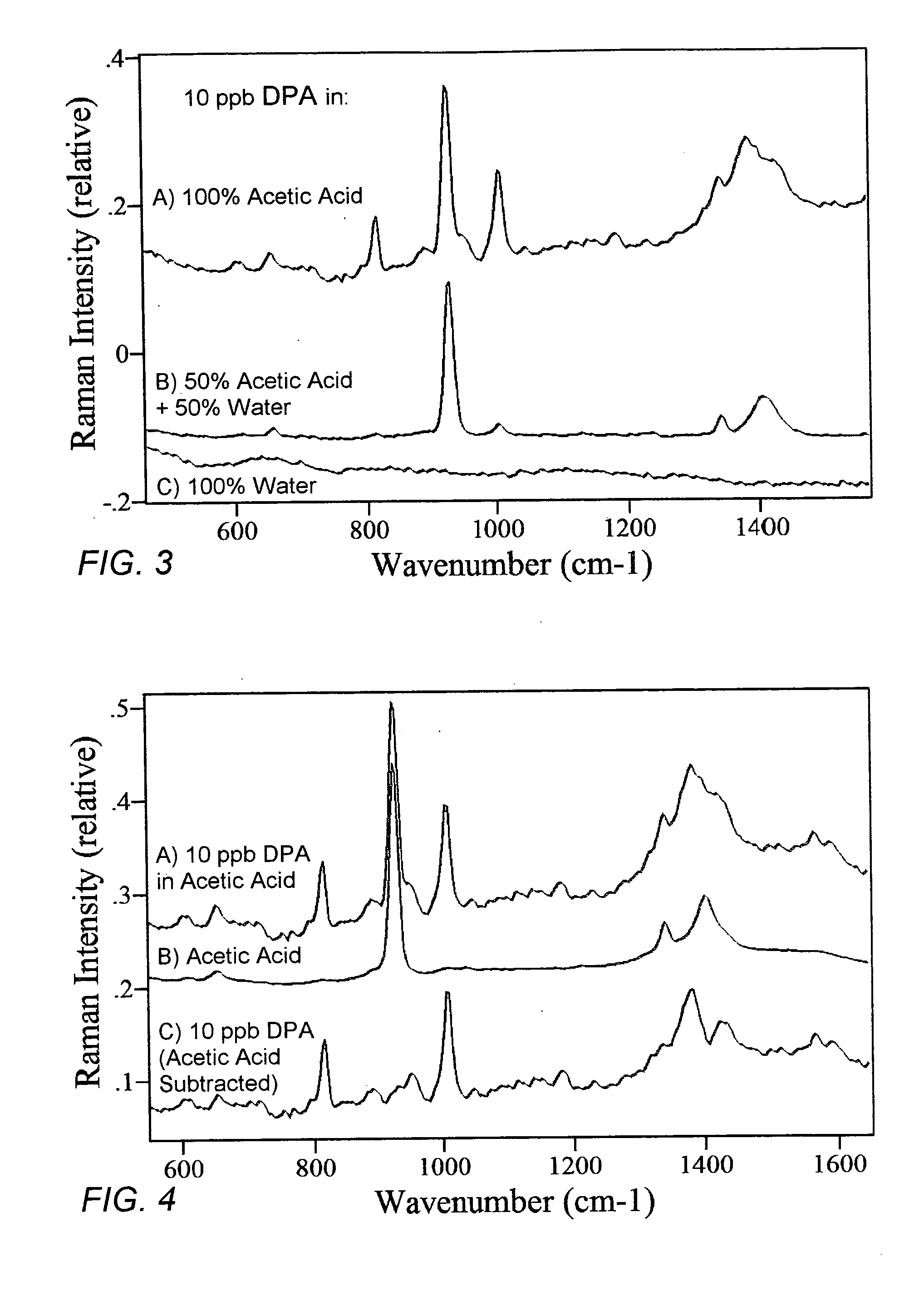
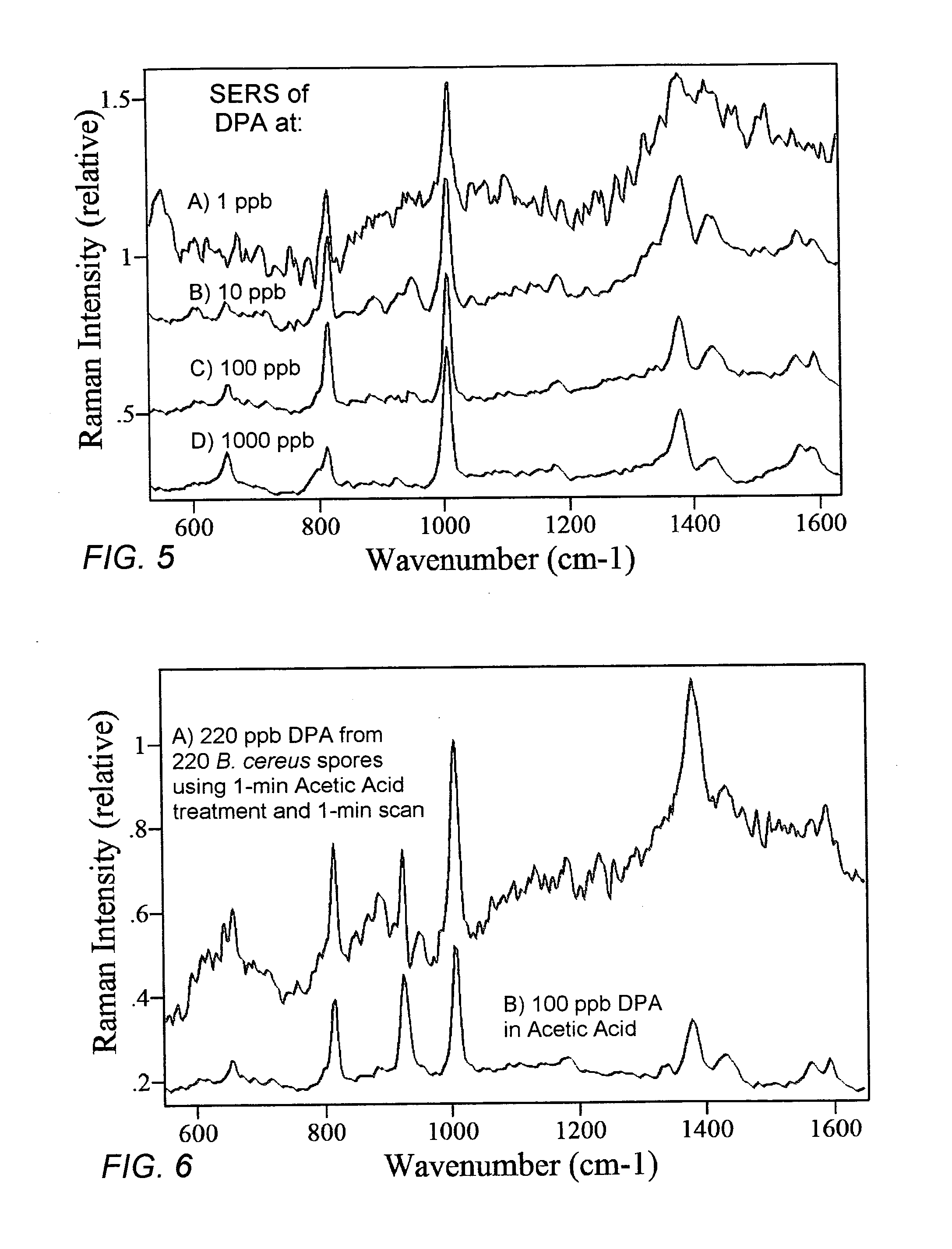
ActiveUS20060257891A1Easy accessEfficient separationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFood borneSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
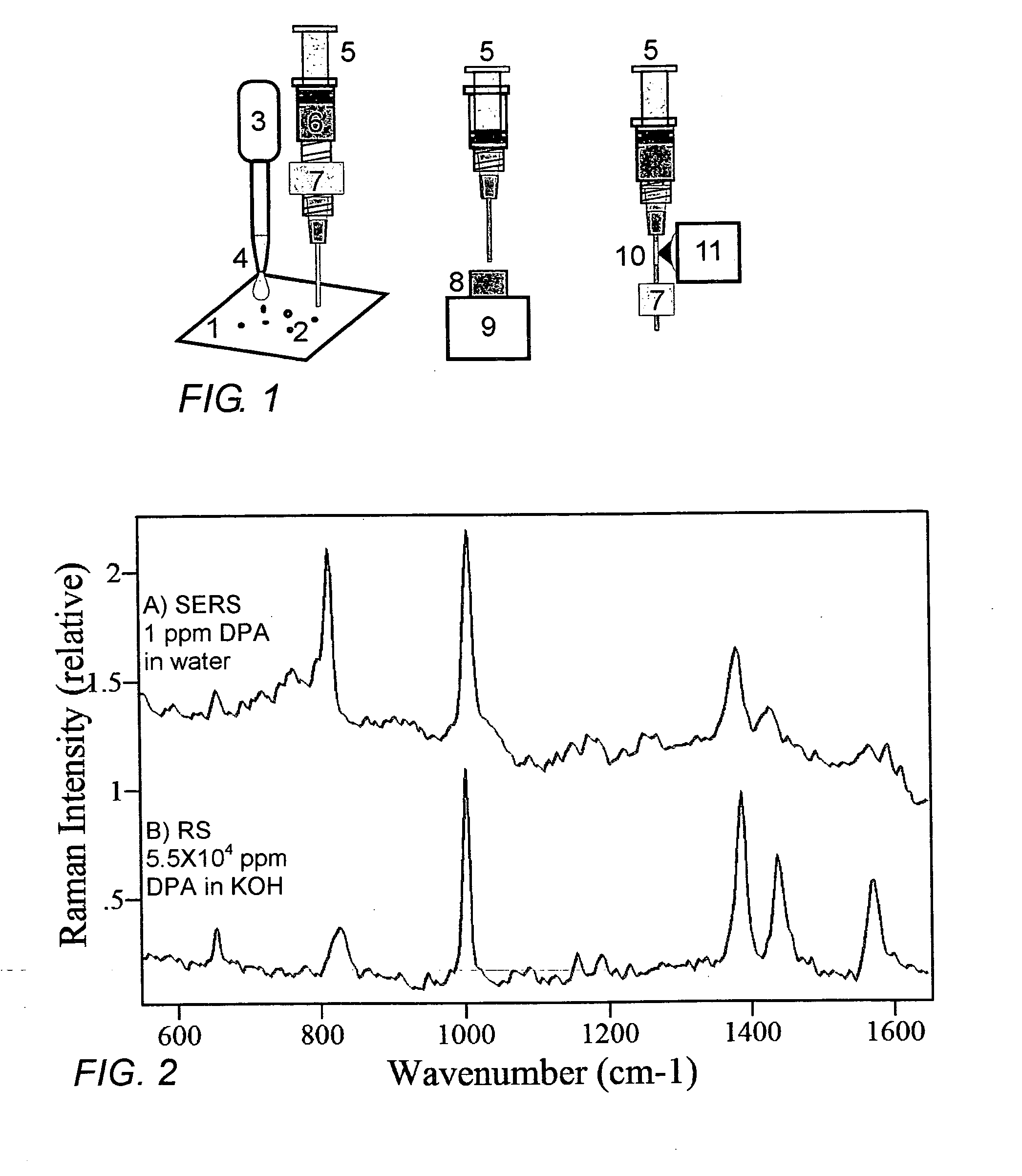
A weak organic acid is used to effect the release of CaDPA from Bacillus or Clostridium endospores, rapidly and at room temperature, to enable detection and measurement of DPA and thereby the assessment of risk associated with exposure to Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium botulinum, and like spores. The method can be applied to airborne, food-borne, and water-borne spores, as well as to spores collected from surfaces or contained in body fluids, and analysis is advantageously carried out using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy.
Owner:REAL TIME ANALYZERS
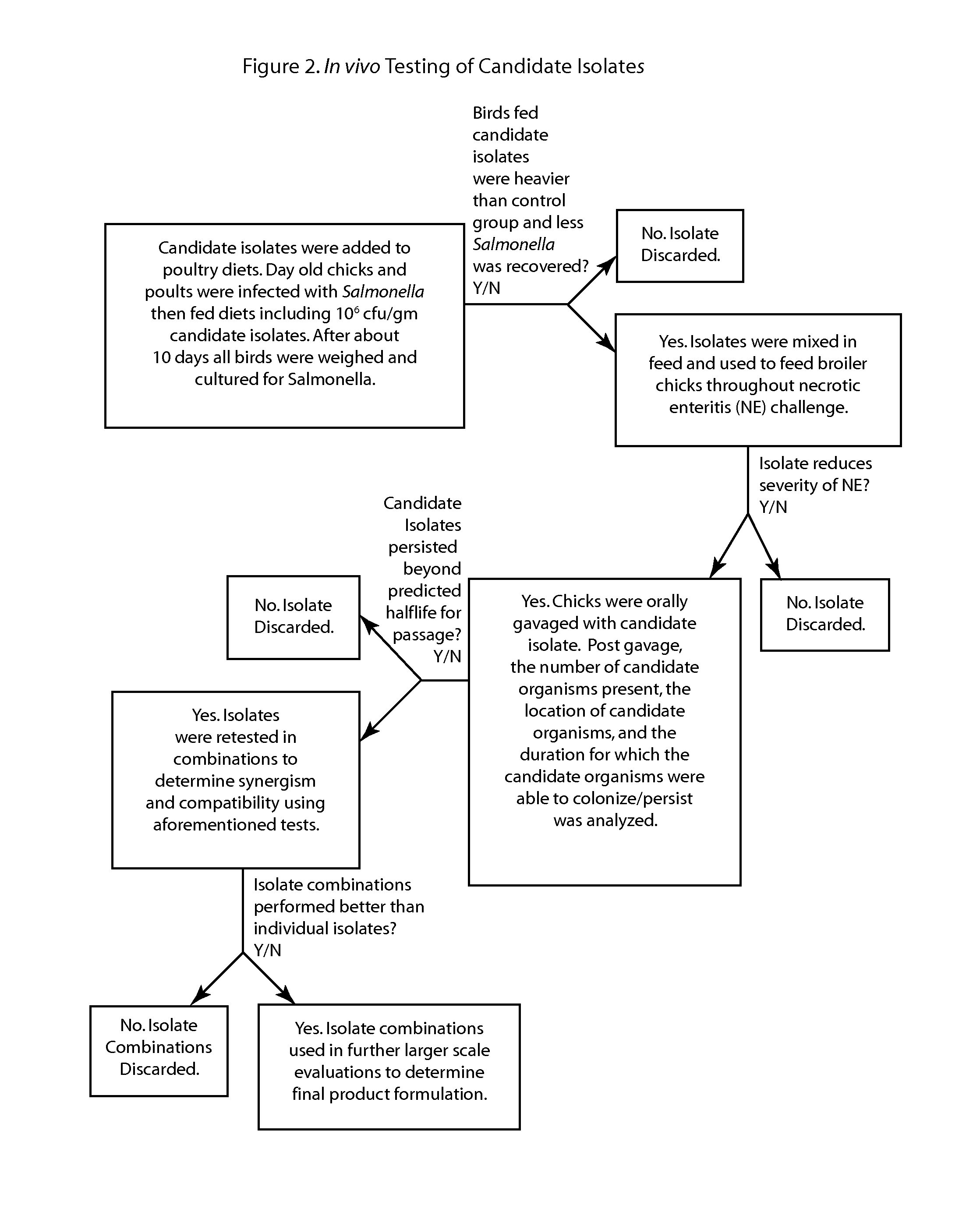
Methods and compositions including spore-forming bacteria for increasing the health of animals
ActiveUS20130136695A1Good for healthIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesBiology
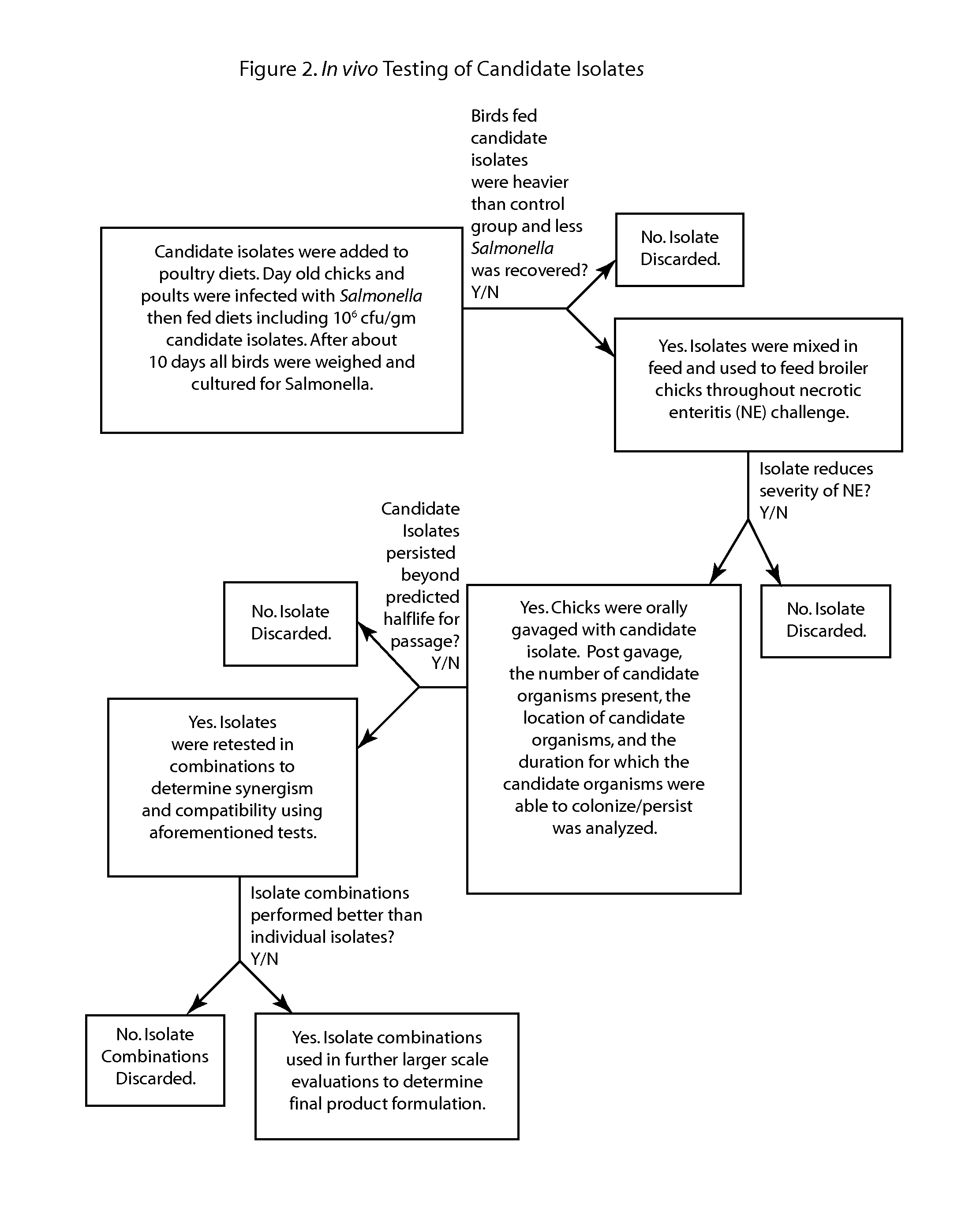
Methods, compositions and bacterial isolates for improving the gastrointestinal health of animals and in particular of poultry are provided herein. The methods include administering an endospore-forming bacteria to an animal. The bacteria are selected for the ability to reduce the growth and presence of bacterial pathogens, such as Salmonella, Clostridium, and Campylobacter, in the gastrointestinal tract of the animal. The bacteria are also selected for the ability to improve at least one production parameter in the animal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
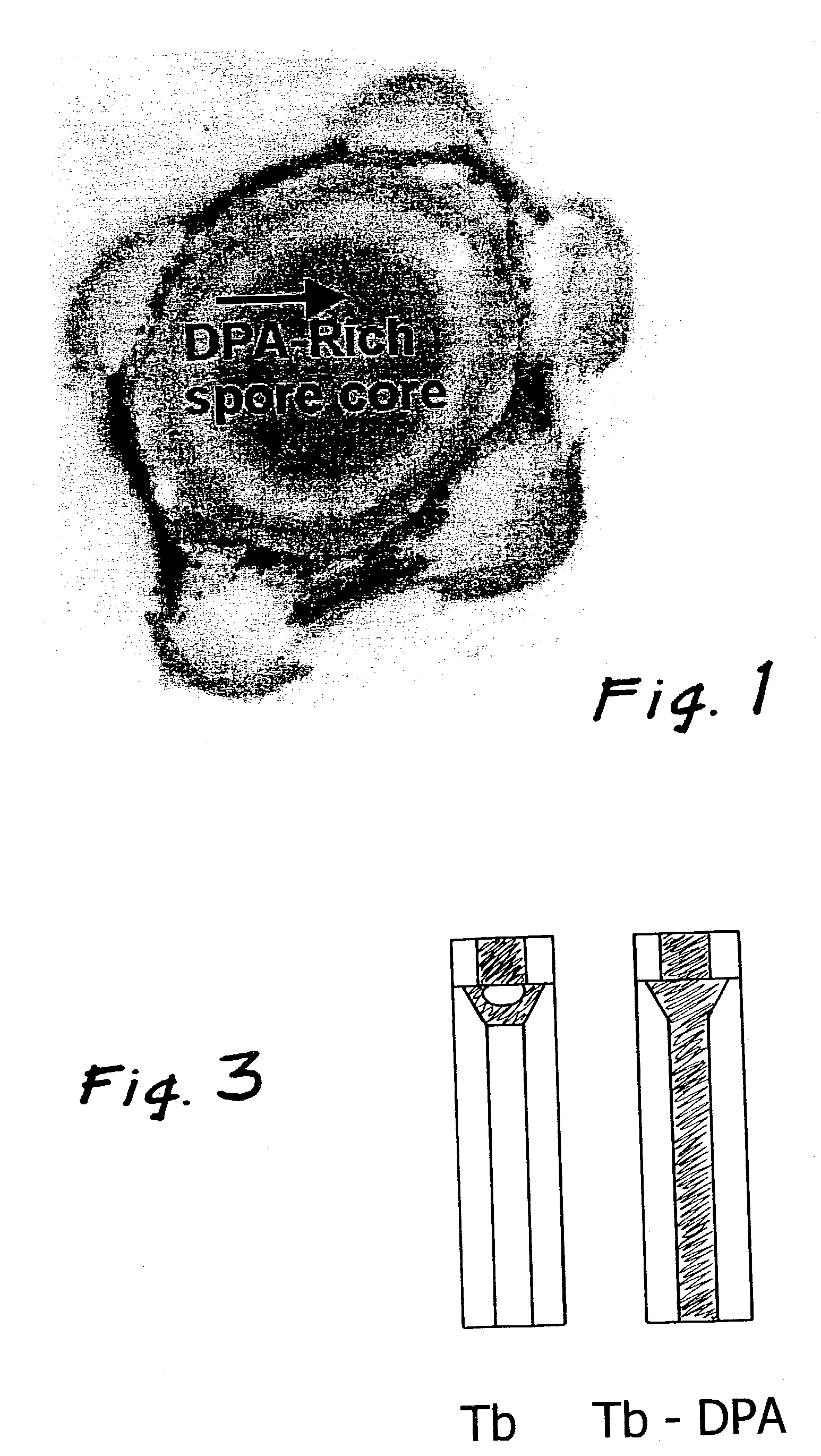
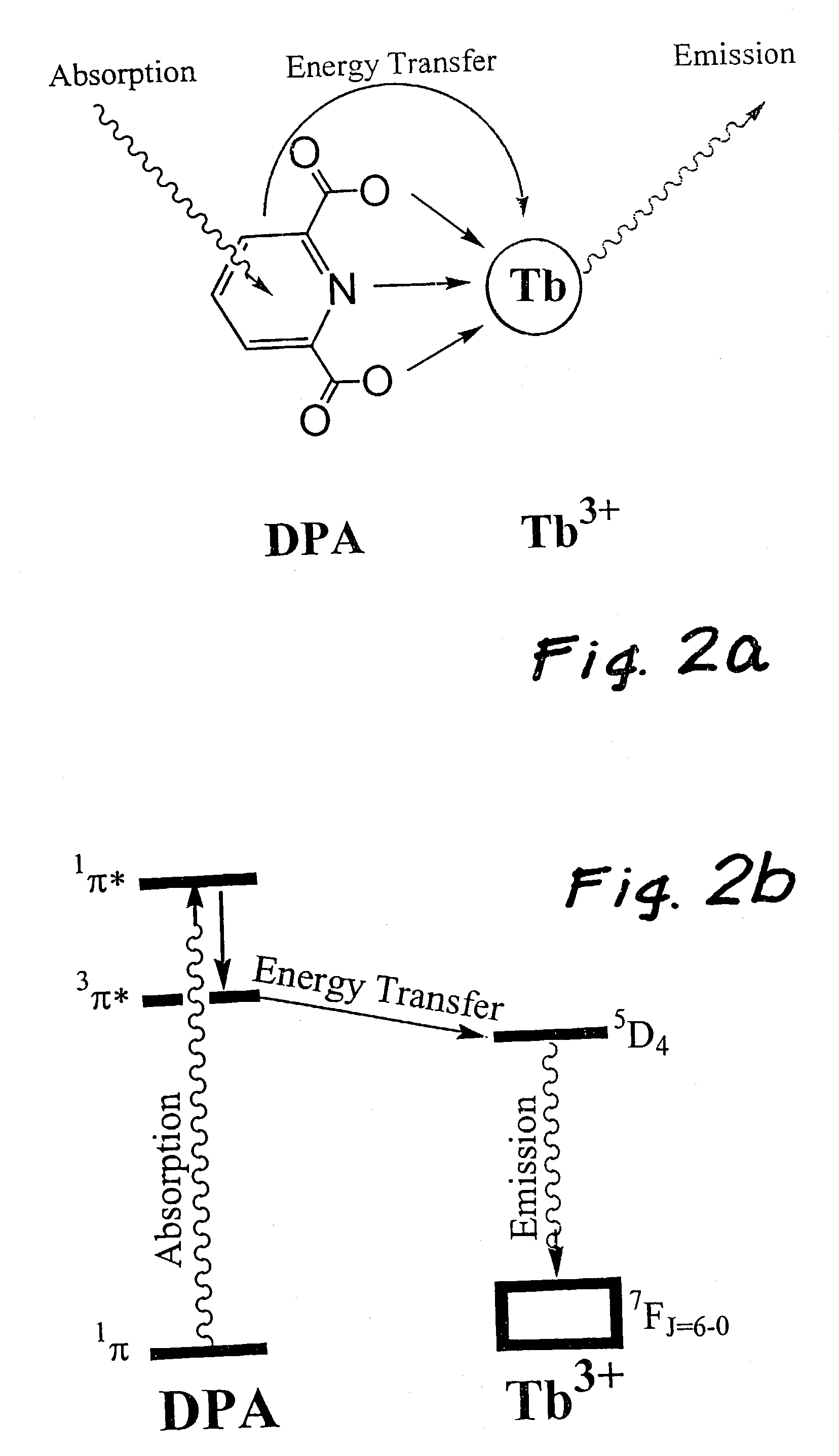
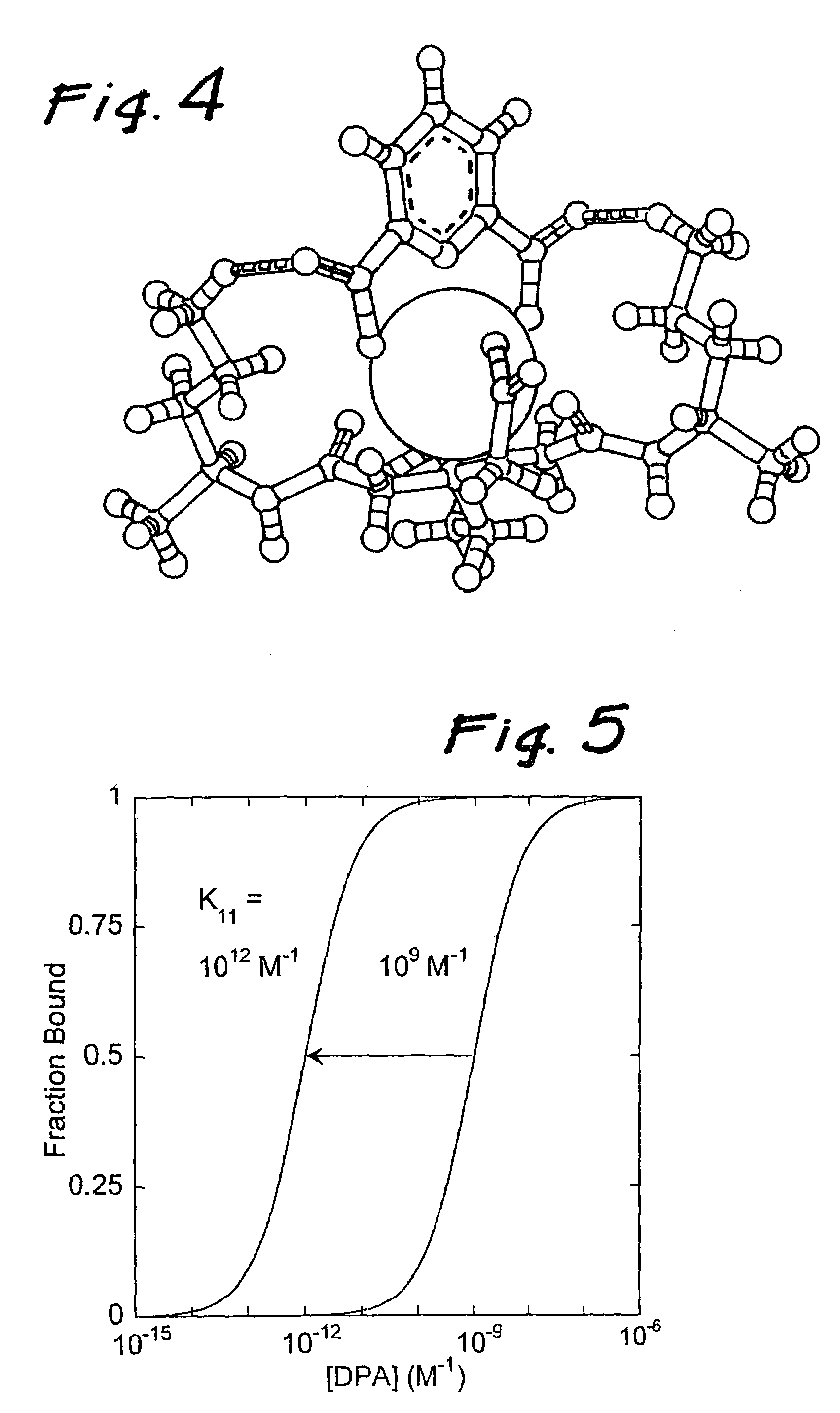
Method bacterial endospore quantification using lanthanide dipicolinate luminescence
ActiveUS7306930B2High sensitivityIncrease dipicolinic acid binding constantMicrobiological testing/measurementPhotoluminescenceLanthanide
A lanthanide is combined with a medium to be tested for endospores. The dipicolinic acid released from the endospores binds the lanthanides, which have distinctive emission (i.e., luminescence) spectra, and are detected using photoluminescence. The concentration of spores is determined by preparing a calibration curve generated from photoluminescence spectra of lanthanide complex mixed with spores of a known concentration. A lanthanide complex is used as the analysis reagent, and is comprised of lanthanide ions bound to multidentate ligands that increase the dipicolinic acid binding constant through a cooperative binding effect with respect to lanthanide chloride. The resulting combined effect of increasing the binding constant and eliminating coordinated water and multiple equilibria increase the sensitivity of the endospore assay by an estimated three to four orders of magnitude over prior art of endospore detection based on lanthanide luminescence.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
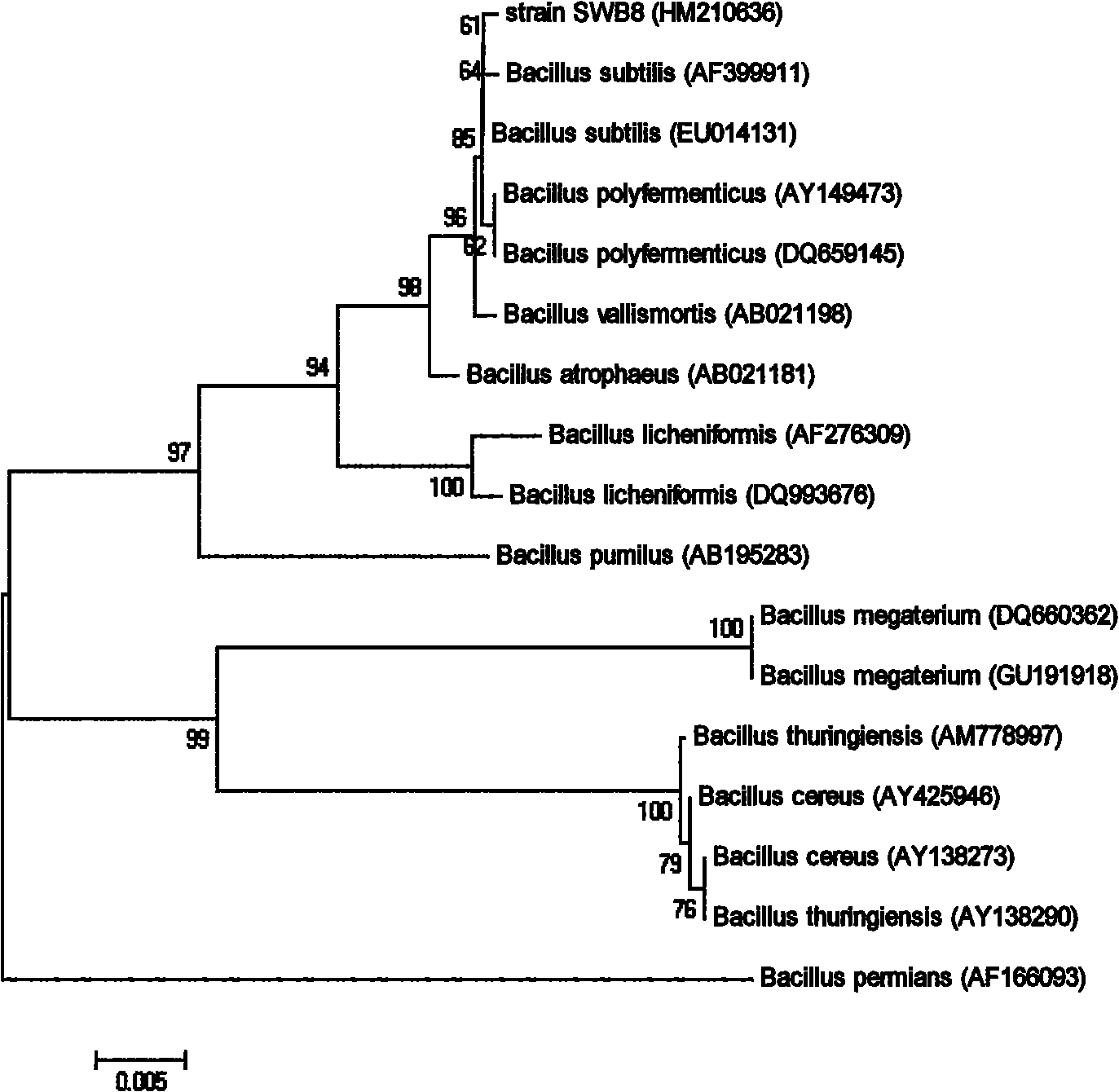
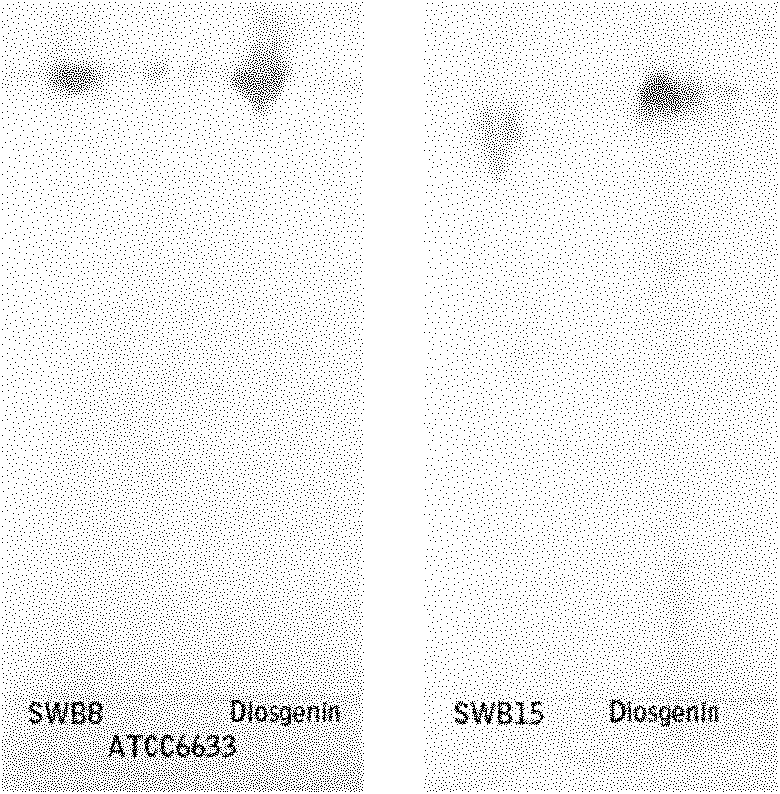
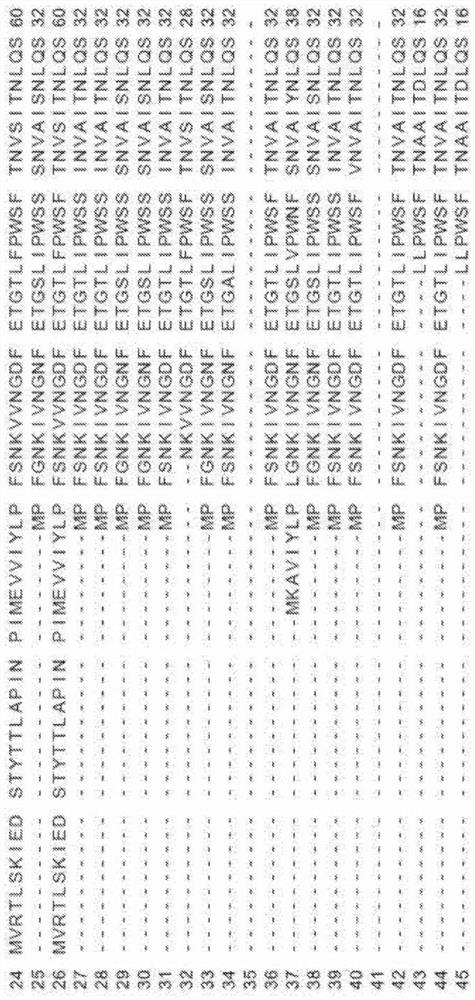
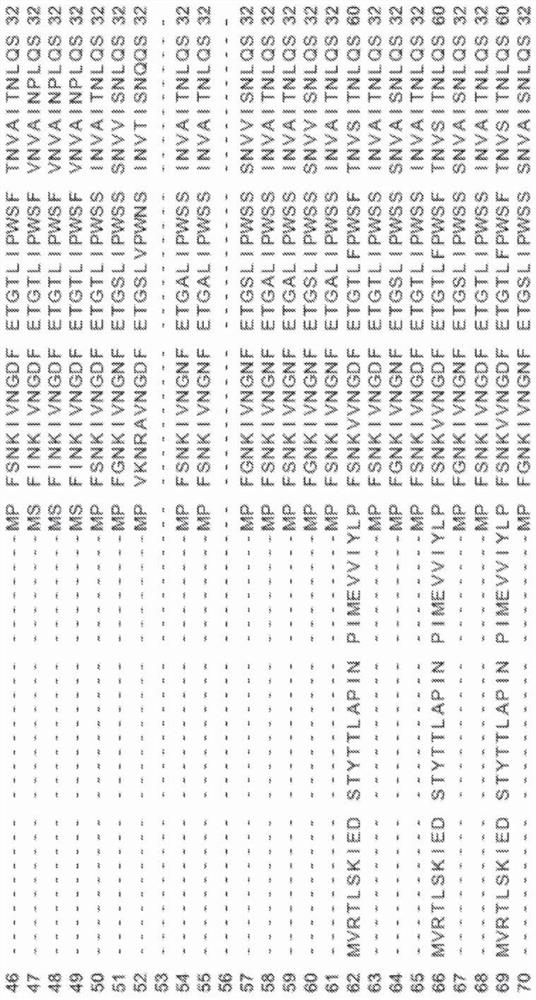
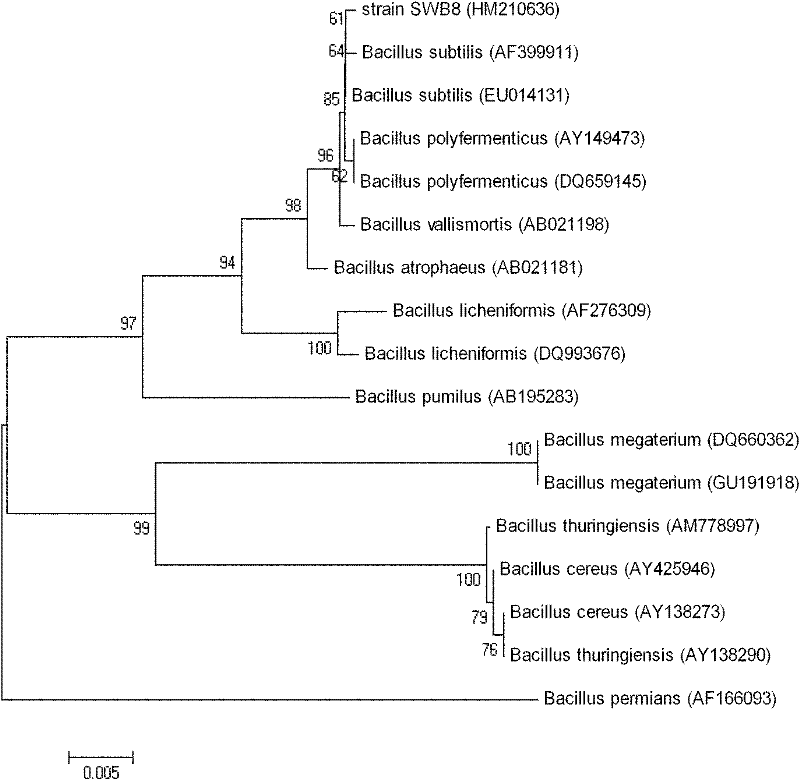
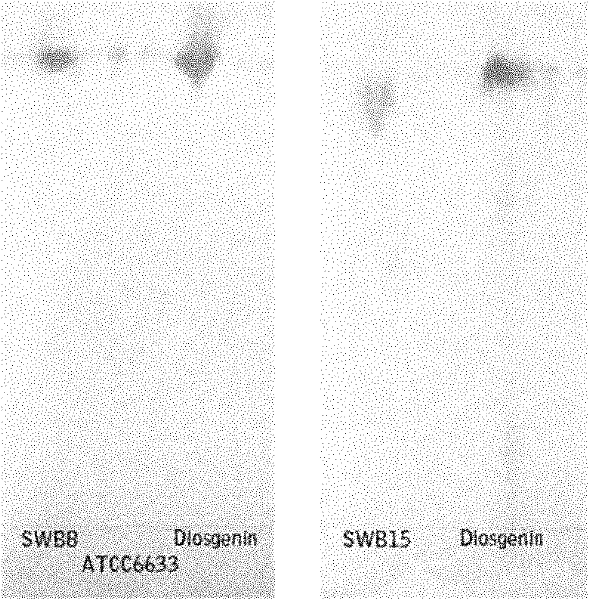
Bacillus subtilis SWB8 for producing diosgenin
InactiveCN102061280AAvoid pollutionThe ability to produce diosgenin is stableAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyHost plants
The invention discloses a Bacillus subtilis WB8 capable of producing diosgenin, and belongs to the technical field of applied microbiology. The strain is separated from internal issues of subterraneous stems of a medicinal plant of Dioscorea zingiberensis wright, can synthesize and secrete a metabolin of a host plant, namely diosgenin, and has the preservation number of CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection) NO:M2010271; and the strain is rod-like, has the size of 1-1.5*3-5 mu m, forms a single-chain sporocarp, releases endospore, has rough colony with grid bulges, forms pellicle through liquid fermentation, has rich foam, and can grow 16SrDNA core sequence 1542bp with the thermophilic temperature of between 30 and 35 DEG C, the pH of 6.0-9.0 and capacity of tolerating 9.0 percent NaCl, wherein the core sequence has the sequence number of HM210636. The strain liquid is fermented by a common culture medium for 48 to 60 hours, the chloroform extract of the fermentation liquor is the diosgenin, and the diosgenin has the activity of inhibiting pathogenic bacteria and resisting tumor cells. The strain provided by the invention can produce the diosgenin; and compared with the conventional process of extracting the diosgenin from yam plants, the method avoids the pollution of strong acid and yam byproducts on environment, and has potential industrial application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Paenibacillus-based endospore display platform, products and methods
ActiveUS20190144874A1Improve root effectivenessImprove environmental resistanceBiocideBacteriaProtein proteinPeptide
Signal sequences useful for targeting proteins and peptides to the surface of endospores produced by Paenibacillus family members and methods of using the same are provided. The display of heterologous molecules, such as peptides, polypeptides and other recombinant constructs, on the spore surface of Paenibacillus family members, using particular N-terminal targeting sequences and derivatives of the same, are also provided.
Owner:GINKGO BIOWORKS INC
Particle of microbial fertilizer
A particle of a microbial fertilizer is provided, and includes the following components that are well-mixed: a culture solution containing probiotic endospores, an aqueous solution of polyol, a bio-degradable filler material, a bio-degradable polymer, and a nutritive substance. The particle of the microbial fertilizer extends storage time of the microbial fertilizer and maintains viability of probiotics, and thus effects of a microbial agent are successfully achieved.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Methods and compositions including spore-forming bacteria for increasing the health of animals
Methods, compositions and bacterial isolates for improving the gastrointestinal health of animals and in particular of poultry are provided herein. The methods include administering an endospore-forming bacteria to an animal. The bacteria are selected for the ability to reduce the growth and presence of bacterial pathogens, such as Salmonella, Clostridium, and Campylobacter, in the gastrointestinal tract of the animal. The bacteria are also selected for the ability to improve at least one production parameter in the animal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
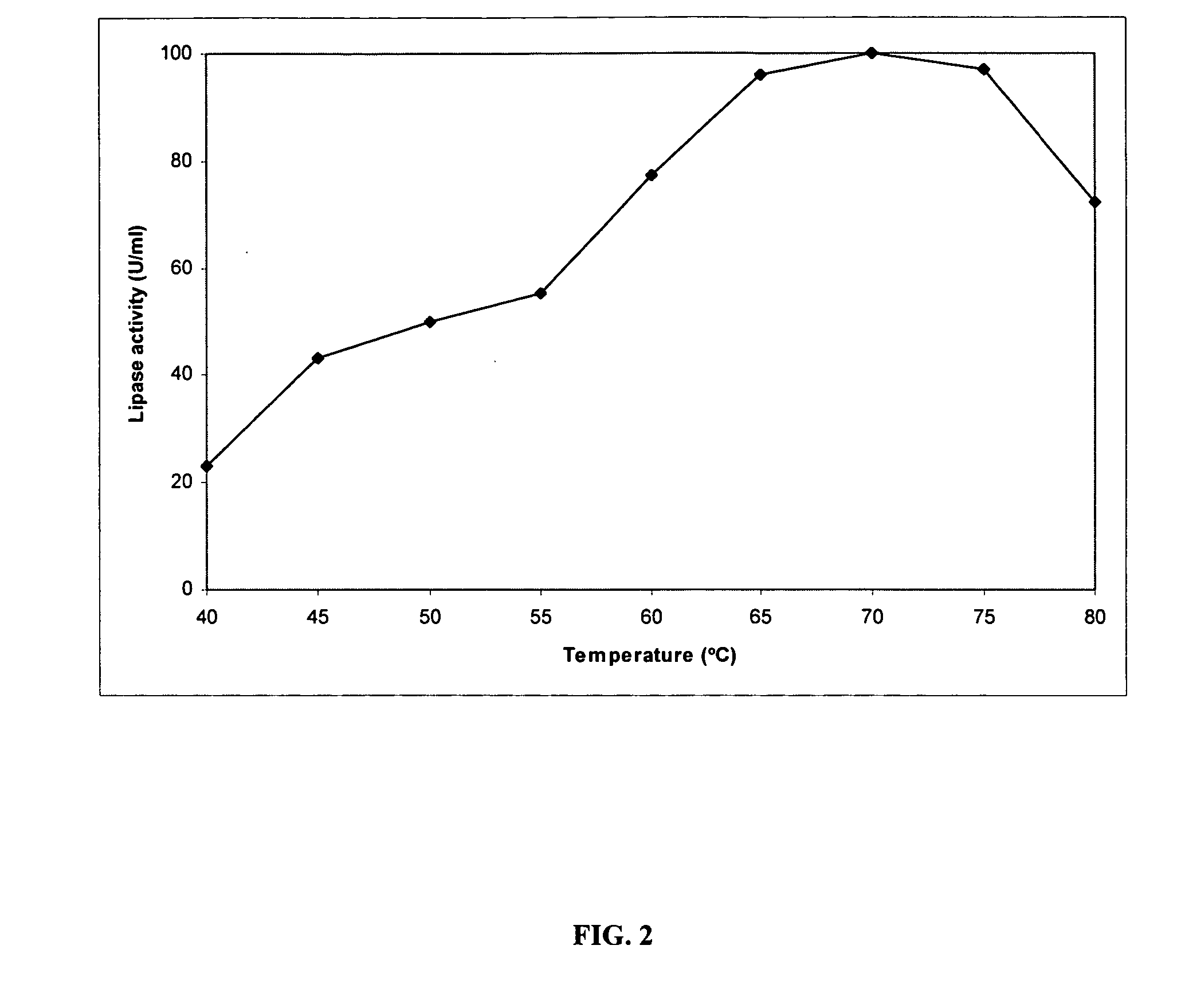
Lipase from Geobacillus sp. strain T1
A biologically pure culture of Geobacillus Strain T1 bacteria isolated from Palm Oil Mill Effluent capable of producing thermostable lipase T1 gene. The production of thermostable lipase T1 gene from a novel Geobacillus bacterium having a designated as strain T1, was aerobic, gram positive and endospore-forming, rod-shaped. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was 52.6%. On the basic of physiological data, phenotypic traits and molecular analysis, strain T1 represents a novel species within the genus Geobacillus, The thermostable T1 lipase gene was subcloned into the pGEX-4T1 vector with and without signal peptide in prokaryotic system. The 28 amino acid residues signal peptide alter the conformation of GST moiety and preventing it from bind to affinity glutathione Sepharose column. By expression and simplification of the purification through single step affinity chromatography shows a specific activity of 292.929 U / mg and 72.55% of fusion lipase was recovered from crude cell lysate. T1 mature lipase was successfully purified with a final recovery of 51.49% and specificity activity of 959.033 U / mg.
Owner:UNIVERSITI PUTRA MALAYSIA
Bacillus mucilaginosus and high-density fermentation method and use thereof
This invention discloses a mutated strain of wild type Bacillus mucilaginosus HSCUP-76-8 and a high-density fermentation method thereof. The mutated strain HSCUP-76-8 was assigned an Accession No. CGMCC No. 8481. A two-stage and regulated high-density fermentation method has been established for the production of HSCUP-76-8. In the first stage, parameters are controlled to reduce the viscosity of the fermentation broth and promote the growth of bacteria, thereby allowing the bacteria to reach an amount in the range of 2.0×109 cfu / mL-2.3×109 cfu / ml. In the second stage, nutritional factors and fermentation conditions are controlled to promote sporulation, thereby producing endospores in the range of 1.5×109 cfu / mL-2.0×109 cfu / ml. The fermentation cycle of the two-stage high-density fermentation is 32-48 hours.
Owner:SHANXI LUTU BIOTECH CO LTD
Methods and compositions for the treatment and/or prophylaxis of clostridium difficile associated disease
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment and / or prophylaxis of Clostridium difficile associated disease (CD AD). In particular, the invention relates to antibodies that bind to C. difficile antigens and are capable of inhibiting C. difficile infection, at least one symptom of C. difficile associated disease, shedding of C. difficile, and C. difficile associated mortality. The compositions of the present application comprise: mammalian or avian antibodies which bind to a C. difficile Toxin B; and mammalian or avian antibodies that bind to a C. difficile vegetative cell antigen and / or a C. difficile endospore antigen.
Owner:IMMURON
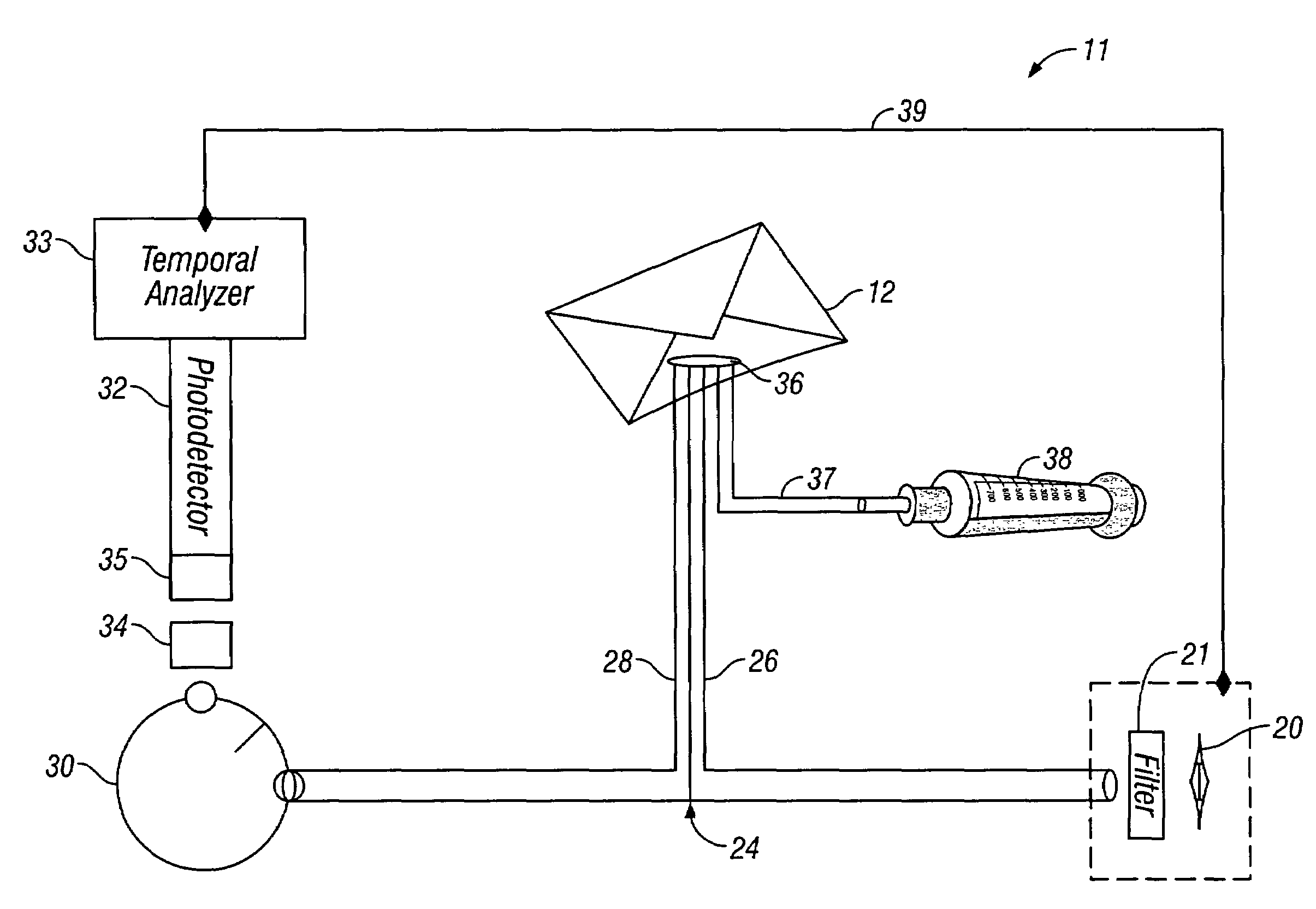
Method for detecting bacterial endospores in a sealed container
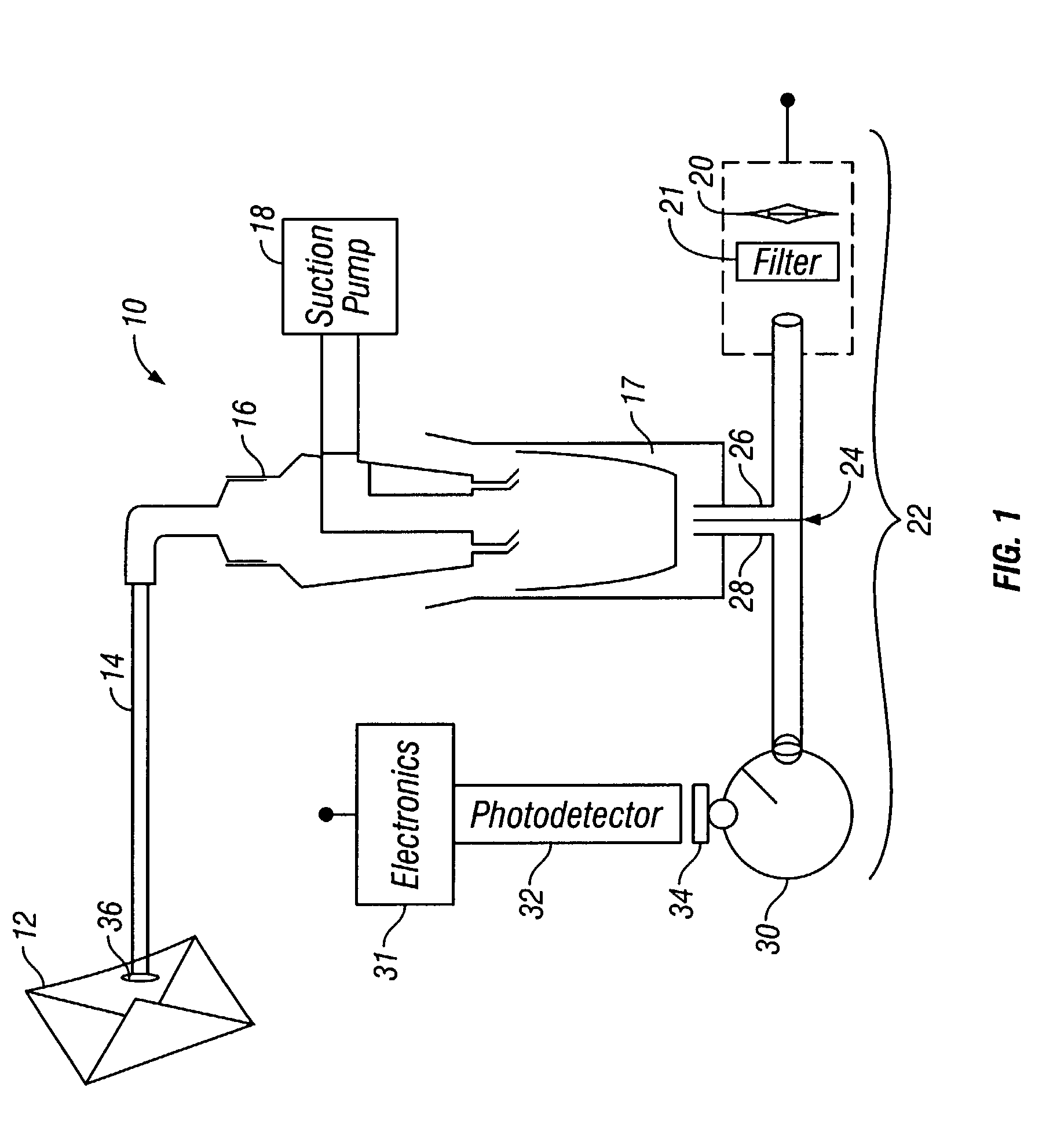
InactiveUS7485437B1Microbiological testing/measurementWithdrawing sample devicesPhysicsEndospore Forming Bacteria
A device for detecting bacterial endospores in a sealed container. The device has a suction tube connected to an aerosol concentrator containing a lanthanide salt solution, a suction pump engaged to the aerosol concentrator, an excitation energy source and an optical set-up for directing the excitation energy source to the lanthanide salt solution and collecting photoluminescence generated by the excited lanthanide salt solution. A method for detecting bacterial endospores is also provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Disinfecting Solutions Effective Against Bacterial Endospores
InactiveUS20070202006A1Rapid DisinfectionQuick destructionBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsSporeMedicine
The present invention is directed to a biguanide-containing disinfecting solutions effective in inactivating bacteria endospores on surfaces, air-borne or in water. The methods of using the present invention are directed to disinfecting endospore laden surfaces, air and water with the subject biguanide-containing solutions.
Owner:AMMON DANIEL M JR +2
Endospore compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20140178496A1Reduce the populationReduce populationBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsPathogenic microorganismDermatology
Provided herein in some embodiments is a composition that comprises (a) a nanoscale particle(s) or a microscale particle(s); and (b) a film-forming polymer. Also provided herein is a method for an immediate and sustained released formulation suitable for topical administration or administration to surfaces. Further provided herein in certain embodiments is a method of reducing the population of pathogenic microorganisms on skin or surfaces, wherein a method comprises applying to the skin or surface a composition, wherein the composition comprises (a) a nanoscale particle(s) or a microscale particle(s); and (b) a film-forming polymer.
Owner:ANNUARY HEALTHCARE
Method for producing high-protein feed from waste distiller's grain of Baijiu
InactiveCN107712312ARich in nutrientsPromote digestion and absorptionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFiberPichia pastoris
The invention relates to a method for producing a high-protein feed from waste distiller's grain of Baijiu, which includes the following steps: (1) material pretreatment: a beater is used for beatingfresh raw distiller's grain of Baijiu into uniform particles, and the diameter of the particles is about 1.5mm to 3mm; (2) defibering treatment: endospore-forming bacteria are screened out and added with 98 to 98.5 percent of raw distiller's grain, 0.9 to 1 percent of starch and 1 to 1.1 percent of soybean flour, solid-state fermentation is carried out, cellulase activity is kept as high as 14.204U / mL, and thereby waste distiller's grain of Baijiu is obtained; (3) fermentation: candida and pichia pastoris are screened out, the proportion of candida to pichia pastoris is 1:1, the inoculation amount is 10 percent, and with 85 to 89 percent of waste distiller's grain of Baijiu, 9 to 11 percent of bran, 1 to 2 percent of ammonium sulfate and 1 to 2 percent of quick lime, solid-state fermentation is carried out for 60 hours. By means of modern microbial technology, the method decomposes substances in the distiller's grain, such as residual starch, crude protein, crude fat and crude fibers,so that the distiller's grain has richer nutritional ingredients and can be better digested and absorbed by animals, consequently, not only is the problem of waste distiller's grain solved, but also value in use and economic benefit are created, and the comprehensive utilization of residual starch of the distiller's grain is realized.
Owner:HEBEI SANJING WINE CO LTD
Antimicrobial composition having efficacy against endospores
A sporicidal composition has a moderately low pH and includes at least one oxidizing acid and the dissociation product of at least one inorganic oxidizing agent. Very high effective solute concentrations can enhance the efficacy of the composition. Embodiments of the composition can be applied to a surface and allowed to absorb into the endospore, ultimately killing at least some of those bacteria in mature endospore form. The surface being treated can be an inanimate surface, particularly a hard surface, or a medical device.
Owner:NEXT SCI IP HLDG PTY LTD
Particles including bacterial endospores
PendingUS20210130737A1Reduce odorOrganic detergent compounding agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyBacterial composition
A composition including a plurality of particles, wherein the particles comprise: at least 40% by weight of the particles of a non-germinant carrier; and from about 0.0001% to about 5% by weight of the particles of a bacterial composition including bacterial endospores; and wherein each of the particles has a mass between about 1 mg to about 5000 mg, preferably between about 5 mg and about 200 mg.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
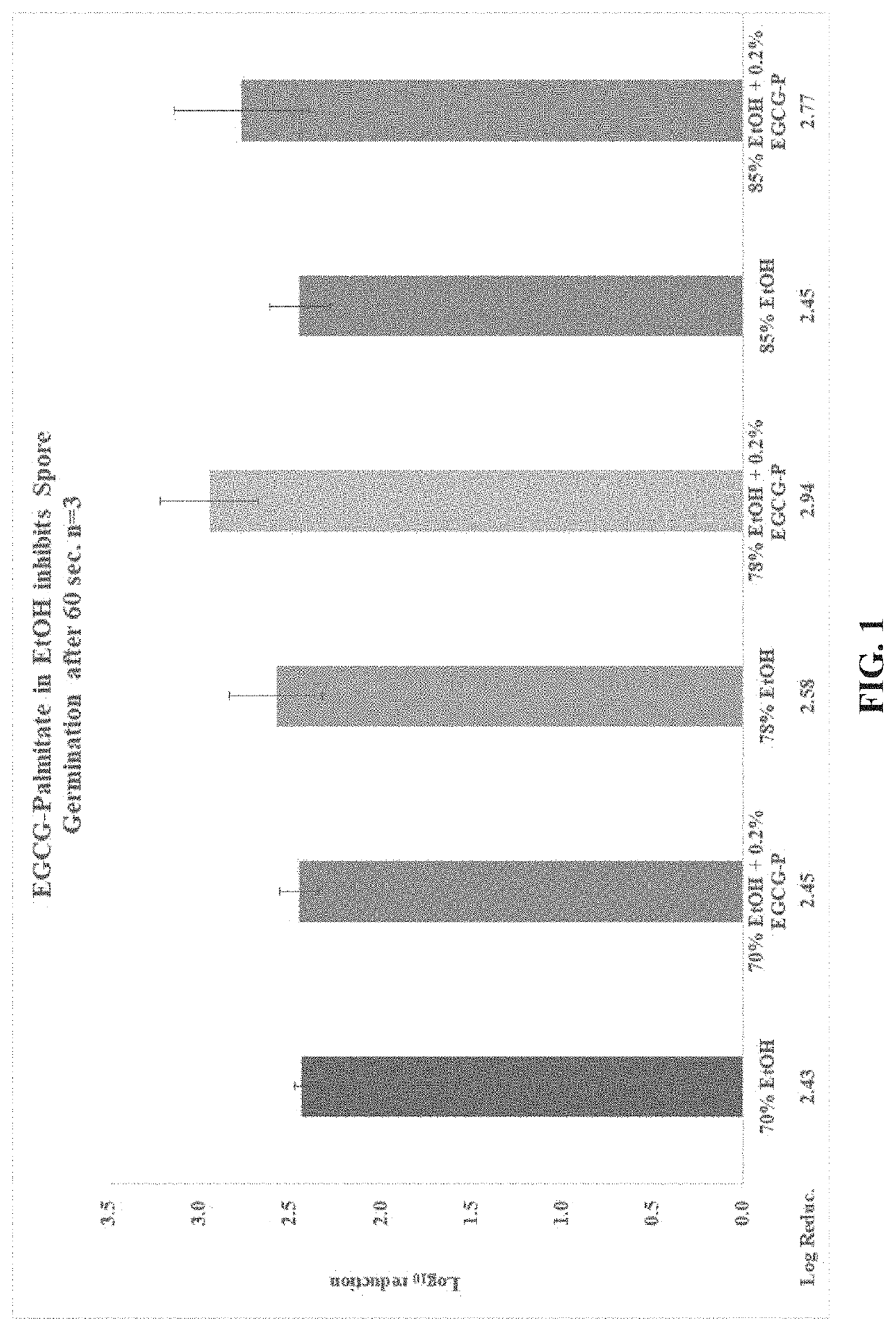
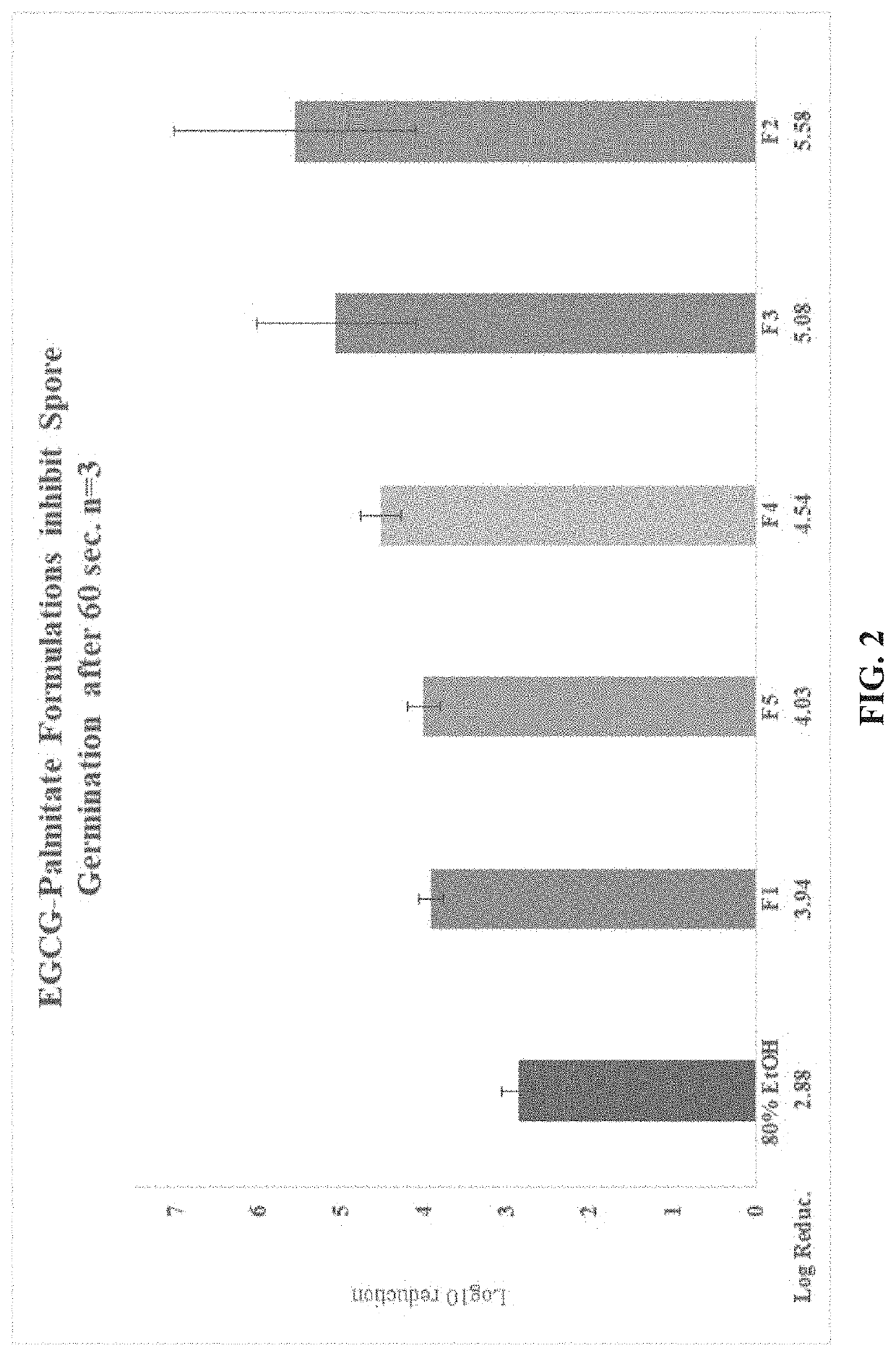
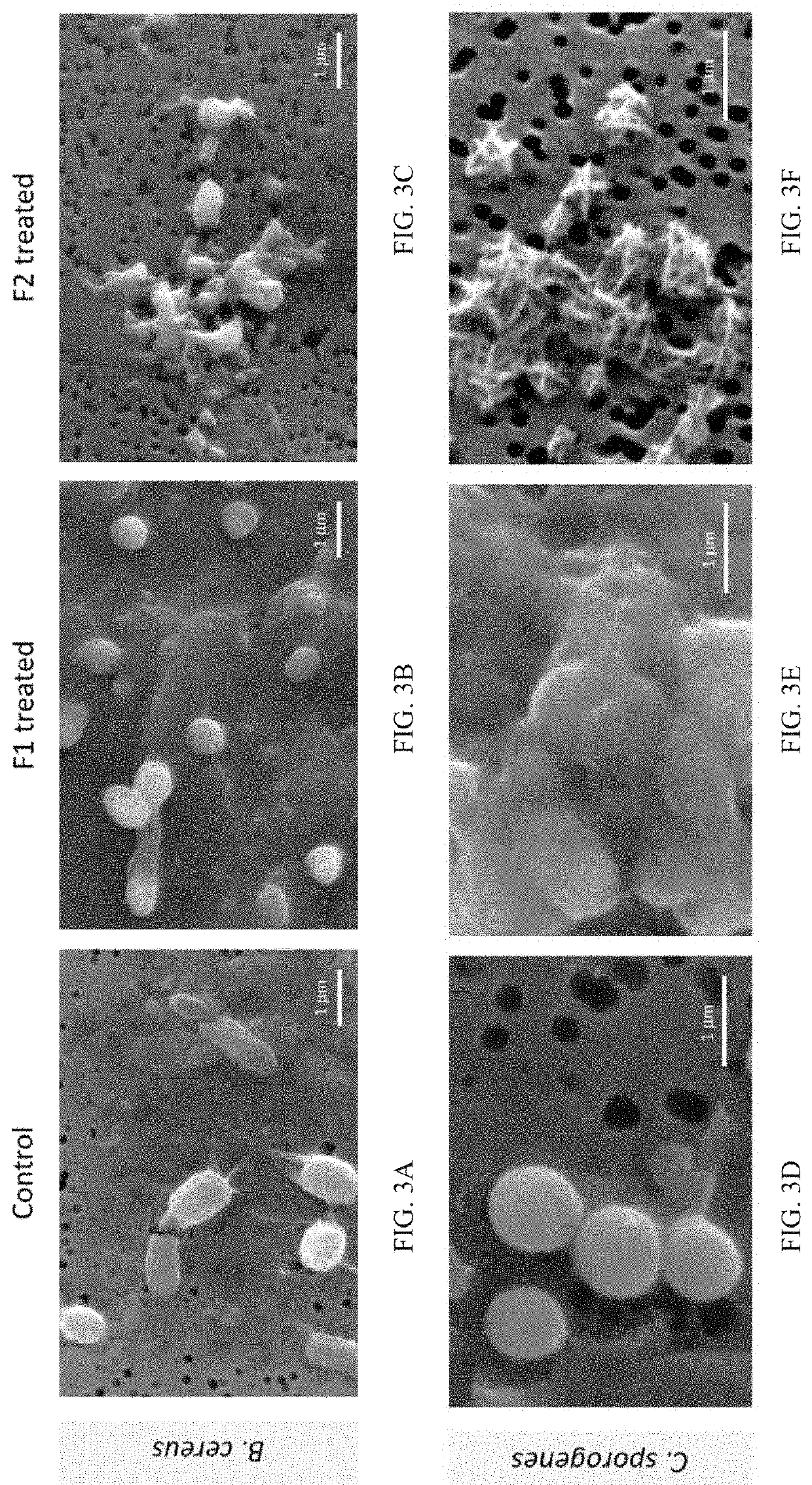
Compositions and Methods for Inhibiting Endospores Using Green Tea Polyphenols
PendingUS20200214290A1Extended shelf lifeReduce delay spoilageBiocideAnimal repellantsBiotechnologyGreen Tea Polyphenols
Compositions and methods of rapidly killing, inactivating, or otherwise reducing the spores such as bacterial spores are disclosed. The methods typically include reducing or preventing spore reactivation comprising contacting spores with an effective amount of one or more green tea polyphenols (GTP), one or more modified green tea polyphenols (LTP), or a combination thereof. In a preferred embodiment, the LTP is (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) esterified at the 4′ position with stearic acid, EGCG esterified at the 4′ position with palmitic acid, or a combination thereof. The compositions and methods can be used in a variety of applications, for example, to increase the shelf-life of a food or a foodstuff, to reduce or delay the spoilage of a food or a foodstuff, or to decontaminate a device contaminated with spores.
Owner:MONTCLAIR STATE UNIVERSITY +2
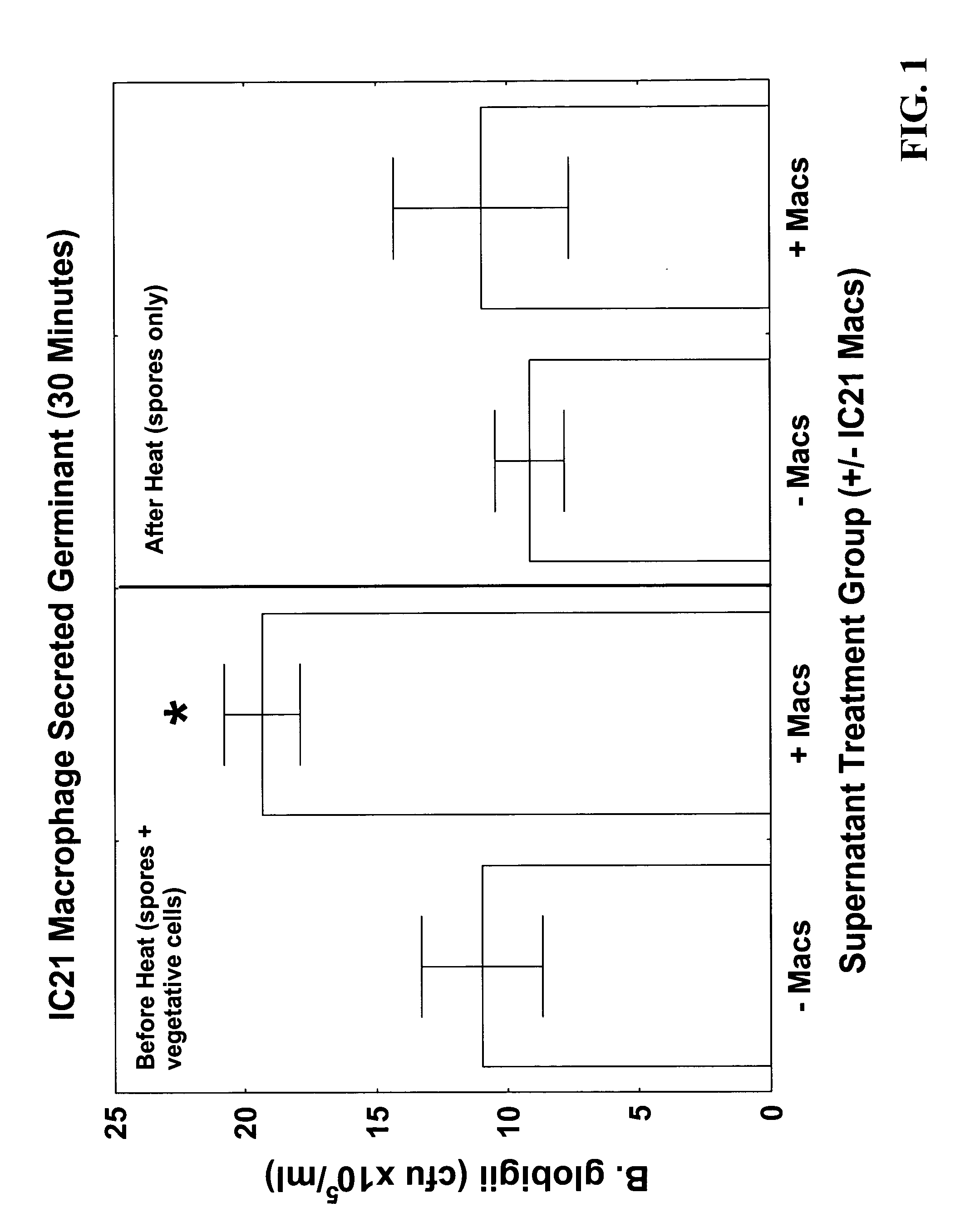
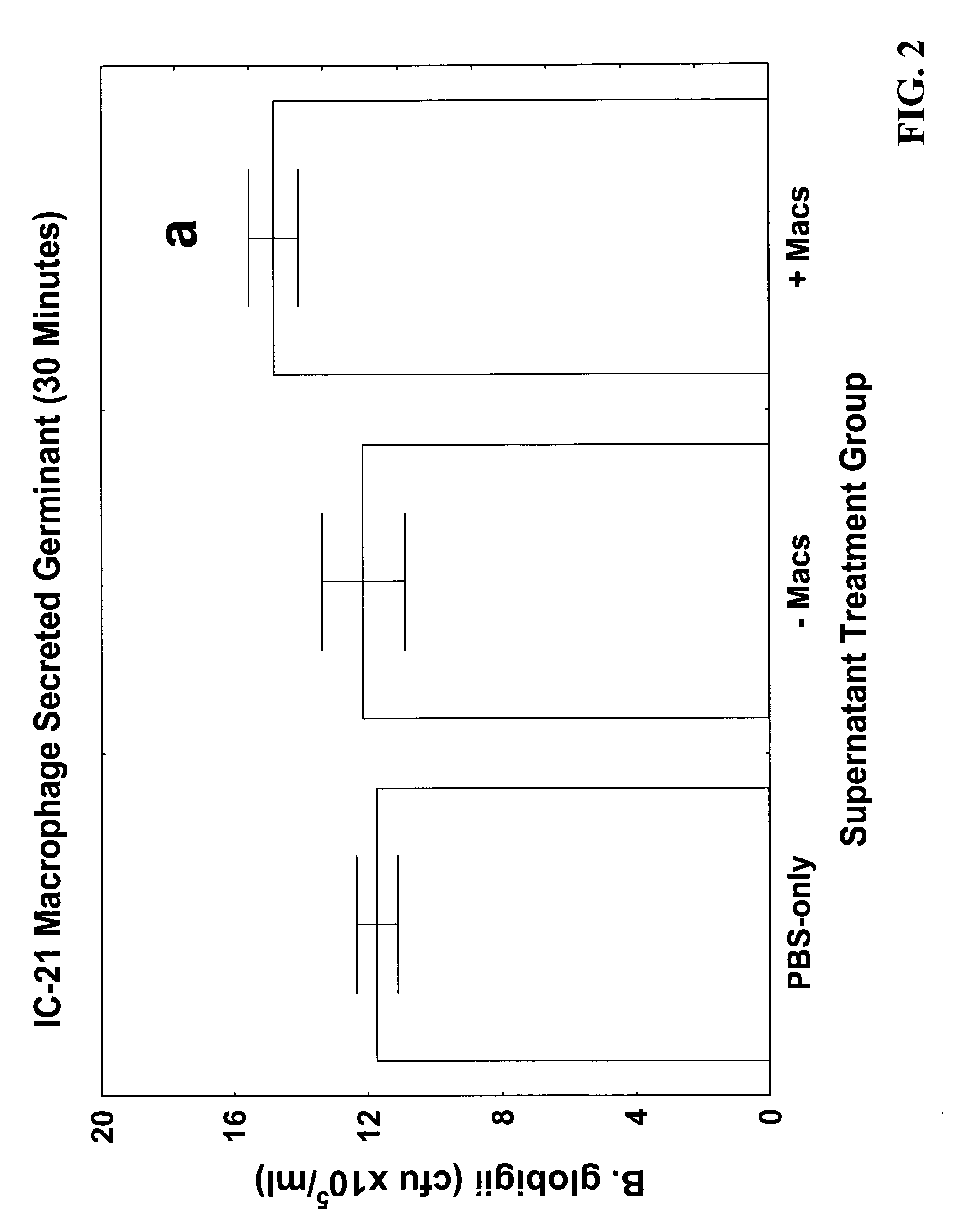
Germinant produced from IC-21 macrophages, method and use thereof
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Paenibacillus-based endospore display platform, products and methods
ActiveUS10988769B2Improve environmental resistanceImprove featuresBiocideBacteriaHeterologousProtein target
Signal sequences useful for targeting proteins and peptides to the surface of endospores produced by Paenibacillus family members and methods of using the same are provided. The display of heterologous molecules, such as peptides, polypeptides and other recombinant constructs, on the spore surface of Paenibacillus family members, using particular N-terminal targeting sequences and derivatives of the same, are also provided.
Owner:GINKGO BIOWORKS INC
Bacillus mucilaginosus and high-density fermentation method and use thereof
This invention discloses a mutated strain of wild type Bacillus mucilaginosus HSCUP-76-8 and a high-density fermentation method thereof. The mutated strain HSCUP-76-8 was assigned an Accession No. CGMCC No. 8481. A two-stage and regulated high-density fermentation method has been established for the production of HSCUP-76-8. In the first stage, parameters are controlled to reduce the viscosity of the fermentation broth and promote the growth of bacteria, thereby allowing the bacteria to reach an amount in the range of 2.0×109 cfu / mL-2.3×109 cfu / ml. In the second stage, nutritional factors and fermentation conditions are controlled to promote sporulation, thereby producing endospores in the range of 1.5×109 cfu / mL-2.0×109 cfu / ml. The fermentation cycle of the two-stage high-density fermentation is 32-48 hours.
Owner:SHANXI LUTU BIOTECH CO LTD
Endospore display platforms, products and methods
Signal sequences useful for targeting proteins and peptides to the surface of endospores produced by Brevibacillus, Lysinibacillus, or Viridibacillus family members and methods of using the same are provided. The display of heterologous molecules, such as peptides, polypeptides and other recombinant constructs, on the exosporium of Brevibacillus, Lysinibacillus, or Viridibacillus family members, using particular N-terminal targeting sequences and derivatives of the same, and likewise are provided.
Owner:GINKGO BIOWORKS INC
Bacillus subtilis SWB8 for producing diosgenin
InactiveCN102061280BAvoid pollutionThe ability to produce diosgenin is stableAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyHost plants
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Endospore display platforms, products and methods
PendingUS20220002736A1Improve environmental resistanceImprove featuresPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBiocideHeterologousProtein target
Signal sequences useful for targeting proteins and peptides to the surface of endospores produced by Brevibacillus, Lysinibacillus, or Viridibacillus family members and methods of using the same are provided. The display of heterologous molecules, such as peptides, polypeptides and other recombinant constructs, on the exosporium of Brevibacillus, Lysinibacillus, or Viridibacillus family members, using particular N-terminal targeting sequences and derivatives of the same, and likewise are provided.
Owner:GINKGO BIOWORKS INC
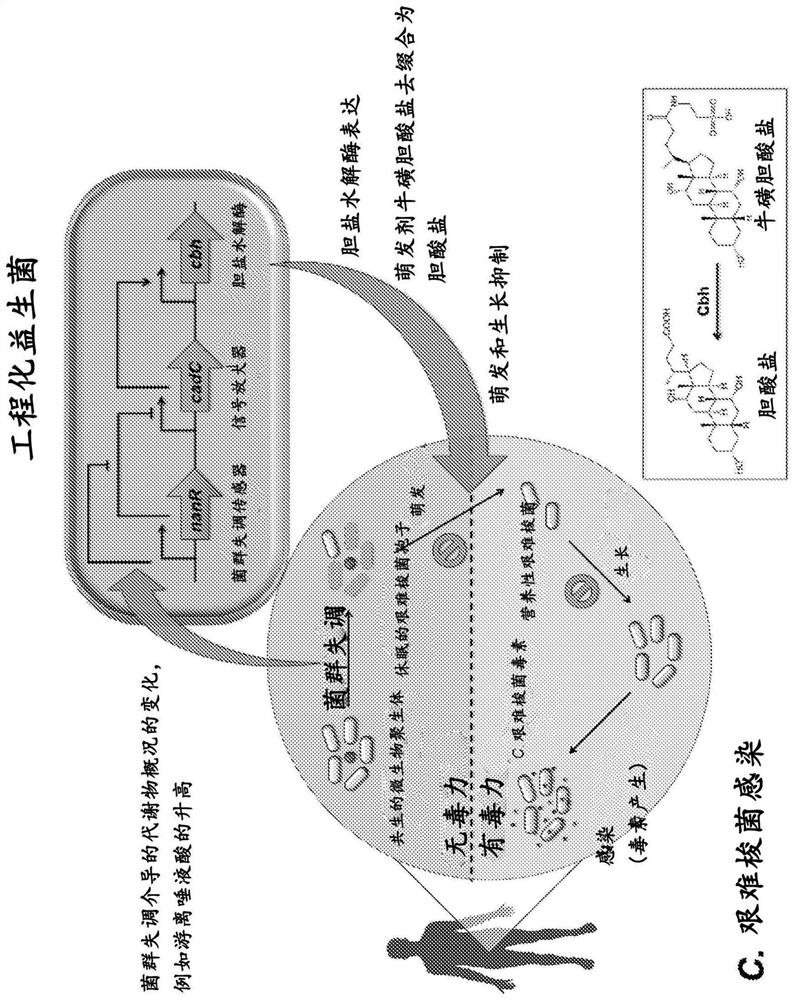
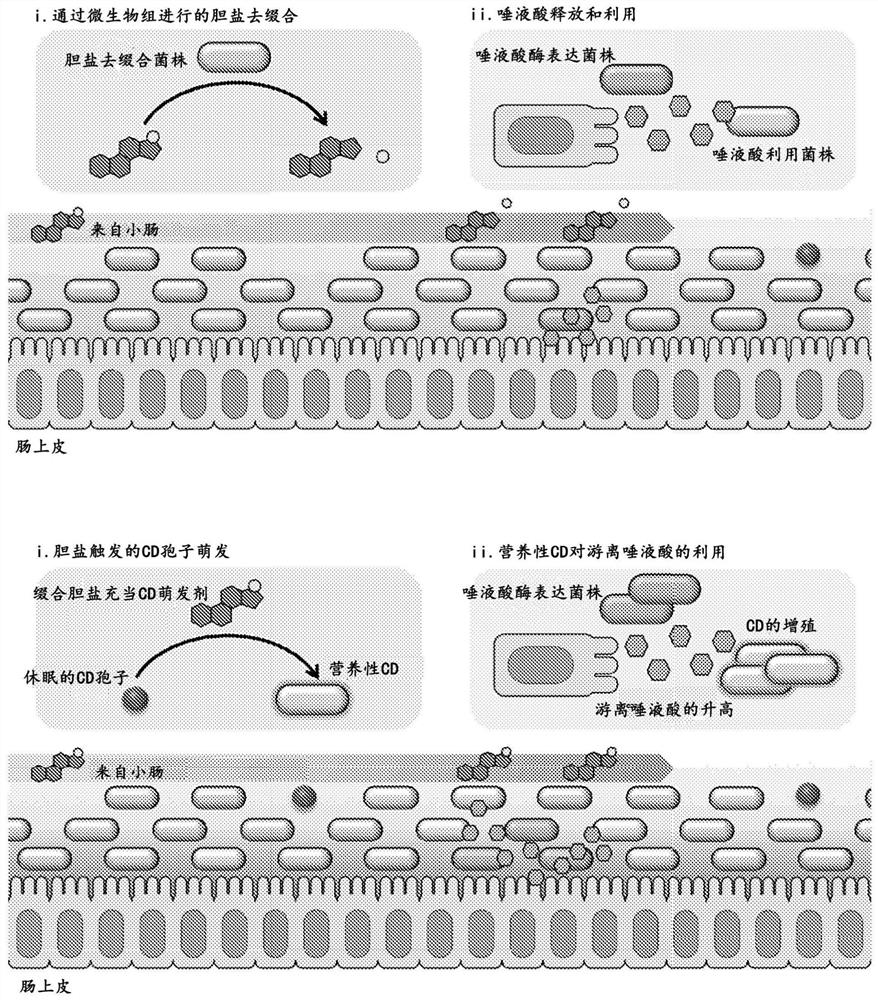
Engineered flora disorder sensing probiotics for clostridium difficile infection and recurrent infection management
PendingCN114269928AOvercome resistanceAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBile salt hydrolaseRecurrent infections
The present invention relates to methods of metabolic engineering of bacterial cells to produce bile salt hydrolases to inhibit germination of clostridium difficile endophytic spores and colonization within the human gastrointestinal tract. The bile salt hydrolase is operably linked to a sialic acid inducible promoter pNanA, wherein the pNanA is in turn controlled by a repressor nanoR. A recombinant bacterium expressing the bile salt hydrolase may be a probiotic strain to be used in the prevention or treatment of Clostridium difficile infection.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
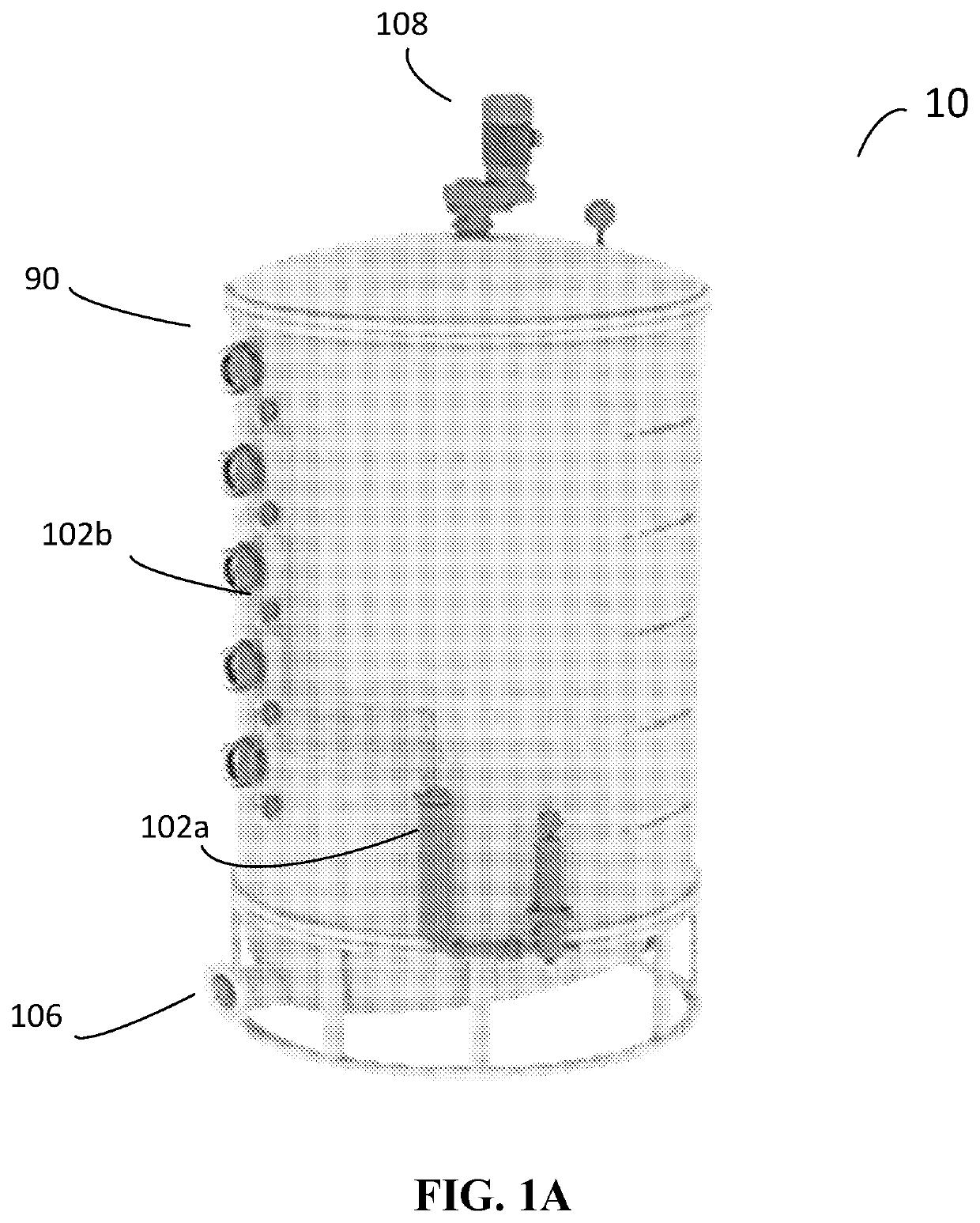
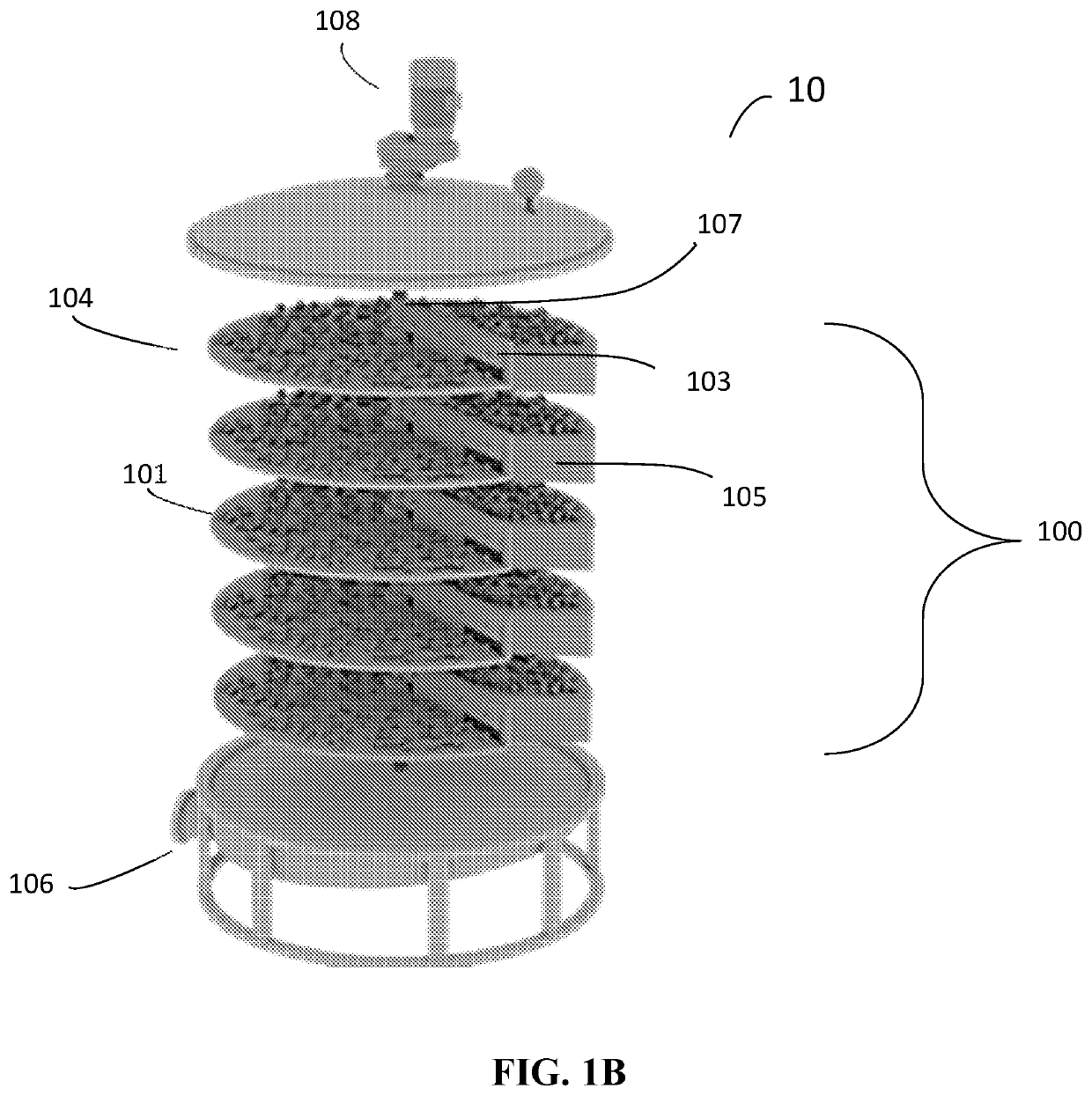
Reactor for Two-Stage Liquid-Solid State Fermentation of Microorganisms
PendingUS20220356441A1Low costProduce significantBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiBiotechnologyMicroorganism
In preferred embodiments, the subject invention provides two-vessel fermentation systems for producing microbe-based products comprising fungal mycelia and / or spores, and / or bacterial endospores, wherein the systems comprise both a submerged fermentation vessel and a solid state fermentation (SSF) vessel. Advantageously use of the two phases improves the efficiency of producing microorganisms by catering to the different requirements for biomass and / or vegetative cell accumulation as well as the requirements for mycelial growth and / or sporulation.
Owner:LOCUS SOLUTIONS IPCO LLC
Seaweed-containing feed
The invention belongs to the field of feeds, and discloses a seaweed-containing composition. The seaweed-containing composition comprises seaweed, probiotics and enzymes, wherein the probiotics are selected from one or more of bacillus subtilis, clostridium butyricum, endospore-forming bacteria, lactic acid bacteria and beer yeast; and the enzymes are selected from one or more of xylanase, glucanase, cellulase, acid phosphatase, phytase, protease, amylase and lipase. The invention further discloses the seaweed-containing feed. The seaweed-containing feed comprises the following components in parts by weight of 30-80 parts of corn, 10-40 parts of soybean meal, 4-30 parts of the seaweed-containing composition, 1-8 parts of fish meal, 0.5-3 parts of soybean oil, 1-2 parts of calcium hydrogen phosphate, 0.1-2 parts of calcium carbonate, 0-0.5 part of lysine, 0.1-0.5 part of table salt, 0-2 parts of citric acid and 0.5-2 parts of an additive. According to the feed disclosed by the invention, antibiotics are not added, so that after the feed is used for feeding sows and after piglets take in milk of the sows, the diarrhea situation of the piglets can be reduced, the survival rate is high and the growth speed is high.
Owner:珠海市斗门区基壮农业发展有限公司
Attenuated vaccine useful for immunizations against Coccidioides spp. infections
InactiveUS20060121061A1Easy to useEffective immune responseBiocideFungiAttenuated vaccineCoccidioides species
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Sporicidal methods and compositions
PendingCN112384067AReduce pollutionReduce generationBiocideOrganic/inorganic per-compounds compounding agentsCarboxylic acidReduction potential
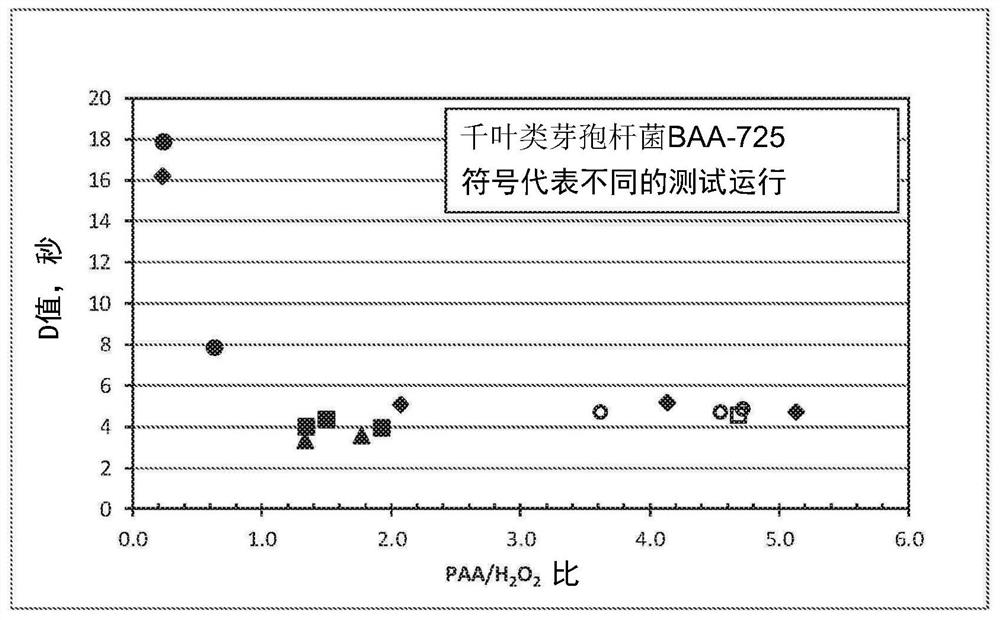
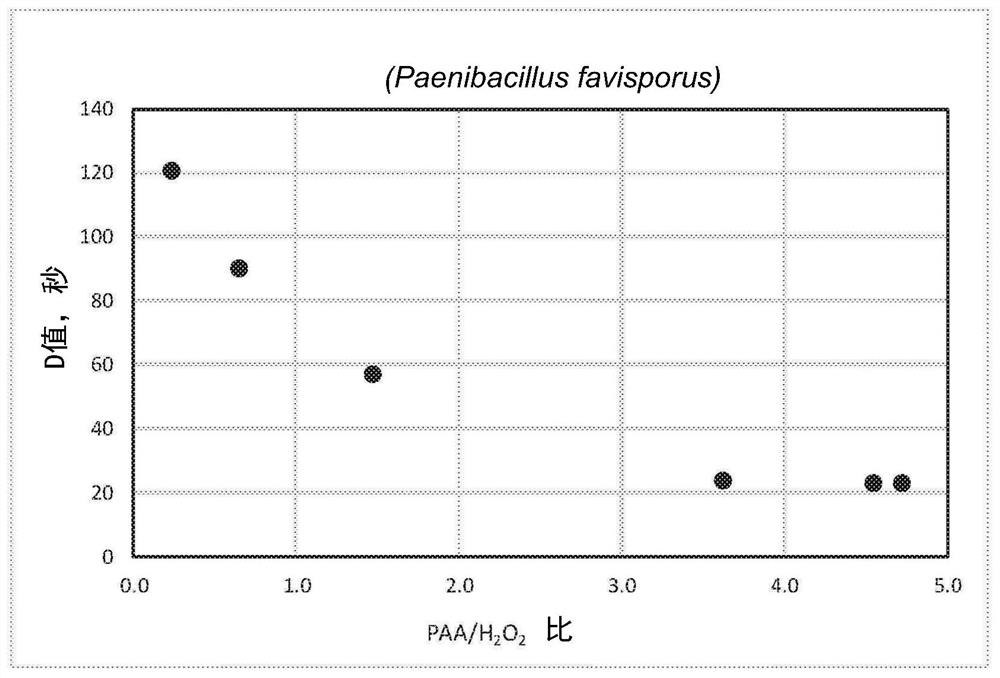
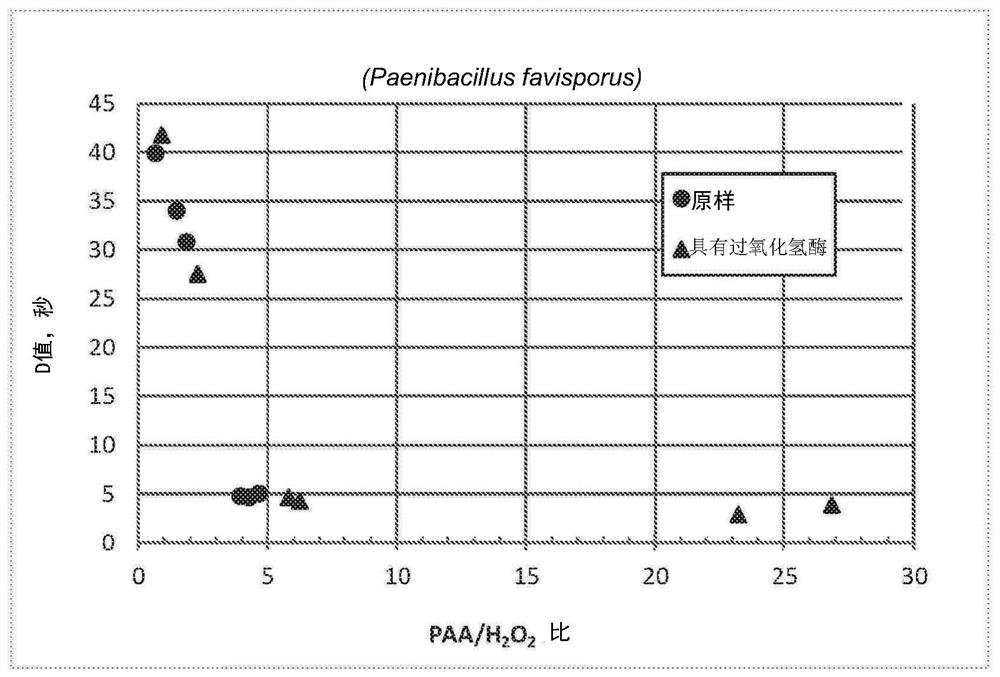
Provided herein are methods and compositions for the reduction of endospore contamination of a substrate with percarboxylic acid-based compositions. The methods can include the step of continuously monitoring the oxidation-reduction potential of the percarboxylic acid-based compositions.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Antimicrobial composition having efficacy against endospores
ActiveUS11118143B2Increase effective solute concentrationEffectively sporicidalInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideBiotechnologyMicrobiology
A sporicidal composition has a moderately low pH and includes a glycosidase and the dissocia-tion product of at least one inorganic oxidizing agent. High effective solute concentrations can enhance the efficacy of the composition. The composition can be applied to a surface and allowed to absorb into an endospore, ultimately killing at least some of those bacteria in mature endospore form. Surfaces to be treated include inanimate (hard) surfaces via cleaning and medical devices such as endoscopes, typically via immersion.
Owner:NEXT SCI IP HLDG PTY LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com